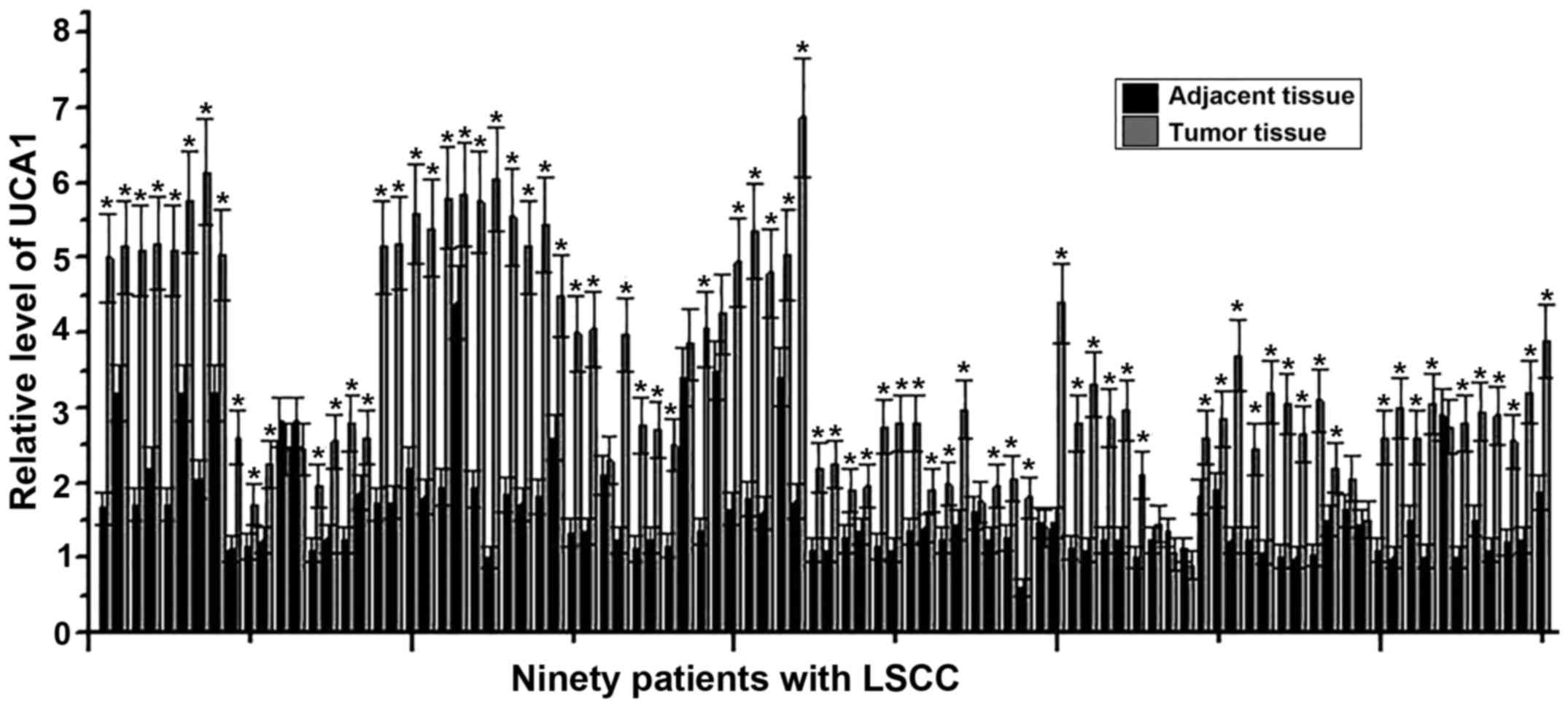
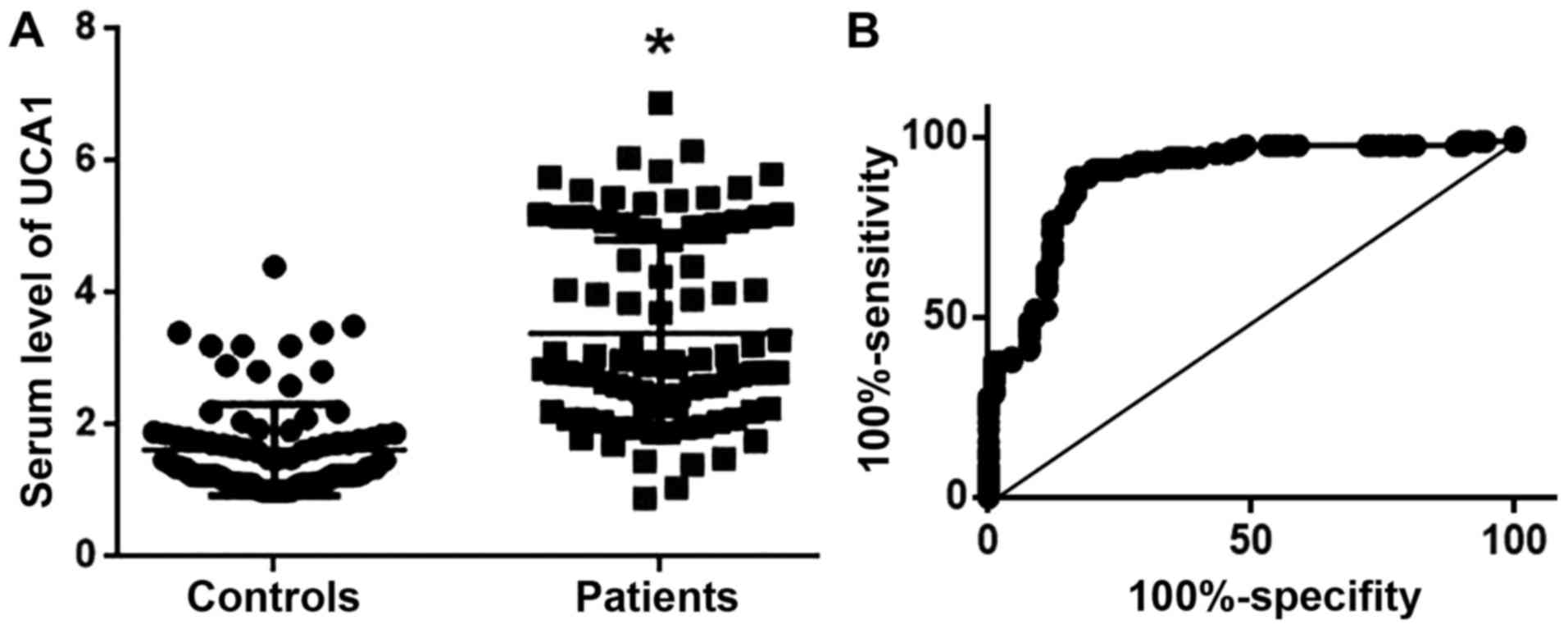
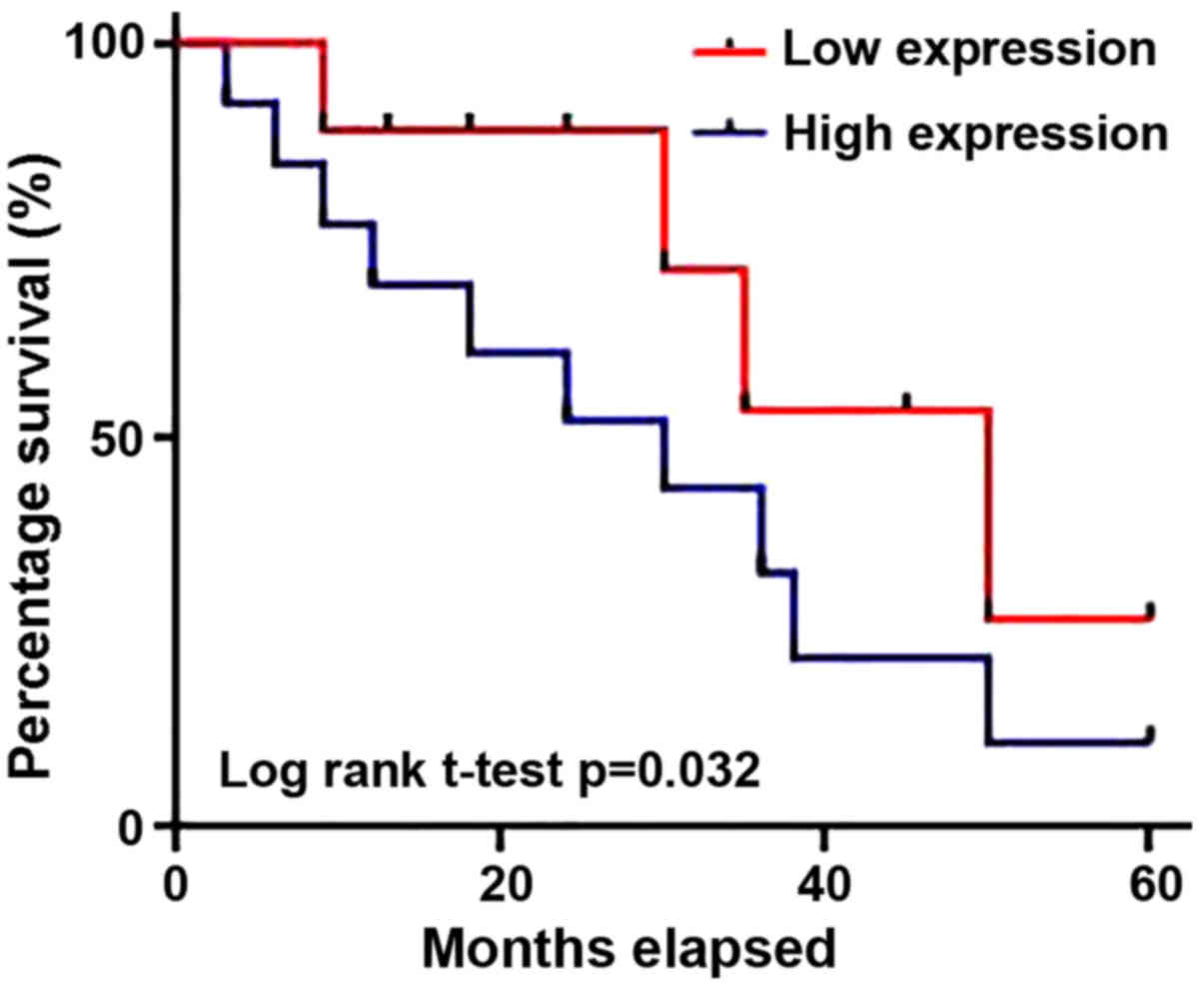
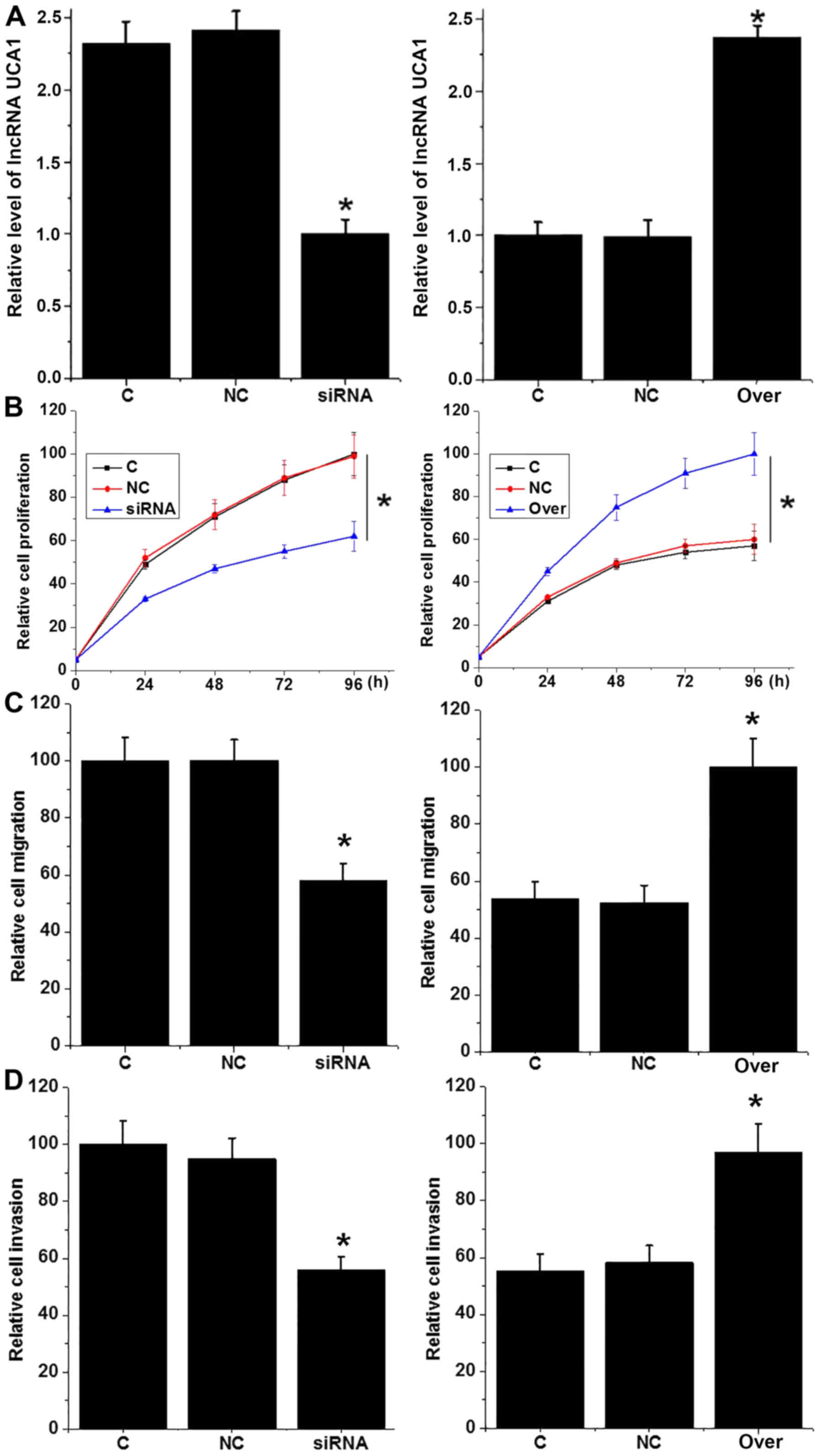
