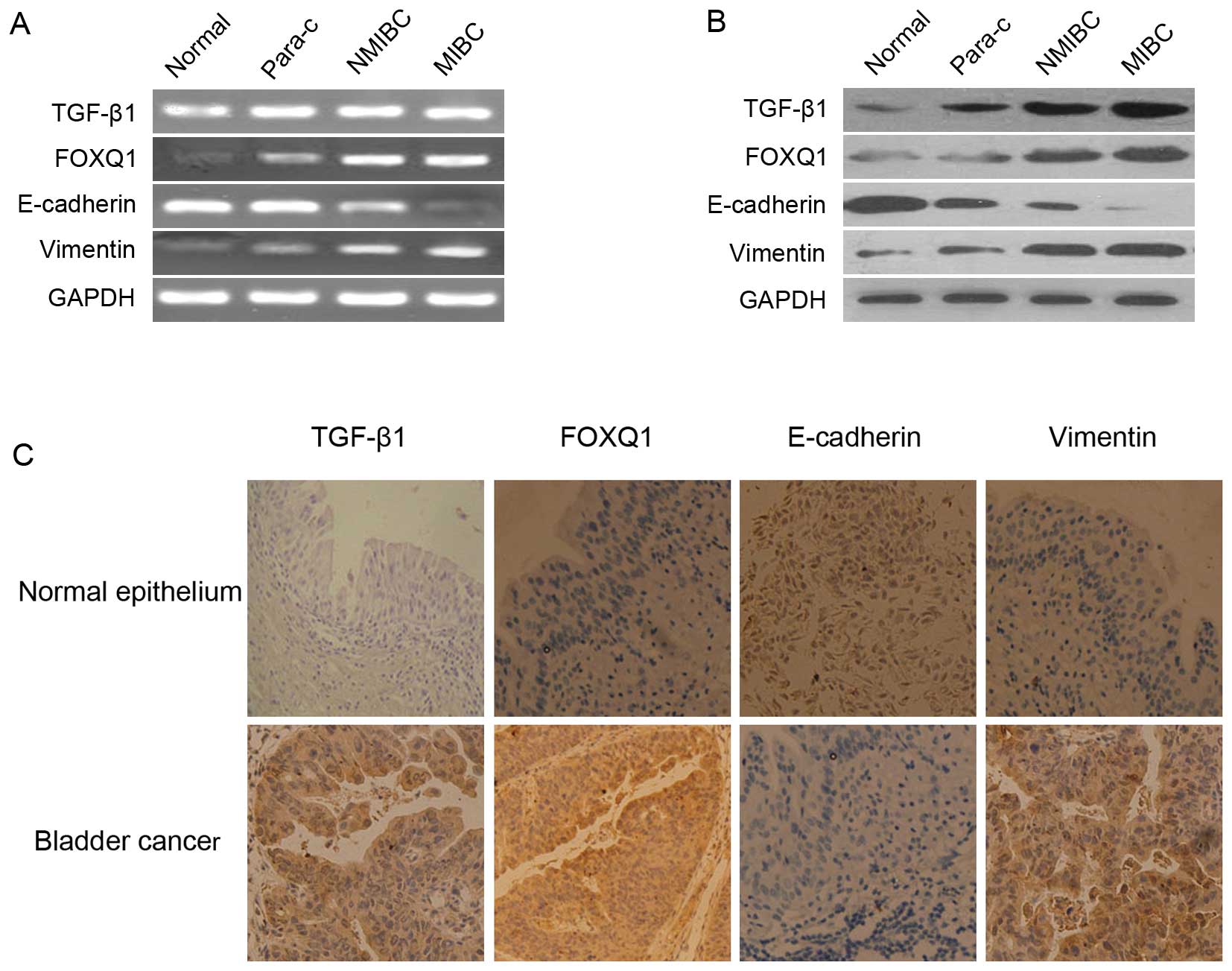
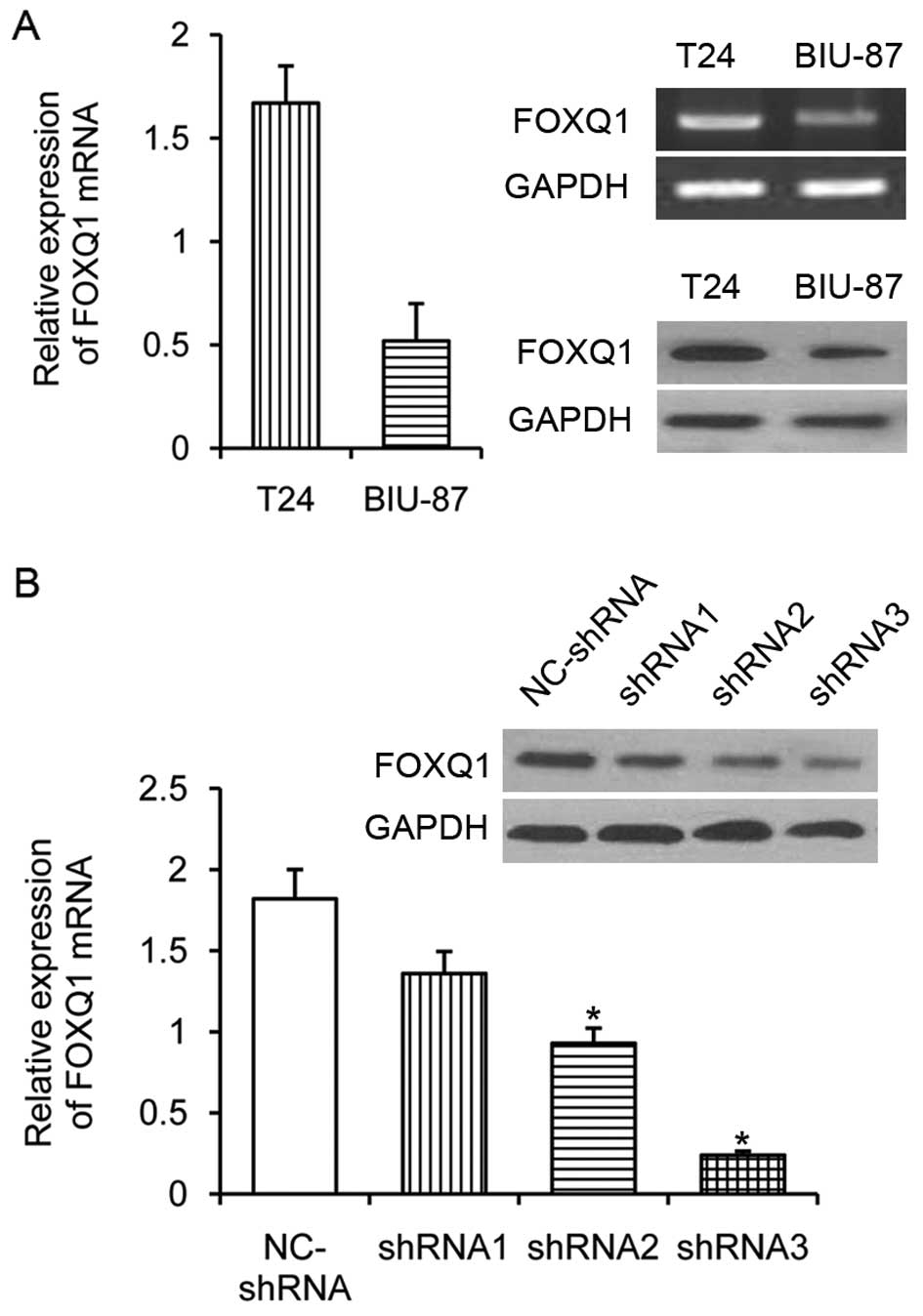
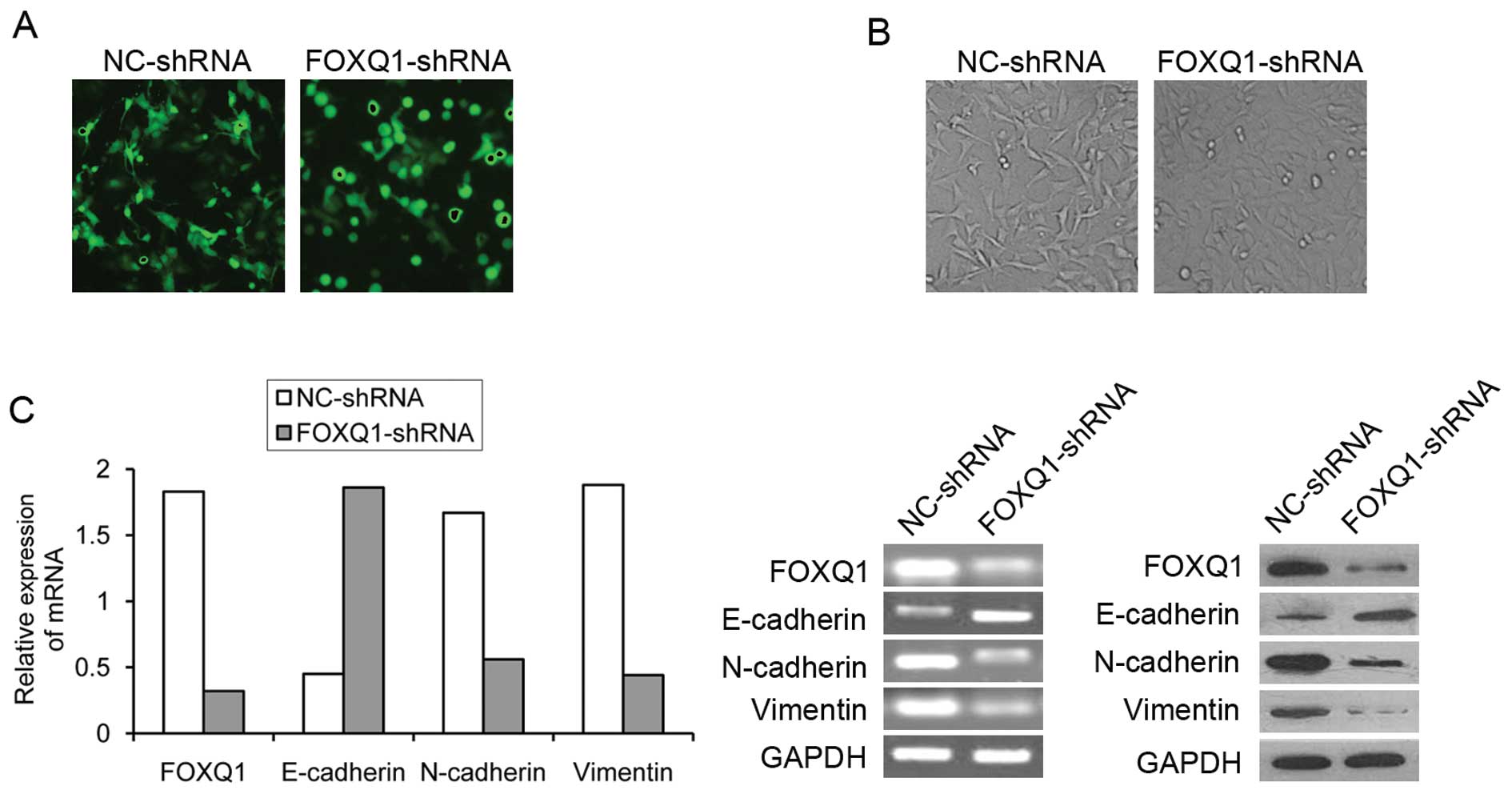
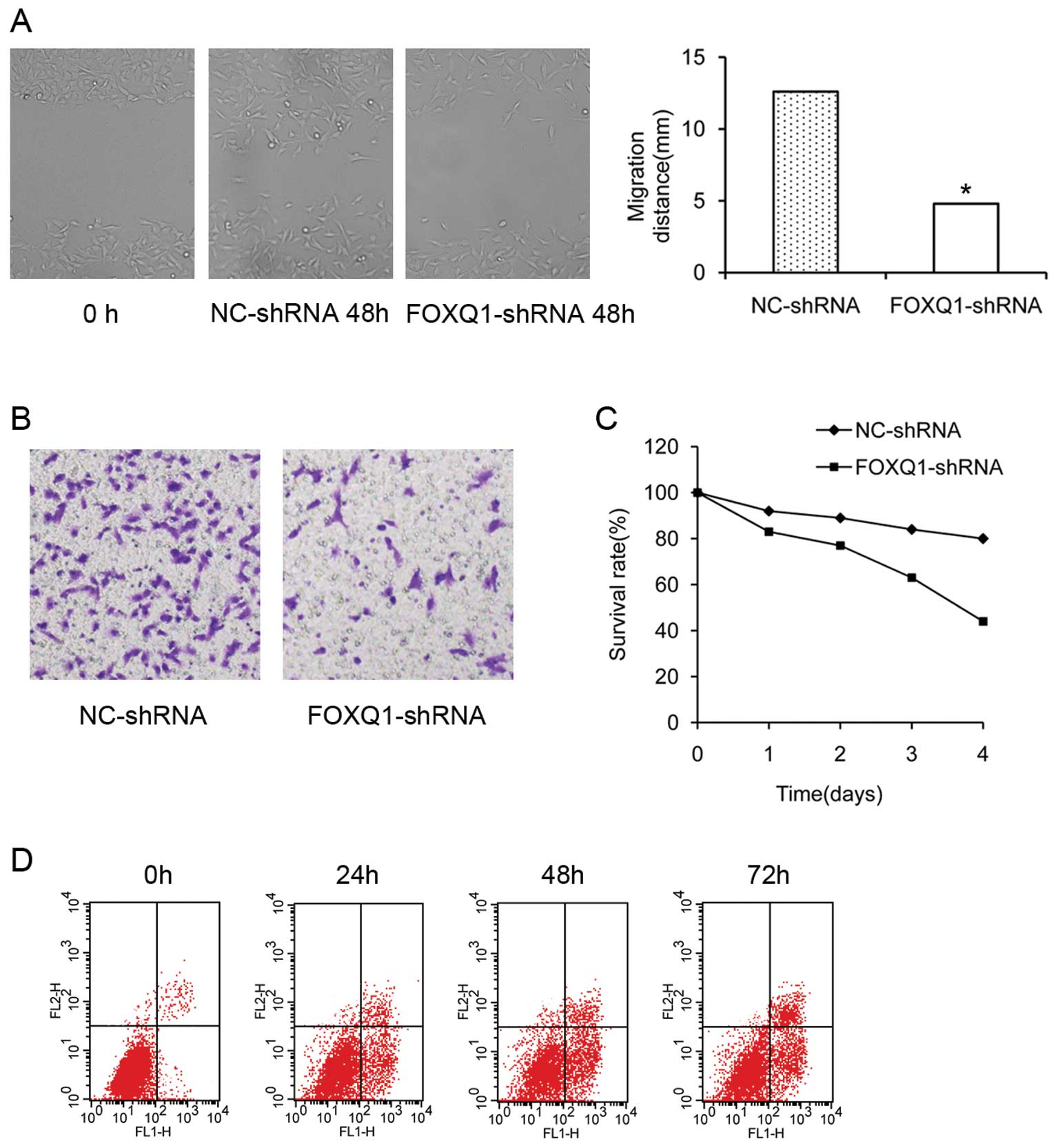
|
1
|
Scheel C, Onder T, Karnoub A and Weinberg
RA: Adaptation versus selection: the origins of metastatic
behavior. Cancer Res. 67:11476–11480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelialmesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:740–746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, et al: The
transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene
expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bolos V, Peinado H, Perez-Moreno MA, et
al: The transcription factor slug represses E-cadherin expression
and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: a comparison
with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell Sci. 116:499–511. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, et al:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perez-Moreno MA, Locascio A, Rodrigo I, et
al: A new role for E12/E47 in the repression of E-cadherin
expression and epithelialmesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem.
