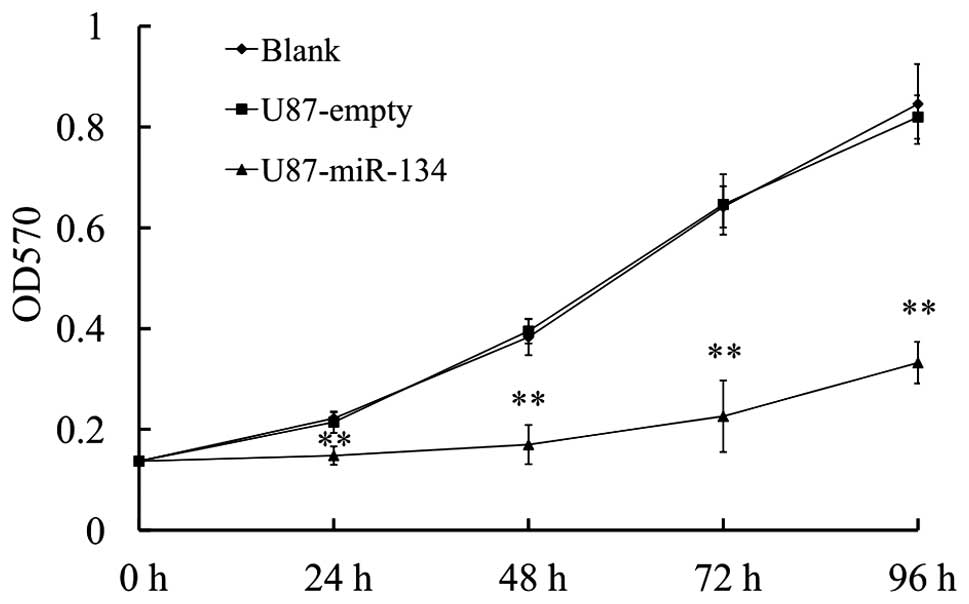
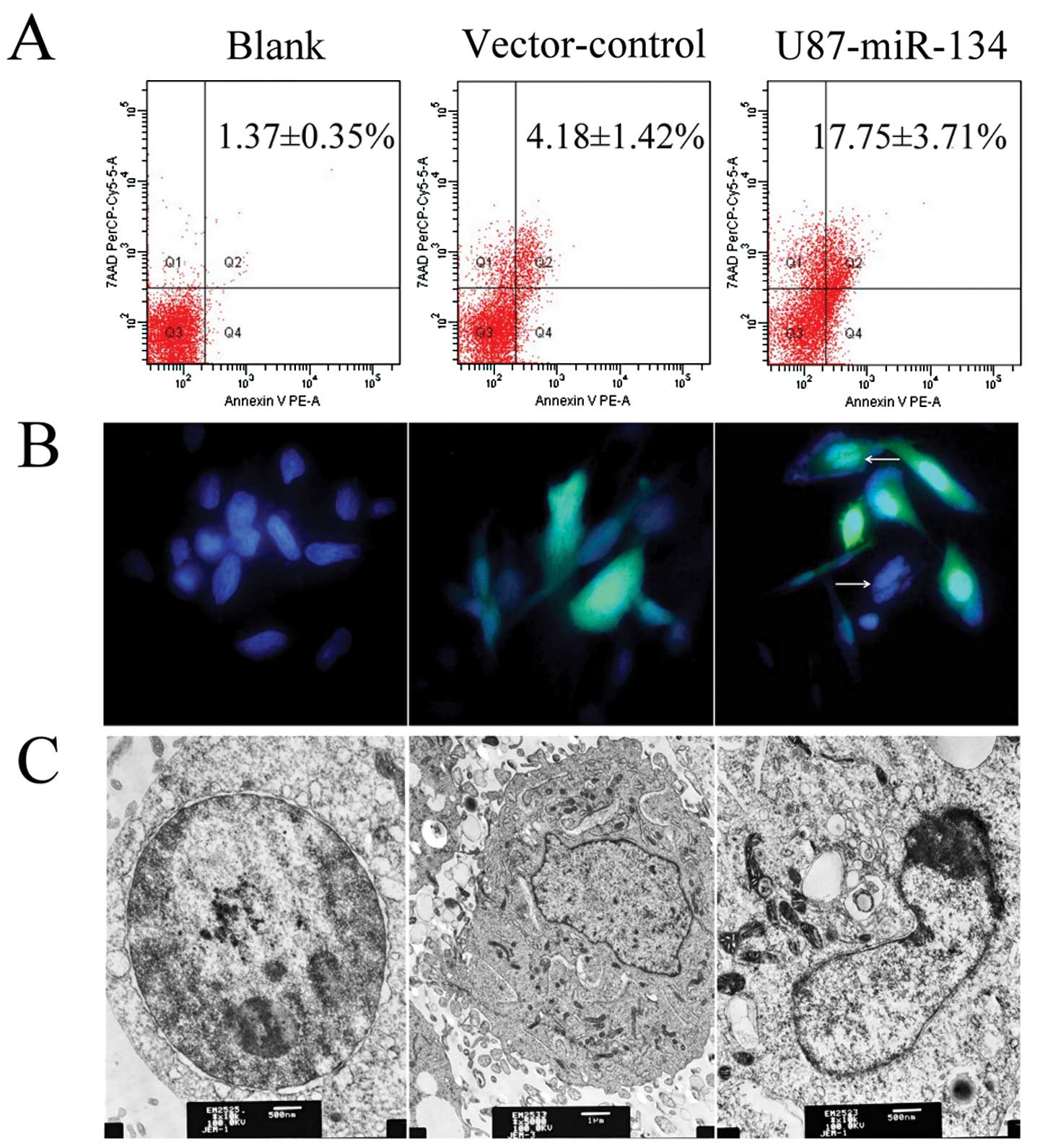
|
1.
