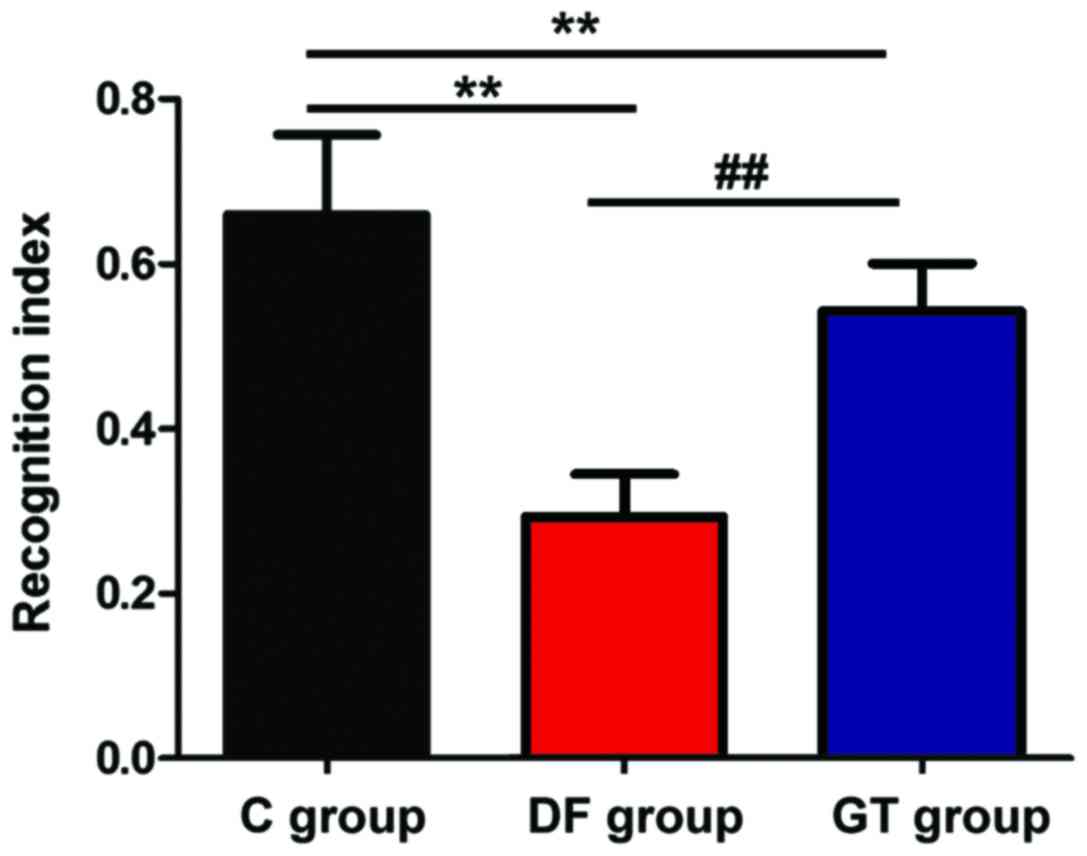
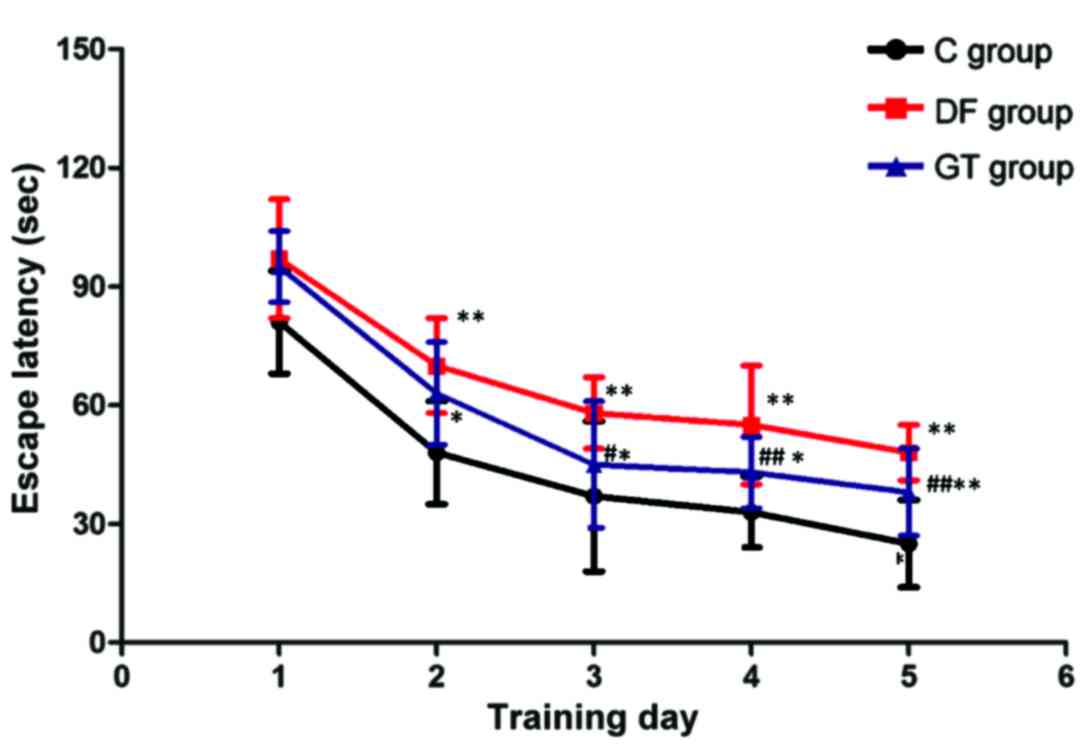
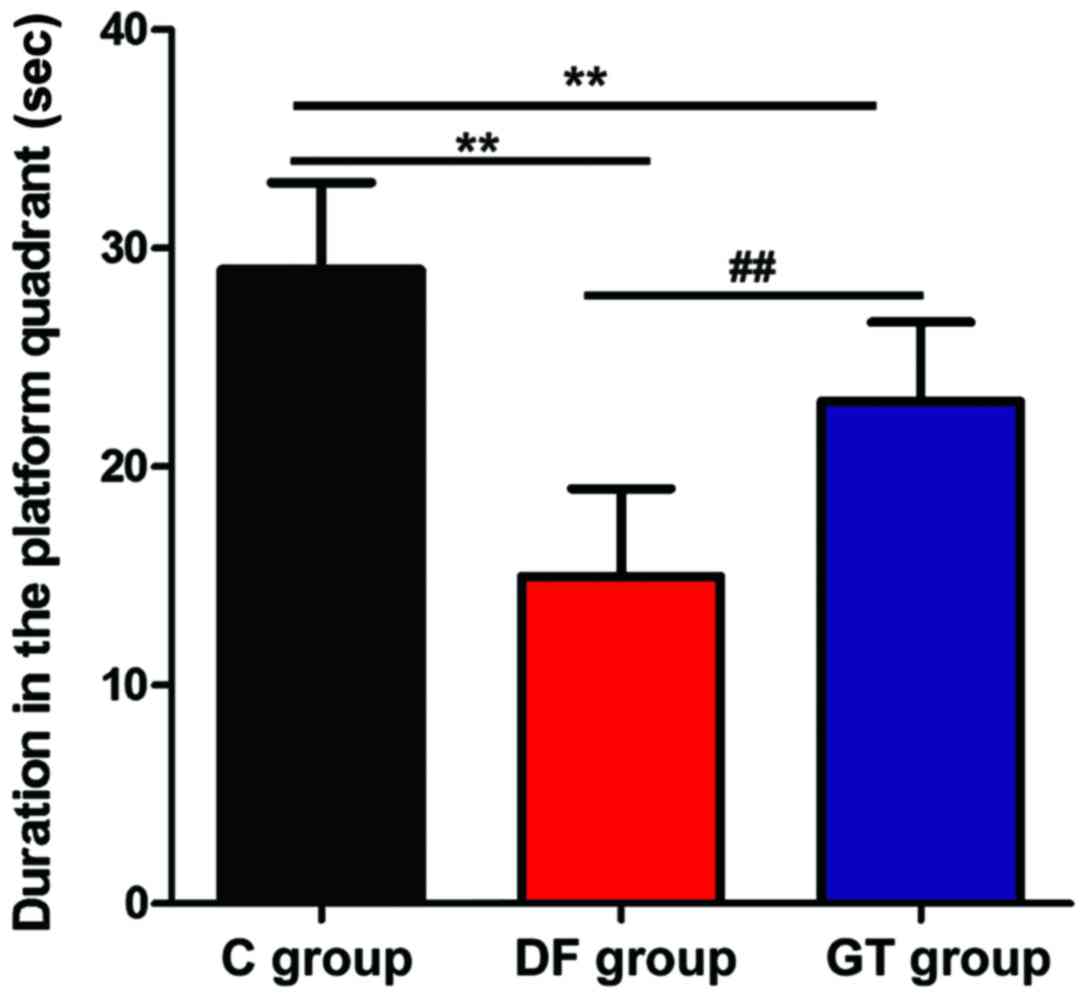
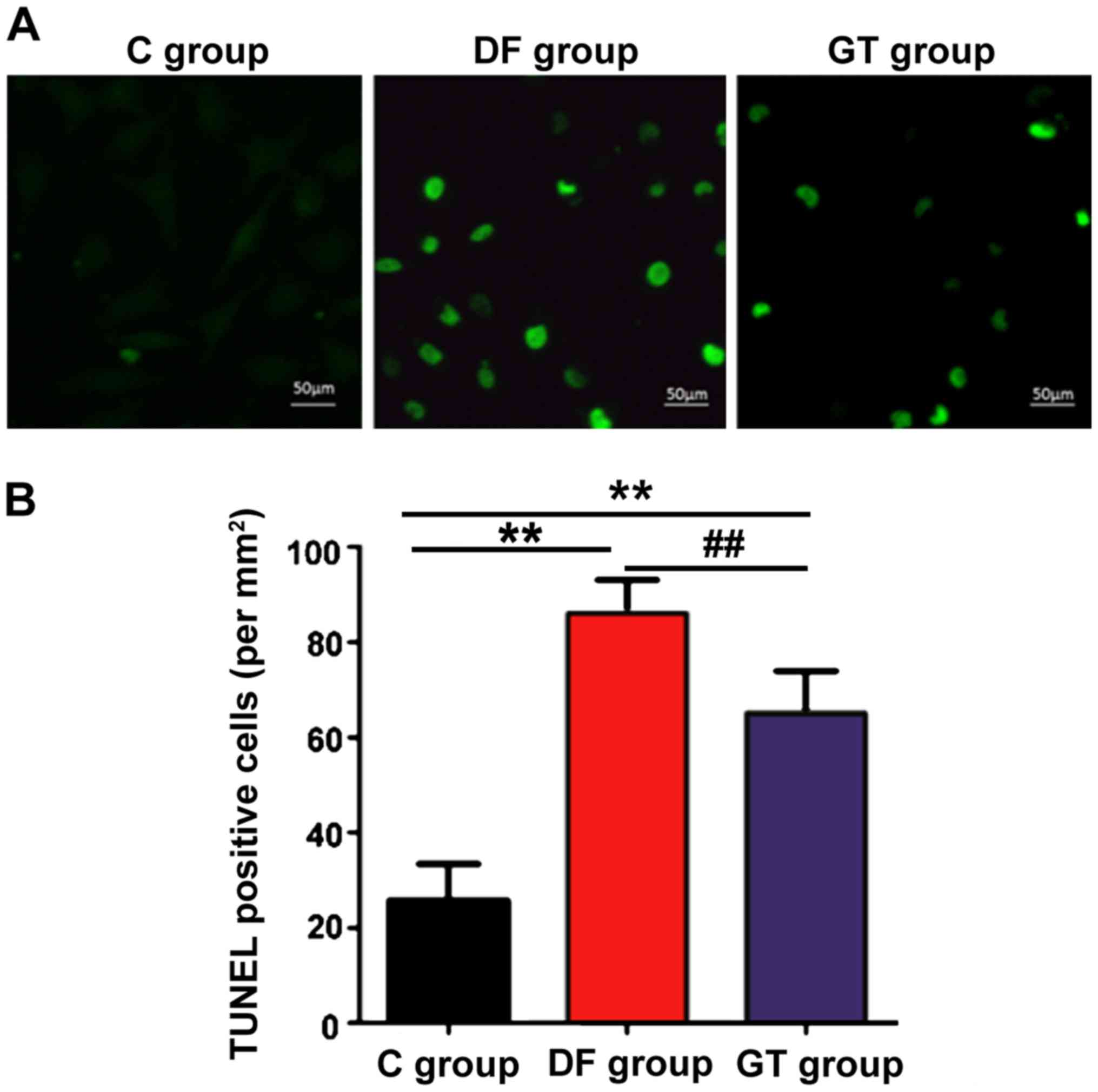
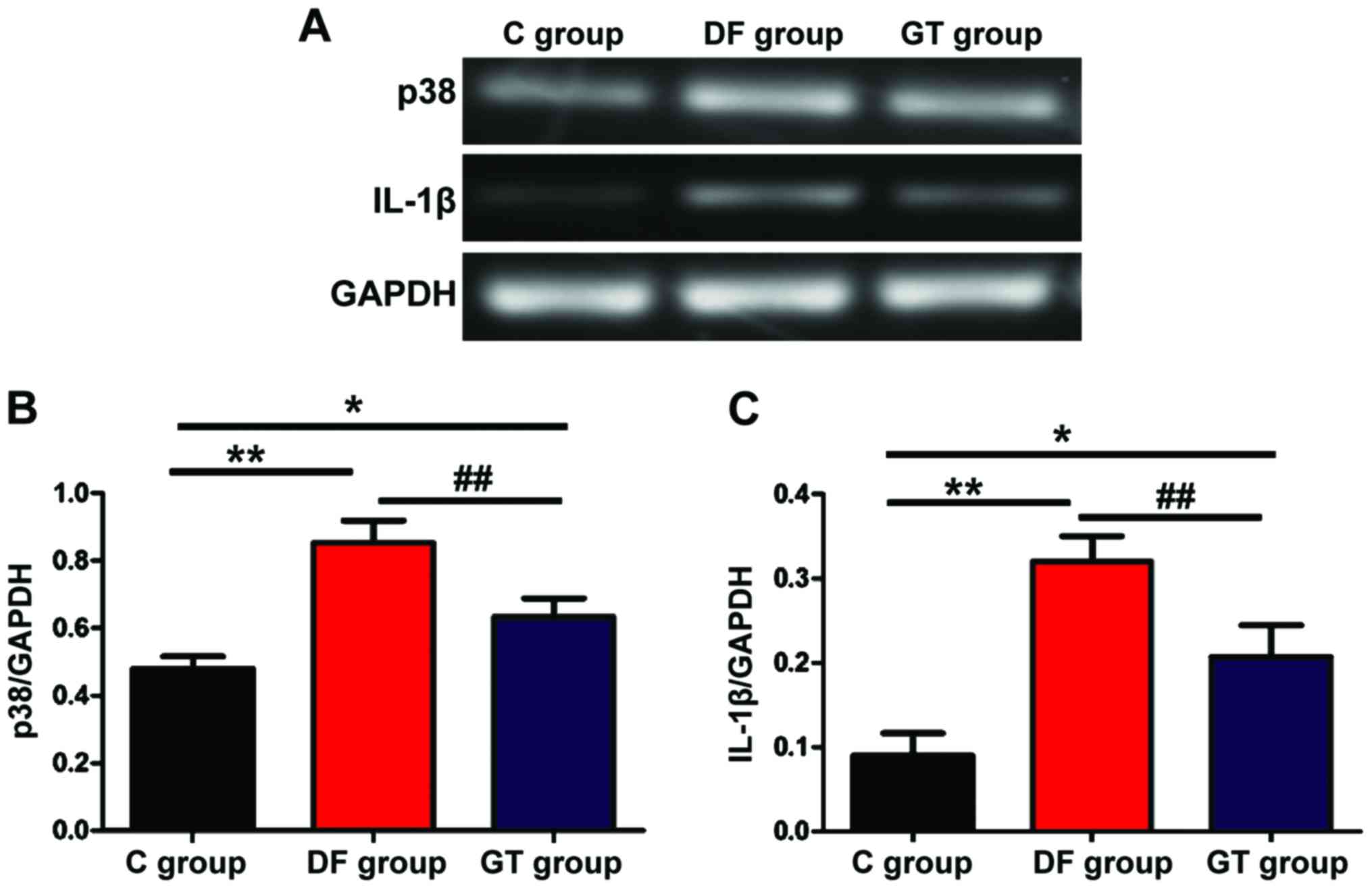
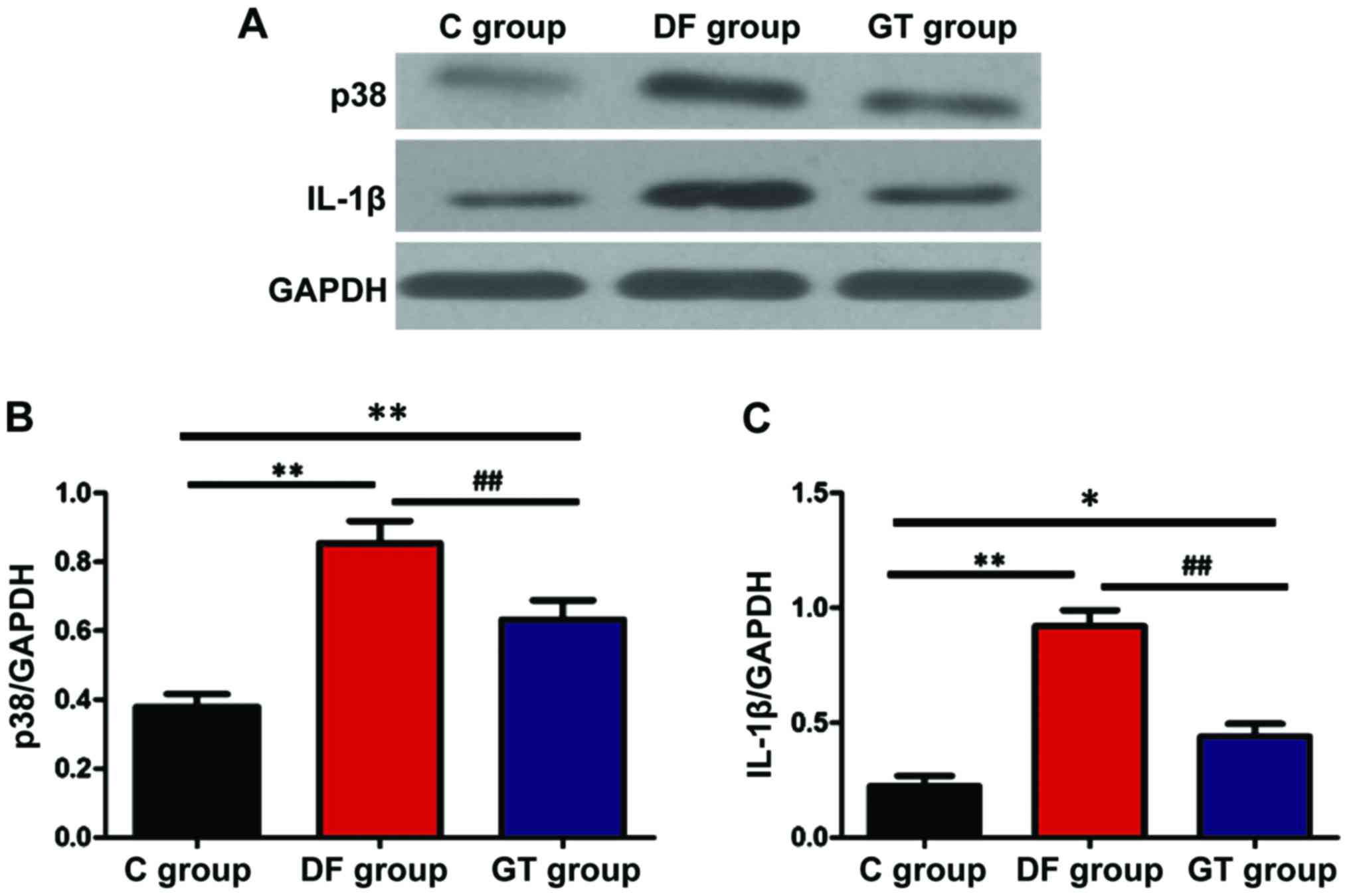
|
1
|
Deng LQ, Hou LN, Song FX, Zhu HY, Zhao HY,
Chen G and Li JJ: Effect of pre-emptive analgesia by continuous
femoral nerve block on early postoperative cognitive function
following total knee arthroplasty in elderly patients. Exp Ther
Med. 13:1592–1597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geng YJ, Wu QH and Zhang RQ: Effect of
propofol, sevoflurane, and isoflurane on postoperative cognitive
dysfunction following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in elderly
patients: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 38:165–171.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jia ZM, Hao HN, Huang ML, Ma DF, Jia XL
and Ma B: Influence of dexmedetomidine to cognitive function during
recovery period for children with general anesthesia. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:1106–1111. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devore EE, Fong TG, Marcantonio ER,
Schmitt EM, Travison TG, Jones RN and Inouye SK: Prediction of
long-term cognitive decline following postoperative delirium in
older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. Mar 15–2017.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Shen R, Wen G, Ding R, Du A, Zhou J,
Dong Z, Ren X, Yao H, Zhao R, et al: Effects of ketamine on levels
of inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the hippocampus
of mice following acute or chronic administration. Front Pharmacol.
