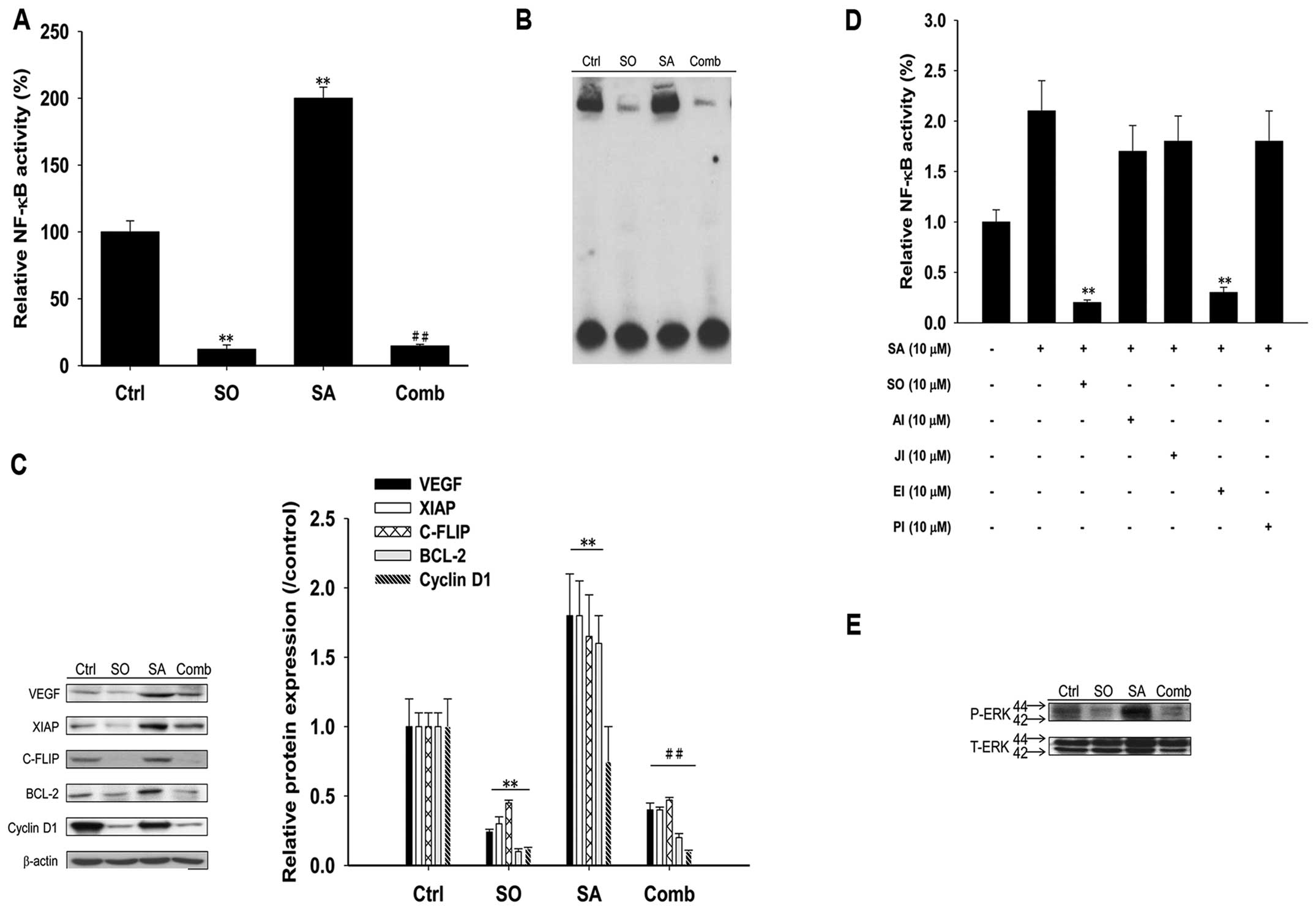
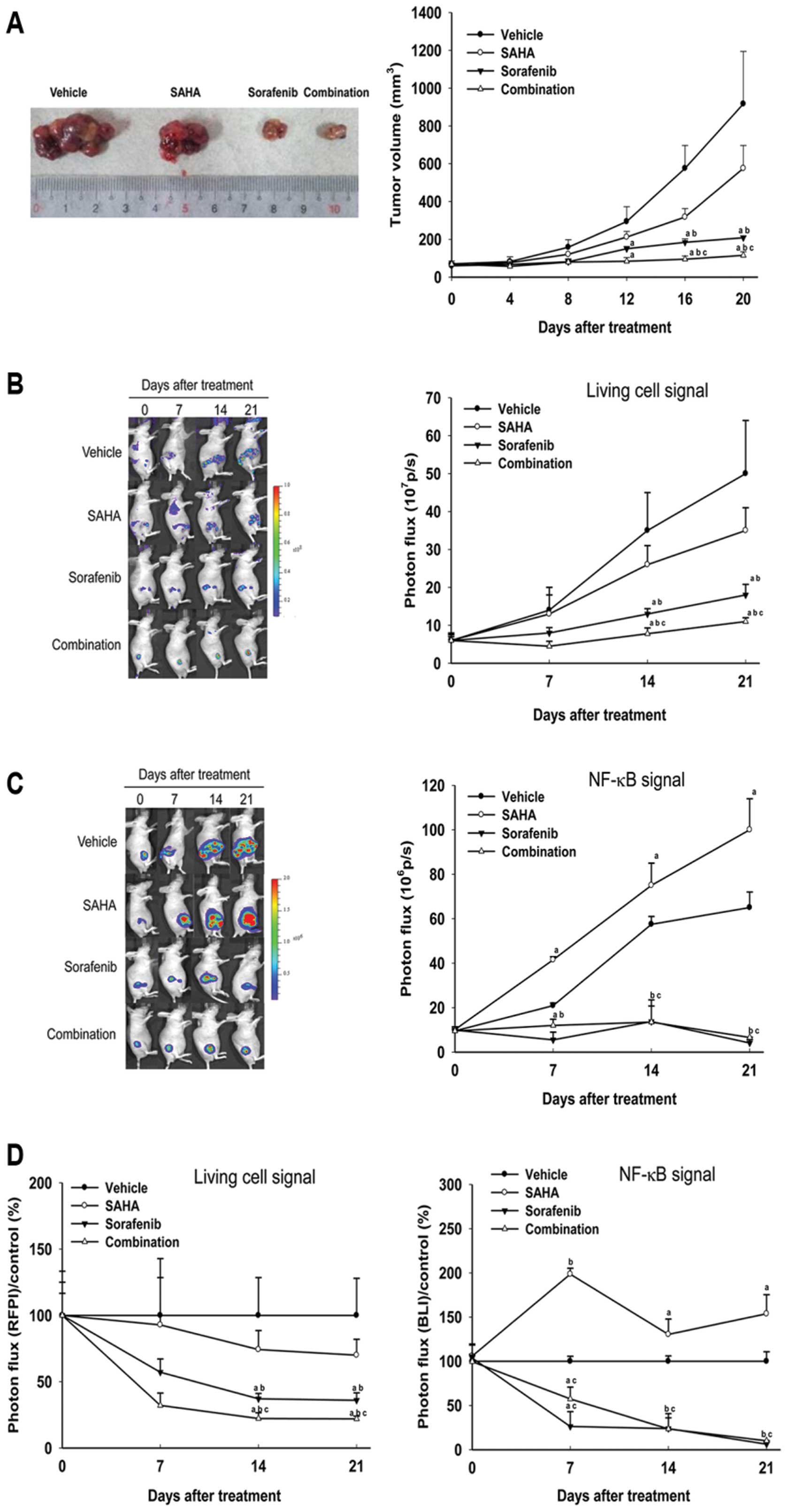
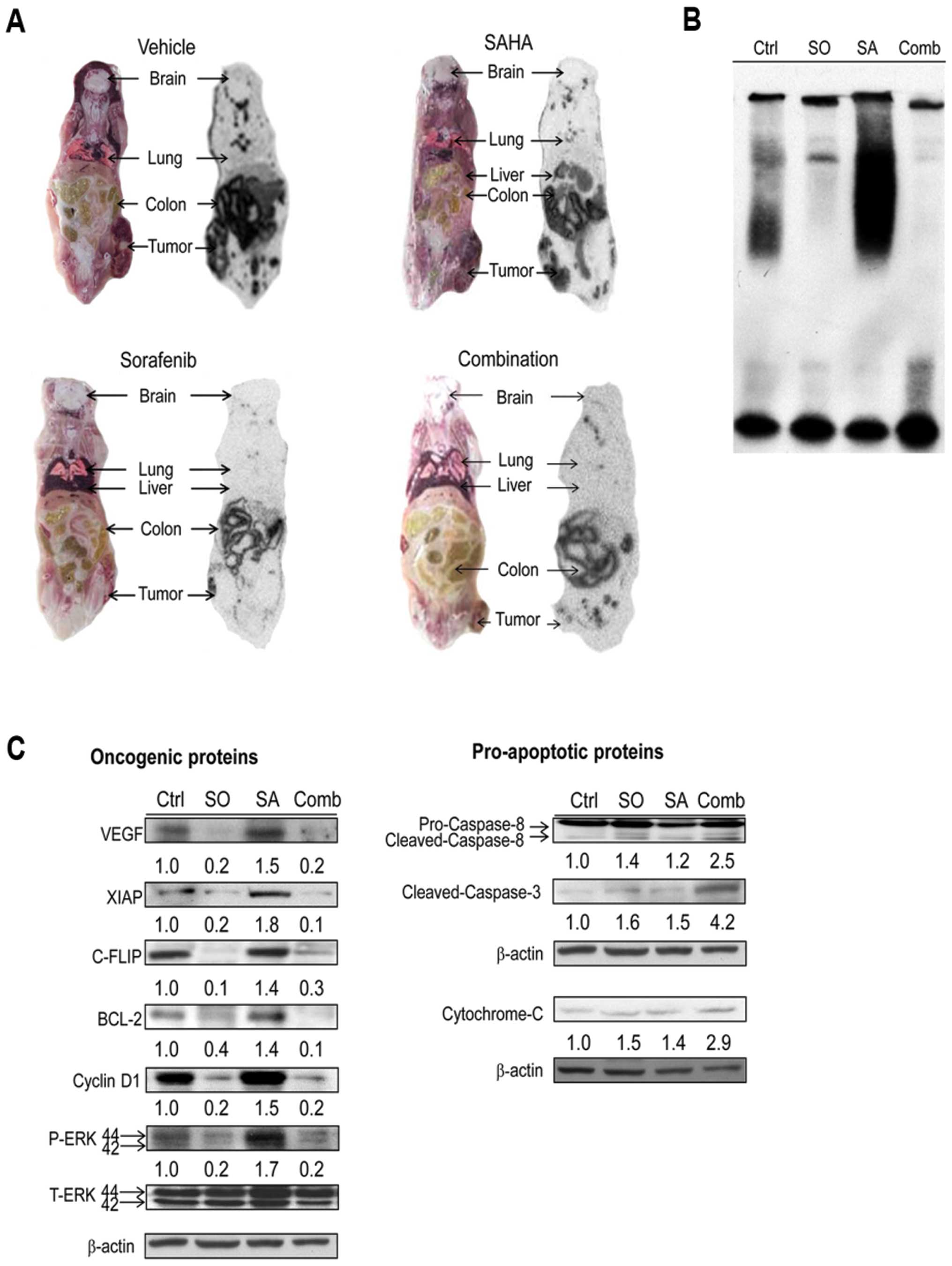
|
1.
|
Feng M and Ben-Josef E: Radiation therapy
for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol. 21:271–277. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Zhang X, Yang XR, Huang XW, et al:
Sorafenib in treatment of patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: a systematic review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
11:458–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kanno K, Kanno S, Nitta H, et al:
Overexpression of histone deacetylase 6 contributes to accelerated
migration and invasion activity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 28:867–873. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Wu J, Du C, Lv Z, et al: The up-regulation
of histone deacetylase 8 promotes proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 58:3545–3553.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Rikimaru T, Taketomi A, Yamashita Y, et
al: Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 72:69–74. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wu LM, Yang Z, Zhou L, et al:
Identification of histone deacetylase 3 as a biomarker for tumor
recurrence following liver transplantation in HBV-associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 5:e144602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Machado MC, Bellodi-Privato M, Kubrusly
MS, et al: Valproic acid inhibits human hepatocellular cancer cells
growth in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Ther Oncol. 9:85–92.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Coradini D and Speranza A: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:1025–1033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yoshida K, Sasaki R, Nishimura H, et al:
Nuclear factor-kappaB expression as a novel marker of
radioresistance in early-stage laryngeal cancer. Head Neck.
32:646–655. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ni W, Chen B, Zhou G, et al: Overexpressed
nuclear BAG-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with
poor prognosis and resistance to doxorubicin. J Cell Biochem.
