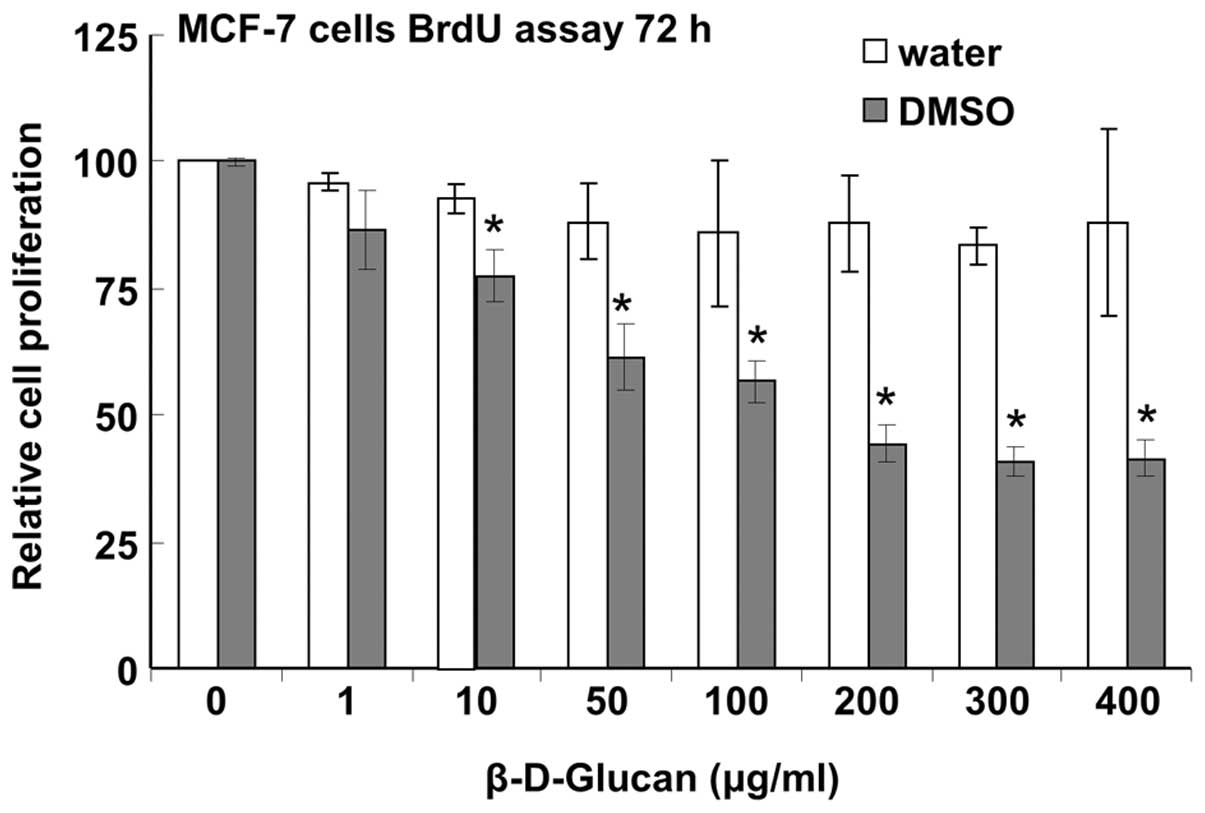
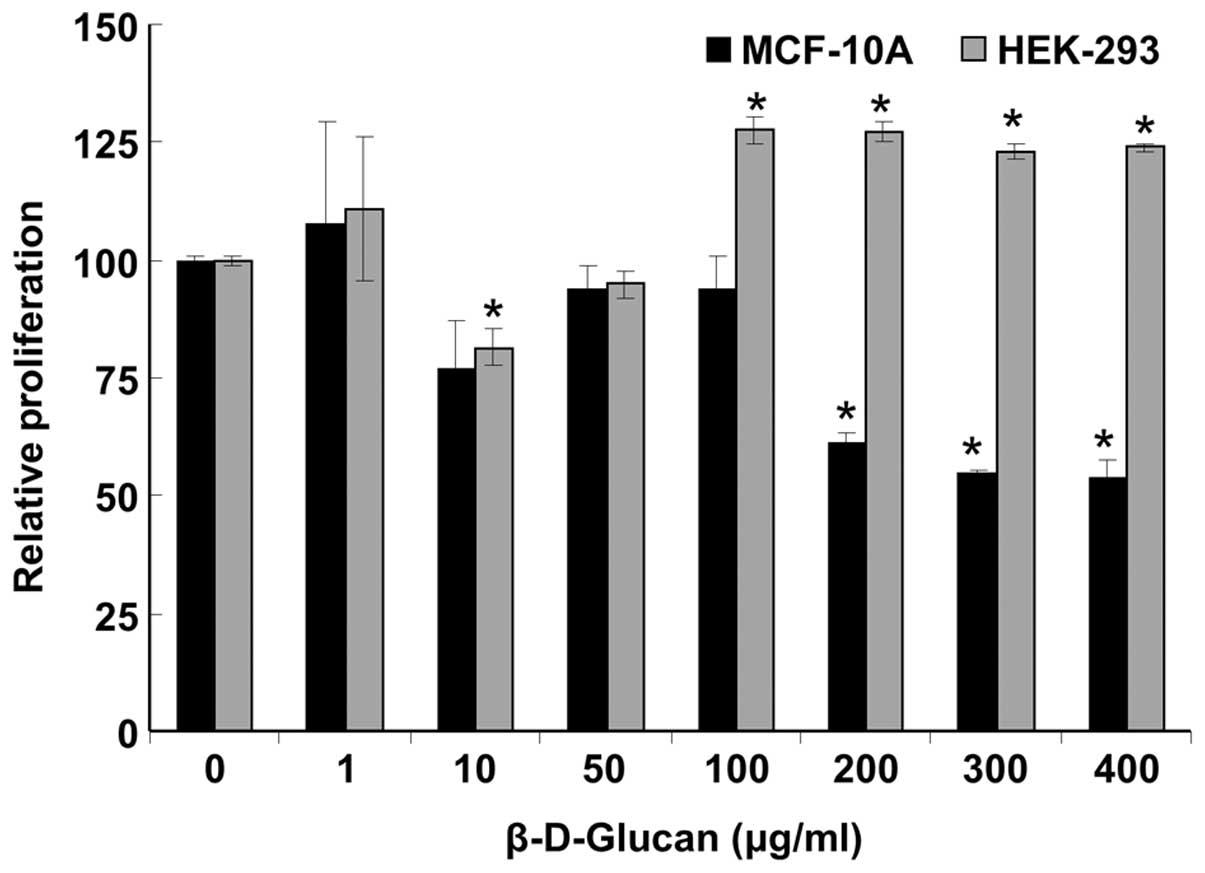
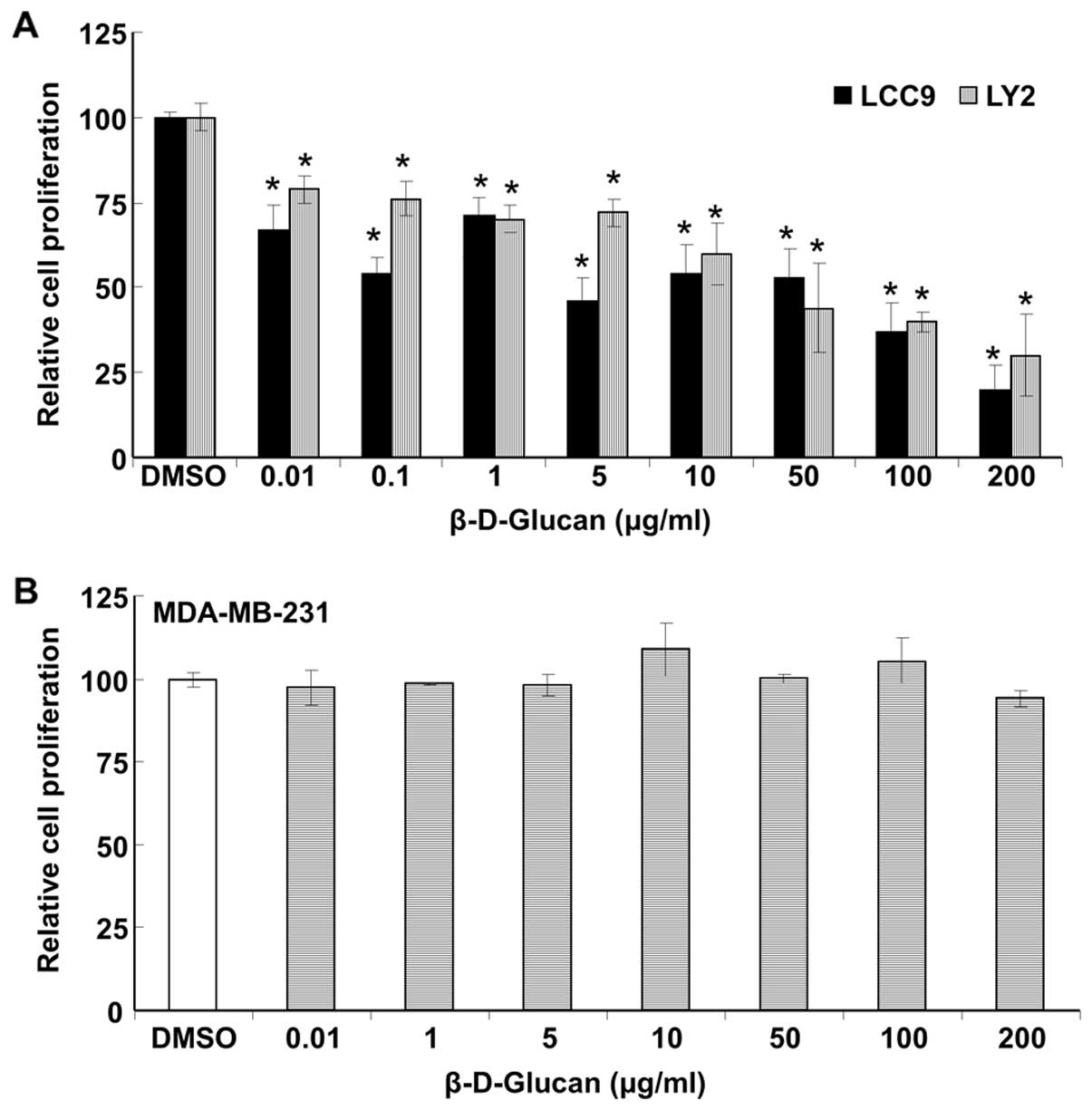
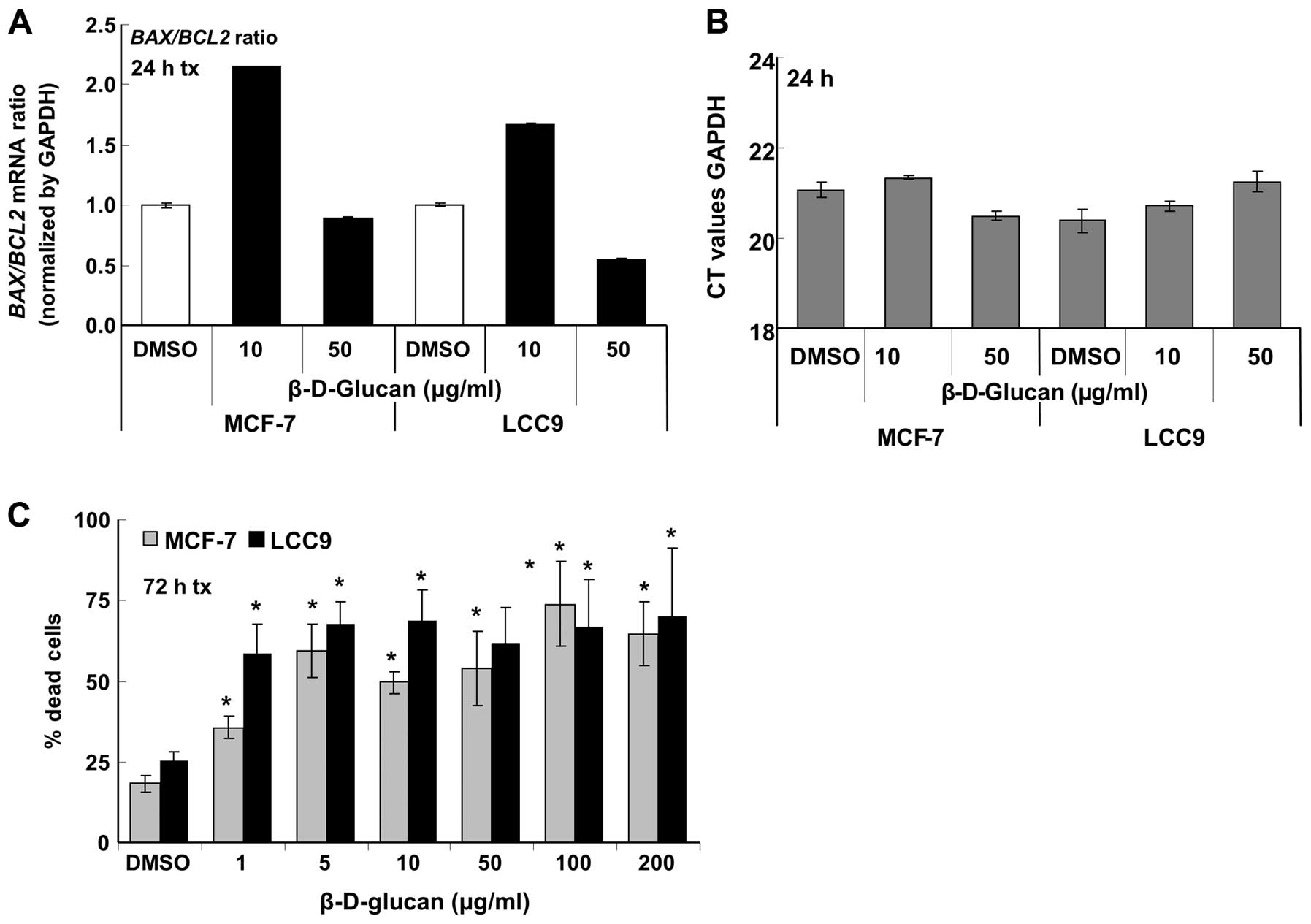
|
1.
|
Ring A and Dowsett M: Mechanisms of
tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer. 11:643–658. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Martin L-A, Pancholi S, Farmer I, Guest S,
Ribas R, Weigel M, Thornhill A, Ghazoui Z, A’Hern R, Evans D, Lane
H, Johnston S and Dowsett M: Effectiveness and molecular
