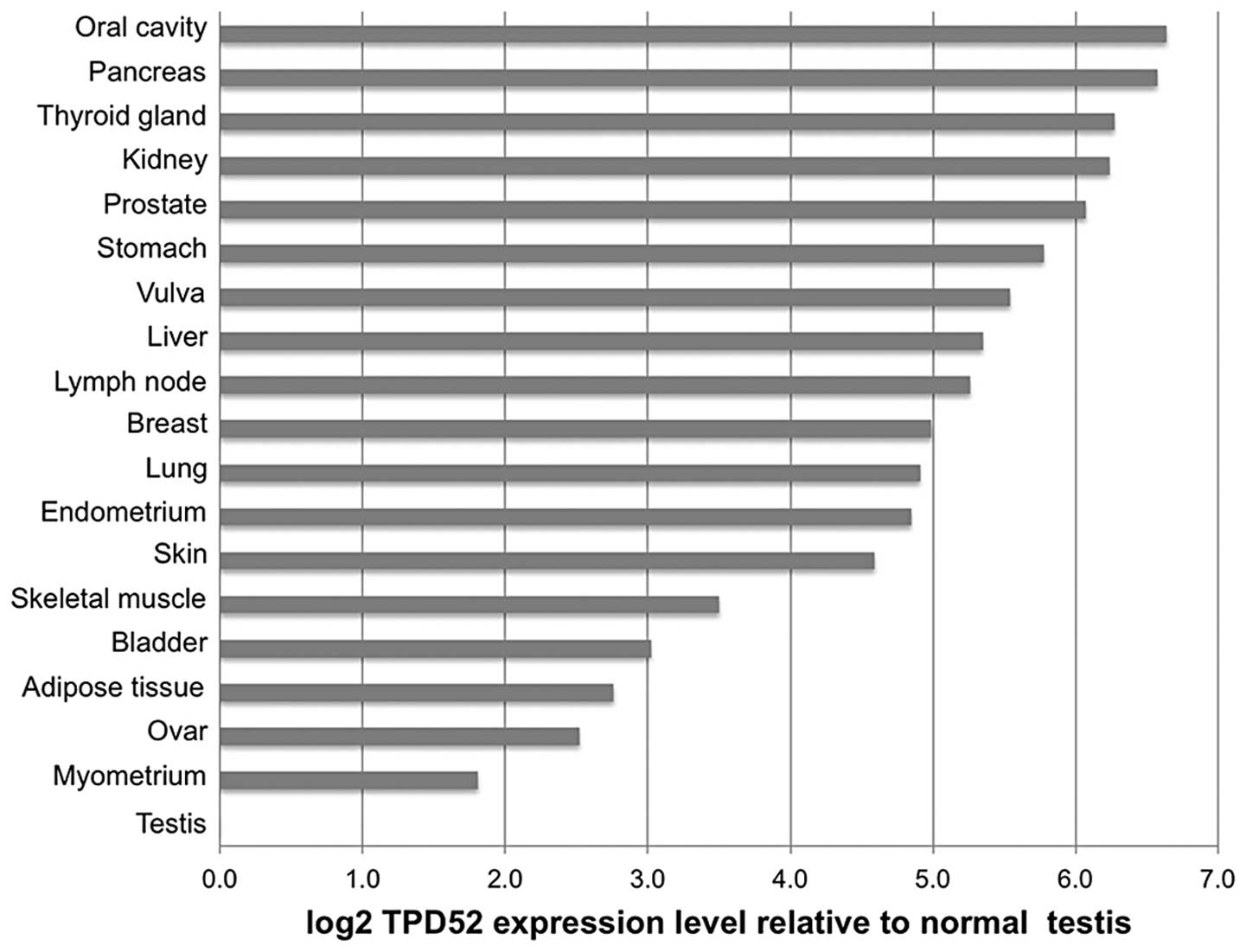
