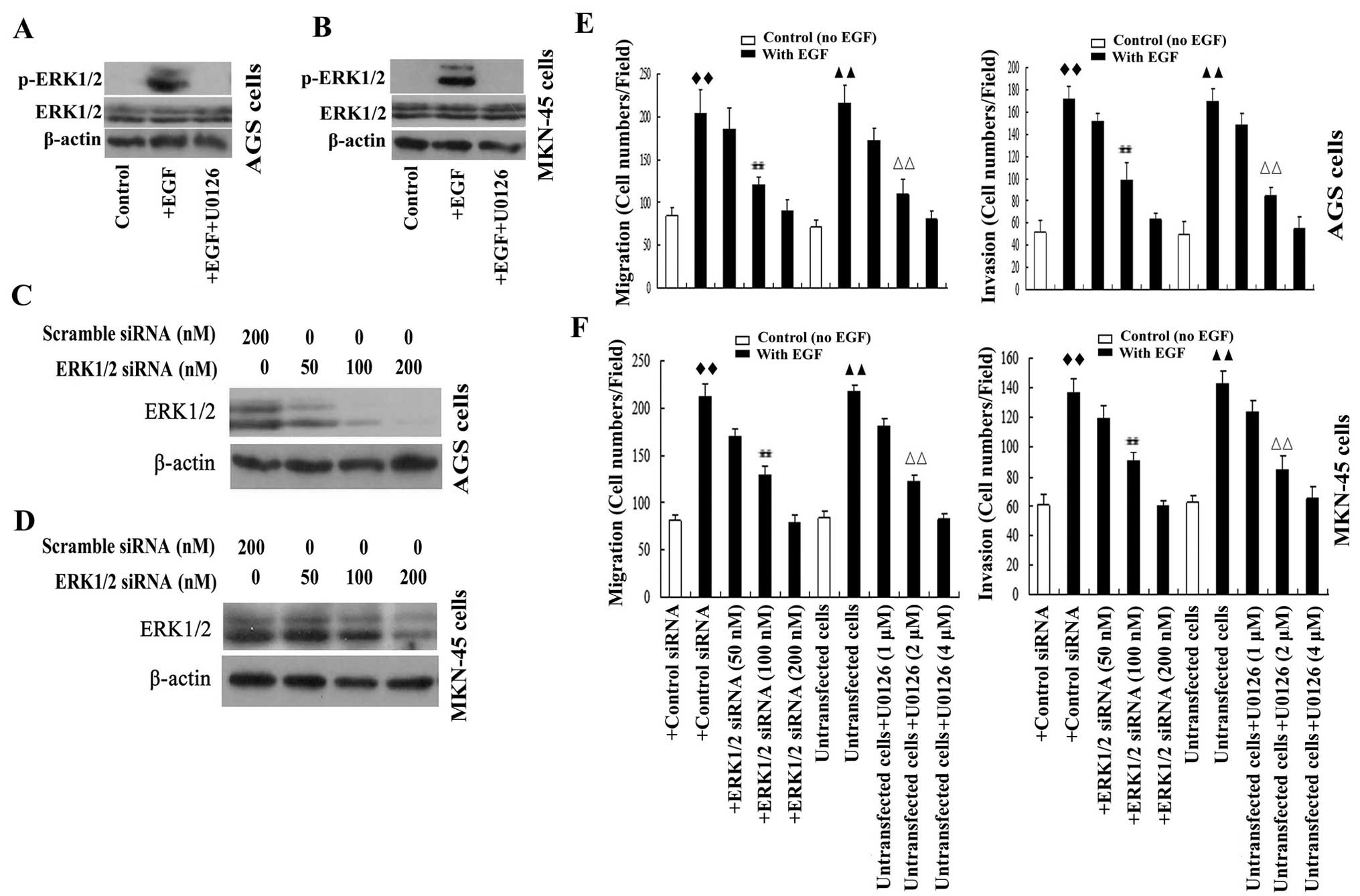
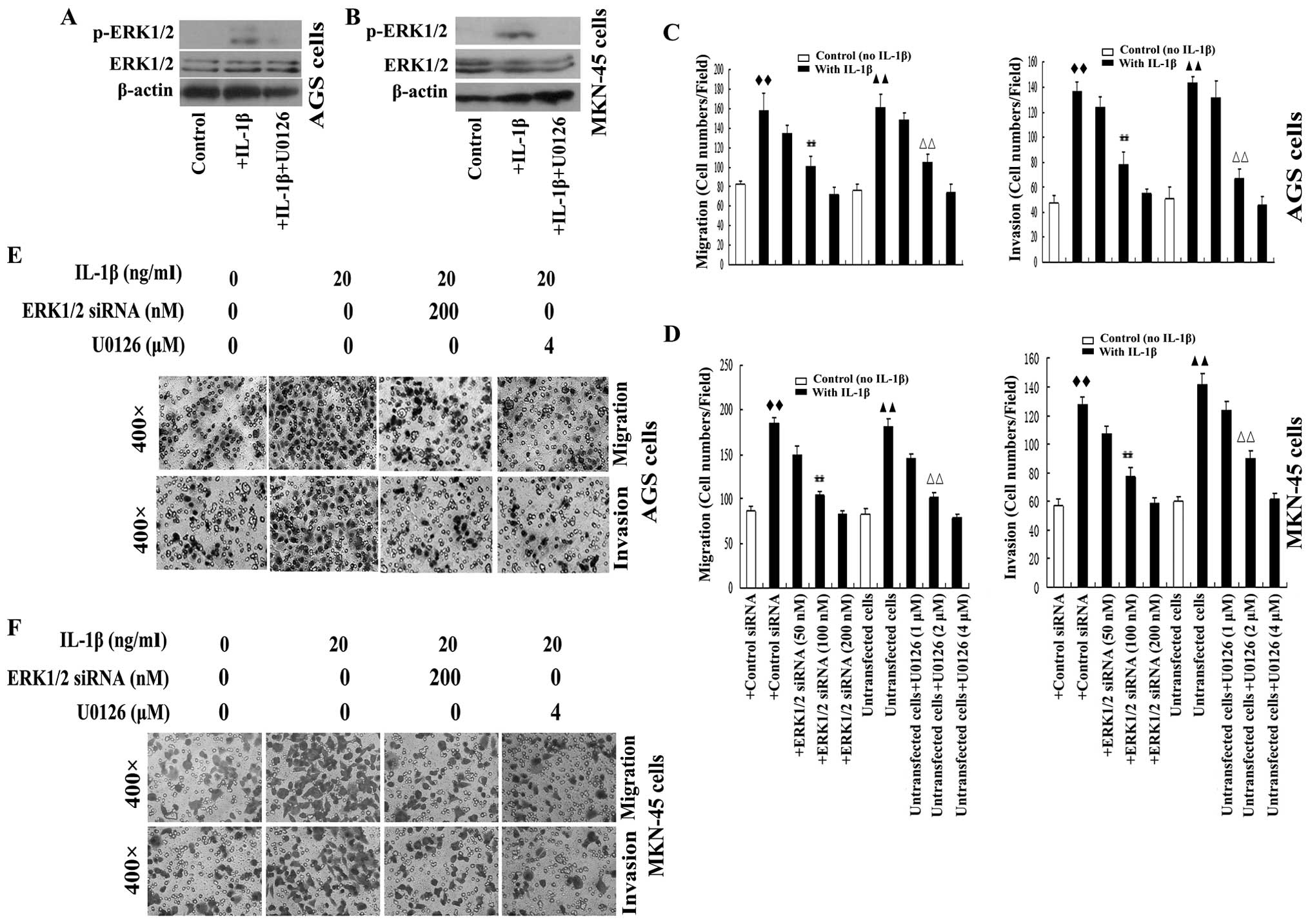
