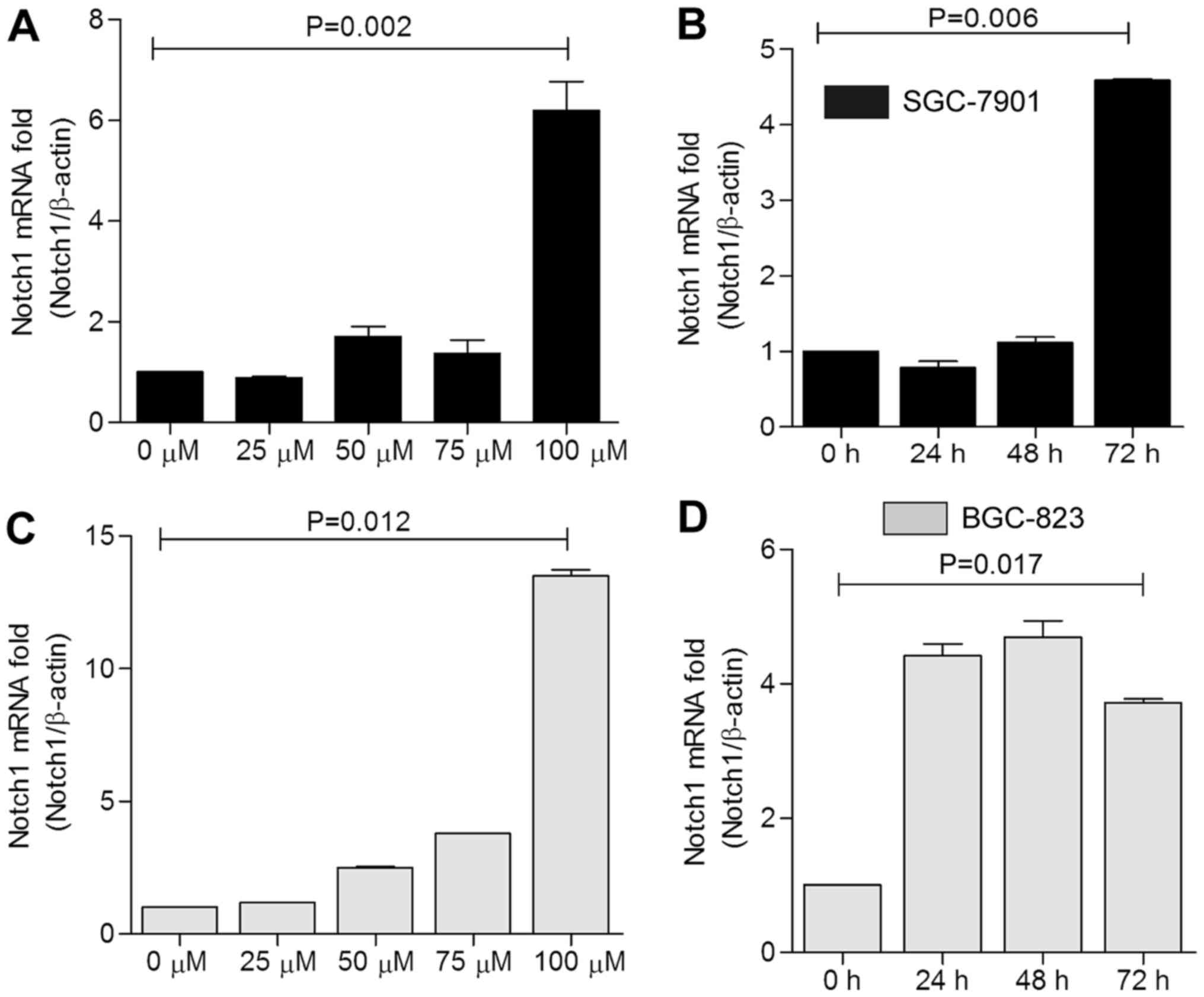
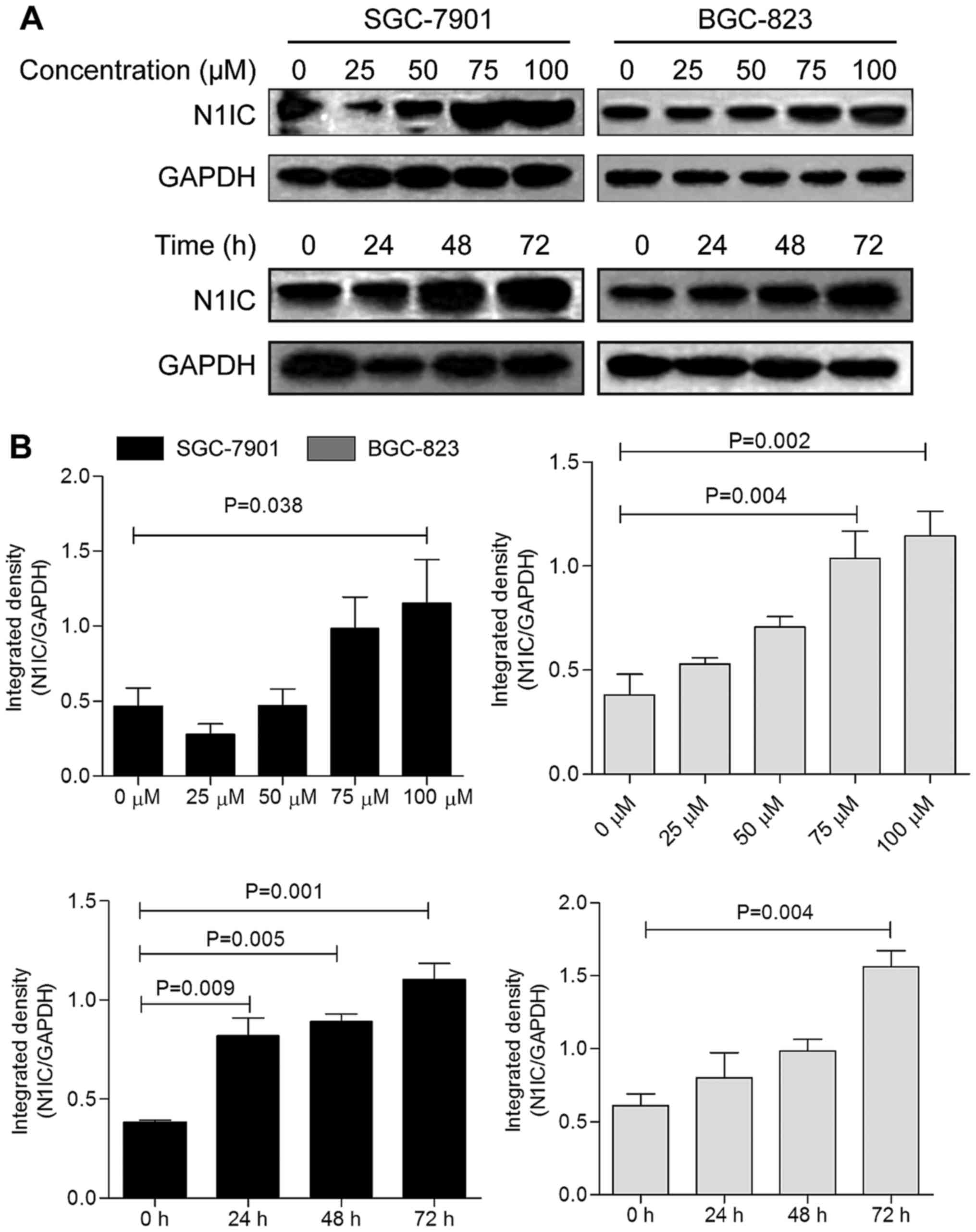
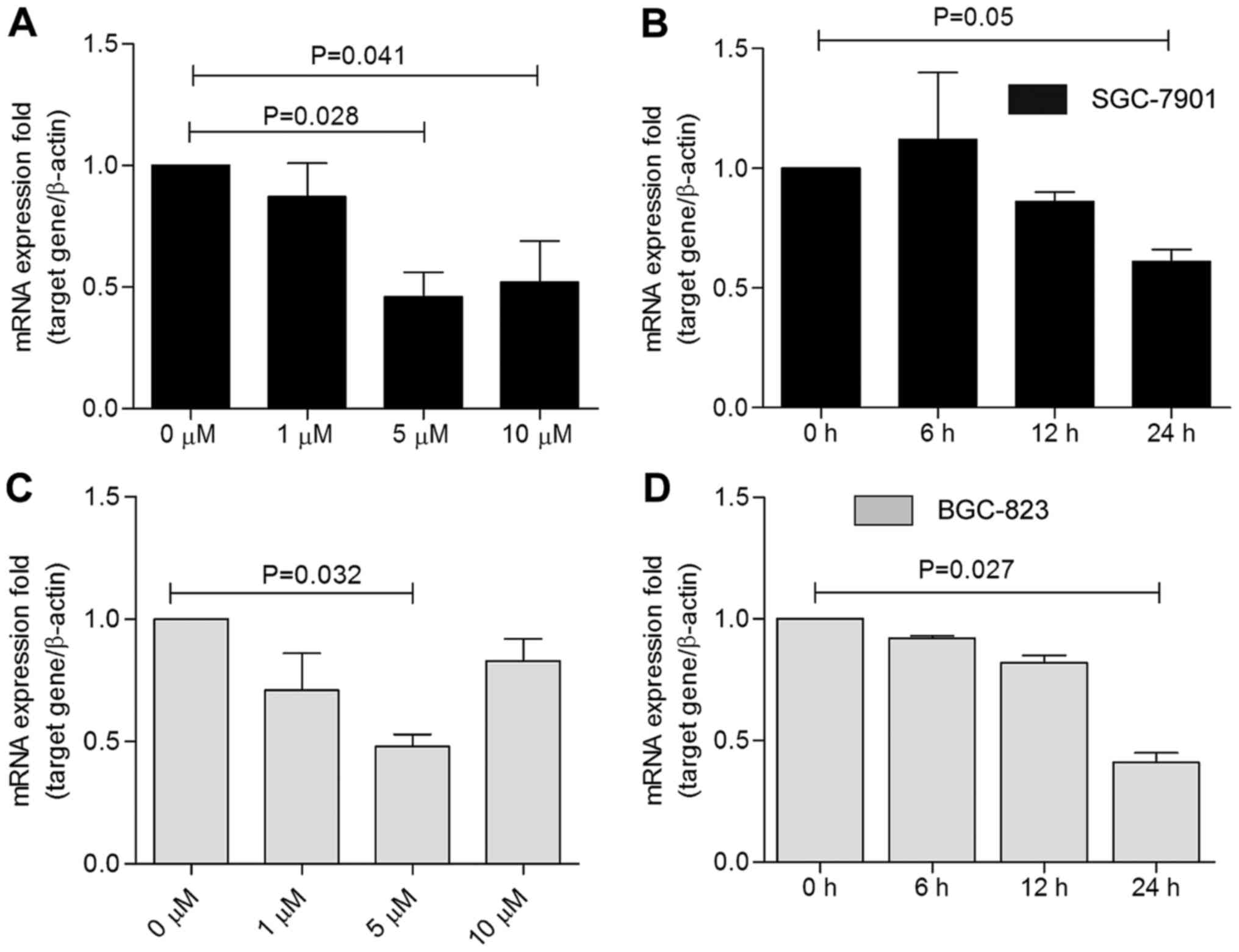
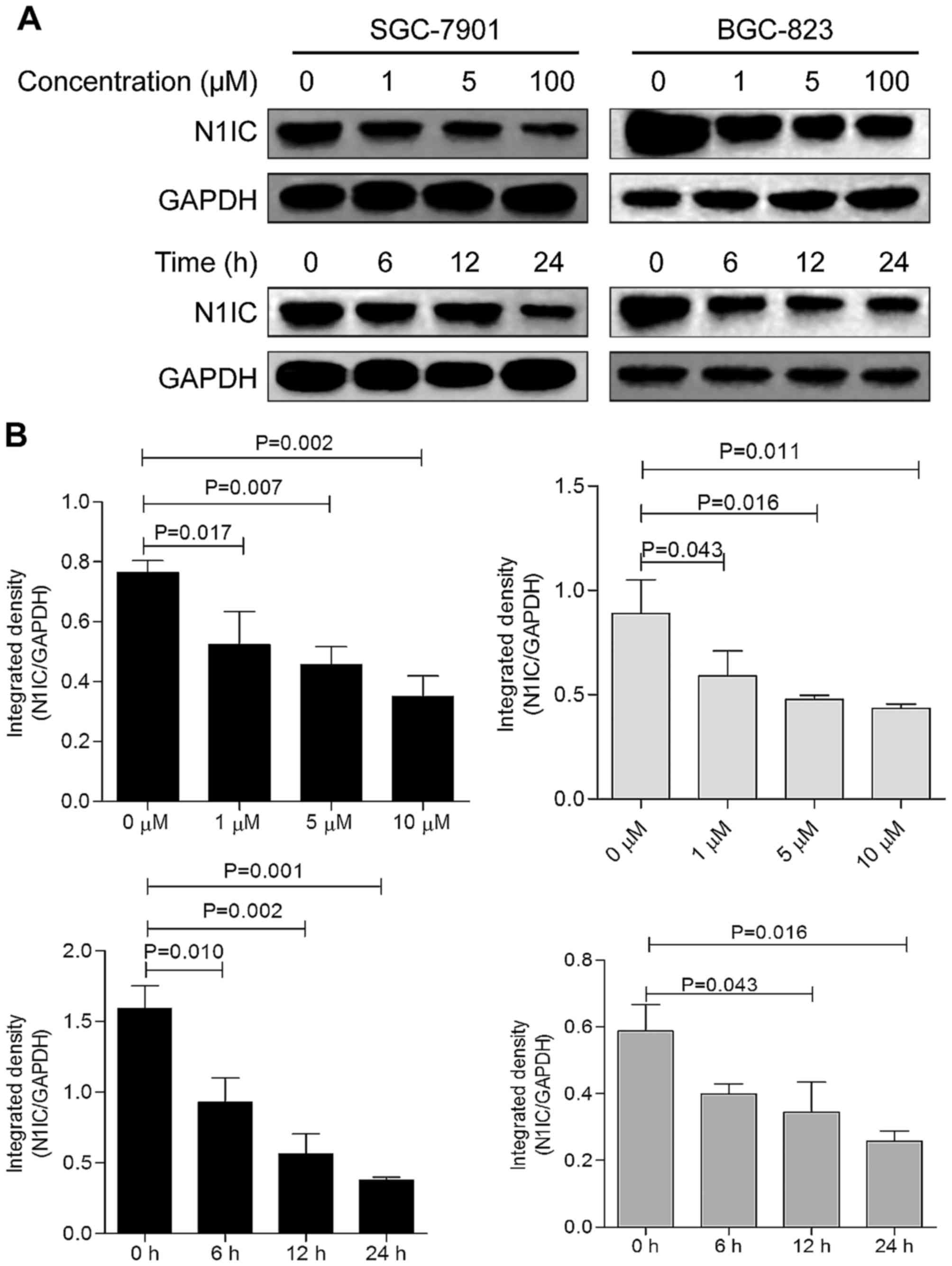
|
1
|
Guggenheim DE and Shah MA: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Surg Oncol. 107:230–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang F, Meng W, Wang B and Qiao L:
Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation and gastric
cancer. Cancer Lett. 345:196–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang ZL, Fan ZQ, Jiang HD and Qu JM:
Selective Cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human lung cancer cells via activating MEK-ERK
signaling. Carcinogenesis. 34:638–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Ji Q, Ye N, Sui H, Zhou L, Zhu H,