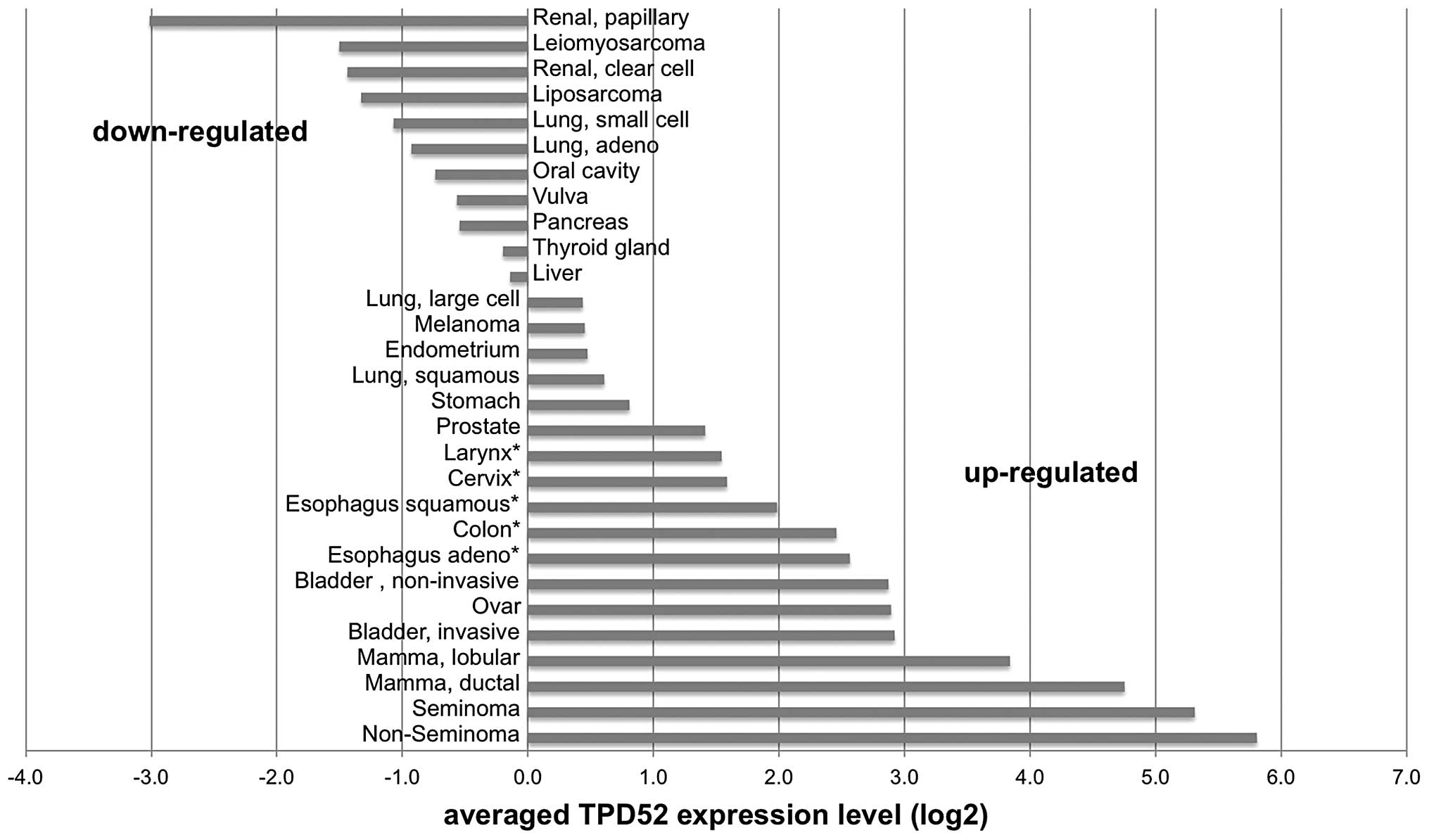
