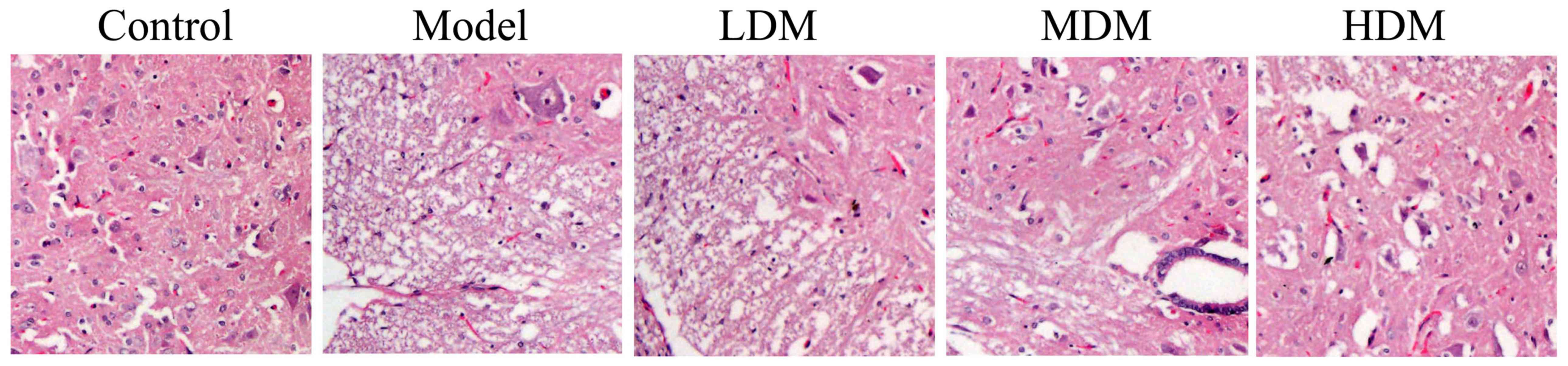
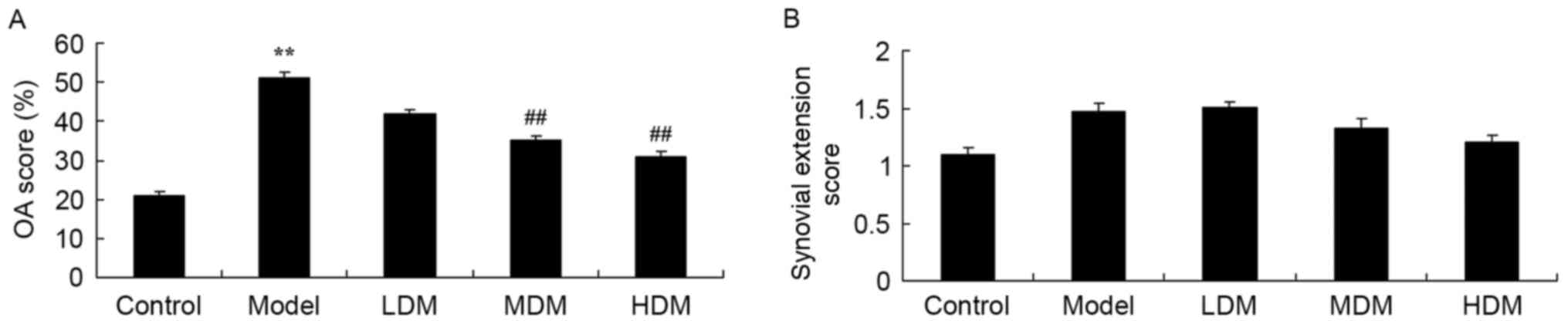
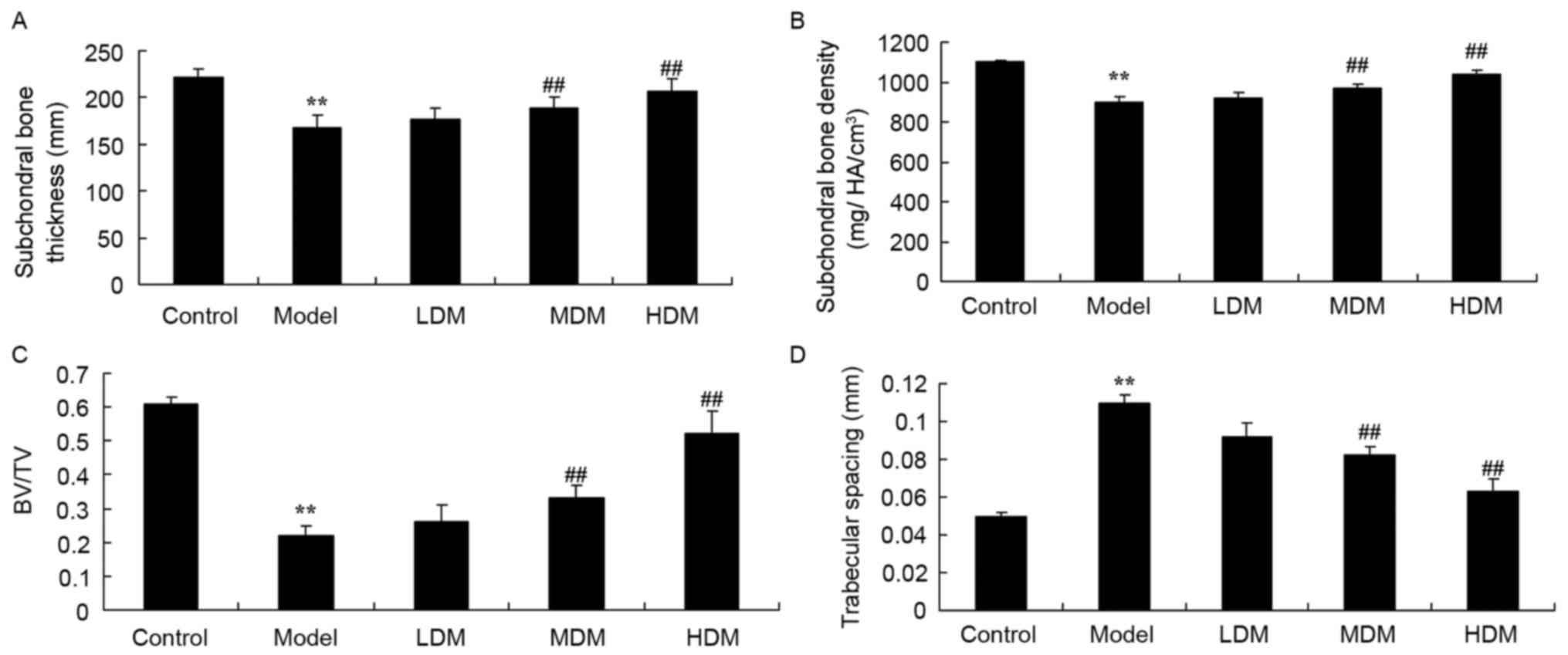
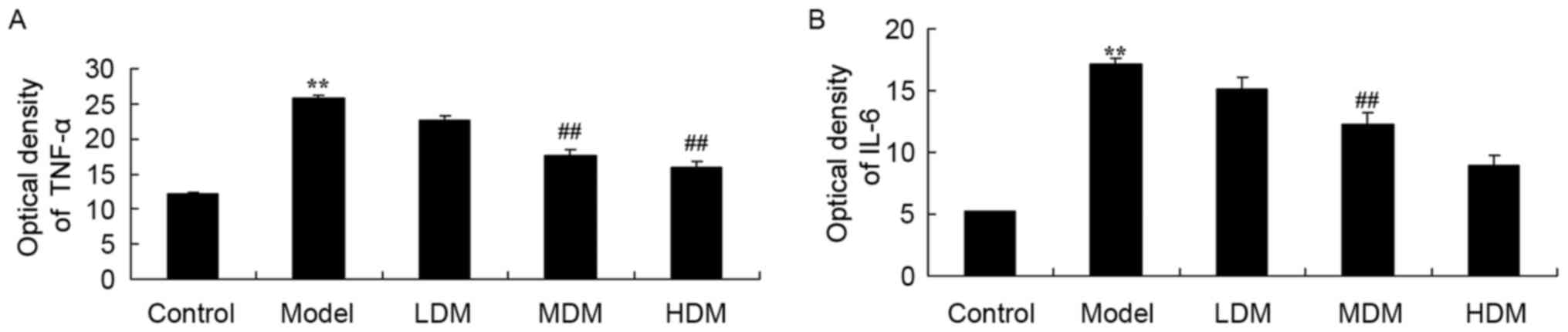
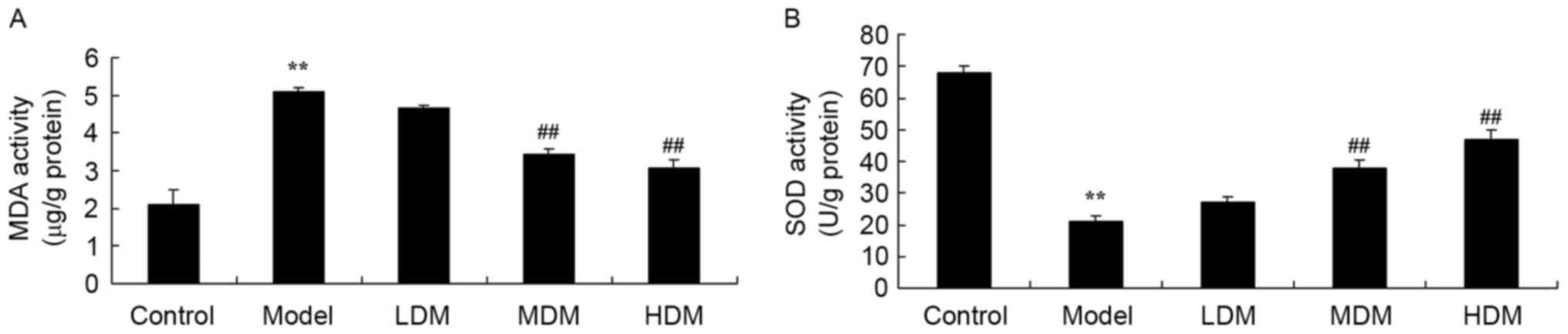
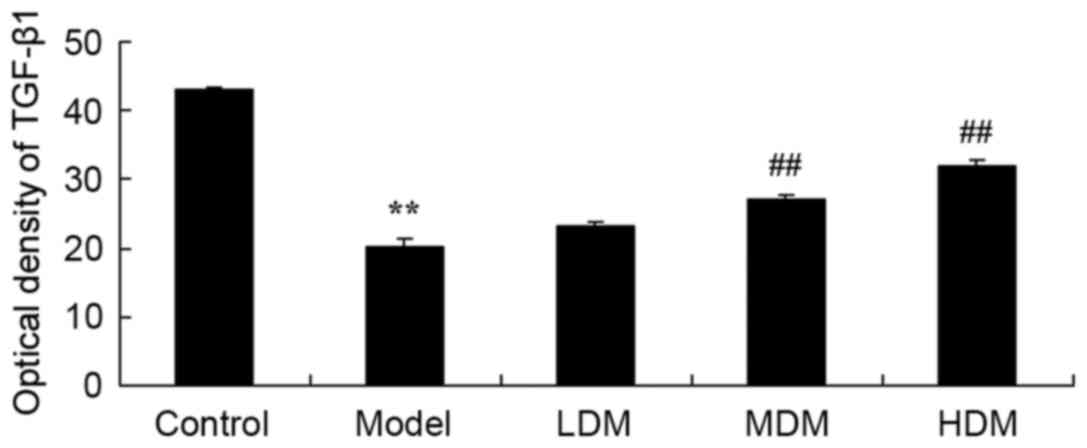
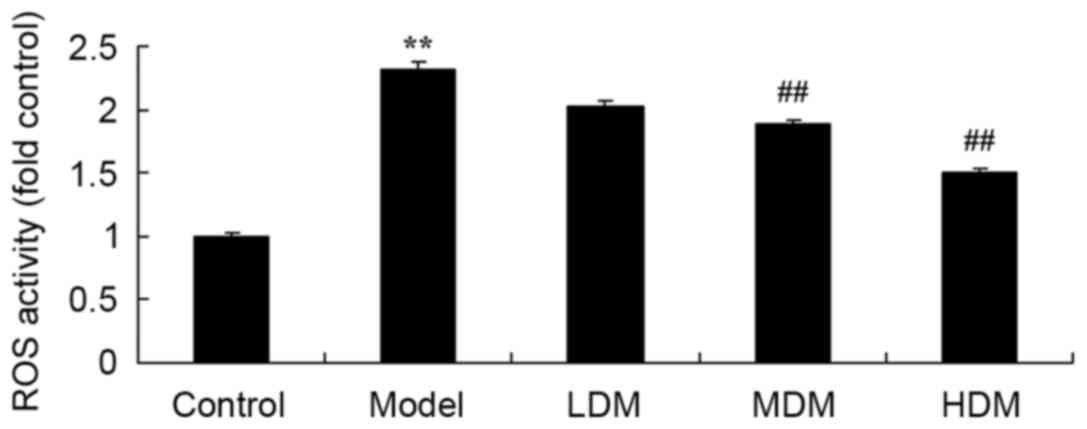
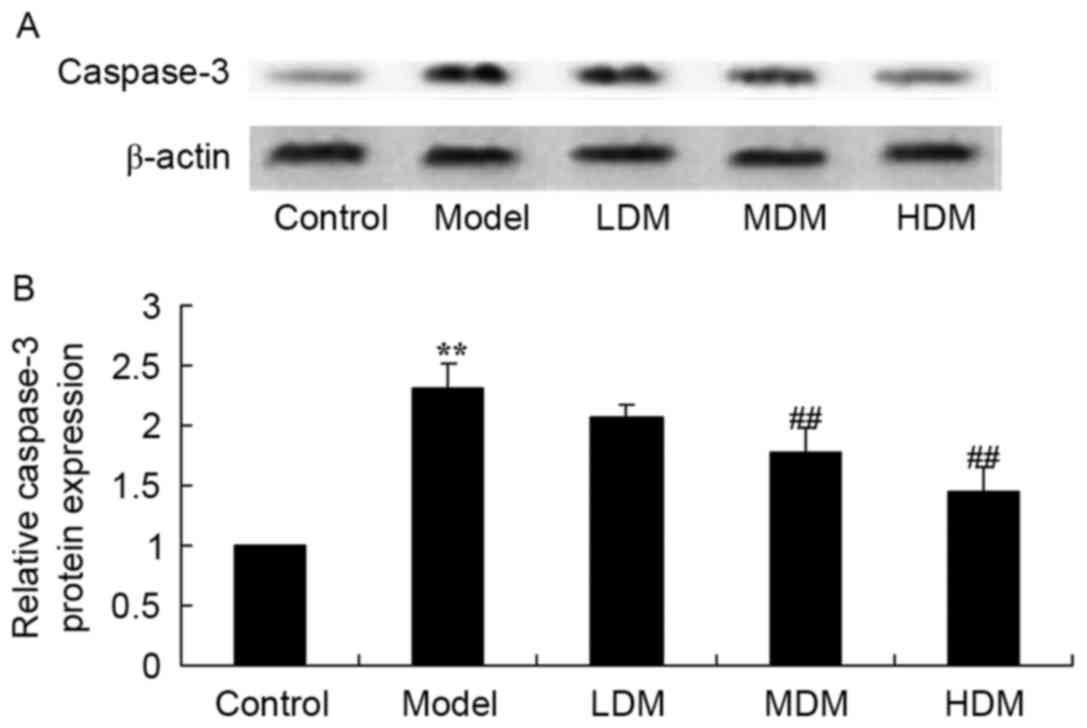
|
1
|
Swärd P, Fridén T, Boegård T, Kostogiannis
I, Neuman P and Roos H: Association between varus alignment and
post-traumatic osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament
injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 21:2040–2047. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolsko PM, Eisenberg DM, Simon LS, Davis
RB, Walleczek J, Mayo-Smith M, Kaptchuk TJ and Phillips RS:
Double-blind placebo-controlled trial of static magnets for the
treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: Results of a pilot study.
Altern Ther Health Med. 10:36–43. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giannini S, Buda R, Ruffilli A, Pagliazzi
G, Ensini A, Grigolo B, Desando G and Vannini F: Failures in
bipolar fresh osteochondral allograft for the treatment of
end-stage knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
23:2081–2089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang Q, Qiu YT, Chen MJ, Zhang ZY and
Yang C: Synovial TGF-β1 and MMP-3 levels and their correlation with
the progression of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis combined
with disc displacement: A preliminary study. Biomed Rep. 1:218–222.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wilbers RH, Westerhof LB, van Raaij DR,
van Adrichem M, Prakasa AD, Lozano-Torres JL, Bakker J, Smant G and
Schots A: Co-expression of the protease furin in Nicotiana