276:27424–27431. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Battula VL, Evans KW, Hollier BG, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-derived cells exhibit
multilineage differentiation potential similar to mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 28:1435–1445. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Katoh M: Human FOX gene family. Int J
Oncol. 25:1495–1500. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hader C, Marlier A and Cantley L:
Mesenchymal-epithelial transition in epithelial response to injury:
the role of Foxc2. Oncogene. 29:1031–1040. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Banerjee S,
et al: Over-expression of FoxM1 leads to epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer
cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:2296–2306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bieller A, Pasche B, Frank S, Gläser B,
Kunz J, et al: Isolation and characterization of the human forkhead
gene FOXQ1. DNA Cell Biol. 20:555–561. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feuerborn A, Srivastava PK, Küffer S,
Grandy WA, Sijmonsma TP, et al: The Forkhead factor FoxQ1
influences epithelial differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 226:710–719.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao D, Hustinx SR, Sui G, Bala P, Sato N,
Martin S, et al: Identification of novel highly expressed genes in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas through a bioinformatics analysis
of expressed sequence tags. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:1081–1091. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paoni NF, Feldman MW, Gutierrez LS,
Ploplis VA and Castellino FJ: Transcriptional profiling of the
transition from normal intestinal epithelia to adenomas and
carcinomas in the APCMin/t mouse. Physiol Genom. 15:228–235. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaneda H, Arao T, Tanaka K, Tamura D,
Aomatsu K, et al: FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and
enhances tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:2053–2063.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiao Y, Jiang X, Lee ST, Karuturi RK, Hooi
SC, et al: FOXQ1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human cancers. Cancer Res. 71:3076–3086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Ethier SP, Miller F, Wu G, et al:
Forkhead transcription factor Foxq1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:1292–1301.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bubenick J, Baresora M, Viklicky V, et al:
Established cell line of urinary bladder carcinoma (T24) containing
tumor-specific antigen. Int J Cancer. 11:765–773. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sobin DH and Witteking C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors. 6th edition. Wiley-Liss; New
York, NY: 2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Miyamoto H, Miller JS, Fajardo DA, et al:
Non-invasive papillary urothelial neoplasms: the 2004 WHO/ISUP
classification system. Pathol Int. 60:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu Q, Zhang K, Wang X, Liu X and Zhang Z:
Expression of transcription factors snail, slug, and twist in human
bladder carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shiozaki H, Tahara H, Oka H, Miyata M, et
al: Expression of immunoreactive E-cadherin adhesion molecules in
human cancers. Am J Pathol. 139:17–23. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng J, Zhang X, Zhu H, Wang X, Ni S and
Huang J: FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT.
PLoS One. 7:e399372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peter ME: Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs:
guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle.
8:843–852. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Desmouliere A: Factors influencing
myofibroblast differentiation during wound healing and fibrosis.
Cell Biol Int. 19:471–476. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, et al:
The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, et al: The
two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates
E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell. 7:1267–1278. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER: The SLUG
zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 62:1613–1618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Craene B, van Roy F and Berx G:
Unraveling signalling cascades for the Snail family of
transcription factors. Cell Signal. 17:535–547. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu AN, Zhu ZH, Chang SJ, Hang XS, et al:
Twist expression associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 367:195–203. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gumbiner BM: Cell adhesion: the molecular
basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 84:345–357.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Christofori G and Semb H: The role of the
cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumour-suppressor gene.
Trends Biochem Sci. 24:73–76. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
McConkey DJ, Lee S, Choi W, et al:
Molecular genetics of bladder cancer: emerging mechanisms of tumor
initiation and progression. Urol Oncol. 28:429–440. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its
clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang A, Chen G, Meng L, Wang Q, et al:
Antisense-Snail transfer inhibits tumor metastasis by inducing
E-cadherin expression. Anticancer Res. 28:621–628. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, et al: Twist
transcriptionally upregulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading
to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel.
Cancer Res. 67:1979–1987. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vannini I, Bonafe M, Tesei A, et al: Short
interfering RNA directed against the SLUG gene increases cell death
induction in human melanoma cell lines exposed to cisplatin and
fotemustine. Cell Oncol. 29:279–287. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|