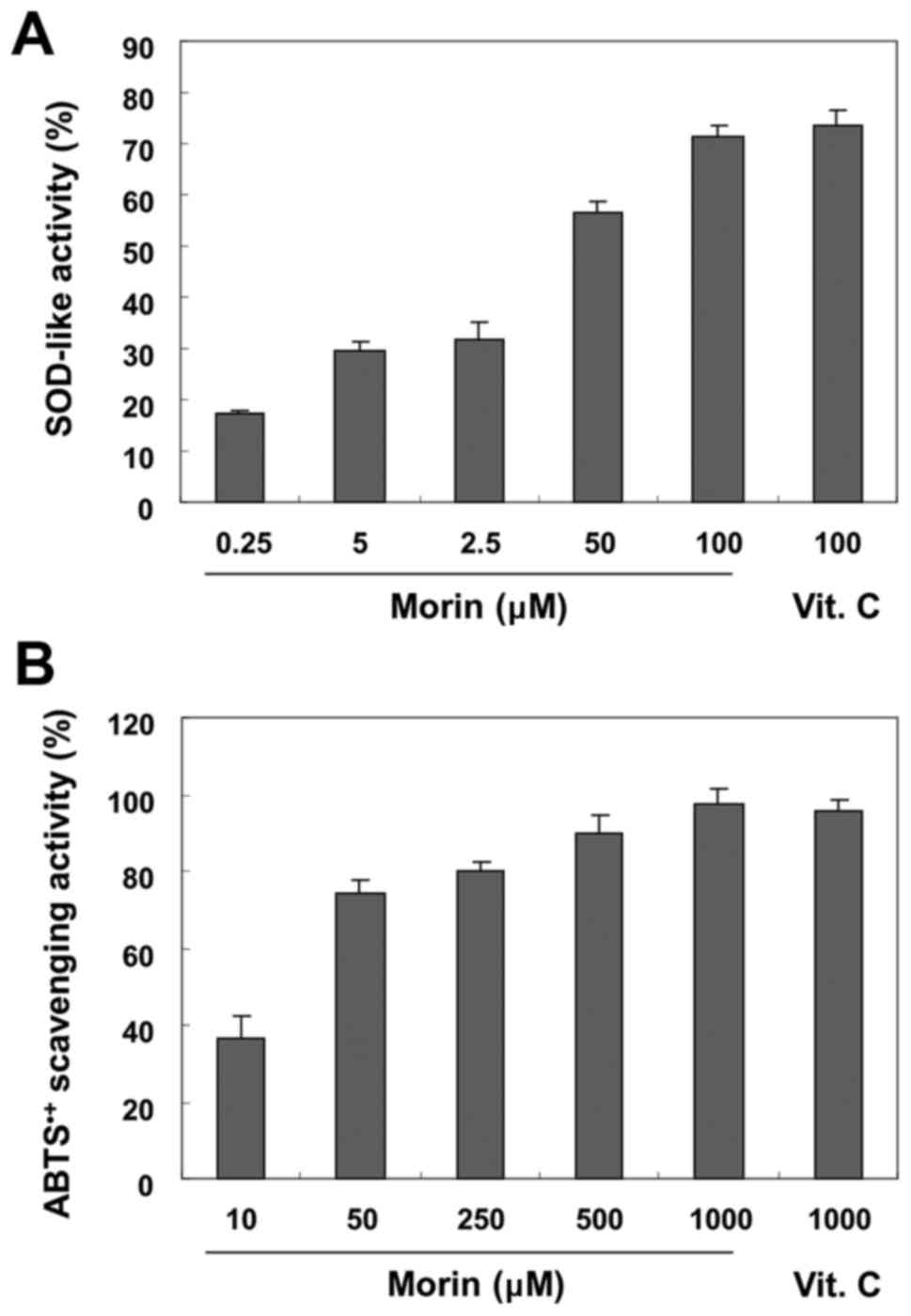
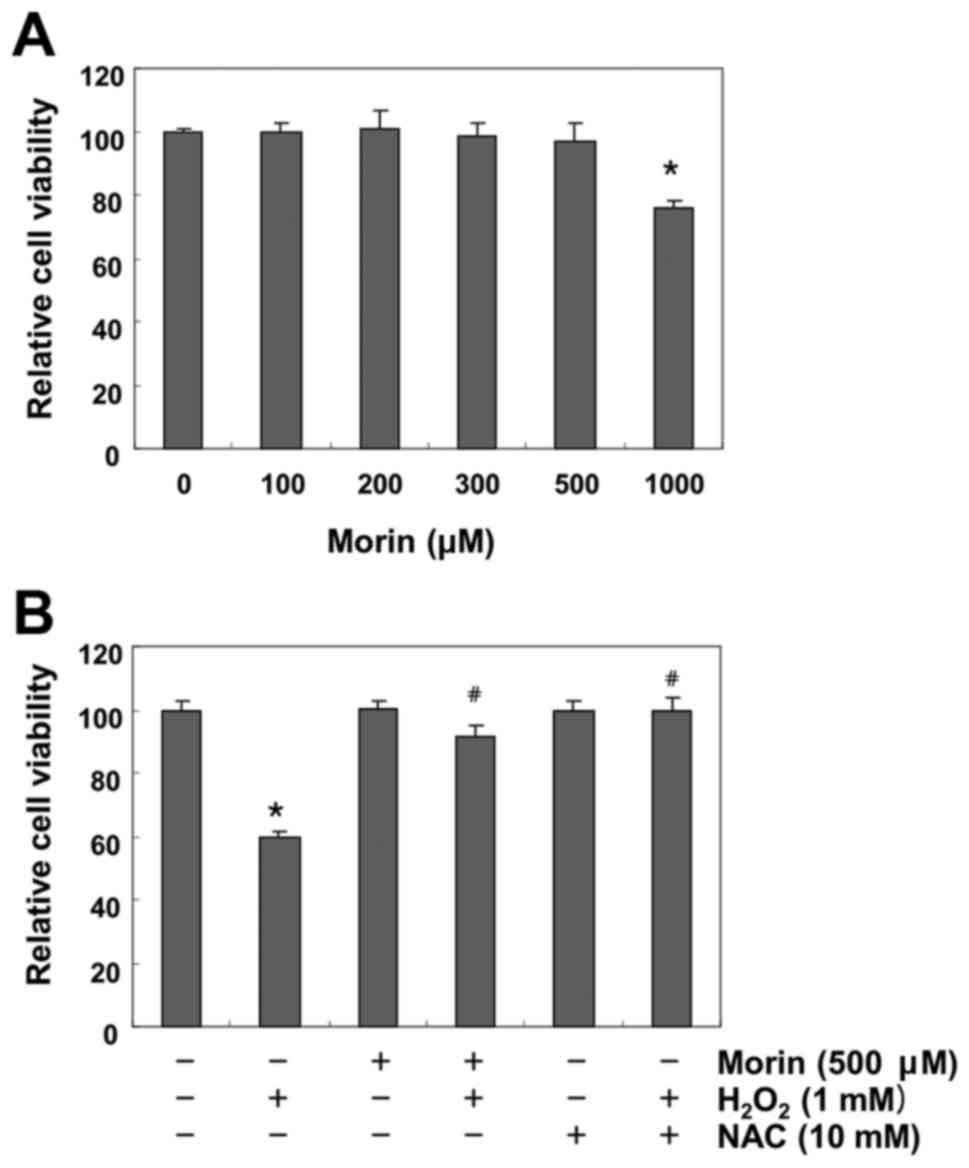