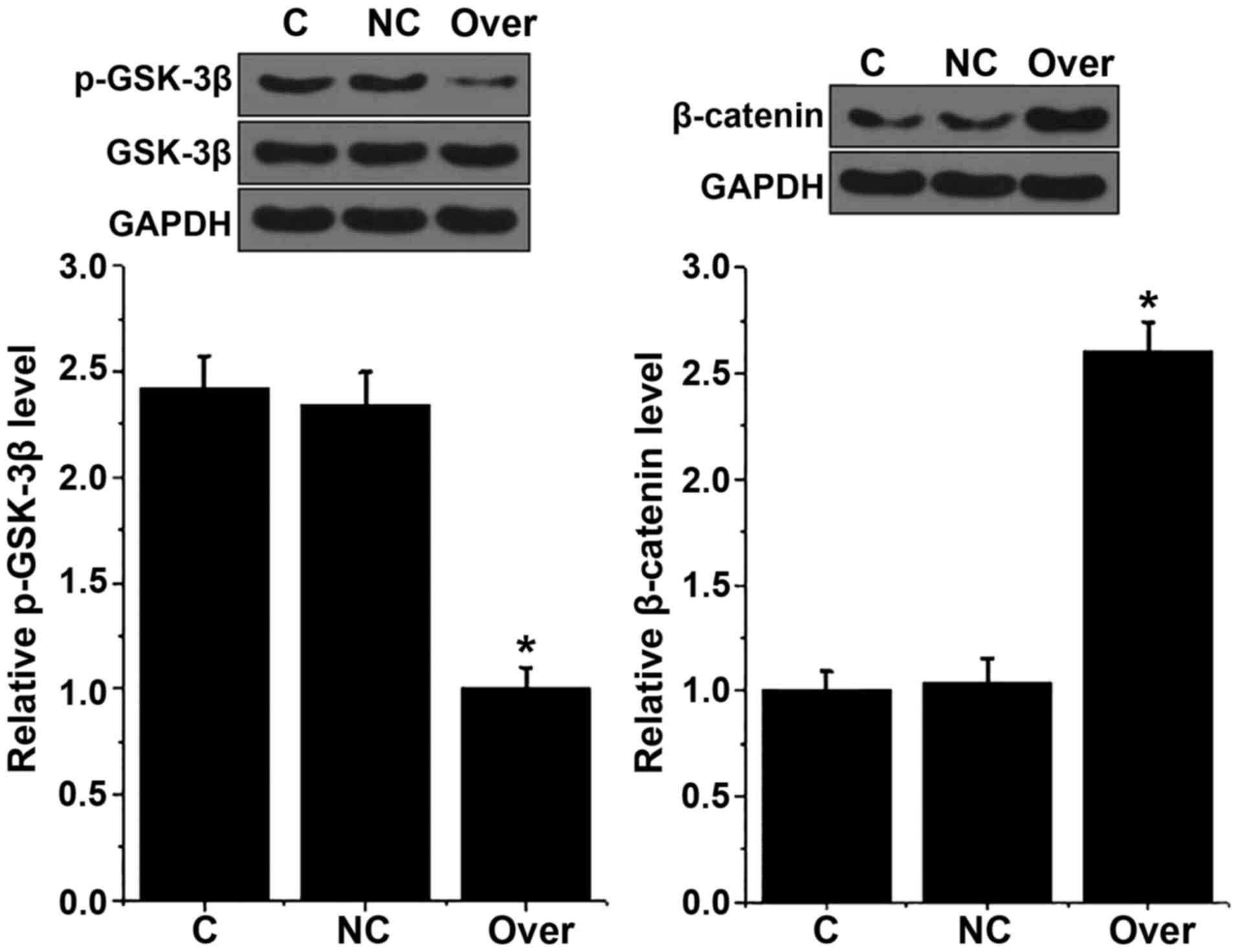
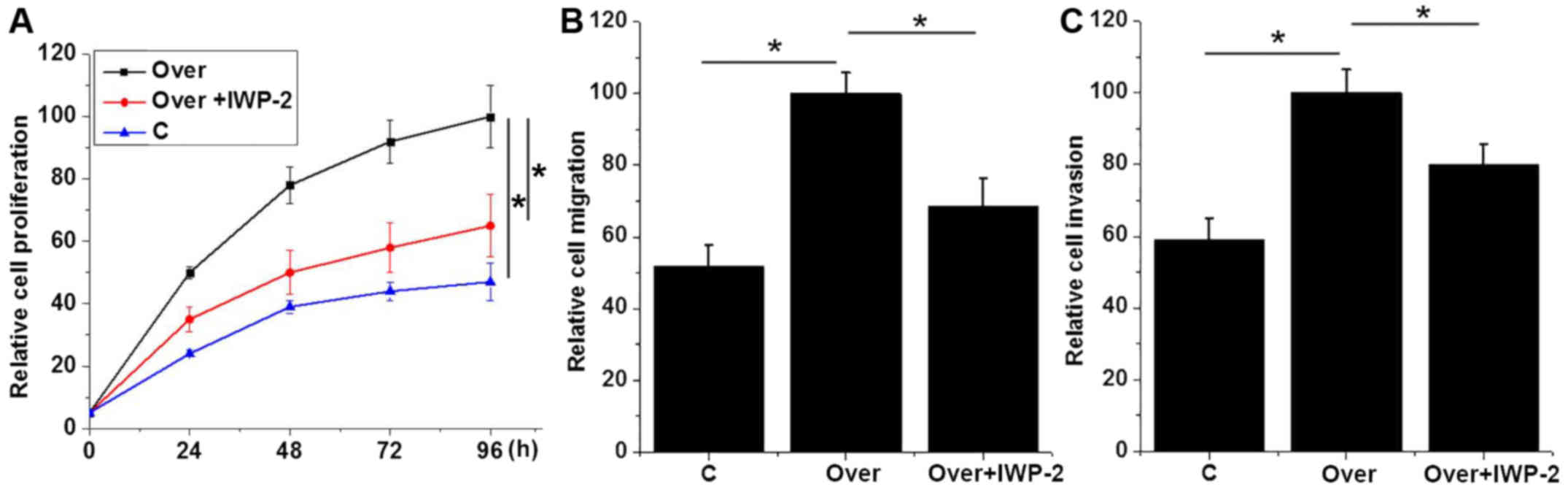
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei Q, Yu D, Liu M, Wang M, Zhao M, Liu M,
Jia W, Ma H, Fang J, Xu W, et al: Genome-wide association study
identifies three susceptibility loci for laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma in the Chinese population. Nat Genet. 46:1110–1114. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Varalakshmi KP, Naik VS, Swapna RS,
Sravani P and Neeraja M: Laryngeal biopsies with special reference
to malignant tumors: A histopathological study. Int J Sci Study.