benthamiana leads to efficient processing of latent transforming
growth factor-β1 into a biologically active protein. Plant
Biotechnol J. 14:1695–1704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fahlgren A, Andersson B and Messner K:
TGF-beta1 as a prognostic factor in the process of early
osteoarthrosis in the rabbit knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
9:195–202. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vonwil D, Trüssel A, Haupt O, Gobaa S,
Barbero A, Shastri VP and Martin I: Substrate elasticity modulates
TGF beta stimulated re-differentiation of expanded human articular
chondrocytes. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2:351–362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heard BJ, Solbak NM, Achari Y, Chung M,
Hart DA, Shrive NG and Frank CB: Changes of early post-traumatic
osteoarthritis in an ovine model of simulated ACL reconstruction
are associated with transient acute post-injury synovial
inflammation and tissue catabolism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
21:1942–1949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lewis JS, Hembree WC, Furman BD, Tippets
L, Cattel D, Huebner JL, Little D, DeFrate LE, Kraus VB, Guilak F
and Olson SA: Acute joint pathology and synovial inflammation is
associated with increased intra-articular fracture severity in the
mouse knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:864–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bradley EW, Carpio LR, McGee-Lawrence ME,
Becerra C Castillejo, Amanatullah DF, Ta LE, Otero M, Goldring MB,
Kakar S and Westendorf JJ: Phlpp1 facilitates post-traumatic
osteoarthritis and is induced by inflammation and promoter
demethylation in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:1021–1028. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huebner KD, Shrive NG and Frank CB:
Dexamethasone inhibits inflammation and cartilage damage in a new
model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 32:566–572.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beuscher N, Kietzmann M, Bien E and
Champeroux P: Interference of myrtol standardized with inflammatory
and allergic mediators. Arzneimittelforschung. 48:985–989.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao DY, Qu HJ, Guo JM, Zhao HN, Yang YY,
Zhang P, Cao K, Lei X, Cui JG, Liu C, et al: Protective effects of
Myrtol standardized against radiation-induced lung injury. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 38:619–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Christiansen BA, Anderson MJ, Lee CA,
Williams JC, Yik JH and Haudenschild DR: Musculoskeletal changes
following non-invasive knee injury using a novel mouse model of
post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
20:773–782. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Furman BD, Strand J, Hembree WC, Ward BD,
Guilak F and Olson SA: Joint degeneration following closed
intraarticular fracture in the mouse knee: A model of posttraumatic
arthritis. J Orthop Res. 25:578–592. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bégué T, Mebtouche N and Levante S:
One-stage procedure for total knee arthroplasty in post-traumatic
osteoarthritis of the knee with wound defect. Usefulness of
navigation and flap surgery. Knee. 19:948–950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nordenvall R, Bahmanyar S, Adami J,
Mattila VM and Felländer-Tsai L: Cruciate ligament reconstruction
and risk of knee osteoarthritis: The association between cruciate