interactions of the clinically active mTORC1 inhibitor everolimus
in combination with tamoxifen or letrozole in vitro and in vivo.
Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Saraswat-Ohri S, Vashishta A, Vetvicka V,
Descroix K, Jamois F, Yvin JC and Ferrieres V: Biological
properties of (1→3)-beta-D-glucan-based synthetic oligosaccharides.
J Med Food. 14:369–376. 2011.
|
|
4.
|
Bohn JA and BeMiller JN: (1→3)-β-d-Glucans
as biological response modifiers: a review of structure-functional
activity relationships. Carbohydr Polym. 28:3–14. 1995.
|
|
5.
|
Kim HS, Hong JT, Kim Y and Han SB:
Stimulatory effect of beta-glucans on immune cells. Immune Netw.
11:191–195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Chan G, Chan W and Sze D: The effects of
beta-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol.
2:252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Zhang M, Chiu LC, Cheung PC and Ooi VE:
Growth-inhibitory effects of a beta-glucan from the mycelium of
Poria cocos on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells: cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Oncol Rep. 15:637–643.
2006.
|
|
8.
|
Brunner N, Boulay V, Fojo A, Freter CE,
Lippman ME and Clarke R: Acquisition of hormone-independent growth
in MCF-7 cells is accompanied by increased expression of
estrogen-regulated genes but without detectable DNA amplifications.