8:1392017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Z, Zhou J, Song D, Sun Y, Liao C and
Jiang X: Gastrodin protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury
by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 8:32147–32156.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jia J, Shi X, Jing X, Li J, Gao J, Liu M,
Lin CI, Guo X and Hua Q: BCL6 mediates the effects of gastrodin on
promoting M2-like macrophage polarization and protecting against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and cell death in macrophages.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:458–464. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen L, Liu X, Wang H and Qu M: Gastrodin
attenuates pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures by modulating the
mitogen-activated protein kinase-associated inflammatory responses
in mice. Neurosci Bull. 33:264–272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun T, Wang J, Li X, Li YJ, Feng D, Shi
WL, Zhao MG, Wang JB and Wu YM: Gastrodin relieved complete
Freund's adjuvant-induced spontaneous pain by inhibiting
inflammatory response. Int Immunopharmacol. 41:66–73. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kline R, Wong E, Haile M, Didehvar S,
Farber S, Sacks A, Pirraglia E, de Leon MJ and Bekker A:
Peri-operative inflammatory cytokines in plasma of the elderly
correlate in prospective study with postoperative changes in
cognitive test scores. Int J Anesthesiol Res. 4:313–321.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rossetti AC, Paladini MS, Racagni G, Riva
MA, Cattaneo A and Molteni R: Genome-wide analysis of LPS-induced
inflammatory response in the rat ventral hippocampus: Modulatory
activity of the antidepressant agomelatine. World J Biol
Psychiatry. Mar 24–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ramírez-Jirano LJ, Zenteno-Savín T,
Gaxiola-Robles R, Ramos-González EJ, Torres-Mendoza BM and
Bitzer-Quintero OK: The neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin in
rat hippocampus in an endotoxic shock model. Rev Invest Clin.
68:292–298. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu J, Liu Z, Su J, Pan N and Song Q:
Anti-inflammatory activity of 3β-hydroxycholest-5-en-7-one isolated
from Hippocampus trimaculatus leach via inhibiting iNOS, TNF-α, and
IL-1β of LPS induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Food Funct.
8:788–795. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mani R, Natesan V and Arumugam R:
Neuroprotective effect of chrysin on hyperammonemia mediated
neuroinflammatory responses and altered expression of astrocytic
protein in the hippocampus. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:762–769. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang R, Zhang H, Wang Y, Song F and Yuan
Y: Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver
fibrosis through the regulation of NF-κB/IκBα, p38 MAPK, and
Bcl-2/Bax signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 47:126–133. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alva-Murillo N, Ochoa-Zarzosa A and
López-Meza JE: Sodium octanoate modulates the innate immune
response of bovine mammary epithelial cells through the
TLR2/P38/JNK/ERK1/2 pathway: Implications during Staphylococcus
aureus internalization. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 7:782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Achanta P, Thompson KJ, Fuss M and
Martinez JL Jr: Gene expression changes in the rodent hippocampus
following whole brain irradiation. Neurosci Lett. 418:143–148.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kong X, Liu L and Sheng X: Effects of
excessive zinc in fodder on brain development and abilities of
learning and memory and their mechanisms in young rats. Zhonghua Yu
Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 32:225–228. 1998.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang TY, Zhou XX, Huang H and Huang QD:
Relationship between IL-1β polymorphisms and obstructive sleep
apnea syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3120–3128.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun L, Zhao ZY, Hu J and Zhou XL:
Potential association of lead exposure during early development of
mice with alteration of hippocampus nitric oxide levels and
learning memory. Biomed Environ Sci. 18:375–378. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|