ligament injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. a population
based nationwide study in Sweden, 1987–2009. PLoS One.
9:e1046812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bala A, Penrose CT, Seyler TM, Mather RC
3rd, Wellman SS and Bolognesi MP: Outcomes after total knee
arthroplasty for post-traumatic arthritis. Knee. 22:630–639. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ying B, Maimaiti AK, Song D and Zhu S:
Myrtol ameliorates cartilage lesions in an osteoarthritis rat
model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1435–1442. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Satkunananthan PB, Anderson MJ, De Jesus
NM, Haudenschild DR, Ripplinger CM and Christiansen BA: In vivo
fluorescence reflectance imaging of protease activity in a mouse
model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
22:1461–1469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang L, Li L, Geng C, Gong D, Jiang L,
Ishikawa N, Kajima K and Zhong L: Monosodium iodoacetate induces
apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway involving ROS production
and caspase activation in rat chondrocytes in vitro. J Orthop Res.
31:364–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Courties A, Gualillo O, Berenbaum F and
Sellam J: Metabolic stress-induced joint inflammation and
osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1955–1965. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ziskoven C, Jäger M, Zilkens C, Bloch W,
Brixius K and Krauspe R: Oxidative stress in secondary
osteoarthritis: From cartilage destruction to clinical
presentation? Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2:e232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie L, Lin AS, Kundu K, Levenston ME,
Murthy N and Guldberg RE: Quantitative imaging of cartilage and