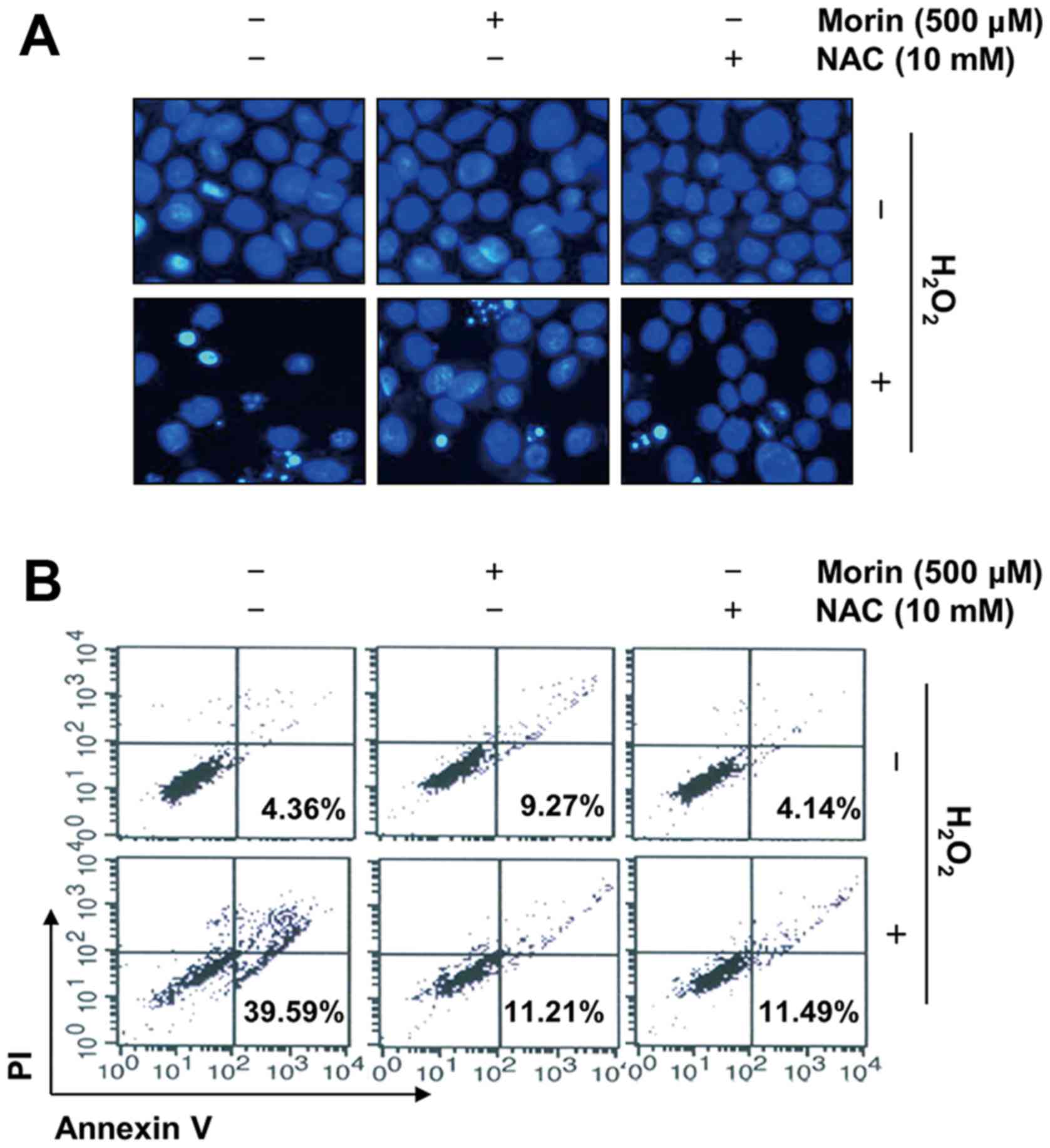
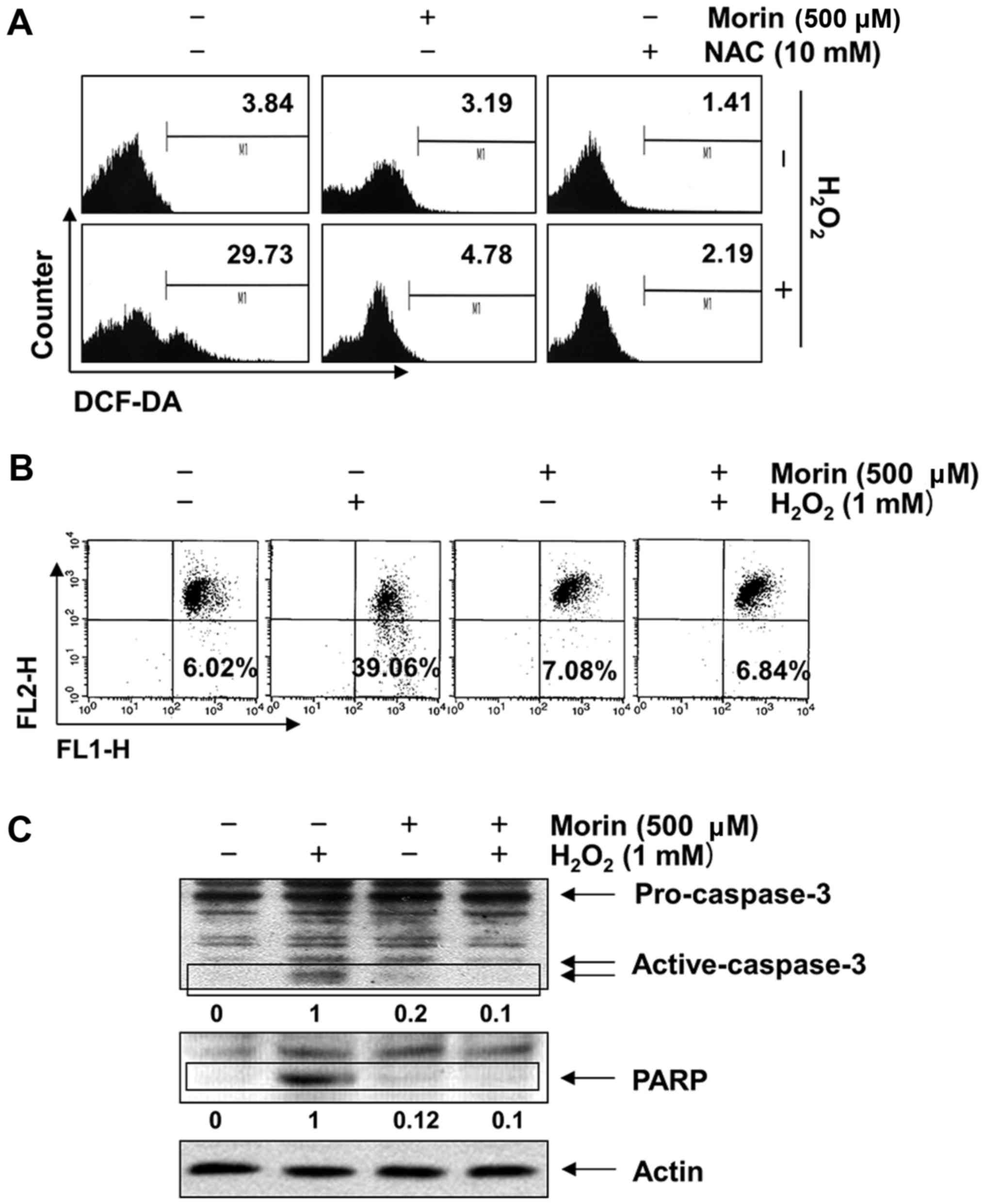
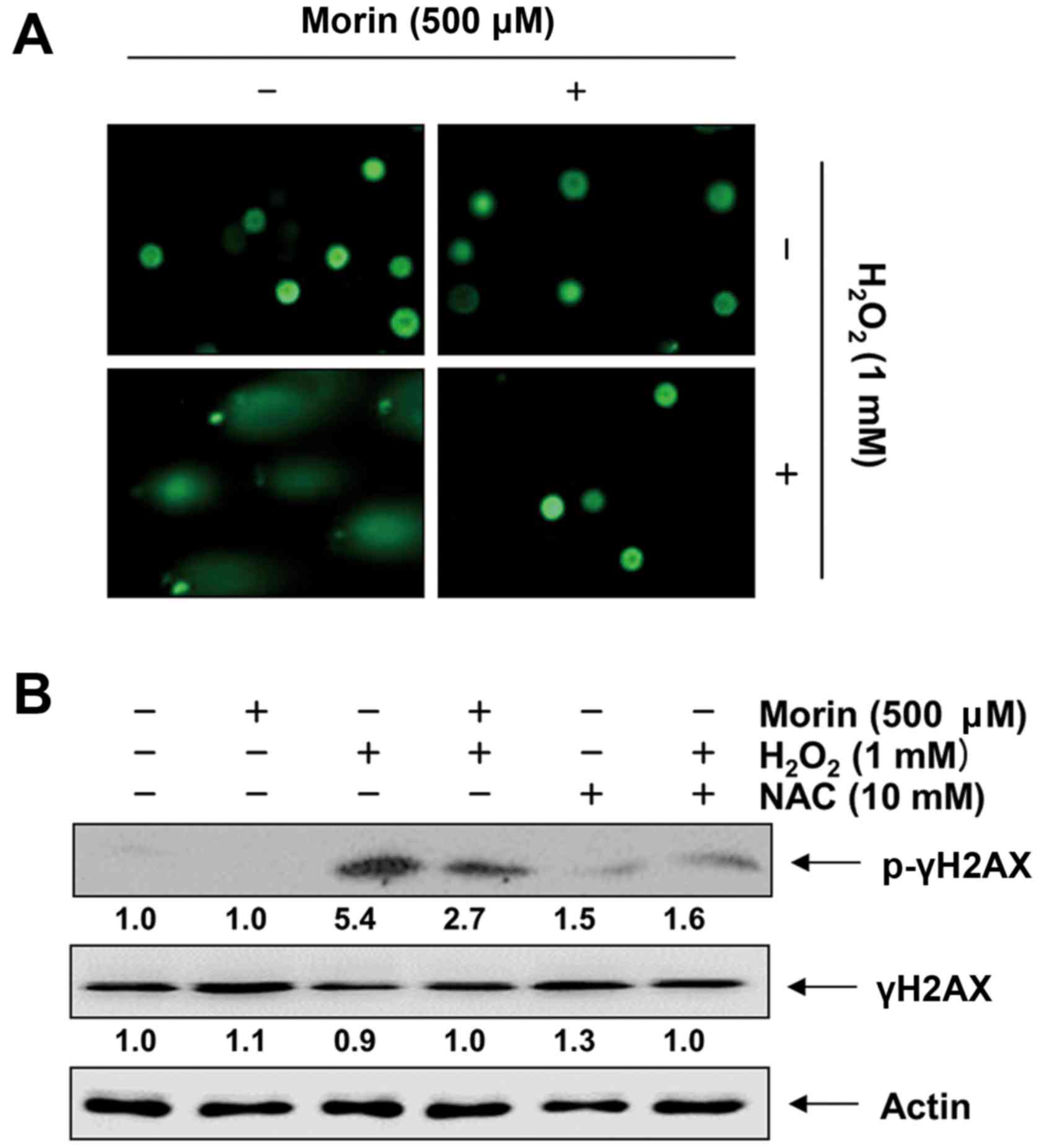