Cancer Res. 53:283–290. 1993.
|
|
9.
|
Brunner N, Boysen B, Jirus S, Skaar TC,
Holst-Hansen C, Lippman J, Frandsen T, Spang-Thomsen M, Fuqua SA
and Clarke R: MCF7/LCC9: an antiestrogen-resistant MCF-7 variant in
which acquired resistance to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182,780
confers an early cross-resistance to the nonsteroidal antiestrogen
tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 57:3486–3493. 1997.
|
|
10.
|
Bronzert DA, Greene GL and Lippman ME:
Selection and characterization of a breast cancer cell line
resistant to the anti-estrogen LY 117018. Endocrinology.
117:1409–1417. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Davidson NE, Bronzert DA, Chambon P,
Gelmann EP and Lippman ME: Use of two MCF-7 cell variants to
evaluate the growth regulatory potential of estrogen-induced
products. Cancer Res. 46:1904–1908. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Chen J-Q and Russo J: ER[alpha]-negative
and triple negative breast cancer: molecular features and potential
therapeutic approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:162–175.
2009.
|
|
13.
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Vetvicka V and Vetvickova J:
beta1,3-Glucan: silver bullet or hot air? Open Glycosci. 3:1–6.
2010.
|
|
15.
|
Wyrębska A, Gach K, Lewandowska U,
Szewczyk K, Hrabec E, Modranka J, Jakubowski R, Janecki T,
Szymański J and Janecka A: Anticancer activity of new synthetic
α-methylene-δ-lactones on two breast cancer cell lines. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013 Aug 19–2013.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Crawford AC, Riggins RB, Shajahan AN,
Zwart A and Clarke R: Co-inhibition of BCL-W and BCL2 restores
antiestrogen sensitivity through BECN1 and promotes an
autophagy-associated necrosis. PLoS One. 5:e86042010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Mansour A, Daba A, Baddour N, El-Saadani M
and Aleem E: Schizophyllan inhibits the development of mammary and
hepatic carcinomas induced by 7,12 dimethylbenz(alpha) anthracene
and decreases cell proliferation: comparison with tamoxifen. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1579–1596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Scarpulla RC: Nuclear control of
respiratory chain expression by nuclear respiratory factors and
PGC-1-related coactivator. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1147:321–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ivanova MM, Luken KH, Zimmer AS, Lenzo FL,
Smith RJ, Arteel MW, Kollenberg TJ, Mattingly KA and Klinge CM:
Tamoxifen increases nuclear respiratory factor 1 transcription by
activating estrogen receptor β and AP-1 recruitment to adjacent
promoter binding sites. FASEB J. 25:1402–1416. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Dammann R, Schagdarsurengin U, Seidel C,
Strunnikova M, Rastetter M, Baier K and Pfeifer GP: The tumor
suppressor RASSF1A in human carcinogenesis: an update. Histol
Histopathol. 20:645–663. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Shukla S, Mirza S, Sharma G, Parshad R,
Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Detection of RASSF1A and RARbeta
hypermethylation in serum DNA from breast cancer patients.
Epigenetics. 1:88–93. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lin S, Xia W, Wang J, Kwong K, Spohn B,
Wen Y, Pestell R and Hung M: Beta-catenin, a novel prognostic
marker for breast cancer: its roles in cyclin D1 expression and
cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4262–4266. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Howe LR and Brown AM: Wnt signaling and
breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:36–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Paul S and Dey A: Wnt signaling and cancer
development: therapeutic implication. Neoplasma. 55:165–176.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Espelund U, Cold S, Frystyk J, Orskov H
and Flyvbjerg A: Elevated free IGF2 levels in localized,
early-stage breast cancer in women. Eur J Endocrinol. 159:595–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Duggan C, Wang CY, Neuhouser ML, Xiao L,
Smith AW, Reding KW, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L,
Ballard-Barbash R and McTiernan A: Associations of insulin-like
growth factor and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 with
mortality in women with breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:1191–1200.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Martin JL, Lin MZ, McGowan EM and Baxter
RC: Potentiation of growth factor signaling by insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-3 in breast epithelial cells requires
sphingosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 284:25542–25552. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
McIntosh J, Dennison G, Holly JMP, Jarrett
C, Frankow A, Foulstone EJ, Winters ZE and Perks CM: IGFBP-3 can
either inhibit or enhance EGF-mediated growth of breast epithelial
cells dependent upon the presence of fibronectin. J Biol Chem.