Fan Z, Cai J and Li Q: Berberine inhibits invasion and metastasis
of colorectal cancer cells via COX-2/PGE2 mediated JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01234782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schildberg C, Abbas M, Merkel S, Agaimy A,
Dimmler A, Schlabrakowski A, Croner R, Leupolt J, Hohenberger W and
Allgayer H: COX-2, TFF1, and Src define better prognosis in young
patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 108:409–413. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shin WG, Kim HJ, Cho SJ, Kim HS, Kim KH,
Jang MK, Lee JH and Kim HY: The COX-2-1195AA genotype is associated
with diffuse-type gastric cancer in Korea. Gut Liver. 6:321–327.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su HJ, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Ma JL, Li JY, Pan
KF and You WC: Methylation status of COX-2 in blood leukocyte DNA
and risk of gastric cancer in a high-risk Chinese population. BMC
Cancer. 15:9792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu XL, Cheng B, Li PY, Huang HJ, Zhao Q,
Dan ZL, Tian DA and Zhang P: MicroRNA-143 suppresses gastric cancer
cell growth and induces apoptosis by targeting COX-2. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:7758–7765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yuan XL, Chen L, Li MX, Dong P, Xue J,
Wang J, Zhang TT, Wang XA, Zhang FM, Ge HL, et al: Elevated
expression of Foxp3 in tumor-infiltrating Treg cells suppresses
T-cell proliferation and contributes to gastric cancer progression
in a COX-2-dependent manner. Clin Immunol. 134:277–288. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cheng J and Fan XM: Role of
cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer development and progression.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:7361–7368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oshima H and Oshima M: The role of
PGE2-associated inflammatory responses in gastric cancer
development. Semin Immunopathol. 35:139–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yao L, Liu F, Hong L, Sun L, Liang S, Wu K
and Fan D: The function and mechanism of COX-2 in angiogenesis of
gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang P, Luo HS, Li M and Tan SY:
Artesunate inhibits the growth and induces apoptosis of human
gastric cancer cells by downregulating COX-2. Onco Targets Ther.
