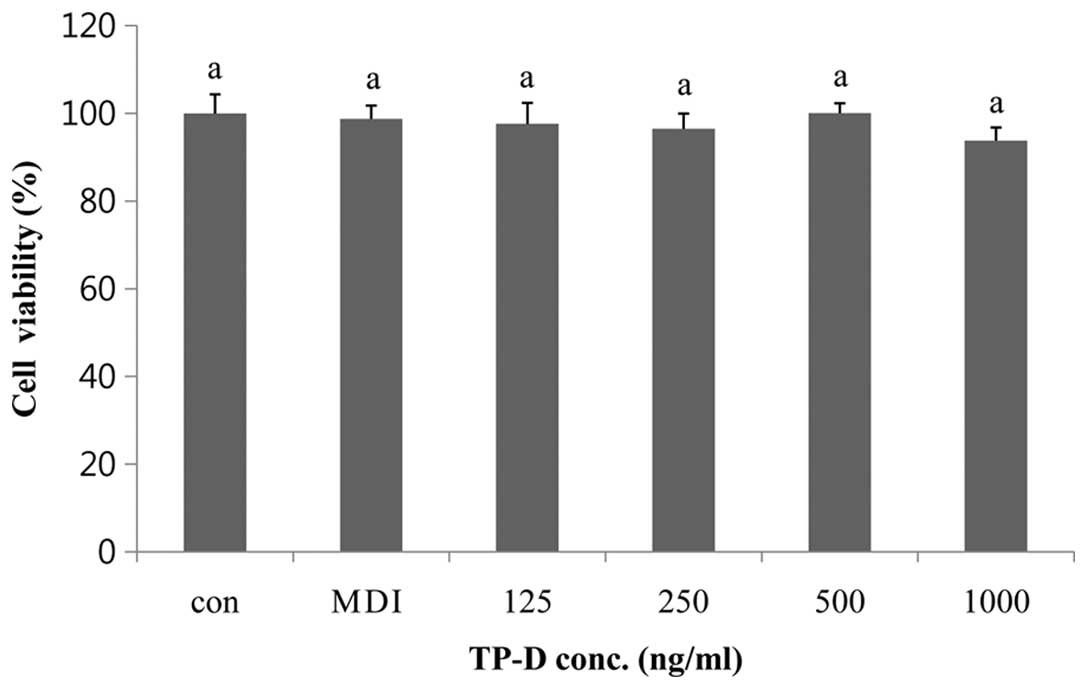
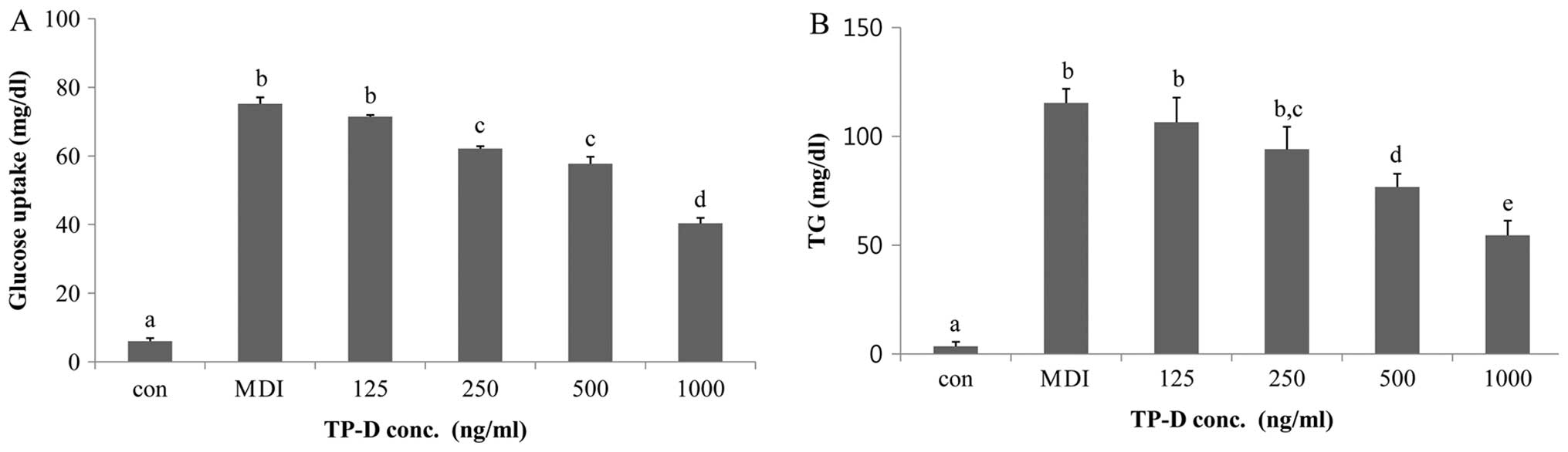
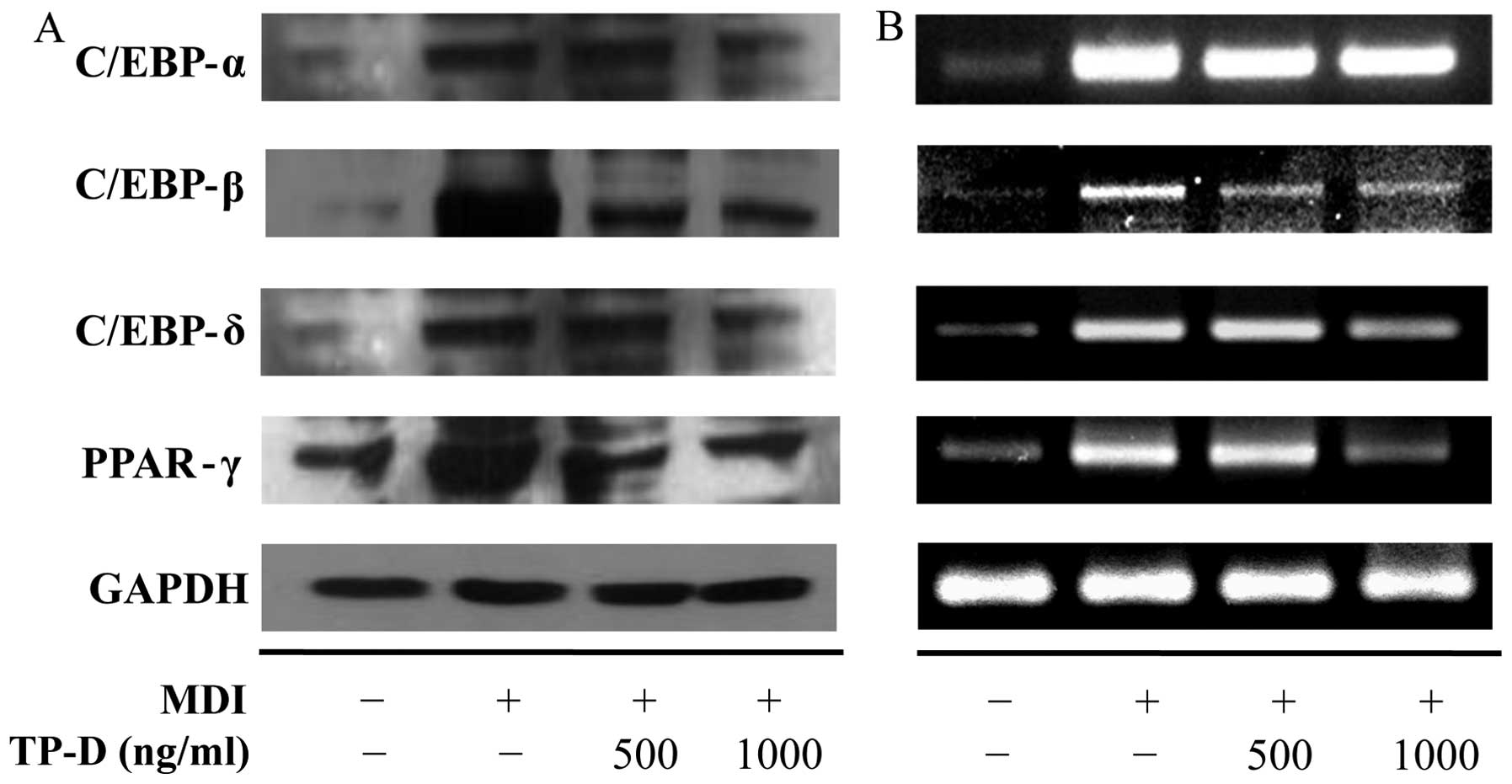
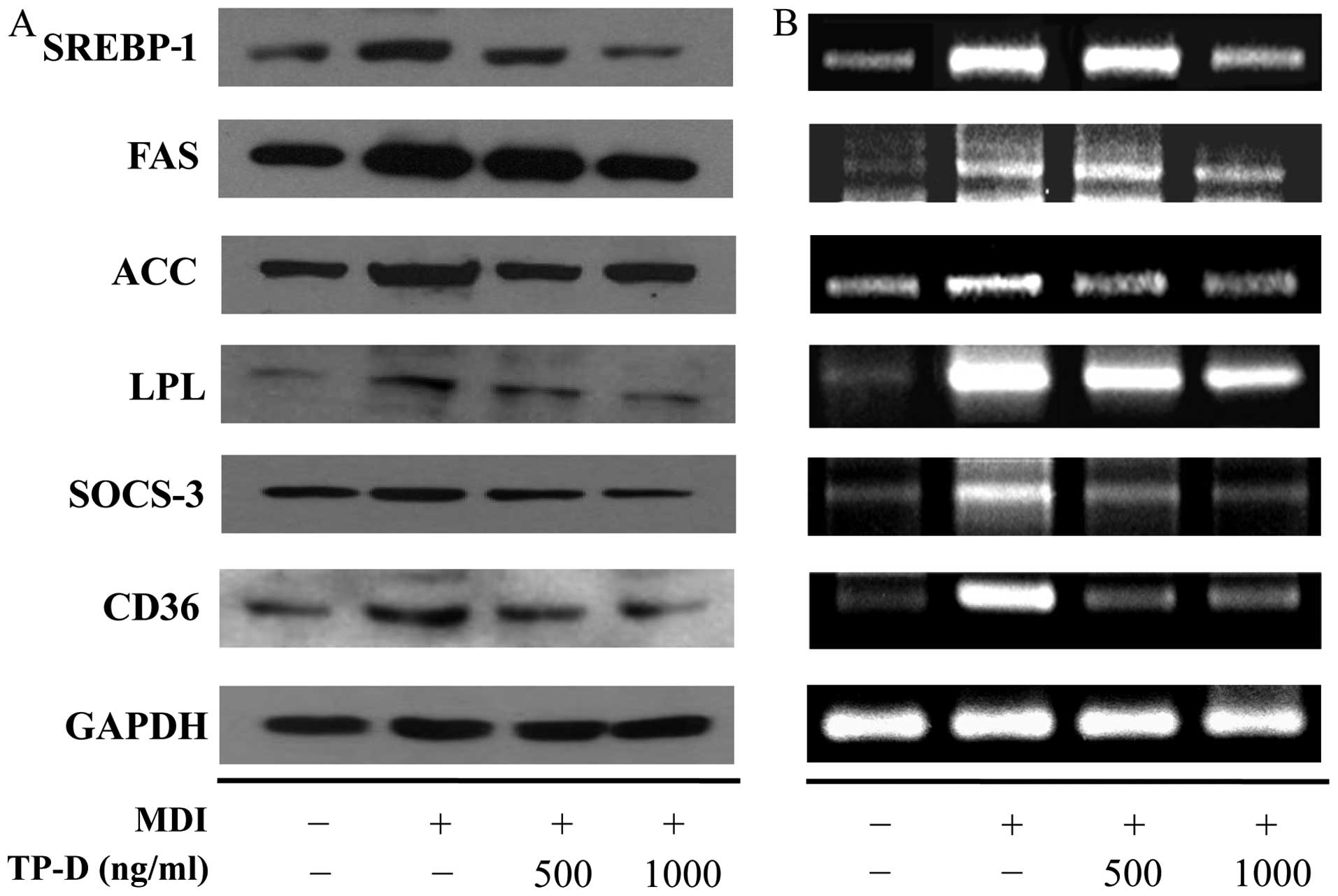
|
1
|
Kim DM, Choi HR, Park A, Shin SM, Bae KH,
Lee SC, Kim IC and Kim WK: Retinoic acid inhibits adipogenesis via
activation of Wnt signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 434:455–459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ordovas JM and Mooser V: Nutrigenomics and
nutrigenetics. Curr Opin Lipidol. 15:101–108. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahn J, Lee H, Kim S and Ha T:
Curcumin-induced suppression of adipogenic differentiation is
accompanied by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 298:C1510–C1516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Symposium of obesity. The ministry of
health welfare korea; 2006
|
|
5
|
Dani C, Smith AG, Dessolin S, Leroy P,
Staccini L, Villageois P, Darimont C and Ailhaud G: Differentiation
of embryonic stem cells into adipocytes in vitro. J Cell Sci.
110:1279–1285. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV and Kaykas
A: WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev
Genet. 5:691–701. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu J and Farmer SR: Regulating the
balance between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
and beta-catenin signaling during adipogenesis. A glycogen synthase
kinase 3beta phosphor-ylation-defective mutant of beta-catenin
inhibits expression of a subset of adipogenic genes. J Biol Chem.