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Stefani G and Slack FJ: Small non-coding
RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ruvkun G: The perfect storm of tiny RNAs.
Nat Med. 14:1041–1045. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Babashah S and Soleimani M: The oncogenic
and tumour suppressive roles of microRNAs in cancer and apoptosis.
Eur J Cancer. 47:1127–1137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Seca H, Almeida GM, Guimaraes JE, et al:
MiR signatures and the role of miRs in acute myeloid leukaemia. Eur
J Cancer. 46:1520–1527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, et al: The Oct4 and
Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse
embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 38:431–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al:
Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic
cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ezeh UI, Turek PJ, Reijo RA, et al: Human
embryonic stem cell genes OCT4, NANOG, STELLAR, and GDF3 are
expressed in both seminoma and breast carcinoma. Cancer.
104:2255–2265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bourguignon LY, Peyrollier K, Xia W, et
al: Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction activates stem cell marker Nanog,
Stat-3-mediated MDR1 gene expression, and ankyrin-regulated
multidrug efflux in breast and ovarian tumor cells. J Biol Chem.
283:17635–17651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
You JS, Kang JK, Seo DW, et al: Depletion
of embryonic stem cell signature by histone deacetylase inhibitor
in NCCIT cells: involvement of Nanog suppression. Cancer Res.
69:5716–5725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zbinden M, Duquet A, Lorente-Trigos A, et
al: NANOG regulates glioma stem cells and is essential in vivo
acting in a cross-functional network with GLI1 and p53. EMBO J.
29:2659–2674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Niu CS, Li DX, Liu YH, et al: Expression
of NANOG in human gliomas and its relationship with
undifferentiated glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 26:593–601.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Tay YM, Tam WL, Ang YS, et al:
MicroRNA-134 modulates the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem
cells, where it causes post-transcriptional attenuation of Nanog
and LRH1. Stem Cells. 26:17–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Gaughwin P, Ciesla M, Yang H, et al:
Stage-specific modulation of cortical neuronal development by
Mmu-miR-134. Cereb Cortex. 21:1857–1869. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, et al: A
brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development.
Nature. 439:283–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Wayman GA, Davare M, Ando H, et al: An
activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by
down-regulating p250GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:9093–9098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hao J, Song X, Song B, et al: Effects of
lentivirus-mediated HIF-1alpha knockdown on hypoxia-related
cisplatin resistance and their dependence on p53 status in
fibrosarcoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 15:449–455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, et al:
Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the
growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab
Invest. 90:144–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Wang P, Zhen X, Jiang X, et al: Boron
neutron capture therapy induces apoptosis of glioma cells through
Bcl-2/Bax. BMC Cancer. 10:6612010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Chen T, Du J and Lu G: Cell growth arrest
and apoptosis induced by Oct4 or Nanog knockdown in mouse embryonic
stem cells: a possible role of Trp53. Mol Biol Rep. 39:1855–1861.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Fiore R, Khudayberdiev S, Christensen M,
et al: Mef2-mediated transcription of the miR379-410 cluster
regulates activity-dependent dendritogenesis by fine-tuning
Pumilio2 protein levels. EMBO J. 28:697–710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Lages E, Guttin A, El Atifi M, et al:
MicroRNA and target protein patterns reveal physiopathological
features of glioma subtypes. PLoS One. 6:e206002011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Bourguignon LY, Earle C, Wong G, et al:
Stem cell marker (Nanog) and Stat-3 signaling promote MicroRNA-21
expression and chemoresistance in hyaluronan/CD44-activated head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 31:149–160. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Po A, Ferretti E, Miele E, et al: Hedgehog
controls neural stem cells through p53-independent regulation of
Nanog. EMBO J. 29:2646–2658. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|