8:845–854. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guruharsha KG, Kankel MW and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: The Notch signalling system: Recent insights
into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet.
13:654–666. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bertrand FE, Angus CW, Partis WJ and
Sigounas G: Developmental pathways in colon cancer: Crosstalk
between WNT, BMP, Hedgehog and Notch. Cell Cycle. 11:4344–4351.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Domingo-Domenech J, Vidal SJ,
Rodriguez-Bravo V, Castillo-Martin M, Quinn SA, Rodriguez-Barrueco
R, Bonal DM, Charytonowicz E, Gladoun N, de la Iglesia-Vicente J,
et al: Suppression of acquired docetaxel resistance in prostate
cancer through depletion of notch- and hedgehog-dependent
tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Cell. 22:373–388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garner JM, Fan M, Yang CH, Du Z, Sims M,
Davidoff AM and Pfeffer LM: Constitutive activation of signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear
factor κB signaling in glioblastoma cancer stem cells regulates the
Notch pathway. J Biol Chem. 288:26167–26176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hassan KA, Wang L, Korkaya H, Chen G,
Maillard I, Beer DG, Kalemkerian GP and Wicha MS: Notch pathway
activity identifies cells with cancer stem cell-like properties and
correlates with worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:1972–1980. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McAuliffe SM, Morgan SL, Wyant GA, Tran
LT, Muto KW, Chen YS, Chin KT, Partridge JC, Poole BB, Cheng KH, et
al: Targeting Notch, a key pathway for ovarian cancer stem cells,
sensitizes tumors to platinum therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:E2939–E2948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsu KW, Hsieh RH, Huang KH, Fen-Yau Li A,
Chi CW, Wang TY, Tseng MJ, Wu KJ and Yeh TS: Activation of the
Notch1/STAT3/Twist signaling axis promotes gastric cancer
progression. Carcinogenesis. 33:1459–1467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hayashi T, Gust KM, Wyatt AW, Goriki A,
Jäger W, Awrey S, Li N, Oo HZ, Altamirano-Dimas M, Buttyan R, et
al: Not all NOTCH is created equal: The oncogenic role of NOTCH2 in
bladder cancer and its implications for targeted therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2981–2992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma Y, Li M, Si J, Xiong Y, Lu F, Zhang J,
Zhang L, Zhang P and Yang Y: Blockade of Notch3 inhibits the
stem-like property and is associated with ALDH1A1 and CD44 via
autophagy in non-small lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:2349–2358.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of Snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hori K, Sen A and Artavanis-Tsakonas S:
Notch signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci. 126:2135–2140. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Acar A, Simões BM, Clarke RB and Brennan
K: A role for Notch signalling in breast cancer and endocrine
resistance. Stem Cells Int. 2016:24987642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Braune EB and Lendahl U: Notch - a
goldilocks signaling pathway in disease and cancer therapy. Discov
Med. 21:189–196. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar R, Juillerat-Jeanneret L and
Golshayan D: Notch antagonists: Potential modulators of cancer and
inflammatory diseases. J Med Chem. 59:7719–7737. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Penton AL, Leonard LD and Spinner NB:
Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:450–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fabbri G, Rasi S, Rossi D, Trifonov V,
Khiabanian H, Ma J, Grunn A, Fangazio M, Capello D, Monti S, et al:
Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of
NOTCH1 mutational activation. J Exp Med. 208:1389–1401. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, Conde L,
Ordóñez GR, Villamor N, Escaramis G, Jares P, Beà S, González-Díaz
M, et al: Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature. 475:101–105. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sethi N, Dai X, Winter CG and Kang Y:
Tumor-derived JAGGED1 promotes osteolytic bone metastasis of breast
cancer by engaging notch signaling in bone cells. Cancer Cell.