285:38788–38800. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Levenson AS, Svoboda KM, Pease KM, Kaiser
SA, Chen B, Simons LA, Jovanovic BD, Dyck PA and Jordan VC: Gene
expression profiles with activation of the estrogen receptor
alpha-selective estrogen receptor modulator complex in breast
cancer cells expressing wild-type estrogen receptor. Cancer Res.
62:4419–4426. 2002.
|
|
30.
|
Wang D-Y, Fulthorpe R, Liss SN and Edwards
EA: Identification of estrogen-responsive genes by complementary
deoxyribonucleic acid microarray and characterization of a novel
early estrogen-induced gene: EEIG1. Mol Endocrinol. 18:402–411.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cook KL, Shajahan AN, Wärri A, Jin L,
Hilakivi-Clarke LA and Clarke R: Glucose-regulated protein 78
controls cross-talk between apoptosis and autophagy to determine
antiestrogen responsiveness. Cancer Res. 72:3337–3349. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Li C, Harada A and Oh Y: IGFBP-3
sensitizes antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cells through
interaction with GRP78. Cancer Lett. 325:200–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
De Amicis F, Thirugnansampanthan J, Cui Y,
Selever J, Beyer A, Parra I, Weigel NL, Herynk MH, Tsimelzon A,
Lewis MT, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Ando S and Fuqua SA: Androgen
receptor overexpression induces tamoxifen resistance in human
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 121:1–11.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Hiscox S, Jiang WG, Obermeier K, Taylor K,
Morgan L, Burmi R, Barrow D and Nicholson RI: Tamoxifen resistance
in MCF7 cells promotes EMT-like behaviour and involves modulation
of beta-catenin phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 118:290–301. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007.
|
|
36.
|
Mattingly KA, Ivanova MM, Riggs KA,
Wickramasinghe NS, Barch MJ and Klinge CM: Estradiol stimulates
transcription of Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1 and increases
mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 22:609–622. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Maxwell P and van den Berg HW: Changes in
the secretion of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins -2 and
-4 associated with the development of tamoxifen resistance and
estrogen independence in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer
Lett. 139:121–127. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Thomas C and Gustafsson J-Å: The different
roles of ER subtypes in cancer biology and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:597–608. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Pfeifer GP and Dammann R: Methylation of
the tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A in human tumors. Biochemistry.
70:576–583. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Vaz JA, Heleno SA, Martins A, Almeida GM,
Vasconcelos MH and Ferreira ICFR: Wild mushrooms Clitocybe
alexandri and Lepista inversa: in vitro antioxidant
activity and growth inhibition of human tumour cell lines. Food
Chem Toxicol. 48:2881–2884. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Doñate F, Parry GC, Shaked Y, Hensley H,
Guan X, Beck I, Tel-Tsur Z, Plunkett ML, Manuia M, Shaw DE, Kerbel
RS and Mazar AP: Pharmacology of the novel antiangiogenic peptide
ATN-161 (Ac-PHSCN-NH2): observation of a U-shaped dose-response
curve in several preclinical models of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2137–2144. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Vandenberg LN, Colborn T, Hayes TB,
Heindel JJ, Jacobs DR, Lee D-H, Shioda T, Soto AM, vom Saal FS,
Welshons WV, Zoeller RT and Myers JP: Hormones and
endocrine-disrupting chemicals: low-dose effects and nonmonotonic
dose responses. Endocr Rev. 33:378–455. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Almstrup K, Fernandez MF, Petersen JH,
Olea N, Skakkebaek NE and Leffers H: Dual effects of phytoestrogens
result in u-shaped dose-response curves. Environ Health Perspect.
110:743–748. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Need EF, Selth LA, Harris TJ, Birrell SN,
Tilley WD and Buchanan G: Research resource: interplay between the
genomic and transcriptional networks of androgen receptor and
estrogen receptor α in luminal breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol.
26:1941–1952. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Fiegl H, Millinger S, Mueller-Holzner E,
Marth C, Ensinger C, Berger A, Klocker H, Goebel G and
Widschwendter M: Circulating tumor-specific DNA: a marker for
monitoring efficacy of adjuvant therapy in cancer patients. Cancer
Res. 65:1141–1145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|