279:45020–45027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moldes M, Zuo Y, Morrison RF, Silva D,
Park BH, Liu J and Farmer SR: Peroxisome-proliferator-activated
receptor gamma suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signalling during
adipogenesis. Biochem J. 376:607–613. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim YM, Kim EY, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Peptide
derived from desalinated boiled tuna extract inhibits adipogenesis
through the downregulation of C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Int J Mol Med. 35:1362–1368. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Browning JD and Horton JD: Molecular
mediators of hepatic steatosis and liver injury. J Clin Invest.
114:147–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Larter CZ and Farrell GC: Insulin
resistance, adiponectin, cytokines in NASH: which is the best
target to treat? J Hepatol. 44:253–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mitro N, Mak PA, Vargas L, Godio C,
Hampton E, Molteni V, Kreusch A and Saez E: The nuclear receptor
LXR is a glucose sensor. Nature. 445:219–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Horton JD, Goldstein JL and Brown MS:
SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty
acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 109:1125–1131. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou J, Febbraio M, Wada T, Zhai Y, Kuruba
R, He J, Lee JH, Khadem S, Ren S, Li S, et al: Hepatic fatty acid
transporter Cd36 is a common target of LXR, PXR, and PPARgamma in
promoting steatosis. Gastroenterology. 134:556–567. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueki K, Kondo T and Kahn CR: Suppressor of
cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance
through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor
substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol.
24:5434–5446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Musso G, Gambino R and Cassader M: Recent
insights into hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). Prog Lipid Res. 48:1–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Klaus S, Ely M, Encke D and Heldmaier G:
Functional assessment of white and brown adipocyte development and
energy metabolism in cell culture. J Cell Sci. 108:3171–3180.
1995.
|
|
20
|
Stephens JM and Pekala PH: Transcriptional
repression of the GLUT4 and C/EBP genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by
tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 266:21839–21845.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qin L, Chen Y, Niu Y, Chen W, Wang Q, Xiao
S, Li A, Xie Y, Li J, Zhao X, et al: A deep investigation into the
adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating
adipogenesis by modulating the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway. BMC Genomics. 11:3202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cadigan KM and Liu YI: Wnt signaling:
Complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci. 119:395–402. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN,
Lucas PC, Erickson RL and MacDougald OA: Inhibition of adipogenesis
by Wnt signaling. Science. 289:950–953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang C, Pattabiraman N, Zhou JN, Fu M,
Sakamaki T, Albanese C, Li Z, Wu K, Hulit J, Neumeister P, et al:
Cyclin D1 repression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma expression and transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 23:6159–6173.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crouch E, Persson A, Chang D and Heuser J:
Molecular structure of pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D). J
Biol Chem. 269:17311–17319. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McCormack FX, Pattanajitvilai S, Stewart
J, Possmayer F, Inchley K and Voelker DR: The Cys6 intermolecular
disulfide bond and the collagen-like region of rat SP-A play
critical roles in interactions with alveolar type II cells and
surfactant lipids. J Biol Chem. 272:27971–27979. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi TB and Kim YJ: Effect of obesity
reduction by exercise therapy and drug therapy. Kor J Aesthet
Cosmetol. 5:133–143. 2010.
|
|
28
|
Kim HO, Hwang YI and Kim GN: Anti-obese
function of demethoxycurcumin through suppression of adipogenesis
in 3T3-L1 cells. Kor J Aesthet Cosmetol. 11:29–34. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Lee HS, Kim HJ, Choi JI, Kim JH, Kim JG,
Chun BS, Ahn DH, Chung YJ, Kim YJ, Byun MW and Lee JW: Antioxidant
activity of the ethanol extract from cooking drips of Thunnus
thynnus by gamma irradiation. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr.
37:810–814. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Carroll KK: Biological effects of fish
oils in relation to chronic disease. Lipids. 21:731–732. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mehta J, Lopez LM and Wargovich T:
Eicosapentaenoic acid: its relevance in atherosclerosis and
coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 59:155–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bennett CN, Ross SE, Longo KA, Bajnok L,
Hemati N, Johnson KW, Harrison SD and Macdougald OA: Regulation of
Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 277:30998–31004.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Willert K and Nusse R: Beta-catenin: a key
mediator of Wnt signaling. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 8:95–102. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D’Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze’ev A: The cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|