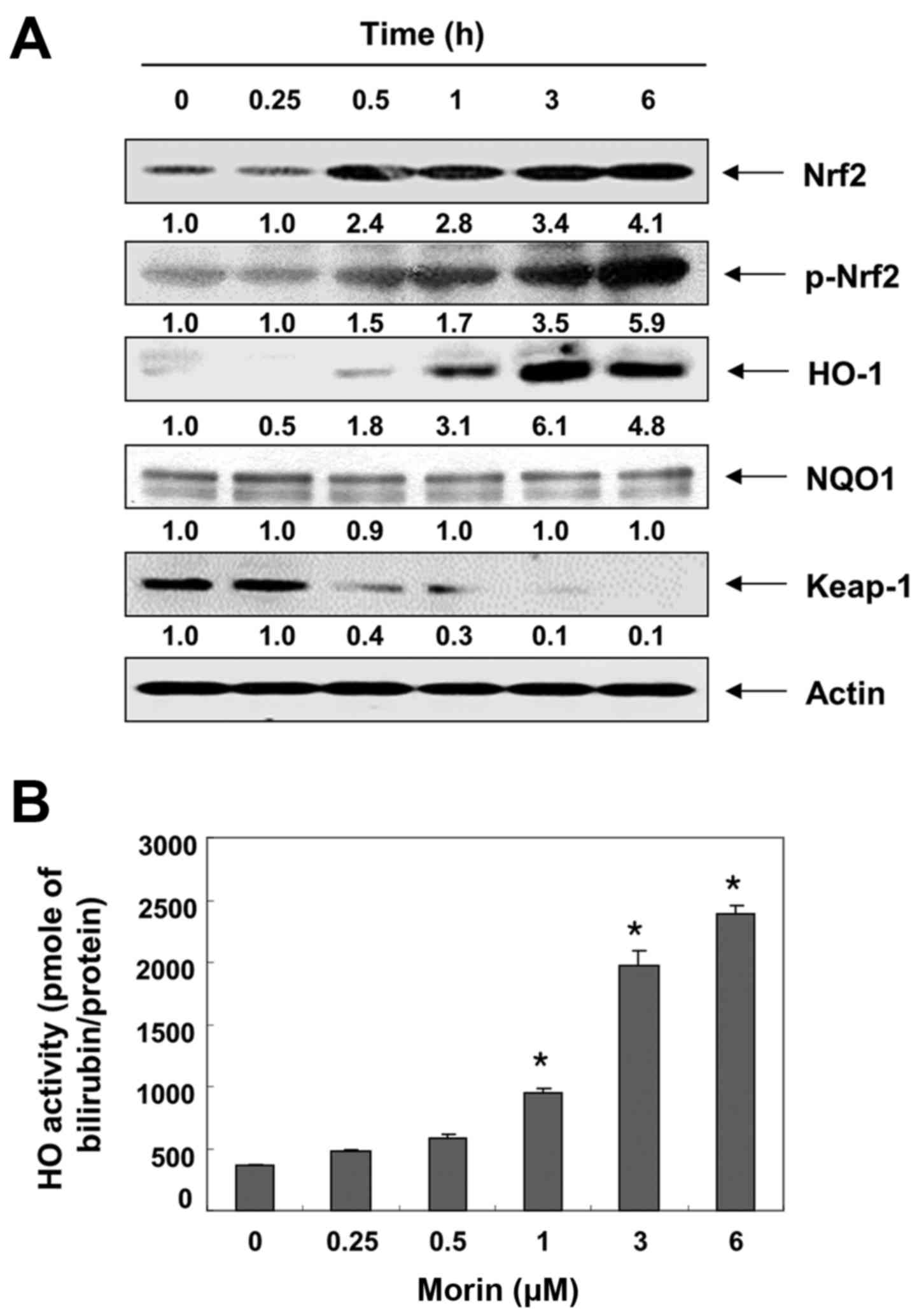
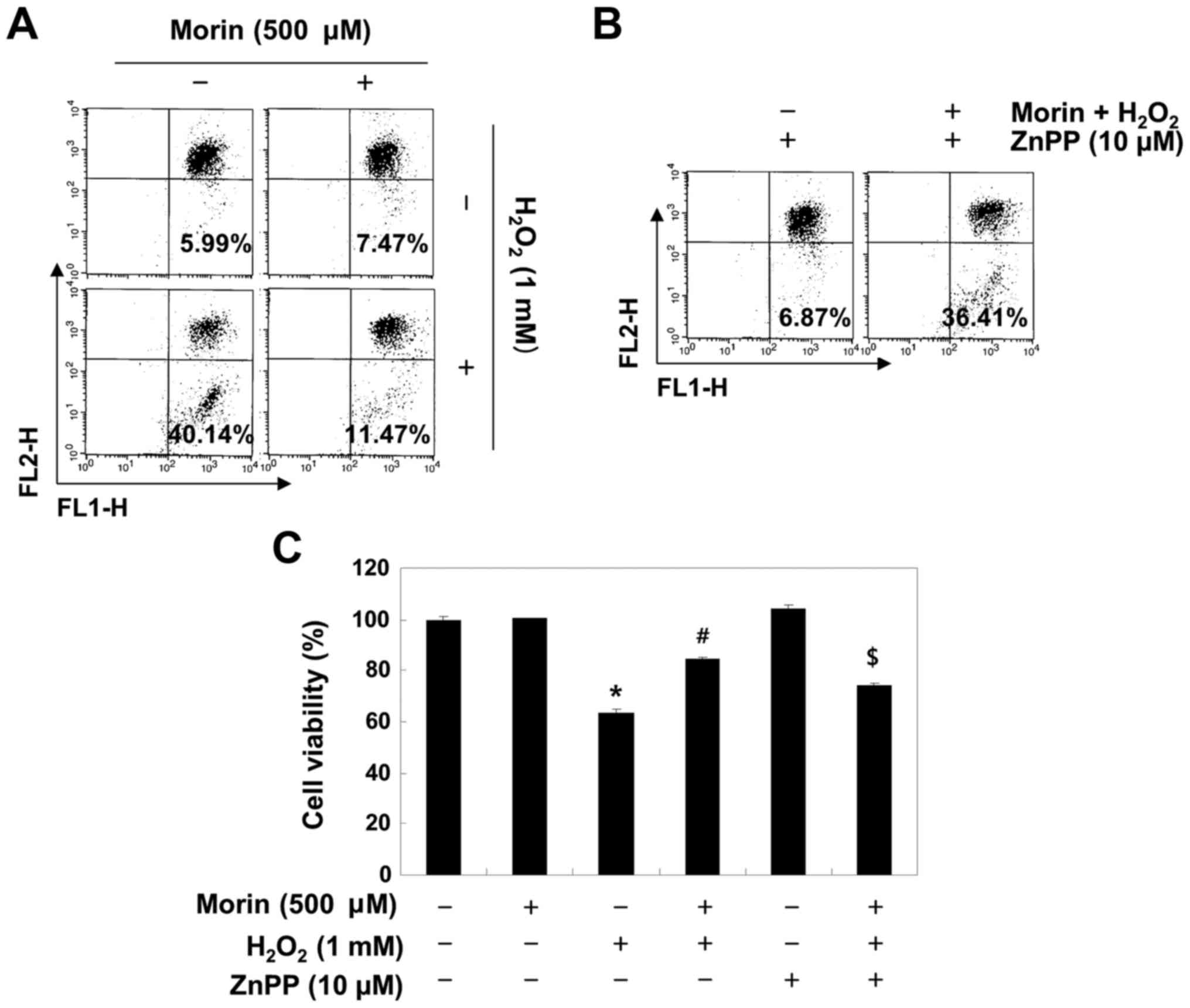
|
1
|
Dröge W: Free radicals in the
physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 82:47–95.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lyakhovich A and Graifer D:
Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress: Old Target for New drugs.
