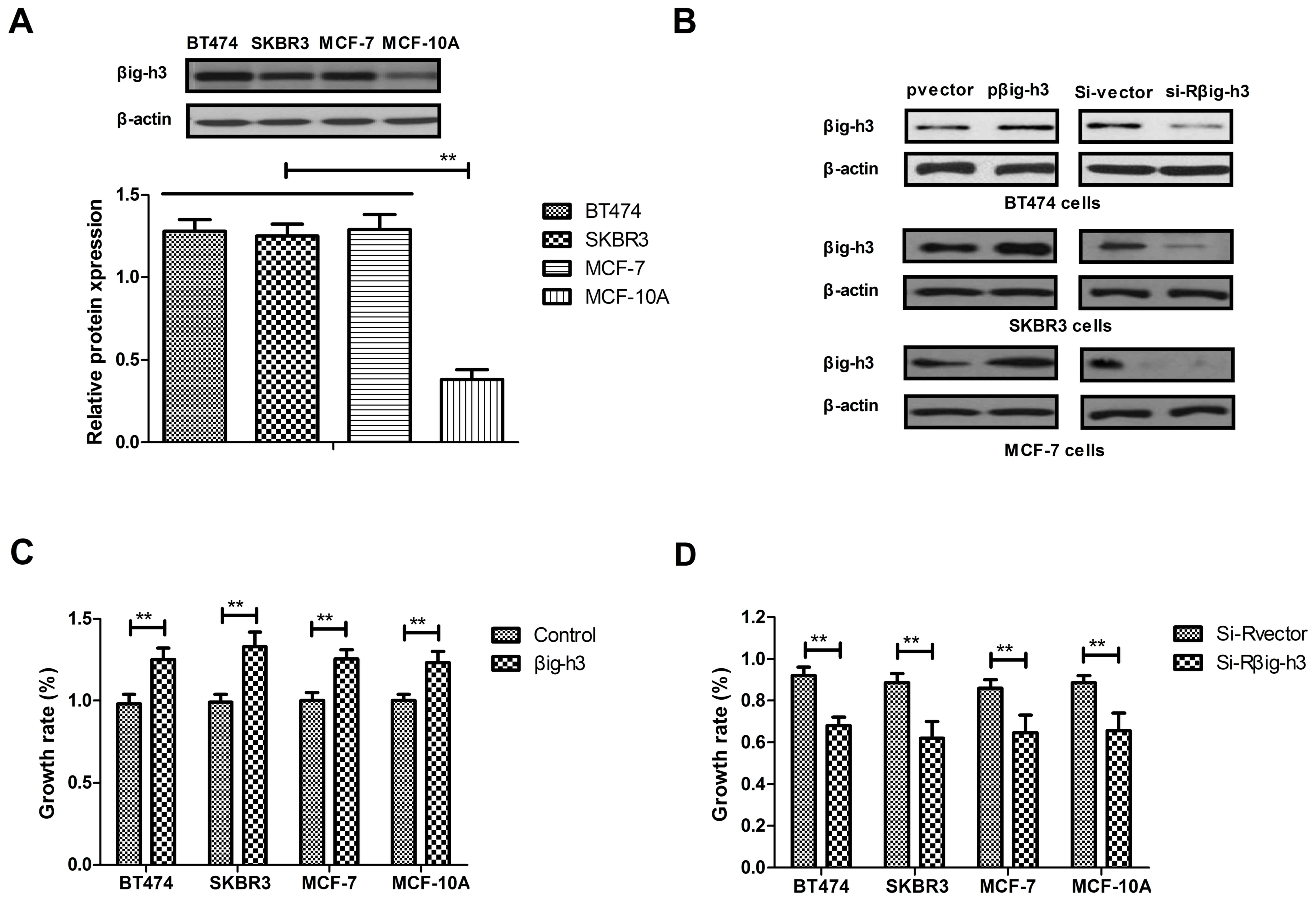
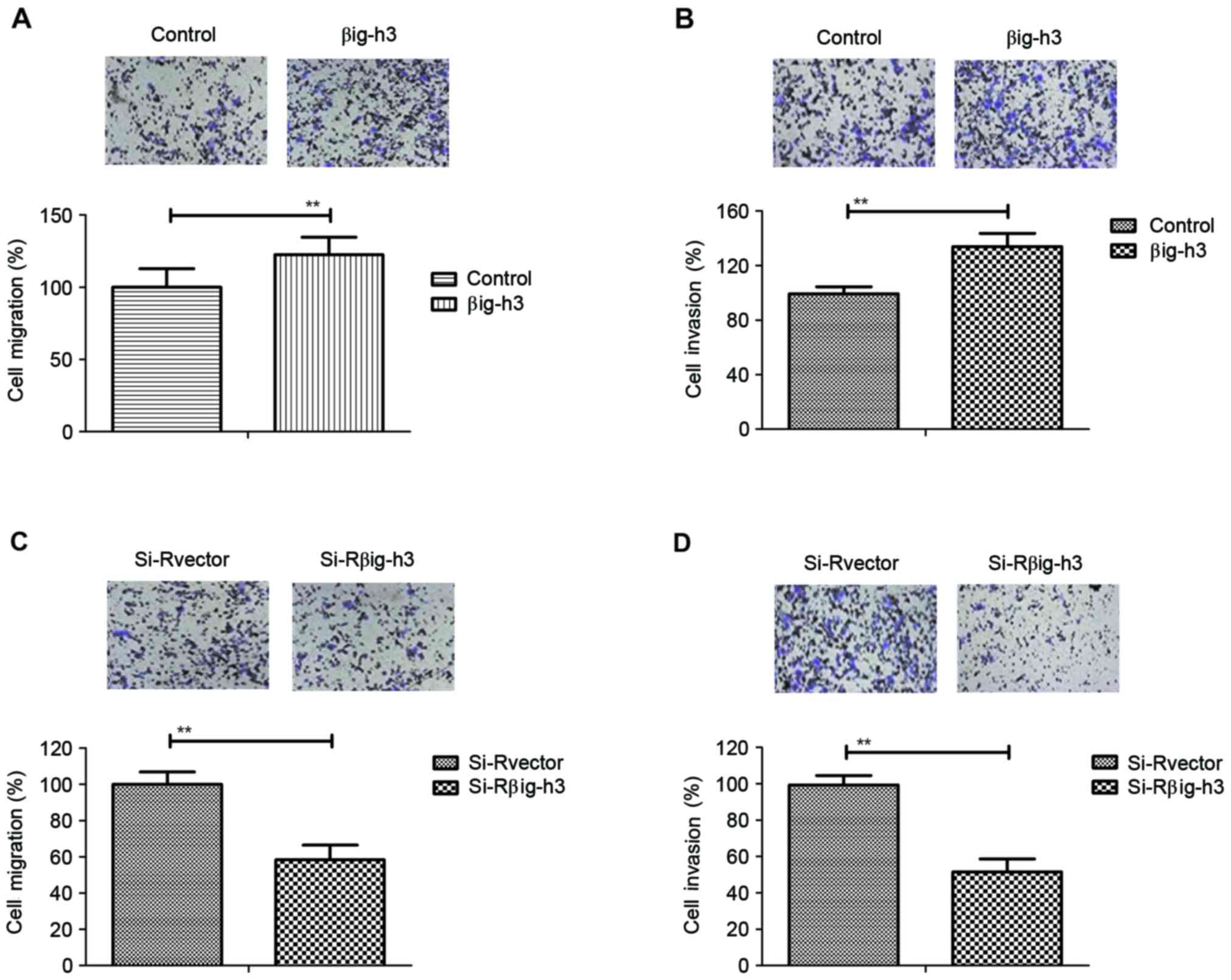
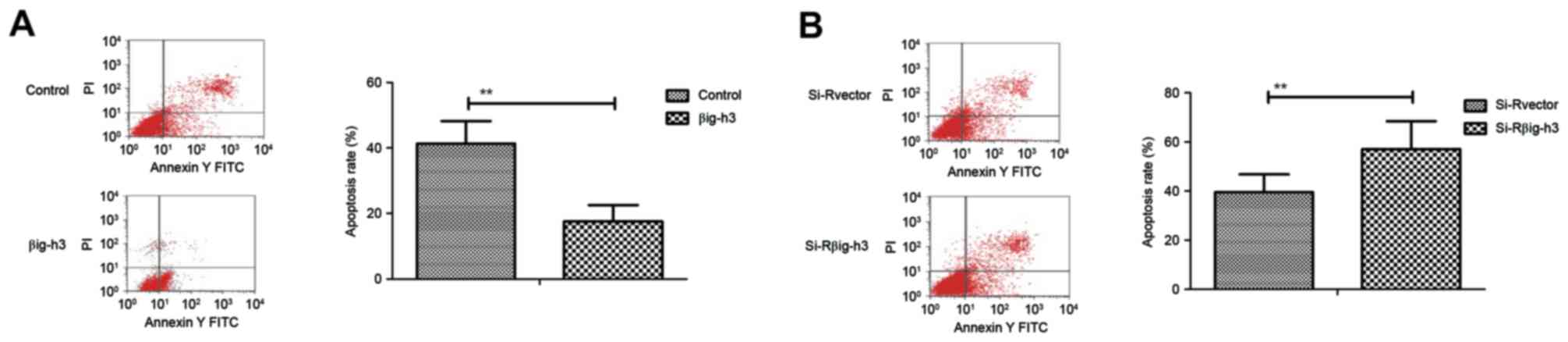
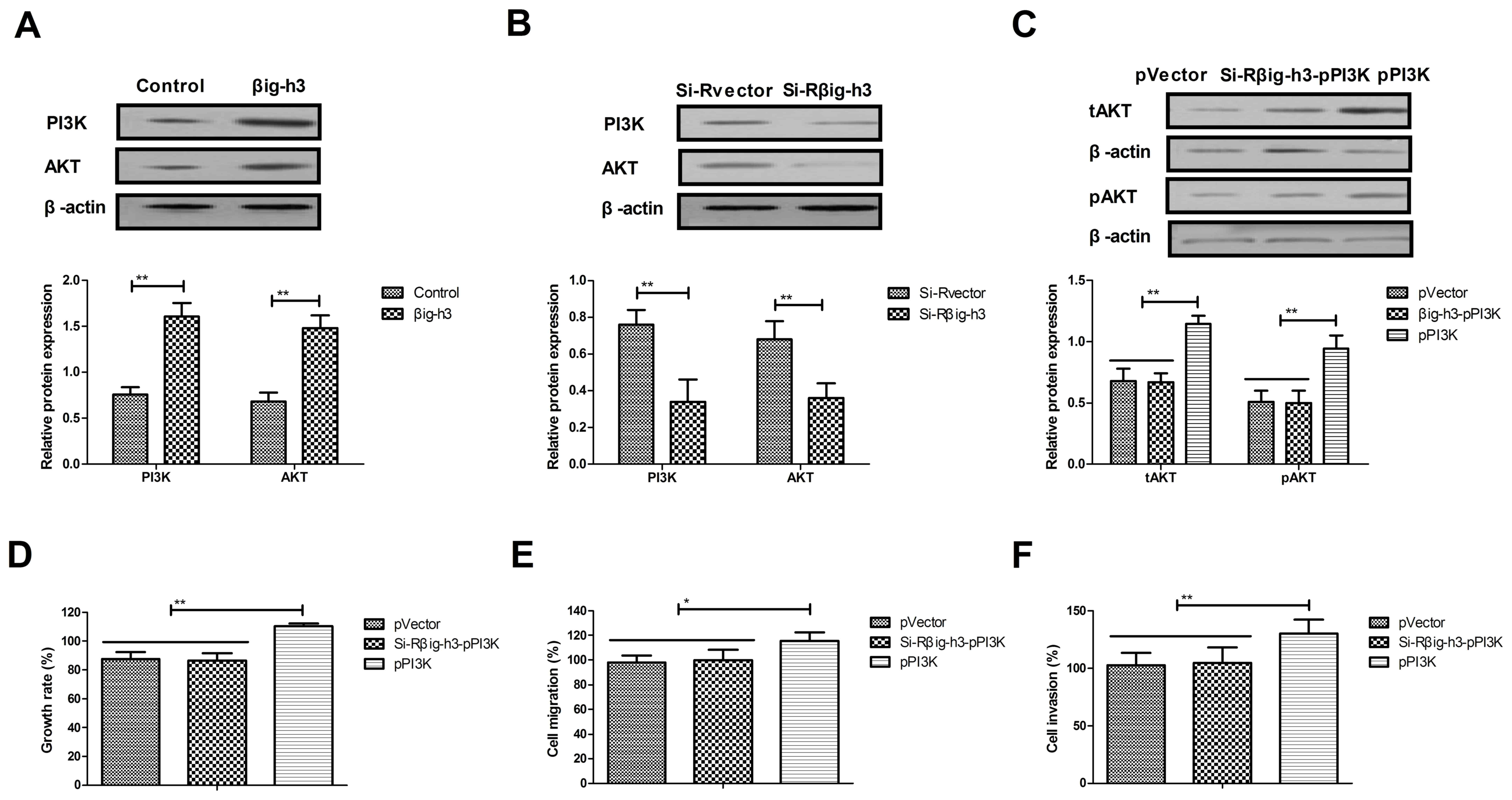
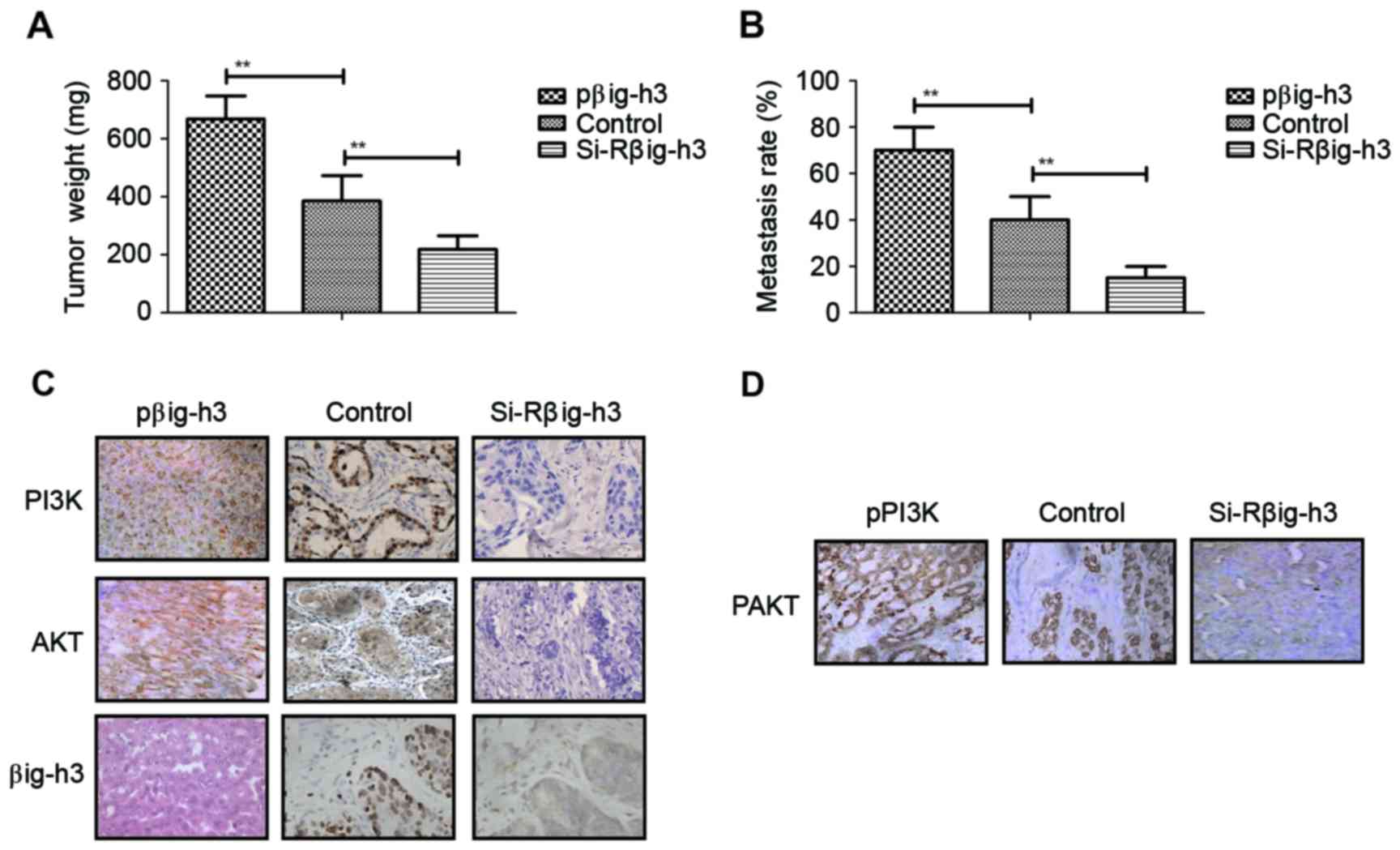
|
1
|
Benson R, Madan R, Julka PK and Rath GK:
Metaplastic carcinoma of breast: A case series of seven patients
from a tertiary care center and review of literature. Gulf J
Oncolog. 1:74–76. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Conlon N, Sadri N, Corben AD and Tan LK:
Acinic cell carcinoma of breast: Morphologic and
immunohistochemical review of a rare breast cancer subtype. Hum
Pathol. 51:16–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Conlon N, Howard J, Catalano J, Gallagher
M, Tan LK and Corben AD: Breast carcinoma in young women: No
evidence of increasing rates of metastatic breast carcinoma in a
single tertiary center review. Breast J. 22:287–292. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ziyadi M, Boujoual M, Raiteb H, Babahabib
MA, Kouach J, Moussaoui DR and Dehayni M: Squamous cell carcinoma
of the breast: Report of a case and review of the literature. Pan
Afr Med J. 24:2132016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zagelbaum NK, Ward MF II, Okby N and
Karpoff H: Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with
osteoclast-like giant cells and clear cell features: A case report
of a novel finding and review of the literature. World J Surg
Oncol. 14:2272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Modesto A, Gandy C, Mery E, Filleron T,
Massabeau C, Izar F, Charitansky H, Roché H and de Lafontan B:
Breast ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion: Pathological
review and clinical implications. Cancer Radiother. 18:107–110.
