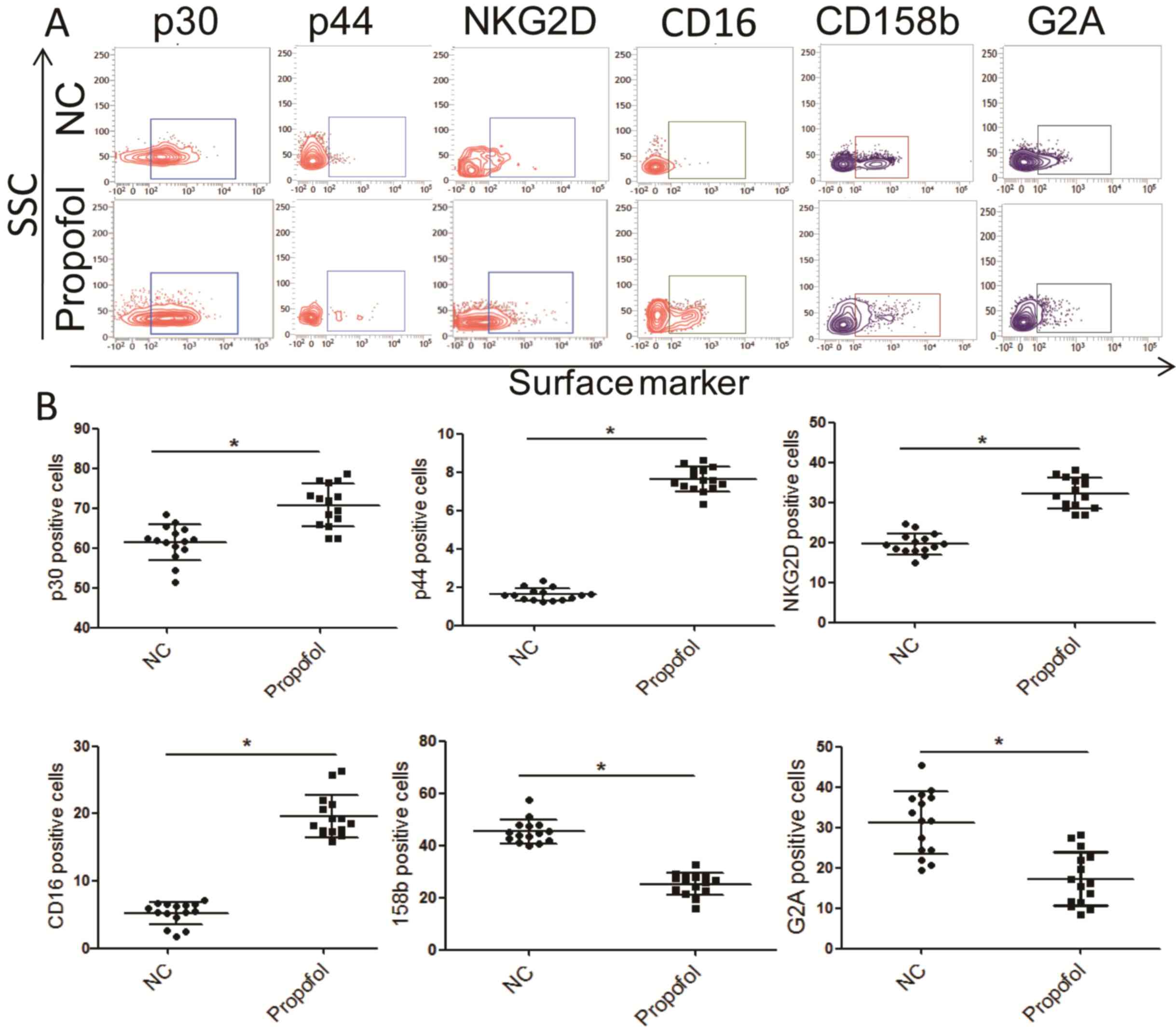
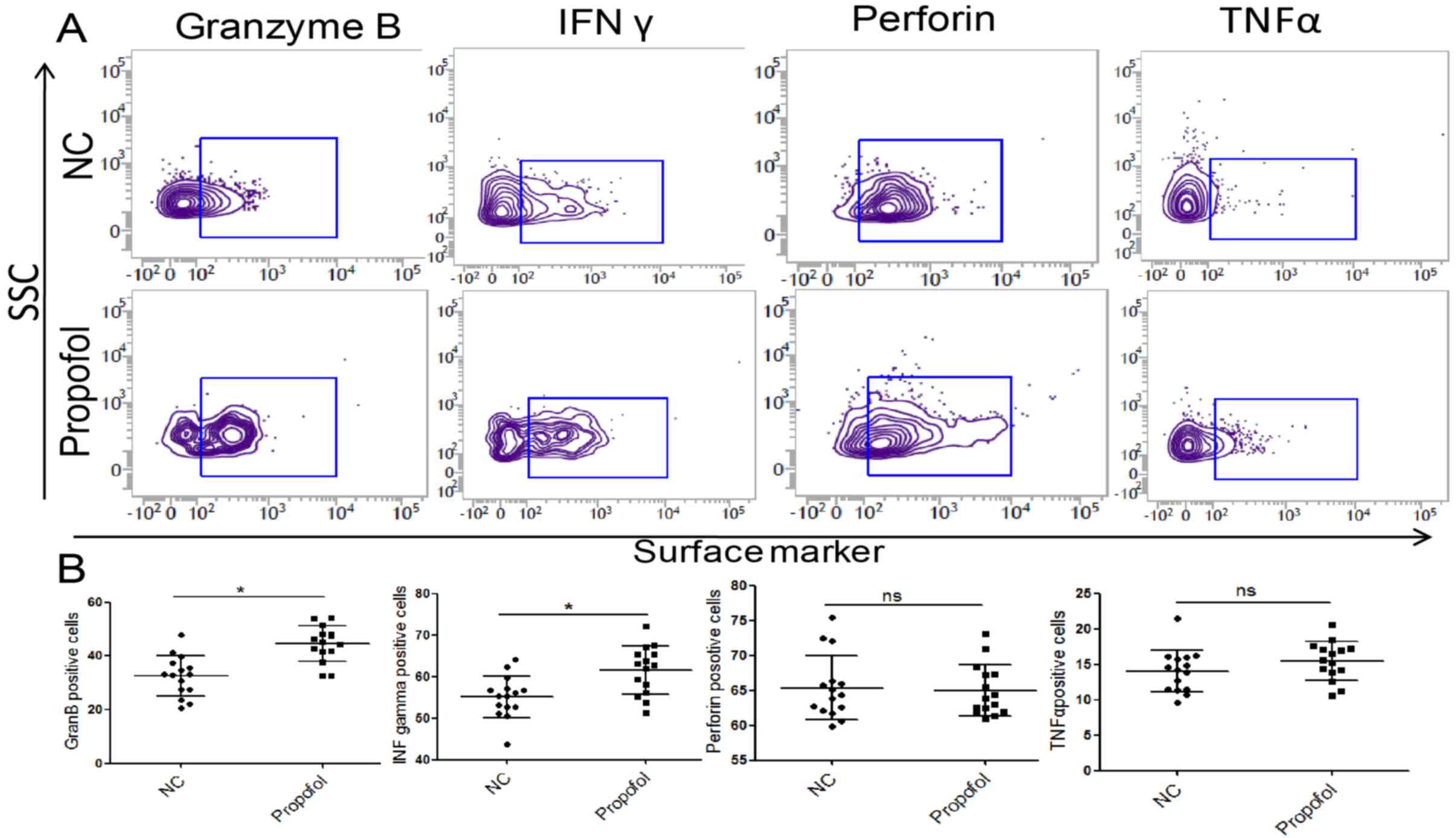
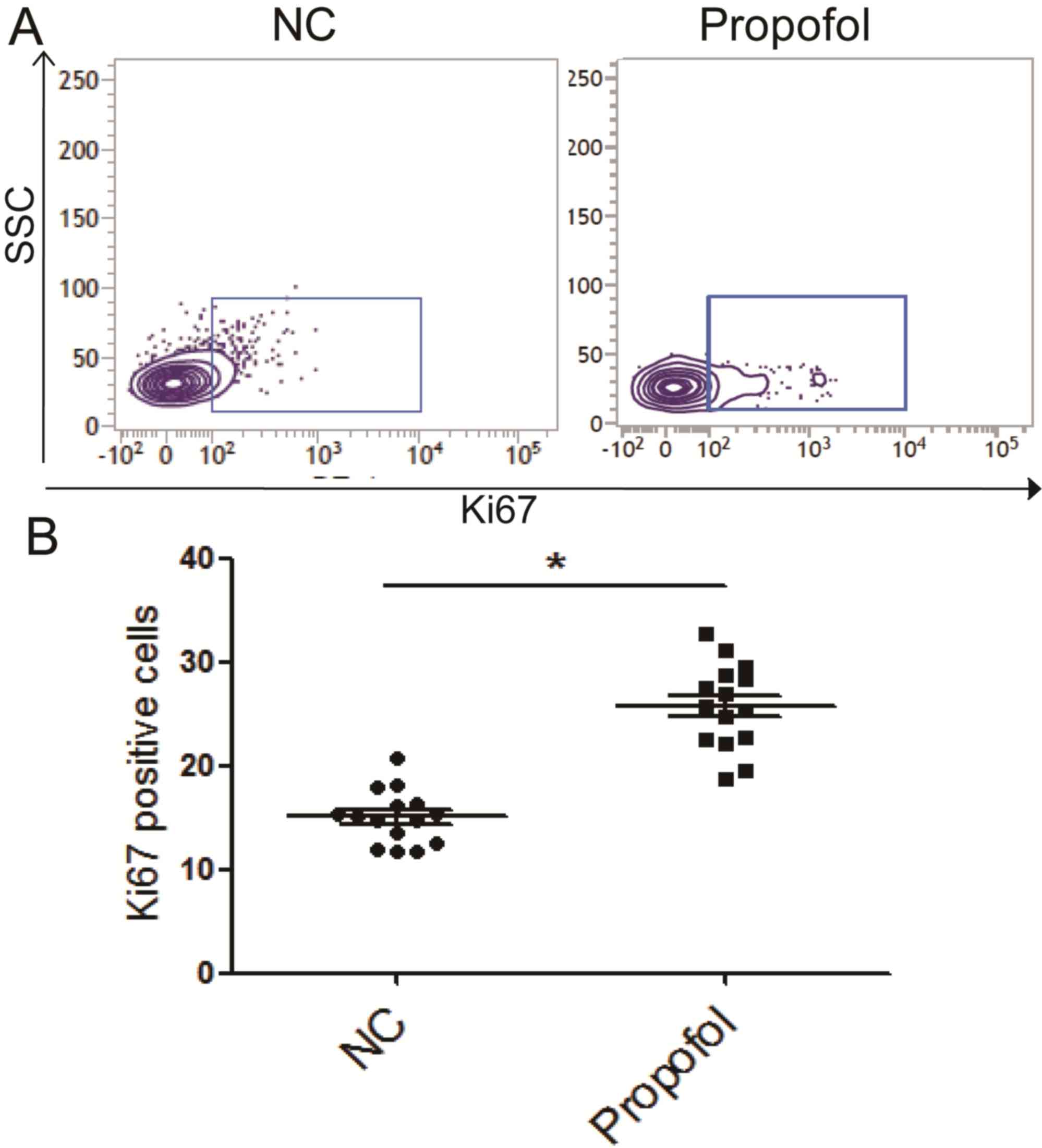
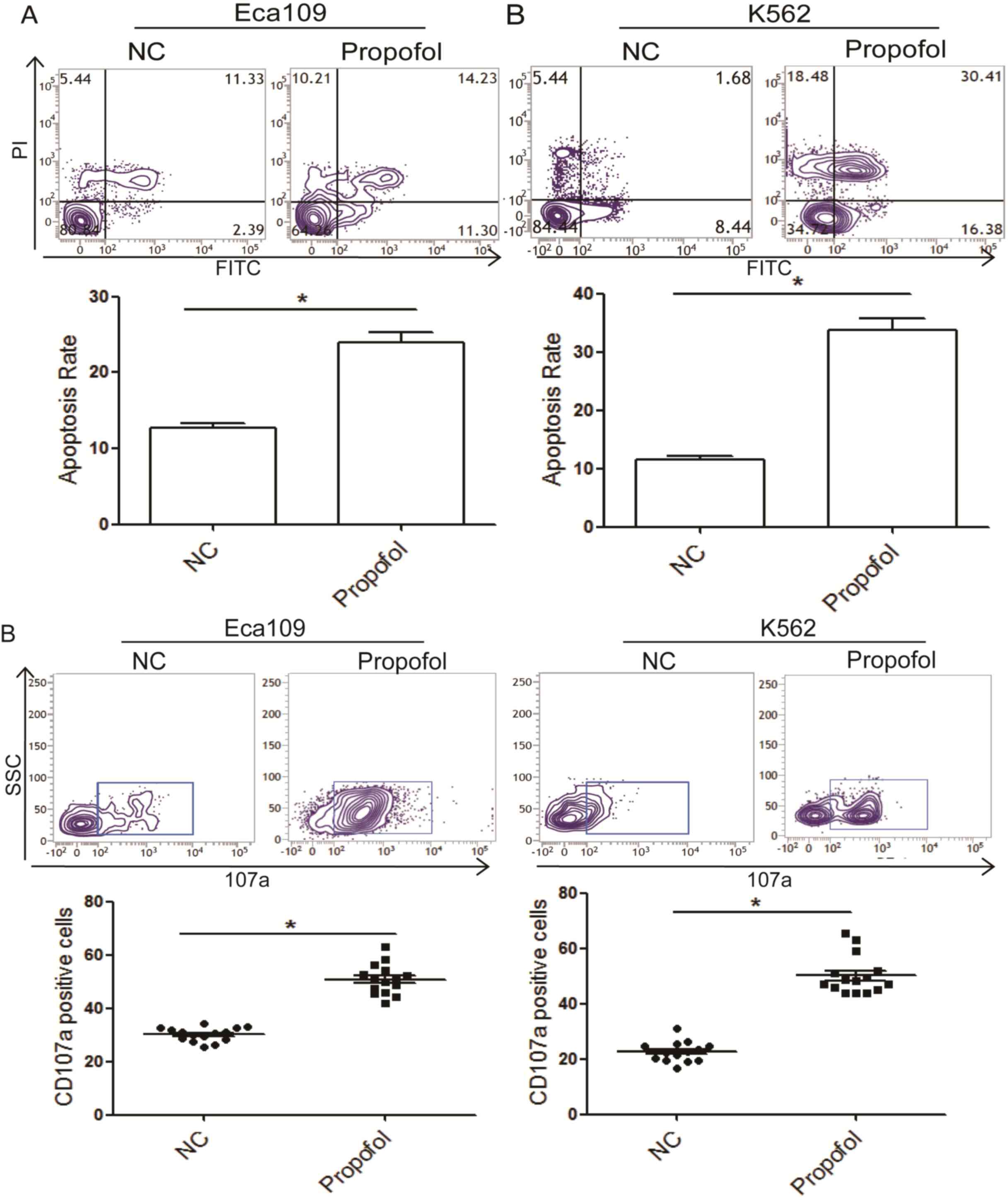
|
1
|
Lin C, Zhang N, Wang Y, Wang Y, Nice E,
Guo C, Zhang E, Yu L, Li M, Liu C, et al: Functional role of a
novel long noncoding RNA TTN-AS1 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma progression and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 24:486–498.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou X, Qiu GQ, Bao WA and Zhang DH: The
prognostic role of nutrition risk score (NRS) in patients with
metastatic or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Oncotarget. 8:77465–77473. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kurimoto K, Hayashi M, Guerrero-Preston R,
Koike M, Kanda M, Hirabayashi S, Tanabe H, Takano N, Iwata N, Niwa
Y, et al: PAX5 gene as a novel methylation marker that predicts
both clinical outcome and cisplatin sensitivity in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Epigenetics. 12:865–874. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu X, Dinglin X, Wang X, Luo W, Shen Q, Li
Y, Gu L, Zhou Q, Zhu H, Li Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA XIST
promotes malignancies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via
regulation of miR-101/EZH2. Oncotarget. 8:76015–76028.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai W, Lu JJ, Xu R, Xin P, Xin J, Chen Y,
Gao B, Chen J and Yang X: Survival based radiographic-grouping for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may impact clinical T stage.
Oncotarget. 9:9512–9530. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Feng Z, Wang W, Dong J, Gong X,
Pu H and Chen X: Expression of heat shock protein-27 (Hsp27) and
P38MAPK in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit.
