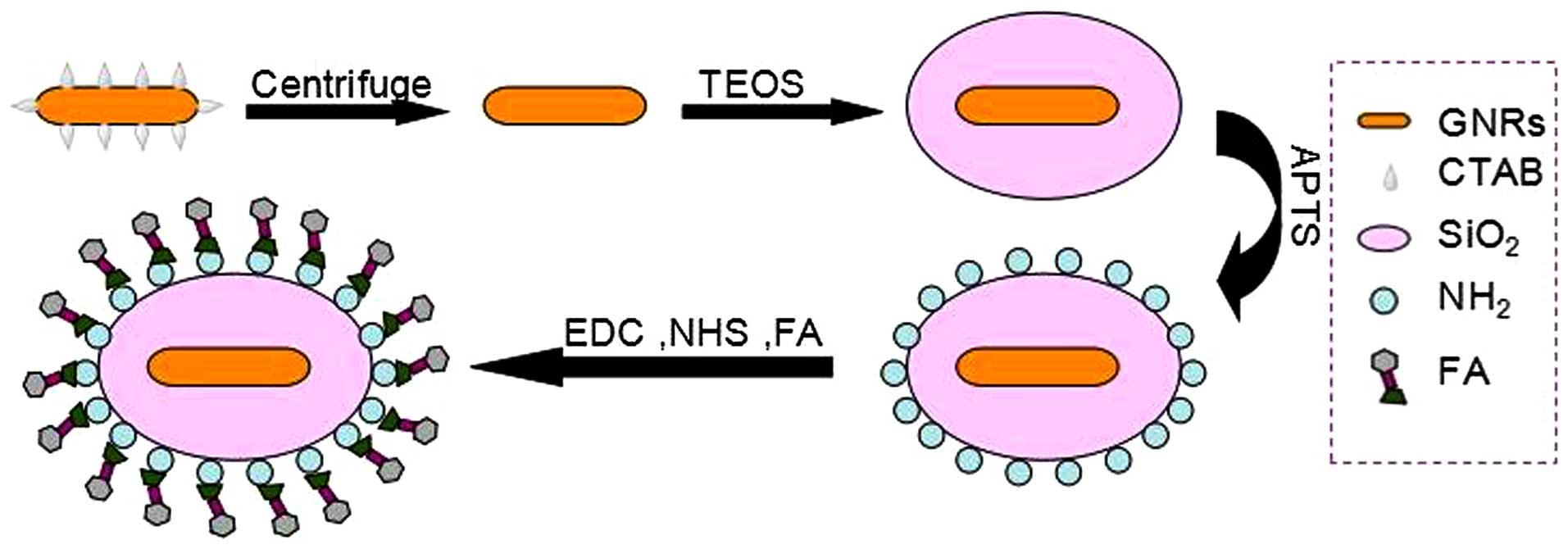
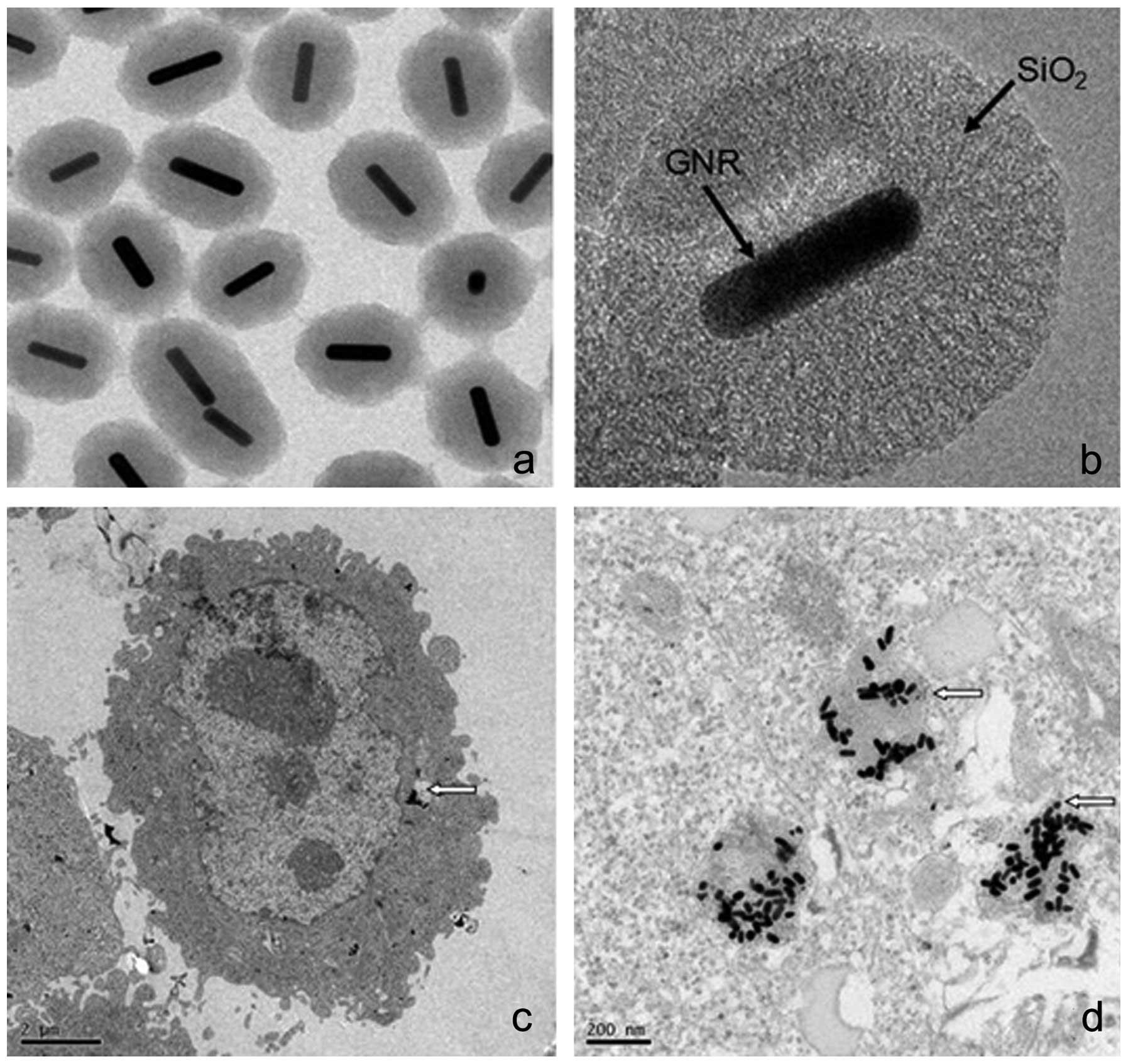
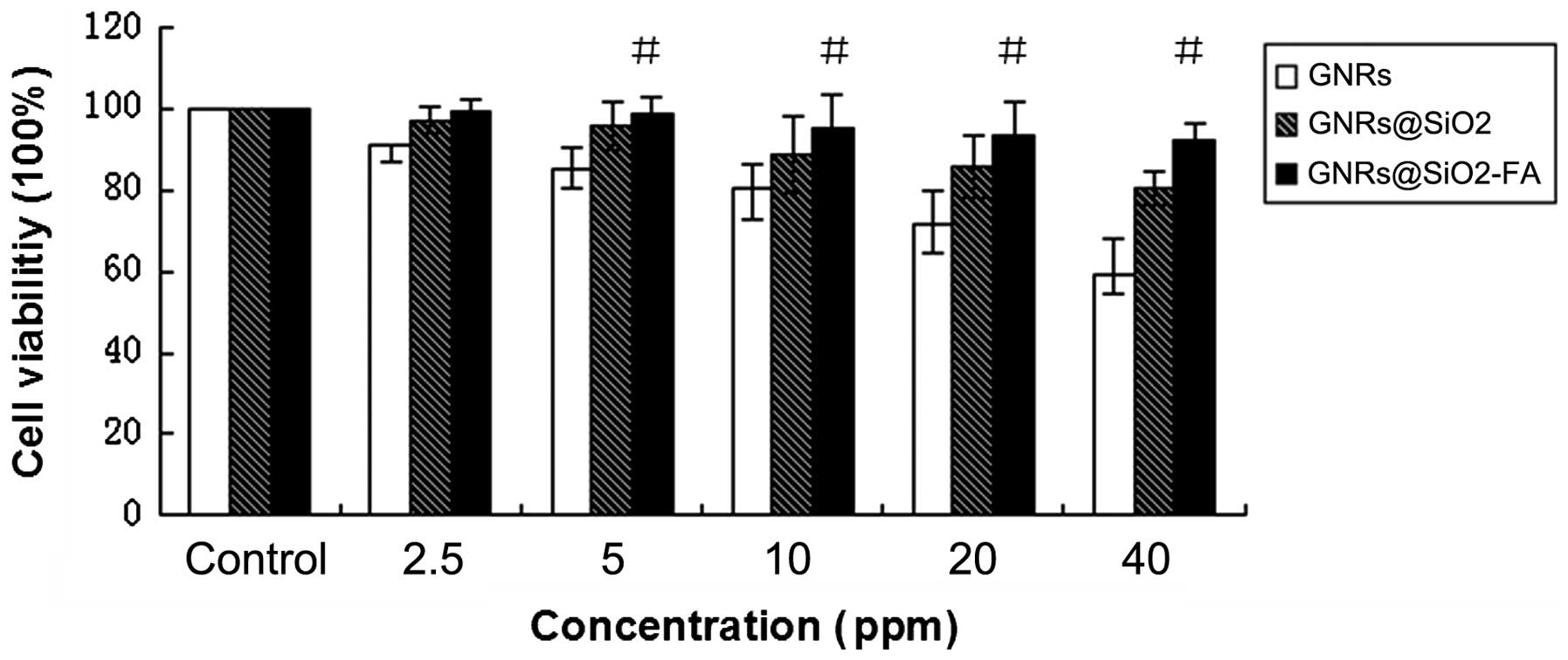
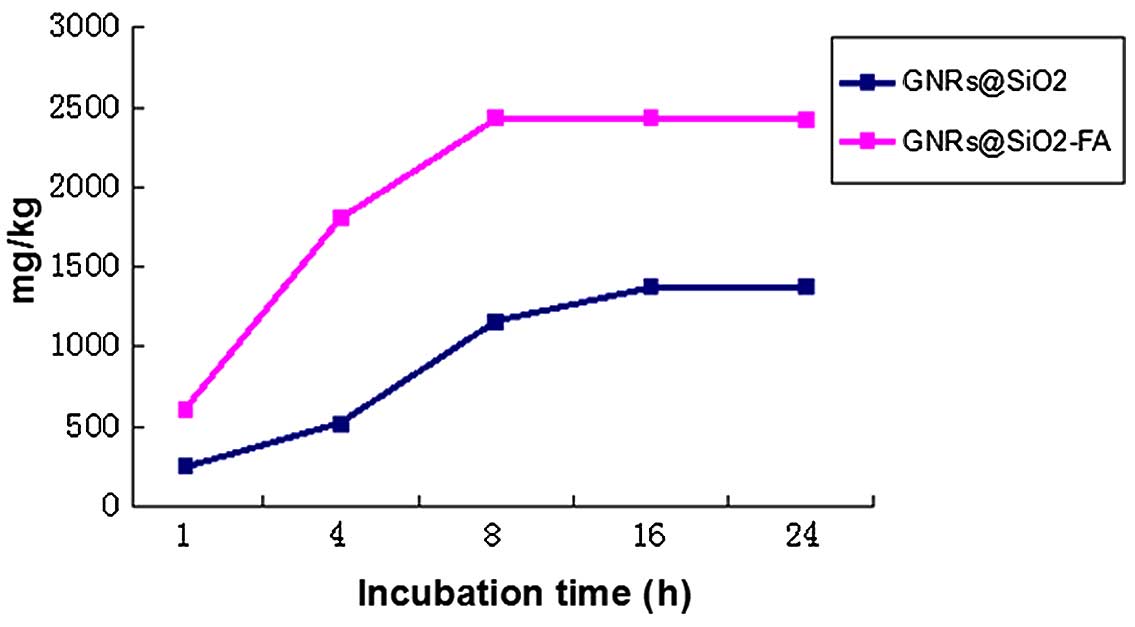
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ciacio O, Voron T, Pittau G, Lewin M,
Vibert E, Adam R, Sa Cunha A, Cherqui D, Schielke A, Soubrane O, et
al: Interest of preoperative immunonutrition in liver resection for
cancer: study protocol of the PROPILS trial, a multicenter
randomized controlled phase IV trial. BMC Cancer. 14(980)2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herron B, Herron A, Howell K, Chin D and
Roads L: A Review of radiation therapy's role in early-stage breast
cancer and an introduction to electronic brachytherapy. Cancer
Treatment - Conventional and Innovative Approaches. Rangel L:
InTech. 223–238. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu W, Zhu Z, Deng K, Li Z, Zhou Y, Qiu H,
Gao Y, Che S and Tang Z: Gold nanorod@chiral mesoporous silica
core-shell nanoparticles with unique optical properties. J Am Chem
Soc. 135:9659–9664. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu XG and Gao XH: Multilayer coating of
gold nanorods for combined stability and biocompatibility. Phys
Chem Chem Phys. 13:10028–10035. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gui C and Cui DX: Functionalized gold
nanorods for tumor imaging and targeted therapy. Cancer Biol Med.
