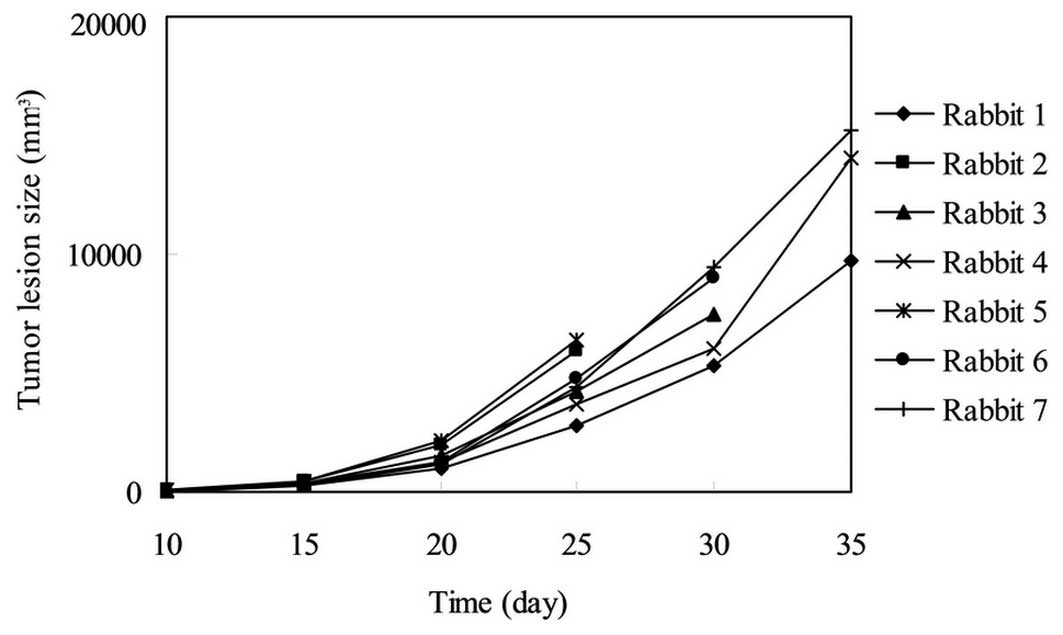
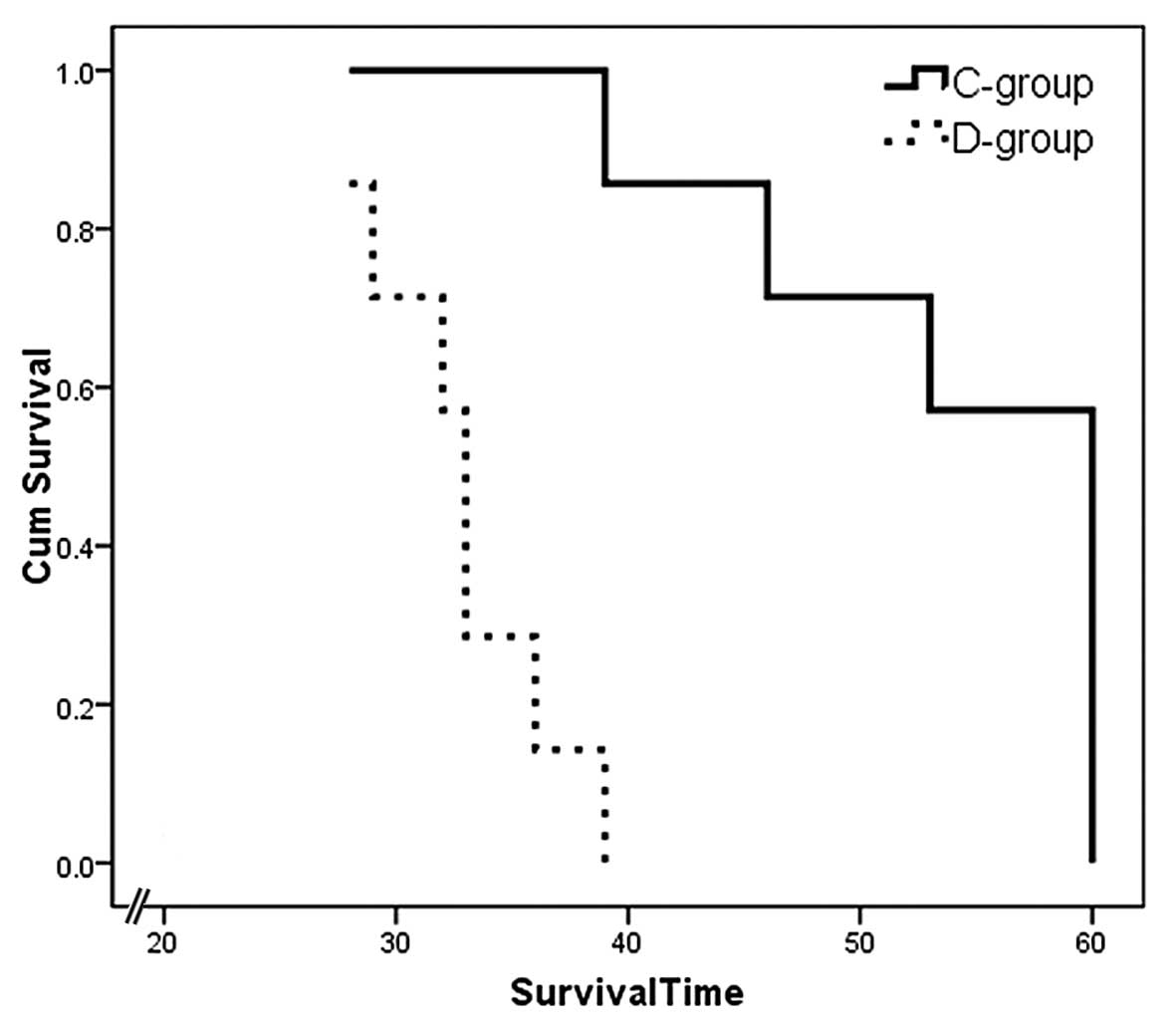
|
1
|
Katchy KC, Alexander S, Al-Nashmi NM and
Al-Ramadan A: Epidemiology of primary brain tumors in childhood and
adolescence in Kuwait. Springerplus. 2:582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ziegler DS, Cohn RJ, McCowage G, et al:
Efficacy of vincristine and etoposide with escalating
cyclophosphamide in poor-prognosis pediatric brain tumors. Neuro
Oncol. 8:53–59. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lehotska V, Tothova L and Valkovic L: The
role of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in differentiation of local
recurrence and residual soft-tissue tumor versus post-treatment
changes. Bratisl Lek Listy. 114:88–92. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu JG, Chen FL, Ge CL, Gong MY, Zuo HB
and Zhang JR: Cryosurgery for treatment of subcutaneously
xenotransplanted tumors in rats and its effect on cellular
immunity. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 10:339–346. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Y, Wang C, Lu Y, et al: Outcomes of
ultrasound-guided percutaneous argon-helium cryoablation of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 19:674–684.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vasil'ev SA, Pesnia-Prasolov SB, Krylov
VV, et al: Cryodestruction in neurosurgery. Khirurgiia (Mosk).
2:105–108. 2013.[(In Russian)]. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bomers JG, Yakar D, Overduin CG, et al: MR
imaging-guided focal cryoablation in patients with recurrent
prostate cancer. Radiology. 268:451–460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jaskólski DJ, Fortuniak J, Majos A, et al:
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in intracranial tumours of glial
origin. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 47:438–449. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun CJ, Li C, Yu JM, et al: Comparison of
64-slice CT perfusion imaging with contrast-enhanced CT for
evaluating the target volume for three-dimensional conformal
radiotherapy in the rabbit VX 2 brain tumor model. J Radiat Res.
53:454–461. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bahn D, de Castro Abreu AL, Gill IS, et
al: Focal cryotherapy for clinically unilateral low-intermediate
risk prostate cancer in 73 men with a median follow-up of 3.7
years. Eur Urol. 62:55–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gangi A, Tsoumakidou G, Abdelli O, et al:
Percutaneous MR-guided cryoablation of prostate cancer: initial
experience. Eur Radiol. 22:1829–1835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anayama T, Nakajima T, Dunne M, et al: A
novel minimally invasive technique to create a rabbit vX2 lung
tumor model for nano-sized image contrast and interventional
studies. PLoS One. 8:e673552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Y, Tu HJ, Lei Z, et al: Experimental
study of apoptosis in C6 rat glioma model induced by cryotherapy.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 12:1615–1618. 2005.[(In
Chinese)].
|
|
14
|
Song J, Li C, Wu L, et al: MRI-guided
brain tumor cryoablation in a rabbit model. J Magn Reson Imaging.
29:545–551. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mei LJ, Yang XJ, Tang L, Hassan AH,
Yonemura Y and Li Y: Establishment and identification of a rabbit
model of peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. BMC Cancer.
10:1242010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Handal JA, Schulz JF, Florez GB, Kwok SC,
Khurana JS and Samuel SP: Creation of rabbit bone and soft tissue
tumor using cultured VX2 cells. J Surg Res. 179:e127–e132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anderson JK, Shingleton WB and Cadeddu JA:
Imaging associated with percutaneous and intraoperative management
of renal tumors. Urol Clin North Am. 33:339–352. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tacke J, Speetzen R, Adam G, et al:
Experimental MR imaging-guided interstitial cryotherapy of the
brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:431–440. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu KW, Li QW, Zuo MH, Sun T and Jiang M:
Clinical observation on the combined treatment of 57 cases of
non-small cell lung cancer using argon-helium cryosurgery and C
hinese herbal medicine. Chin J Integr Med. 13:224–227. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mack MG and Vogl TJ: MR-guided ablation of
head and neck tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 14:853–859. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao H, Liao Q, Cheng M, et al:
5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid photodynamic diagnosis guided
microsurgery and photodynamic therapy on VX 2 brain tumour
implanted in a rabbit model. Chin Med J (Engl). 122:1316–1321.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|