23:5246–5253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kunizaki M, Hamasaki K, Wakata K, Tobinaga
S, Sumida Y, Hidaka S, Yasutake T, Miyazaki T, Matsumoto K,
Yamasaki T, et al: Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the
diagnosis and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 38:1807–1813. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen K, Zhu Z, Zhang N, Cheng G, Zhang F,
Jin J, Wu J, Ying L, Mao W and Su D: Tumor-infiltrating CD4+
lymphocytes predict a favorable survival in patients with operable
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 23:4619–4632.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jesinghaus M, Steiger K, Slotta-Huspenina
J, Drecoll E, Pfarr N, Meyer P, Konukiewitz B, Bettstetter M,
Wieczorek K, Ott K, et al: Increased intraepithelial CD3+
T-lymphocytes and high PD-L1 expression on tumor cells are
associated with a favorable prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and allow prognostic immunogenic subgrouping. Oncotarget.
8:46756–46768. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yankuzo HM, Baraya YS, Mustapha Z, Wong KK
and Yaacob NS: Immunomodulatory effects of a bioactive fraction of
Strobilanthes crispus in NMU-induced rat mammary tumor model. J
Ethnopharmacol. 213:31–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhuang PY, Zhang KW, Wang JD, Zhou XP, Liu
YB, Quan ZW and Shen J: Effect of TALEN-mediated IL-6 knockout on
cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and anti-cancer therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC-LM3) cells. Oncotarget.
8:77915–77927. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maj T, Wang W, Crespo J, Zhang H, Wang W,
Wei S, Zhao L, Vatan L, Shao I, Szeliga W, et al: Oxidative stress
controls regulatory T cell apoptosis and suppressor activity and
PD-L1-blockade resistance in tumor. Nat Immunol. 18:1332–1341.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Wang C, Wang J, Huang X and Cheng
Y: A novel systemic immune-inflammation index predicts survival and
quality of life of patients after curative resection for esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:2077–2086.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pérez-González O, Cuéllar-Guzmán LF, Soliz
J and Cata JP: Impact of regional anesthesia on recurrence,
metastasis, and immune response in breast cancer surgery: A
Systematic review of the literature. Reg Anesth Pain Med.
42:751–756. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eroglu T, Bozkurt M, Kapi E, Selcuk CT,
Kuvat SV, Tufek A, Isik FB, Bozarslan BH, Firat U and Satici O: A
study on the effects of the use of propofol in experimental model
inferior epigastric island flap on ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Craniofac Surg. 28:2193–2198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim R, Kawai A, Wakisaka M, Funaoka Y,
Ohtani S, Ito M, Kadoya T and Okada M: Differences in immune
response to anesthetics used for day surgery versus hospitalization
surgery for breast cancer patients. Clin Transl Med. 6:342017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Javaheri A, Wang AR, Prak Luning E, Lal P,
Goldberg LR and Kamoun M: Fatal accelerated rejection with a
prominent natural killer cell infiltrate in a heart transplant
recipient with peripartum cardiomyopathy. Transpl Immunol.
47:49–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pollmann J, Götz JJ, Rupp D, Strauss O,
Granzin M, Grünvogel O, Mutz P, Kramer C, Lasitschka F, Lohmann V,
et al: Hepatitis C virus-induced natural killer cell proliferation
involves monocyte-derived cells and the OX40/OX40L axis. J Hepatol.
68:421–430. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baltner K, Kübler A, Pal M, Balvociute M,
Mezger M, Handgretinger R and André MC: Expression of KIR2DS1 does
not significantly contribute to NK cell cytotoxicity in HLA-C1/C2
heterozygous haplotype B donors. Int Immunol. 29:423–429. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dansako H, Imai H, Ueda Y, Satoh S, Wakita
T and Kato N: ULBP1 is induced by hepatitis C virus infection and
is the target of the NK cell-mediated innate immune response in
human hepatocytes. FEBS Open Bio. 8:361–371. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang Z, Cheng F, Yan G, Xiong L and Liu H:
Propofol protects against endotoxin-induced myocardial injury by
inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation. Exp Ther Med. 15:2032–2036.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klöß S, Oberschmidt O, Morgan M, Dahlke J,
Arseniev L, Huppert V, Granzin M, Gardlowski T, Matthies N,
Soltenborn S, et al: Optimization of human NK cell manufacturing:
Fully automated separation, improved ex vivo expansion using IL-21
with autologous feeder cells, and generation of
anti-CD123-CAR-expressing effector cells. Hum Gene Ther.