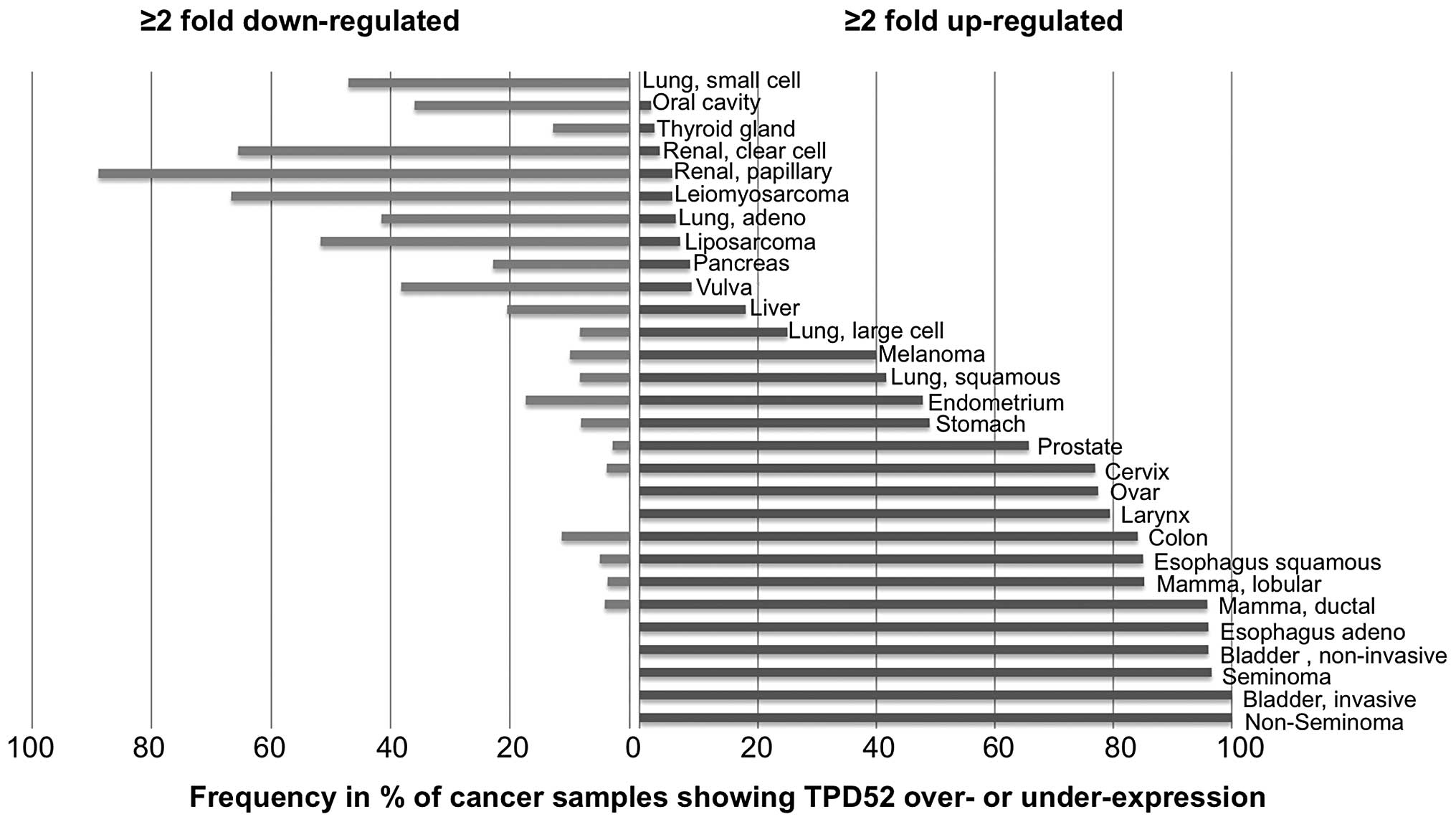
|
1.