bone morphology, reactive oxygen species, and vascularization in a
rodent model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1899–1908.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rantzsch U, Vacca G, Dück R and Gillissen
A: Anti-inflammatory effects of Myrtol standardized and other
essential oils on alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Med Res. 14 Suppl 4:S205–S209.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bar-Yehuda S, Rath-Wolfson L, Del Valle L,
Ochaion A, Cohen S, Patoka R, Zozulya G, Barer F, Atar E,
Piña-Oviedo S, et al: Induction of an antiinflammatory effect and
prevention of cartilage damage in rat knee osteoarthritis by CF101
treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3061–3071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Lei M, Yu C, Lv Y, Song Y and Yang
L: Mechano growth factor-E regulates apoptosis and inflammatory
responses in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of knee osteoarthritis.
Int Orthop. 39:2503–2509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee CH, Wen ZH, Chang YC, Huang SY, Tang
CC, Chen WF, Hsieh SP, Hsieh CS and Jean YH: Intra-articular
magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) reduces experimental osteoarthritis and
nociception: Association with attenuation of N-methyl-D-aspartate
(NMDA) receptor subunit 1 phosphorylation and apoptosis in rat
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:1485–1493. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bouderlique T, Vuppalapati KK, Newton PT,
Li L, Barenius B and Chagin AS: Targeted deletion of Atg5 in
chondrocytes promotes age-related osteoarthritis. Ann -Rheum Dis.
75:627–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|