Curr Med Chem. 22:3040–3053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ermakov AV, Konkova MS, Kostyuk SV,
Izevskaya VL, Baranova A and Veiko NN: Oxidized extracellular DNA
as a stress signal in human cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2013:6497472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang HY and Lee TH: Antioxidant enzymes as
redox-based biomarkers: A brief review. BMB Rep. 48:200–208. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alfadda AA and Sallam RM: Reactive oxygen
species in health and disease. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:9364862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cha MY, Kim DK and Mook-Jung I: The role
of mitochondrial DNA mutation on neurodegenerative diseases. Exp
Mol Med. 47:e1502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ginter E, Simko V and Panakova V:
Antioxidants in health and disease. Bratisl Lek Listy. 115:603–606.
2014.
|
|
8
|
Cirillo G, Curcio M, Vittorio O, Iemma F,
Restuccia D, Spizzirri UG, Puoci F and Picci N: Polyphenol
conjugates and human health: A perspective review. Crit Rev Food
Sci Nutr. 56:326–337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Landete JM: Dietary intake of natural
antioxidants: Vitamins and polyphenols. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
53:706–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kehrer JP and Klotz LO: Free radicals and
related reactive species as mediators of tissue injury and disease:
Implications for Health. Crit Rev Toxicol. 45:765–798. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kancheva VD and Kasaikina OT:
Bio-antioxidants - a chemical base of their antioxidant activity
and beneficial effect on human health. Curr Med Chem. 20:4784–4805.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bondonno CP, Croft KD, Ward N, Considine
MJ and Hodgson JM: Dietary flavonoids and nitrate: Effects on
nitric oxide and vascular function. Nutr Rev. 73:216–235. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stockert JC, Colman OD and Cañete M:
Fluorescence reaction of leukocyte granules by morin. Acta
Histochem Suppl. 31:243–252. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Srinivas NR: Recent trends in preclinical
drug-drug interaction studies of flavonoids - Review of case
studies, issues and perspectives. Phytother Res. 29:1679–1691.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Caselli A, Cirri P, Santi A and Paoli P:
Morin: A Promising natural drug. Curr Med Chem. 23:774–791. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim JM, Lee EK, Park G, Kim MK, Yokozawa
T, Yu BP and Chung HY: Morin modulates the oxidative stress-induced
NF-kappaB pathway through its anti-oxidant activity. Free Radic
Res. 44:454–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Komirishetty P, Areti A, Sistla R and
Kumar A: Morin mitigates chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced
peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress induced PARP
over-activation and neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res. 41:2029–2042.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ola MS, Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS,
Abuohashish HM, Parmar MY, Alhomida AS and Ahmed MM: Flavonoid,
morin inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and enhances
neurotrophic support in the brain of streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Neurol Sci. 35:1003–1008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
MadanKumar P, NaveenKumar P, Manikandan S,
Devaraj H and NiranjaliDevaraj S: Morin ameliorates chemically
induced liver fibrosis in vivo and inhibits stellate cell
proliferation in vitro by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 277:210–220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ganguli A, Das A, Nag D, Bhattacharya S
and Chakrabarti G: Potential role of autophagy in smokeless tobacco
extract-induced cytotoxicity and in morin-induced protection in
oral epithelial cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 90:160–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paoli P, Cirri P, Caselli A, Ranaldi F,
Bruschi G, Santi A and Camici G: The insulin-mimetic effect of
Morin: A promising molecule in diabetes treatment. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1830:3102–3111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sendrayaperumal V, Iyyam Pillai S and
Subramanian S: Design, synthesis and characterization of
zinc-morin, a metal flavonol complex and evaluation of its
antidiabetic potential in HFD-STZ induced type 2 diabetes in rats.
Chem Biol Interact. 219:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qureshi AA, Guan XQ, Reis JC, Papasian CJ,
Jabre S, Morrison DC and Qureshi N: Inhibition of nitric oxide and
inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages by
resveratrol, a potent proteasome inhibitor. Lipids Health Dis.