|
Schraml P, Kononen J, Bubendorf L, et al:
Tissue microarrays for gene amplification surveys in many different
tumor types. Clin Cancer Res. 5:1966–1975. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R, et
al: Overexpression, amplification, and androgen regulation of TPD52
in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64:3814–3822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Choschzick M, Lassen P, Lebeau A, et al:
Amplification of 8q21 in breast cancer is independent of MYC and
associated with poor patient outcome. Mod Pathol. 23:603–610. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Richter J, Jiang F, Gorog JP, et al:
Marked genetic differences between stage pTa and stage pT1
papillary bladder cancer detected by comparative genomic
hybridization. Cancer Res. 57:2860–2864. 1997.
|
|
5.
|
Sauter GH, Munzing W, von Ritter C and
Paumgartner G: Bile acid malabsorption as a cause of chronic
diarrhea: diagnostic value of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in
serum. Dig Dis Sci. 44:14–19. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
El Gedaily A, Bubendorf L, Willi N, et al:
Discovery of new DNA amplification loci in prostate cancer by
comparative genomic hybridization. Prostate. 46:184–190.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Al-Kuraya K, Schraml P, Torhorst J, et al:
Prognostic relevance of gene amplifications and coamplifications in
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:8534–8540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Byrne JA, Balleine RL, Schoenberg Fejzo M,
et al: Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) is overexpressed and a gene
amplification target in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer.
117:1049–1054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Balleine RL, Fejzo MS, Sathasivam P,
Basset P, Clarke CL and Byrne JA: The hD52 (TPD52) gene is a
candidate target gene for events resulting in increased 8q21 copy
number in human breast carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
29:48–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Van Duin M, van Marion R, Vissers K, et
al: High-resolution array comparative genomic hybridization of
chromosome arm 8q: evaluation of genetic progression markers for
prostate cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 44:438–449.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hicks J, Krasnitz A, Lakshmi B, et al:
Novel patterns of genome rearrangement and their association with
survival in breast cancer. Genome Res. 16:1465–1479. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rodriguez V, Chen Y, Elkahloun A, Dutra A,
Pak E and Chandrasekharappa S: Chromosome 8 BAC array comparative
genomic hybridization and expression analysis identify
amplification and overexpression of TRMT12 in breast cancer. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 46:694–707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kim JH, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, et al:
Integrative analysis of genomic aberrations associated with
prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 67:8229–8239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Boutros R, Fanayan S, Shehata M and Byrne
JA: The tumor protein D52 family: many pieces, many puzzles.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:1115–1121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Thomas DD, Frey CL, Messenger SW, August
BK and Groblewski GE: A role for tumor protein TPD52
phosphorylation in endo-membrane trafficking during cytokinesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:583–587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Loukopoulos P, Shibata T, Katoh H, et al:
Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis
of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: identification of genetic indicators
that predict patient outcome. Cancer Sci. 98:392–400. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Largo C, Alvarez S, Saez B, et al:
Identification of overexpressed genes in frequently
gained/amplified chromosome regions in multiple myeloma.
Haematologica. 91:184–191. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Tiacci E, Orvietani PL, Bigerna B, et al:
Tumor protein D52 (TPD52): a novel B-cell/plasma-cell molecule with
unique expression pattern and Ca(2+)-dependent association with
annexin VI. Blood. 105:2812–2820. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Dave SS, Fu K, Wright GW, et al: Molecular
diagnosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 354:2431–2442.
2006.
|
|
20.
|
Roesch A, Becker B, Bentink S, et al:
Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated gene is a possible biomarker for
discrimination of infiltrative deep penetrating nevi and metastatic
vertical growth phase melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:2486–2490. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Skotheim RI, Autio R, Lind GE, et al:
Novel genomic aberrations in testicular germ cell tumors by
array-CGH, and associated gene expression changes. Cell Oncol.