28:897–913. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Voutsadakis IA: Expression and function of
immune ligand-receptor pairs in NK cells and cancer stem cells:
Therapeutic implications. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 41:107–121. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cameron G and Godfrey DI: Differential
surface phenotype and context-dependent reactivity of functionally
diverse NKT cells. Immunol Cell Biol. Mar 5–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nham T, Poznanski SM, Fan IY, Shenouda MM,
Chew MV, Lee AJ, Vahedi F, Karimi Y, Butcher M, Lee DA, et al: Ex
vivo-expanded NK cells from blood and ascites of ovarian cancer
patients are cytotoxic against autologous primary ovarian cancer
cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:575–587. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nakashima Y, Deie M, Yanada S, Sharman P
and Ochi M: Magnetically labeled human natural killer cells,
accumulated in vitro by an external magnetic force, are
effective against HOS osteosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol. 27:965–971.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu S, Gu X, Zhu L, Wu G, Zhou H, Song Y
and Wu C: Effects of propofol and sevoflurane on perioperative
immune response in patients undergoing laparoscopic radical
hysterectomy for cervical cancer. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e54792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Glasner A, Isaacson B, Viukov S, Neuman T,
Friedman N, Mandelboim M, Sexl V, Hanna JH and Mandelboim O:
Increased NK cell immunity in a transgenic mouse model of NKp46
overexpression. Sci Rep. 7:130902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Erokhina SA, Streltsova MA, Kanevskiy LM,
Telford WG, Sapozhnikov AM and Kovalenko EI: HLA-DR+ NK cells are
mostly characterized by less mature phenotype and high functional
activity. Immunol Cell Biol. 96:212–228. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsota P, Kostopanagiotou G, Kalimeris K,
Pandazi A, Kotsaki A, Kontogiannopoulou S and
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ: Transient effects of anesthesia on
leukocyte apoptosis and monocyte cytokine stimulation: A clinical
study. Immunol Invest. 1–8. 2018.
|
|
31
|
Rossaint J and Zarbock A: Perioperative
inflammation and its modulation by anesthetics. Anesth Analg.
126:1058–1067. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Acuff NV, Li X, Latha K, Nagy T and
Watford WT: Tpl2 promotes innate cell recruitment and effector T
cell differentiation to limit citrobacter rodentium burden and
dissemination. Infect Immun. 85:pii: e00193. –17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li L, Li W, Wang C, Yan X, Wang Y, Niu C,
Zhang X, Li M, Tian H, Yao C, et al: Adoptive transfer of natural
killer cells in combination with chemotherapy improves outcomes of
patients with locally advanced colon carcinoma. Cytotherapy.
20:134–148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gumbleton M, Sudan R, Fernandes S,
Engelman RW, Russo CM, Chisholm JD and Kerr WG: Dual enhancement of
T and NK cell function by pulsatile inhibition of SHIP1 improves
antitumor immunity and survival. Sci Signal. 10:pii: eaam5353.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sedghi S, Kutscher HL, Davidson BA and
Knight PR: Volatile anesthetics and immunity. Immunol Invest.
46:793–804. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cho JS, Lee MH, Kim SI, Park S, Park HS,
Oh E, Lee JH and Koo BN: The effects of perioperative anesthesia
and analgesia on immune function in patients undergoing breast
cancer resection: A prospective randomized stud. Int J Med Sci.
14:970–976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Inada T, Hirota K and Shingu K:
Intravenous anesthetic propofol suppresses prostaglandin E2 and
cysteinyl leukotriene production and reduces edema formation in
arachidonic acid-induced ear inflammation. J Immunotoxicol.
12:261–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai K, Huang Y, Chen Z, Sun X, Yang L and
Jiang Y: Kbtbd2 inhibits the cytotoxic activity of immortalized NK
cells through down-regulating mTOR signaling in a mouse
hepatocellular carcinoma model. Eur J Immunol. Jan 13–2018.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hoshikawa M, Aoki T, Matsushita H,
Karasaki T, Hosoi A, Odaira K, Fujieda N, Kobayashi Y, Kambara K,
Ohara O, et al: NK cell and IFN signatures are positive prognostic
biomarkers for resectable pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 495:2058–2065. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stangl S, Tontcheva N, Sievert W, Shevtsov
M, Niu M, Schmid TE, Pigorsch S, Combs SE, Haller B, Balermpas P,
et al: Heat shock protein 70 and tumor-infiltrating NK cells as
prognostic indicators for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck after radiochemotherapy: A multicentre
retrospective study of the German Cancer Consortium Radiation
Oncology Group (DKTK-ROG). Int J Cancer. 142:1911–1925. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|