11:762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dhanasekar C, Kalaiselvan S and Rasool M:
Morin, a bioflavonoid suppresses monosodium urate crystal-induced
inflammatory immune response in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the
inhibition of inflammatory mediators, intracellular ROS levels and
NF-κB activation. PLoS One. 10:e01450932015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dilshara MG, Jayasooriya RG, Lee S, Choi
YH and Kim GY: Morin downregulates nitric oxide and prostaglandin
E2 production in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by
suppressing NF-κB activity and activating HO-1 induction. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 44:62–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gupta SC, Phromnoi K and Aggarwal BB:
Morin inhibits STAT3 tyrosine 705 phosphorylation in tumor cells
through activation of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP1. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:898–912. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manna SK, Aggarwal RS, Sethi G, Aggarwal
BB and Ramesh GT: Morin (3,5,7,2′,4′-pentahydroxyflavone) abolishes
nuclear factor-kappaB activation induced by various carcinogens and
inflammatory stimuli, leading to suppression of nuclear
factor-kappaB-regulated gene expression and up-regulation of
apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2290–2297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park C, Lee WS, Go SI, Nagappan A, Han MH,
Hong SH, Kim GS, Kim GY, Kwon TK, Ryu CH, et al: Morin, a flavonoid
from Moraceae, induces apoptosis by induction of BAD protein in
human leukemic cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:645–659. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hyun HB, Lee WS, Go SI, Nagappan A, Park
C, Han MH, Hong SH, Kim G, Kim GY, Cheong J, et al: The flavonoid
morin from Moraceae induces apoptosis by modulation of Bcl-2 family
members and Fas receptor in HCT 116 cells. Int J Oncol.
46:2670–2678. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park JY, Kang KA, Kim KC, Cha JW, Kim EH
and Hyun JW: Morin induces heme oxygenase-1 via ERK-Nrf2 signaling
pathway. J Cancer Prev. 18:249–256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rizvi F, Mathur A and Kakkar P: Morin
mitigates acetaminophen-induced liver injury by potentiating Nrf2
regulated survival mechanism through molecular intervention in
PHLPP2-Akt-Gsk3β axis. Apoptosis. 20:1296–1306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mathur A, Rizvi F and Kakkar P: PHLPP2
down regulation influences nuclear Nrf2 stability via
Akt-1/Gsk3β/Fyn kinase axis in acetaminophen induced oxidative
renal toxicity: Protection accorded by morin. Food Chem Toxicol.
89:19–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee YJ, Koh EK, Kim JE, Go J, Song SH,
Seong JE, Son HJ, Kang BC and Hwang DY: Beneficial effects of
ethanol extracts of Red Liriope platyphylla on vascular dysfunction
in the aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Lab Anim Res.
31:13–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sreejayan N and Rao MN: Nitric oxide
scavenging by curcuminoids. J Pharm Pharmacol. 49:105–107. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim SH, Kang SH and Kang BS: Therapeutic
effects of dihydroartemisinin and transferrin against glioblastoma.
Nutr Res Pract. 10:393–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eom SA, Kim DW, Shin MJ, Ahn EH, Chung SY,
Sohn EJ, Jo HS, Jeon SJ, Kim DS, Kwon HY, et al: Protective effects
of PEP-1-Catalase on stress-induced cellular toxicity and
MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease. BMB Rep. 48:395–400. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Chun SK, Go K, Yang MJ, Zendejas I, Behrns
KE and Kim JS: Autophagy in ischemic livers: A critical role of
Sirtuin 1/Mitofusin 2 axis in autophagy induction. Toxicol Res.
32:35–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alaoui-Jamali MA, Bismar TA, Gupta A,
Szarek WA, Su J, Song W, Xu Y, Xu B, Liu G, Vlahakis JZ, et al: A
novel experimental heme oxygenase-1-targeted therapy for
hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 69:8017–8024. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hensley P, Mishra M and Kyprianou N:
Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Biol Chem. 394:831–843.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
MacKenzie SH and Clark AC: Targeting cell
death in tumors by activating caspases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
8:98–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S,
Poirier GG and Earnshaw WC: Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 371:346–347.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Azqueta A, Slyskova J, Langie SA, O'Neill
Gaivão I and Collins A: Comet assay to measure DNA repair: Approach
and applications. Front Genet. 5:2882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS
and Bonner WM: DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX
phosphory-lation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 273:5858–5868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN,
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M and Talalay P: Direct
evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating
induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and
oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:11908–11913. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gan L and Johnson JA: Oxidative damage and
the Nrf2-ARE pathway in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:1208–1218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Yang J and Yi J: Redox sensing by
proteins: Oxidative modifications on cysteines and the consequent
events. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:649–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Clerkin JS, Naughton R, Quiney C and
Cotter TG: Mechanisms of ROS modulated cell survival during
carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 266:30–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kaspar JW and Jaiswal AK: Tyrosine
phosphorylation controls nuclear export of Fyn, allowing Nrf2
activation of cytoprotective gene expression. FASEB J.
25:1076–1087. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Jain AK and Jaiswal AK: Phosphorylation of
tyrosine 568 controls nuclear export of Nrf2. J Biol Chem.
281:12132–12142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|