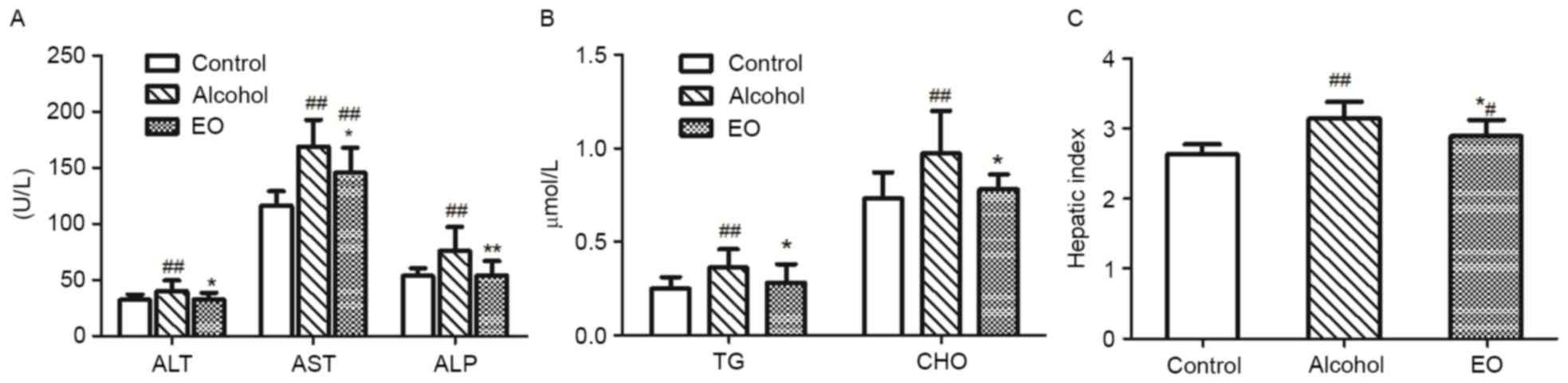
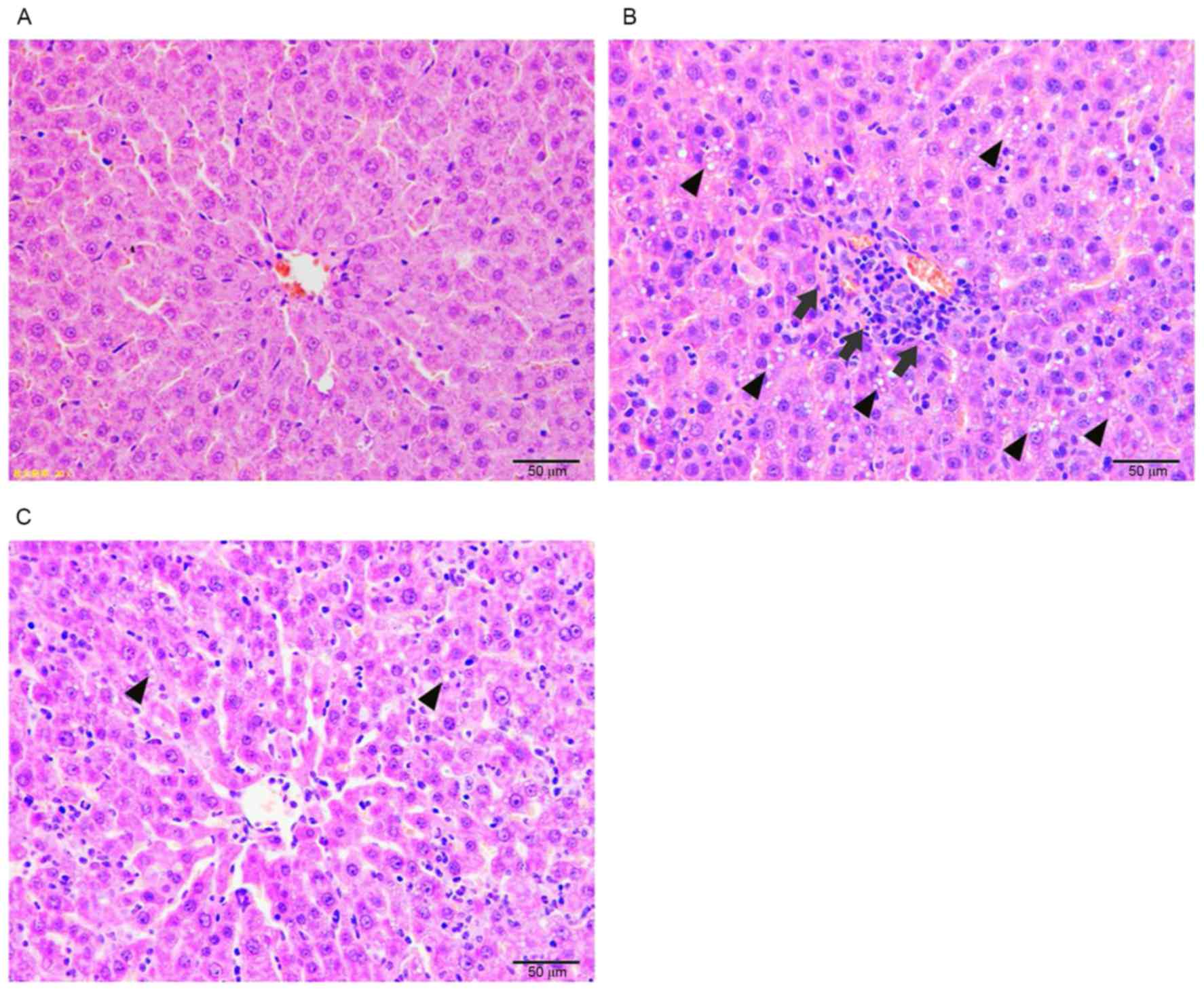
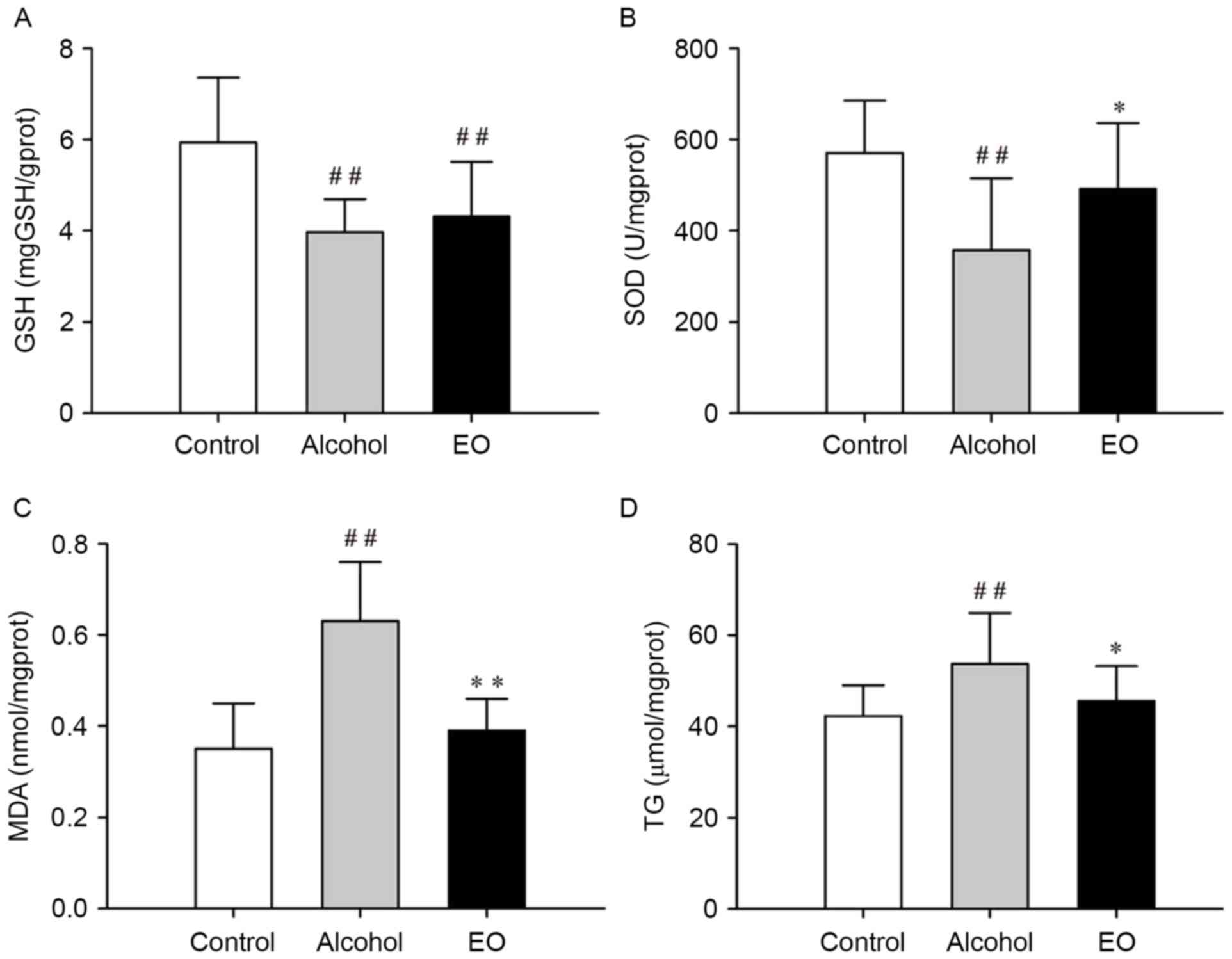
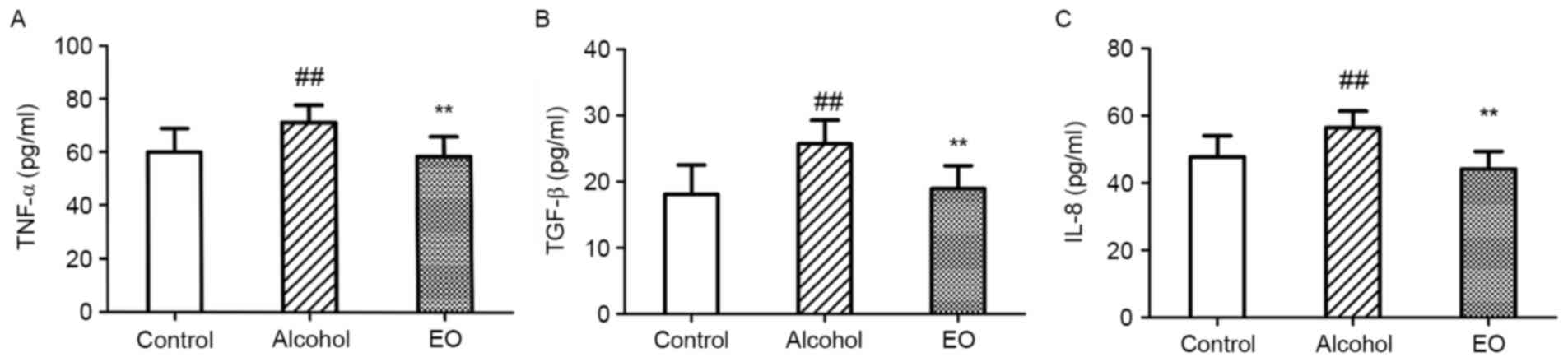
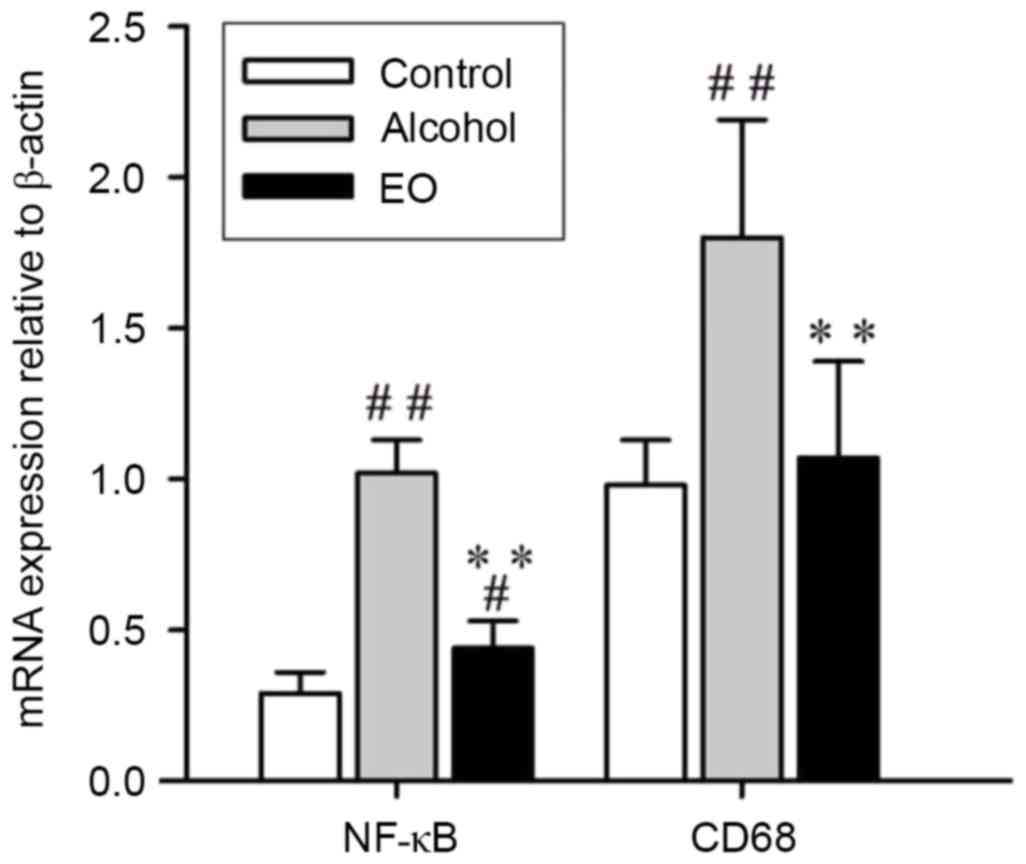
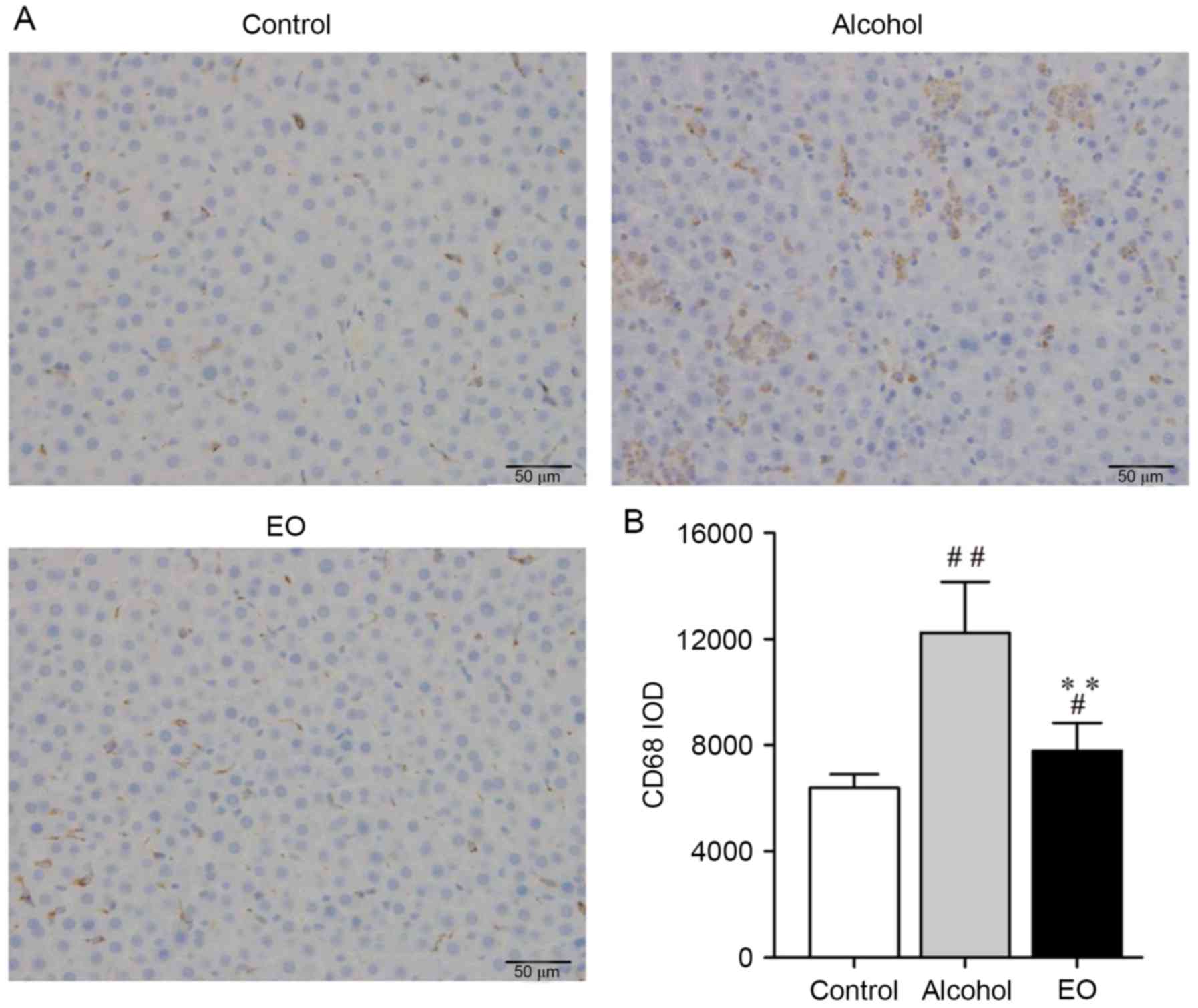
|
1
|
Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S,
Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y and Patra J: Global burden
of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use
and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet. 373:2223–2233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan JG: Epidemiology of alcoholic and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28 Suppl 1:S11–S17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lieber CS: Alcoholic fatty liver: Its
pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and
fibrosis. Alcohol. 34:9–19. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gramenzi A, Caputo F, Biselli M, Kuria F,
Loggi E, Andreone P and Bernardi M: Review article: Alcoholic liver
disease-pathophysiological aspects and risk factors. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 24:1151–1161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang CC, Huang HP, Lee YJ, Tang YH and
Wang CJ: Hepatoprotective effect of mulberry water extracts on
ethanol-induced liver injury via anti-inflammation and inhibition
of lipogenesis in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 62:786–796.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu T, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Han X and Peng J: Protective effects of dioscin against
alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol. 88:739–753.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Qi X, Cao S and Li P: Protective
effect of flavonoid extract from Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra
Sieb. et Zucc.) fruit on alcoholic liver oxidative injury in mice.