9:221–233. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Xu W, Luo T, Li P, Zhou C, Cui D, Pang B,
Ren Q and Fu S: RGD-conjugated gold nanorods induce
radiosensitization in melanoma cancer cells by downregulating
alpha(v)beta(3) expression. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:915–924.
2012.
|
|
8
|
Mackey MA, Ali MR, Austin LA, Near RD and
El-Sayed MA: The most effective gold nanorod size for plasmonic
photothermal therapy: theory and in vitro experiments. J Phys Chem
B. 118:1319–1326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Franzen SA: A comparison of peptide and
folate receptor targeting of cancer cells: from single agent to
nanoparticle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 8:281–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
D'Angelica M, Ammori J, Gonen M, Klimstra
DS, Low PS, Murphy L, Weiser MR, Paty PB, Fong Y, Dematteo RP, et
al: Folate receptor-alpha expression in resectable hepatic
colorectal cancer metastases: patterns and significance. Mod
Pathol. 24:1221–1228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leamon CP: Folate-targeted drug strategies
for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 9:1277–1286.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pastoriza-Santos I, Perez-Juste J and
Liz-Marzan LM: Silica-coating and hydrophobation of CTAB-stabilized
gold nanorods. Chem Mater. 8:2465–2467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lo Muzio L, Staibano S, Pannone G,
Mignogna MD, Mariggiò A, Salvatore G, Chieffi P, Tramontano D, De
Rosa G and Altieri DC: Expression of the apoptosis inhibitor
survivin in aggressive squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
70:249–254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ribas J, Bettayeb K, Ferandin Y, Knockaert
M, Garrofé-Ochoa X, Totzke F, Schächtele C, Mester J,
Polychronopoulos P, Magiatis P, et al: 7-Bromoindirubin-3′-oxim
induces caspase-independent cell death. Oncogene. 25:6304–6318.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang P, Dong B, Yu X, Yu D, Cheng Z, Su
L, Peng J, Nan Q and Wang H: Computer-aided dynamic simulation of
microwave-induced thermal distribution in coagulation of liver
cancer. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 48:821–829. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Skowronek J: Low-dose-rate or
high-dose-rate brachytherapy in treatment of prostate cancer -
between options. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 5:33–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roeske JC, Nunez L, Hoggarth M, Labay E
and Weichselbaum RR: Characterization of the theorectical radiation
dose enhancement from nanoparticles. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
6:395–401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cho SH, Jones BL and Krishnan S: The
dosimetric feasibility of gold nanoparticle-aided radiation therapy
(GNRT) via brachy-therapy using low-energy gamma-/x-ray sources.
Phys Med Biol. 54:4889–4905. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Conde J, Doria G and Baptista P: Noble
metal nanoparticles applications in cancer. J Drug Deliv.
2012(751075)2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jones B, Krishnan S and Cho SH: Estimation
of microscopic dose enhancement factor around gold nanoparticles by
Monte Carlo calculations. Med Phys. 37:3809–3816. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim JH, Minai-Tehrani A, Kim YK, Shin JY,
Hong SH, Kim HJ, Lee HD, Chang SH, Yu KN, Bang YB, et al:
Suppression of tumor growth in H-ras12V liver cancer mice by
delivery of programmed cell death protein 4 using galactosylated
poly(ethylene glycol)-chitosan-graft-spermine. Biomaterials.
33:1894–1902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: The
pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 305:626–629.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goodsell DS: The molecular perspective:
Bcl-2 and apoptosis. Stem Cells. 20:355–361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adrain C, Creagh EM and Martin SJ:
Apotosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondrial
requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J.
20:6627–6663. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liang H, Zhan HJ, Wang BG, Pan Y and Hao
XS: Change in expression of apoptosis genes after hyperthermia,
chemotherapy and radiotherapy in human colon cancer transplanted
into nude mice. World J Gastroenterol. 13:4365–4371.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeong SY and Seol DW: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. BMB Rep. 41:11–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stroescu C, Dragnea A, Ivanov B, Pechianu
C, Herlea V, Sgarbura O, Popescu A and Popescu I: Expression of
p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and prognostic significance in
hepato-cellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 17:411–417.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pichu S, Krishnamoorthy S, Shishkov A,
Zhang B, McCue P and Ponnappa BC: Knockdown of Ki-67 by
dicer-substrate small interfering RNA sensitizes bladder cancer
cells to curcumin-induced tumor Inhibition. PLoS One. 7:e485672012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|