28:315–326. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liu R, Wang X, Chen GY, et al: The
prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer
cells. N Engl J Med. 356:217–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lewis JD, Payton LA, Whitford JG, et al:
Induction of tumorigenesis and metastasis by the murine orthologue
of tumor protein D52. Mol Cancer Res. 5:133–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, et al:
Altered expression of tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and
migration of prostate cancer cells. FEBS J. 275:5703–5713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Shehata M, Bieche I, Boutros R, et al:
Nonredundant functions for tumor protein D52-like proteins support
specific targeting of TPD52. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5050–5060. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Porter D, Lahti-Domenici J, Keshaviah A,
et al: Molecular markers in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast.
Mol Cancer Res. 1:362–375. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et al:
Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor
subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Gruvberger S, Ringner M, Chen Y, et al:
Estrogen receptor status in breast cancer is associated with
remarkably distinct gene expression patterns. Cancer Res.
61:5979–5984. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Wang R, Xu J, Saramaki O, et al: PrLZ, a
novel prostate-specific and androgen-responsive gene of the TPD52
family, amplified in chromosome 8q21.1 and overexpressed in human
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64:1589–1594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Dhanasekaran SM, Barrette TR, Ghosh D, et
al: Delineation of prognostic biomarkers in prostate cancer.
Nature. 412:822–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Welsh JB, Sapinoso LM, Su AI, et al:
Analysis of gene expression identifies candidate markers and
pharmacological targets in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
61:5974–5978. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Bhattacharjee A, Richards WG, Staunton J,
et al: Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression
profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:13790–13795. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, et
al: Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13784–13789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Beer DG, Kardia SL, Huang CC, et al:
Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. Nat Med. 8:816–824. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Dyrskjot L, Thykjaer T, Kruhoffer M, et
al: Identifying distinct classes of bladder carcinoma using
microarrays. Nat Genet. 33:90–96. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, et al:
Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based
on gene expression. Nature. 415:436–442. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Huang Y, Prasad M, Lemon WJ, et al: Gene
expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma reveals highly consistent
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:15044–15049. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Risinger JI, Maxwell GL, Chandramouli GV,
et al: Microarray analysis reveals distinct gene expression
profiles among different histologic types of endometrial cancer.
Cancer Res. 63:6–11. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Mutter GL, Baak JP, Fitzgerald JT, et al:
Global expression changes of constitutive and hormonally regulated
genes during endometrial neoplastic transformation. Gynecol Oncol.
83:177–185. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Giordano TJ, Thomas DG, Kuick R, et al:
Distinct transcriptional profiles of adrenocortical tumors
uncovered by DNA microarray analysis. Am J Pathol. 162:521–531.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, et al: Gene
expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell.
13:1929–1939. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Pollack JR, Sorlie T, Perou CM, et al:
Microarray analysis reveals a major direct role of DNA copy number
alteration in the transcriptional program of human breast tumors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12963–12968. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Adelaide J, Finetti P, Bekhouche I, et al:
Integrated profiling of basal and luminal breast cancers. Cancer
Res. 67:11565–11575. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Pache M, Glatz-Krieger K, Sauter G and
Meyer P: Expression of sex hormone receptors and cell cycle
proteins in melanocytic lesions of the ocular conjunctiva. Graefes
Archive Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 244:113–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Jonsson G, Staaf J, Olsson E, et al:
High-resolution genomic profiles of breast cancer cell lines
assessed by tiling BAC array comparative genomic hybridization.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 46:543–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Bulavin DV, Demidov ON, Saito S, et al:
Amplification of PPM1D in human tumors abrogates p53
tumor-suppressor activity. Nat Genet. 31:210–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Parris TZ, Danielsson A, Nemes S, et al:
Clinical implications of gene dosage and gene expression patterns
in diploid breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3860–3874. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Hawthorn L, Luce J, Stein L and Rothschild
J: Integration of transcript expression, copy number and LOH
analysis of infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. BMC
Cancer. 10:4602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Melchor L, Alvarez S, Honrado E, et al:
The accumulation of specific amplifications characterizes two
different genomic pathways of evolution of familial breast tumors.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:8577–8584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Hernandez L, Wilkerson PM, Lambros MB, et
al: Genomic and mutational profiling of ductal carcinomas in situ
and matched adjacent invasive breast cancers reveals intra-tumour
genetic heterogeneity and clonal selection. J Pathol. 227:42–52.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Valk PJ, Verhaak RG, Beijen MA, et al:
Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 350:1617–1628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Maia S, Haining WN, Ansen S, et al: Gene
expression profiling identifies BAX-delta as a novel tumor antigen
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 65:10050–10058. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Andersson A, Ritz C, Lindgren D, et al:
Microarray-based classification of a consecutive series of 121
childhood acute leukemias: prediction of leukemic and genetic
subtype as well as of minimal residual disease status. Leukemia.