J Nat Med. 68:521–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng T, Guo FF, Zhang CL, Zhao S, Dou DD,
Gao XC and Xie KQ: The anti-fatty liver effects of garlic oil on
acute ethanol-exposed mice. Chem Biol Interact. 176:234–242. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McClain CJ, Song Z, Barve SS, Hill DB and
Deaciuc I: Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease. IV.
Dysregulated cytokine metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G497G5022004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Szuster-Ciesielska A, Mizerska-Dudka M,
Daniluk J and Kandefer-Szerszen M: Butein inhibits ethanol-induced
activation of liver stellate cells through TGF-β, NFκB, p38, and
JNK signaling pathways and inhibition of oxidative stress. J
Gastroenterol. 48:222–237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zima T and Kalousová M: Oxidative stress
and signal transduction pathways in alcoholic liver disease.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 29 11 Suppl:S110–S115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Horiguchi N, Wang L, Mukhopadhyay P, Park
O, Jeong WI, Lafdil F, Osei-Hyiaman D, Moh A, Fu XY, Pacher P, et
al: Cell type-dependent pro- and anti-inflammatory role of signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 in alcoholic liver
injury. Gastroenterology. 134:1148–1158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mari M, Morales A, Colell A, Garcia-Ruiz C
and Fernández-Checa JC: Mitochondrial cholesterol accumulation in
alcoholic liver disease: Role of ASMase and endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Redox Biol. 3:100–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gurung RB, Purbe B, Gyawali P and Risal P:
The ratio of aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase
(AST/ALT): The correlation of value with underlying severity of
alcoholic liver disease. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 11:233–236.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lai CL, Ng RP and Lok AS: The diagnostic
value of the ratio of serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to
alkaline phosphatase in alcoholic liver disease. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 17:41–47. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lichtenthäler R, Rodrigues RB, Maia JG,
Papagiannopoulos M, Fabricius H and Marx F: Total oxidant
scavenging capacities of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açaí) fruits. Int
J Food Sci Nutr. 56:53–64. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pacheco-Palencia LA, Mertens-Talcott S and
Talcott ST: Chemical composition, antioxidant properties, and
thermal stability of a phytochemical enriched oil from Acai
(Euterpe oleracea Mart.). J Agric Food Chem. 56:4631–4636. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moura RS, Ferreira TS, Lopes AA, Pires KM,
Nesi RT, Resende AC, Souza PJ, Silva AJ, Borges RM, Porto LC and
Valenca SS: Effects of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (AÇAÍ) extract in
acute lung inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in the mouse.
Phytomedicine. 19:262–269. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zapata-Sudo G, da Silva JS, Pereira SL,
Souza PJ, de Moura RS and Sudo RT: Oral treatment with Euterpe
oleracea Mart. (açaí) extract improves cardiac dysfunction and
exercise intolerance in rats subjected to myocardial infarction.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:2272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Silva DF, Vidal FC, Santos D, Costa MC,
Morgado-Díaz JA; do Desterro Soares Brandão Nascimento M, ; de
Moura RS: Cytotoxic effects of Euterpe oleracea Mart. in malignant
cell lines. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:1752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li D, Guo HZ, Yang CS, Huang AQ and Rong
CZ: Modelling the chronic alcoholic liver disease (ALD) in rat and
its pathologic observation. Chin J Integrated Traditional And
Western Med Liver Dis. 10:2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Altamirano J and Bataller R: Alcoholic
liver disease: Pathogenesis and new targets for therapy. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:491–501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang J, Xie C, Li Z, Nagarajan S, Schauss
AG, Wu T and Wu X: Flavonoids from acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.)
pulp and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Food
Chem. 128:152–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu D and Cederbaum AI: Oxidative stress
and alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 29:141–154. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Z, Wang L, Song Z, Lambert JC,
McClain CJ and Kang YJ: A critical involvement of oxidative stress
in acute alcohol-induced hepatic TNF-alpha production. Am J Pathol.