2014.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Falco G, Buggi F, Sanna PA, Dubini A and
Folli S: Breast metastases from a renal cell carcinoma. A case
report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep.
5:193–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Miao Z, Jin G, Li X, Li H, Lv Z and
Xu HM: βig-h3 supports gastric cancer cell adhesion, migration and
proliferation in peritoneal carcinomatosis. Mol Med Rep. 6:558–564.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shao G, Berenguer J, Borczuk AC, Powell
CA, Hei TK and Zhao Y: Epigenetic inactivation of Betaig-h3 gene in
human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:4566–4573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao Y, El-Gabry M and Hei TK: Loss of
Betaig-h3 protein is frequent in primary lung carcinoma and related
to tumorigenic phenotype in lung cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
45:84–92. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schneider D, Kleeff J, Berberat PO, Zhu Z,
Korc M, Friess H and Büchler MW: Induction and expression of
betaig-h3 in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1588:1–6. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang F, Li XW, Lu WB and Jin JH: betaig-h3
correlates with related factors of peritoneal metastasis of gastric
cancer. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 29:181–186. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ween MP, Oehler MK and Ricciardelli C:
Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein
(TGFBI)/(betaig-H3): A matrix protein with dual functions in
ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:10461–10477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma C, Rong Y, Radiloff DR, Datto MB,
Centeno B, Bao S, Cheng AW, Lin F, Jiang S, Yeatman TJ and Wang XF:
Extracellular matrix protein betaig-h3/TGFBI promotes metastasis of
colon cancer by enhancing cell extravasation. Genes Dev.
22:308–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo L, Wu H, Zhu J, Zhang C, Ma J, Lan J
and Xie X: Genetic variations in the PI3K/AKT pathway predict
platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapeutic sensitivity in squamous
cervical cancer. Life Sci. 143:217–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Komeili-Movahhed T, Fouladdel S, Barzegar
E, Atashpour S, Hossein Ghahremani M, Nasser Ostad S, Madjd Z and
Azizi E: PI3K/Akt inhibition and down-regulation of BCRP
re-sensitize MCF7 breast cancer cell line to mitoxantrone
chemotherapy. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 18:472–477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhuang T, Djemil T, Qi P, Magnelli A,
Stephans K, Videtic G and Xia P: Dose calculation differences
between Monte Carlo and pencil beam depend on the tumor locations
and volumes for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. J Appl
Clin Med Phys. 14:40112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davey G and Wu Z: Attitudes in China
toward the use of animals in laboratory research. Altern Lab Anim.
35:313–316. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Castillo-Pichardo L, Cubano LA and
Dharmawardhane S: Dietary grape polyphenol resveratrol increases
mammary tumor growth and metastasis in immunocompromised mice. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 13:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Beck RE, Kim L, Yue NJ, Haffty BG, Khan AJ
and Goyal S: Treatment techniques to reduce cardiac irradiation for
breast cancer patients treated with breast-conserving surgery and
radiation therapy: A review. Front Oncol. 4:3272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma J, Cui W, He SM, Duan YH, Heng LJ, Wang
L and Gao GD: Human U87 astrocytoma cell invasion induced by
interaction of βig-h3 with integrin α5β1 involves calpain-2. PLoS
One. 7:e372972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim YH, Kwon HJ and Kim DS: Matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9)-dependent processing of βig-h3 protein
regulates cell migration, invasion, and adhesion. J Biol Chem.
287:38957–38969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeong HW and Kim IS: TGF-beta1 enhances
betaig-h3-mediated keratinocyte cell migration through the
alpha3beta1 integrin and PI3K. J Cell Biochem. 92:770–780. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|