114:2120–2130. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Zhang G, Park MA, Mitchell C, et al:
Vorinostat and sorafenib synergistically kill tumor cells via FLIP
suppression and CD95 activation. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5385–5399.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Spratlin JL, Pitts TM, Kulikowski GN, et
al: Synergistic activity of histone deacetylase and proteasome
inhibition against pancreatic and hepatocellular cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 31:1093–1103. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wang WH, Chiang IT, Liu YC, et al:
Simultaneous imaging of temporal changes of NF-kappaB activity and
viable tumor cells in Huh7/NF-kappaB-tk-luc2/rfp tumor-bearing
mice. In vivo. 27:339–350. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Dent P and Grant S:
Blockade of histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced RelA/p65
acetylation and NF-kappaB activation potentiates apoptosis in
leukemia cells through a process mediated by oxidative damage, XIAP
downregulation, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:5429–5444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Domingo-Domenech J, Pippa R, Tapia M,
Gascon P, Bachs O and Bosch M: Inactivation of NF-kappaB by
proteasome inhibition contributes to increased apoptosis induced by
histone deacetylase inhibitors in human breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 112:53–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Dai Y, Guzman ML, Chen S, et al: The NF
(nuclear factor)-kappaB inhibitor parthenolide interacts with
histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce MKK7/JNK1-dependent
apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol.
151:70–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Dai Y, Chen S, Wang L, et al: Disruption
of IkappaB kinase (IKK)-mediated RelA serine 536 phosphorylation
sensitizes human multiple myeloma cells to histone deacetylase
(HDAC) inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 286:34036–34050. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Schelman WR, Traynor AM, Holen KD, et al:
A phase I study of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib in
patients with advanced malignancies. Invest New Drugs.
31:1539–1546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Deming DA, Ninan J, Bailey HH, et al: A
Phase I study of intermittently dosed vorinostat in combination
with bortezomib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New
Drugs. 32:323–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Liu YC, Chiang IT, Hsu FT and Hwang JJ:
Using NF-kappaB as a molecular target for theranostics in radiation
oncology research. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 12:139–146. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Chiang IT, Liu YC, Wang WH, et al:
Sorafenib inhibits TPA-induced MMP-9 and VEGF expression via
suppression of ERK/NF-kappaB pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. In vivo. 26:671–681. 2012.
|
|
22.
|
Bankston D, Dumas J, Natero R, et al: A
scaleable synthesis of BAY 43-9006 a potent Raf kinase inhibitor
for the treatment of cancer. Org Process Res Dev. 6:777–781. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Marks PA and Breslow R: Dimethyl sulfoxide
to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as
an anticancer drug. Nat Biotechnol. 25:84–90. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Li F and Sethi G: Targeting transcription
factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in
cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1805:167–180. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Galimberti S, Canestraro M, Khan R, et al:
Vorinostat and bortezomib significantly inhibit WT1 gene expression
in MO7-e and P39 cell lines. Leukemia. 22:628–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Takada Y, Gillenwater A, Ichikawa H and
Aggarwal BB: Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid potentiates apoptosis,
inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis by suppressing
nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem. 281:5612–5622. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Chen KF, Chen HL, Tai WT, et al:
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway
mediates acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Pharm Exp Ther. 337:155–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Park MA, Zhang G, Martin AP, et al:
Vorinostat and sorafenib increase ER stress, autophagy and
apoptosis via ceramide-dependent CD95 and PERK activation. Cancer
Biol Ther. 7:1648–1662. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Park MA, Mitchell C, Zhang G, et al:
Vorinostat and sorafenib increase CD95 activation in
gastrointestinal tumor cells through a Ca(2+)-de novo
ceramide-PP2A-reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling pathway.
Cancer Res. 70:6313–6324. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Dasari A, Gore L, Messersmith WA, et al: A
phase I study of sorafenib and vorinostat in patients with advanced
solid tumors with expanded cohorts in renal cell carcinoma and
non-small cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs. 31:115–125. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Warlick ED, Cao Q and Miller J: Bortezomib
and vorinostat in refractory acute myelogenous leukemia and
high-risk myelodys-plastic syndromes: produces stable disease but
at the cost of high toxicity. Leukemia. 27:1789–1791. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hoang T, Campbell TC, Zhang C, et al:
Vorinostat and bortezomib as third-line therapy in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Wisconsin Oncology Network
Phase II study. Invest New Drugs. 32:195–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Friday BB, Anderson SK, Buckner J, et al:
Phase II trial of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib in
recurrent glioblastoma: a north central cancer treatment group
study. Neuro Oncol. 14:215–221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|