21:1198–1203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54.
|
Basso K, Margolin AA, Stolovitzky G, Klein
U, Dalla-Favera R and Califano A: Reverse engineering of regulatory
networks in human B cells. Nat Genet. 37:382–390. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Storz MN, van de Rijn M, Kim YH,
Mraz-Gernhard S, Hoppe RT and Kohler S: Gene expression profiles of
cutaneous B cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 120:865–870. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, et al:
High-resolution genome-wide mapping of genetic alterations in human
glial brain tumors. Cancer Res. 65:4088–4096. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Sun L, Hui AM, Su Q, et al: Neuronal and
glioma-derived stem cell factor induces angiogenesis within the
brain. Cancer Cell. 9:287–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Murat A, Migliavacca E, Gorlia T, et al:
Stem cell-related ‘self-renewal’ signature and high epidermal
growth factor receptor expression associated with resistance to
concomitant chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
26:3015–3024. 2008.
|
|
59.
|
Detwiller KY, Fernando NT, Segal NH, Ryeom
SW, D’Amore PA and Yoon SS: Analysis of hypoxia-related gene
expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of
vascular endothelial cell growth factor A. Cancer Res.
65:5881–5889. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Riker AI, Enkemann SA, Fodstad O, et al:
The gene expression profiles of primary and metastatic melanoma
yields a transition point of tumor progression and metastasis. BMC
Med Genomics. 1:132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Skrzypczak M, Goryca K, Rubel T, et al:
Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional
analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical
reliability. PLoS One. 5:e130912010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Hong Y, Downey T, Eu KW, Koh PK and Cheah
PY: A ‘metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair
proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications
for possible therapeutics. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:83–90. 2010.
|
|
63.
|
Korkola JE, Heck S, Olshen AB, et al: In
vivo differentiation and genomic evolution in adult male germ cell
tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:43–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
McIntyre A, Summersgill B, Lu YJ, et al:
Genomic copy number and expression patterns in testicular germ cell
tumours. Br J Cancer. 97:1707–1712. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Payton LA, Lewis JD, Byrne JA and Bright
RK: Vaccination with metastasis-related tumor associated antigen
TPD52 and CpG/ODN induces protective tumor immunity. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 57:799–811. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Lewis J, Sullivan L, Byrne J, de Riese W
and Bright R: Memory and cellular immunity induced by a DNA vaccine
encoding self antigen TPD52 administered with soluble GM-CSF.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:1337–1349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Talantov D, Mazumder A, Yu JX, et al:
Novel genes associated with malignant melanoma but not benign
melanocytic lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7234–7242. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Zhu H, Lam DC, Han KC, et al: High
resolution analysis of genomic aberrations by metaphase and array
comparative genomic hybridization identifies candidate tumour genes
in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 245:303–314. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69.
|
Yamagata N, Shyr Y, Yanagisawa K, et al: A
training-testing approach to the molecular classification of
resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4695–4704.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Wachi S, Yoneda K and Wu R:
Interactome-transcriptome analysis reveals the high centrality of
genes differentially expressed in lung cancer tissues.