163:1137–1146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang N, Li L, Wang P, Sun H, Wu Z, Piao C
and Wang X: Pharmacokinetics of the main compounds absorbed into
blood after oral administration of Liu Wei Di Huang Wan, a typical
combinatorial intervention of Chinese medical formula. J Nat Med.
67:36–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Galicia-Moreno M and Gutierrez-Reyes G:
The role of oxidative stress in the development of alcoholic liver
disease. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 79:135–144. 2014.(In English,
Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li G, Ye Y, Kang J, Yao X, Zhang Y, Jiang
W, Gao M, Dai Y, Xin Y, Wang Q, et al: l-Theanine prevents
alcoholic liver injury through enhancing the antioxidant capability
of hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:363–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu JW, Wang SP, Alvarez F, Casavant S,
Gauthier N, Abed L, Soni KG, Yang G and Mitchell GA: Deficiency of
liver adipose triglyceride lipase in mice causes progressive
hepatic steatosis. Hepatology. 54:122–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Oliveira PR, da Costa CA, de Bem GF,
Cordeiro VS, Santos IB, de Carvalho LC, da Conceição EP, Lisboa PC,
Ognibene DT, Sousa PJ, et al: Euterpe oleracea Mart.-derived
polyphenols protect mice from diet-induced obesity and fatty liver
by regulating hepatic lipogenesis and cholesterol excretion. PLoS
One. 10:e01437212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gheita TA and Kenawy SA: Measurement of
malondialdehyde, glutathione, and glutathione peroxidase in SLE
patients. Methods Mol Biol. 1134:193–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCord JM and Edeas MA: SOD, oxidative
stress and human pathologies: A brief history and a future vision.
Biomed Pharmacother. 59:139–142. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chakraborty I, Kunti S, Bandyopadhyay M,
Dasgupta A, Chattopadhyay GD and Chakraborty S: Evaluation of serum
zinc level and plasma SOD activity in senile cataract patients
under oxidative stress. Indian J Clin Biochem. 22:109–113. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Balasubramaniyan V, Kalaivani Sailaja J
and Nalini N: Role of leptin on alcohol-induced oxidative stress in
Swiss mice. Pharmacol Res. 47:211–216. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee WS, McKiernan PJ and Kelly DA: Serum
ferritin level in neonatal fulminant liver failure. Arch Dis Child
Fetal Neonatal Ed. 85:F2262001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ananian P, Hardwigsen J, Bernard D and Le
Treut YP: Serum acute-phase protein level as indicator for liver
failure after liver resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 52:857–861.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li W, Liu Y, Wang Z, Han Y, Tian YH, Zhang
GS, Sun YS and Wang YP: Platycodin D isolated from the aerial parts
of Platycodon grandiflorum protects alcohol-induced liver injury in
mice. Food Funct. 6:1418–1427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen YL, Peng HC, Hsieh YC and Yang SC:
Epidermal growth factor improved alcohol-induced inflammation in
rats. Alcohol. 48:701–706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suk KT, Kim MY and Baik SK: Alcoholic
liver disease: Treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 20:12934–12944.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao XQ, Liang B, Liu Y and Huang XQ:
Agaricoglycerides protect against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury by attenuating inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and
expression of NF-κB. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:1427362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ruiz-Miyazawa KW, Zarpelon AC,
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Pavão-de-Souza GF, Casagrande R and Verri WA Jr:
Vinpocetine reduces carrageenan-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress, cytokine production and
NF-κB activation in the paw and spinal cord. PLoS One.
10:e01189422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Matyja E, Taraszewska A and Marszalek P:
Necrosis and apoptosis of tumor cells in embolized meningiomas:
Histopathology and P53, BCL-2, CD-68 immunohistochemistry. Folia
Neuropathol. 37:93–98. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yan SL, Yang HT, Lee HL and Yin MC:
Protective effects of maslinic acid against alcohol-induced acute
liver injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 74:149–155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|