19:192–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim SH, Sehrawat A and Singh SV: Notch2
activation by benzyl isothiocyanate impedes its inhibitory effect
on breast cancer cell migration. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
134:1067–1079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta N, Xu Z, El-Sehemy A, Steed H and Fu
Y: Notch3 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and attenuates
carboplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 130:200–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nicolas M, Wolfer A, Raj K, Kummer JA,
Mill P, van Noort M, Hui CC, Clevers H, Dotto GP and Radtke F:
Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin. Nat Genet.
33:416–421. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hanlon L, Avila JL, Demarest RM, Troutman
S, Allen M, Ratti F, Rustgi AK, Stanger BZ, Radtke F, Adsay V, et
al: Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in a model of
K-ras-induced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res.
70:4280–4286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Viatour P, Ehmer U, Saddic LA, Dorrell C,
Andersen JB, Lin C, Zmoos AF, Mazur PK, Schaffer BE, Ostermeier A,
et al: Notch signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma following
inactivation of the RB pathway. J Exp Med. 208:1963–1976. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fanelli MFLTDC, Chinen LT, Begnami MD,
Costa WL Jr, Fregnami JH, Soares FA and Montagnini AL: The
influence of transforming growth factor-α, cyclooxygenase-2, matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-7, MMP-9 and CXCR4 proteins involved in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition on overall survival of patients
with gastric cancer. Histopathology. 61:153–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lazăr D, Tăban S, Ardeleanu C, Simionescu
C, Sporea I, Cornianu M and Vernic C: Immuno-histochemical
expression of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in gastric cancer. The
correlations with the tumor angiogenesis and patients' survival.
Rom J Morphol Embryol. 49:371–379. 2008.
|
|
40
|
Song J, Bai Z and Zhang Z: MicroRNAs are
implicated in the initiation and progression of gastric cancer.
Chin Med J (Engl). 127:554–559. 2014.
|
|
41
|
Yu CH, Li L, Li YM, Zhang BF, Fang J, Zhou
Q, Hu Y and Gao HJ: Expression of tissue microarray p53, p16 and
cyclooxy-genase-2 in gastric cancer. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi.
45:658–660. 2006.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Patriarca C, Macchi RM, Marschner AK and
Mellstedt H: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326)
in cancer: A short review. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:68–75. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Valiente M, Obenauf AC, Jin X, Chen Q,
Zhang XH, Lee DJ, Chaft JE, Kris MG, Huse JT, Brogi E, et al:
Serpins promote cancer cell survival and vascular co-option in
brain metastasis. Cell. 156:1002–1016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Yue P, Page BD, Li T, Zhao W,
Namanja AT, Paladino D, Zhao J, Chen Y, Gunning PT, et al: Orally
bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of transcription factor Stat3
regresses human breast and lung cancer xenografts. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:9623–9628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Wahlbuhl M,
Dimmler A, Bauer K, Sultan A, Hlubek F, Jung A, Strand D, Eger A,
et al: The transcriptional repressor ZEB1 promotes metastasis and
loss of cell polarity in cancer. Cancer Res. 68:537–544. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Z, Liu M, Liu X, Huang S, Li L, Song
B, Li H, Ren Q, Hu Z, Zhou Y, et al: COX-2 regulates E-cadherin
expression through the NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway in gastric
cancer. Int J Mol Med. 32:93–100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu LX, Zhou L, Li M, Li ZW, Wang DS and
Zhang SG: The Notch1/cyclooxygenase-2/Snail/E-cadherin pathway is
associated with hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell
invasion and migration. Oncol Rep. 29:362–370. 2013.
|
|
48
|
Zhou L, Wang DS, Li QJ, Sun W, Zhang Y and
Dou KF: The down-regulation of Notch1 inhibits the invasion and
migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inactivating the
cyclo-oxygenase-2/Snail/E-cadherin pathway in vitro. Dig Dis Sci.
58:1016–1025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|