Bioinformatics. 21:4205–4208. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Su LJ, Chang CW, Wu YC, et al: Selection
of DDX5 as a novel internal control for Q-RT-PCR from microarray
data using a block bootstrap re-sampling scheme. BMC Genomics.
8:1402007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Hou J, Aerts J, den Hamer B, et al: Gene
expression-based classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas
and survival prediction. PLoS One. 5:e103122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Yu K, Lee CH, Tan PH and Tan P:
Conservation of breast cancer molecular subtypes and
transcriptional patterns of tumor progression across distinct
ethnic populations. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5508–5517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Scanlan MJ, Gout I, Gordon CM, et al:
Humoral immunity to human breast cancer: antigen definition and
quantitative analysis of mRNA expression. Cancer Immun.
1:42001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Byrne JA, Tomasetto C, Garnier JM, et al:
A screening method to identify genes commonly overexpressed in
carcinomas and the identification of a novel complementary DNA
sequence. Cancer Res. 55:2896–2903. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Byrne JA, Maleki S, Hardy JR, et al: MAL2
and tumor protein D52 (TPD52) are frequently overexpressed in
ovarian carcinoma, but differentially associated with histological
subtype and patient outcome. BMC Cancer. 10:4972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Tothill RW, Tinker AV, George J, et al:
Novel molecular subtypes of serous and endometrioid ovarian cancer
linked to clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5198–5208. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Hendrix ND, Wu R, Kuick R, Schwartz DR,
Fearon ER and Cho KR: Fibroblast growth factor 9 has oncogenic
activity and is a downstream target of Wnt signaling in ovarian
endometrioid adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 66:1354–1362. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Petrova DT, Asif AR, Armstrong VW, et al:
Expression of chloride intracellular channel protein 1 (CLIC1) and
tumor protein D52 (TPD52) as potential biomarkers for colorectal
cancer. Clin Biochem. 41:1224–1236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Buffart TE, Coffa J, Hermsen MA, et al:
DNA copy number changes at 8q11-24 in metastasized colorectal
cancer. Cell Oncol. 27:57–65. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Kaiser S, Park YK, Franklin JL, et al:
Transcriptional recapitulation and subversion of embryonic colon
development by mouse colon tumor models and human colon cancer.
Genome Biol. 8:R1312007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82.
|
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, et al: A
unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor
relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer
Res. 70:10202–10212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83.
|
Wang R, Xu J, Mabjeesh N, et al: PrLZ is
expressed in normal prostate development and in human prostate
cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6040–6048. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Cho-Vega JH, Tsavachidis S, Do KA,
Nakagawa J, Medeiros LJ and McDonnell TJ: Dicarbonyl/L-xylulose
reductase: a potential biomarker identified by laser-capture
microdissection-micro serial analysis of gene expression of human
prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:2615–2622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85.
|
Hendriksen PJ, Dits NF, Kokame K, et al:
Evolution of the androgen receptor pathway during progression of
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66:5012–5020. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86.
|
Bismar TA, Demichelis F, Riva A, et al:
Defining aggressive prostate cancer using a 12-gene model.
Neoplasia. 8:59–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87.
|
Rhodes DR, Barrette TR, Rubin MA, Ghosh D
and Chinnaiyan AM: Meta-analysis of microarrays: interstudy
validation of gene expression profiles reveals pathway
dysregulation in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 62:4427–4433.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88.
|
Luo J, Duggan DJ, Chen Y, et al: Human
prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: molecular
dissection by gene expression profiling. Cancer Res. 61:4683–4688.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89.
|
Dyrskjot L, Zieger K, Real FX, et al: Gene
expression signatures predict outcome in non-muscle-invasive
bladder carcinoma: a multicenter validation study. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3545–3551. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90.
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|