4:197–202. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Perkel JM: Visiting ‘noncodarnia’.
Biotechniques. 54(301): 303–304. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han Y, Yang Y, Yuan H, Zhang TT, Sui H,
Wei XL, Liu L, Huang P, Zhang WJ and Bai YX: UCA1, a long
non-coding RNA up-regulated in colorectal cancer influences cell
proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle distribution. Pathology.
46:396–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang N, Hui L, Wang Y, Yang H and Jiang X:
Overexpression of SOX2 promotes migration, invasion, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in laryngeal cancer AMC-HN-8 cells. Tumor Biol. 35:7965–7973. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang YT, Wang YF, Lai JY, Shen SY, Wang F,
Kong J, Zhang W and Yang HY: Long non-coding RNA UCA1 contributes
to the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating
the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 107:1581–1589.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hanley JA and McNeil BJ: The meaning and
use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC)
curve. Radiology. 143:29–36. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Zhou N, Watabe K, Lu Z, Wu F, Xu
M and Mo YY: Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes breast tumor growth
by suppression of p27 (Kip1). Cell Death Dis. 5:e10082015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tian Y, Zhang X, Hao Y, Fang Z and He Y:
Potential roles of abnormally expressed long noncoding RNA UCA1 and
Malat-1 in metastasis of melanoma. Melanoma Res. 24:335–341. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hardisson D: Molecular pathogenesis of
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.
260:502–508. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen Z, Li Q, Deng H, Lu D, Song H and Guo
J: Long non-coding RNA profiling in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma and its clinical significance: Potential biomarkers for
LSCC. PLoS One. 9:e1082372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nie W, Ge HJ, Yang XQ, Sun X, Huang H, Tao
X, Chen WS and Li B: LncRNA-UCA1 exerts oncogenic functions in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-193a-3p. Cancer Lett.
371:99–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burgdorf SK, Claesson MH, Nielsen HJ and
Rosenberg J: Changes in cytokine and biomarker blood levels in
patients with colorectal cancer during dendritic cell-based
vaccination. Acta Oncol. 48:1157–1164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Srivastava AK, Singh PK, Rath SK, Dalela
D, Goel MM and Bhatt ML: Appraisal of diagnostic ability of UCA1 as
a biomarker of carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Tumor Biol.
35:11435–11442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Cao R and Mu H: Long non-coding RNA
UCA1 may be a novel diagnostic and predictive biomarker in plasma
for early gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12936–12942.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Qiu M, Xu Y, Li M, Dong G, Mao Q,
Yin R and Xu L: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 correlates with smoking in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36:5523–5528. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu V, Singh P, Rahimy E, Zheng H, Kuo SZ,
Kim E, Wang-Rodriguez J and Ongkeko WM: RNA-seq analysis identifies
key long non-coding RNAs connected to the pathogenesis of
alcohol-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 12:2846–2853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nagaraj AB, Joseph P, Kovalenko O, Singh
S, Armstrong A, Redline R, Resnick K, Zanotti K, Waggoner S and
DiFeo A: Critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in driving
epithelial ovarian cancer platinum resistance. Oncotarget.
6:23720–23734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang N, Wang Y, Hui L, Li X and Jiang X:
SOX 1, contrary to SOX 2, suppresses proliferation, migration, and
invasion in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Tumor Biol. 36:8625–8635. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu H, Wang G, Yang L, Qu J, Yang Z and
Zhou X: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA UCA1 increases the
tamoxifen sensitivity of breast cancer cells through inhibition of
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS One. 11:e01684062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|