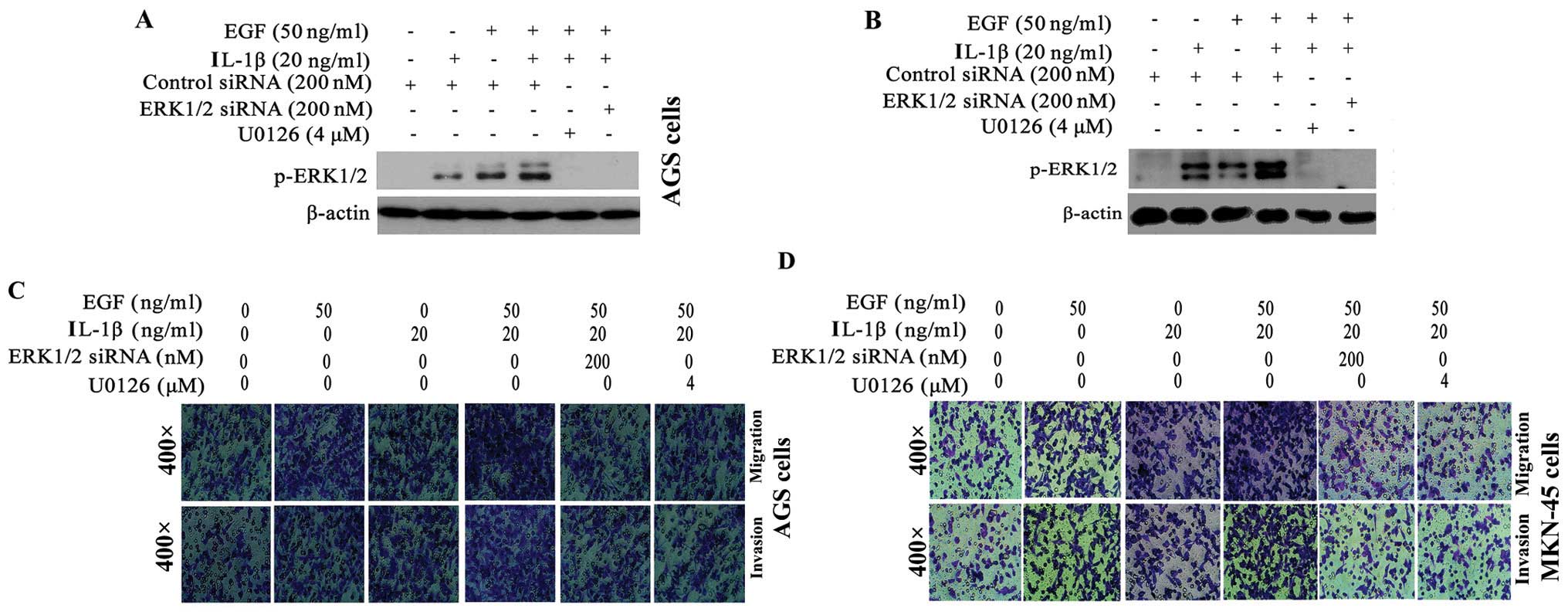
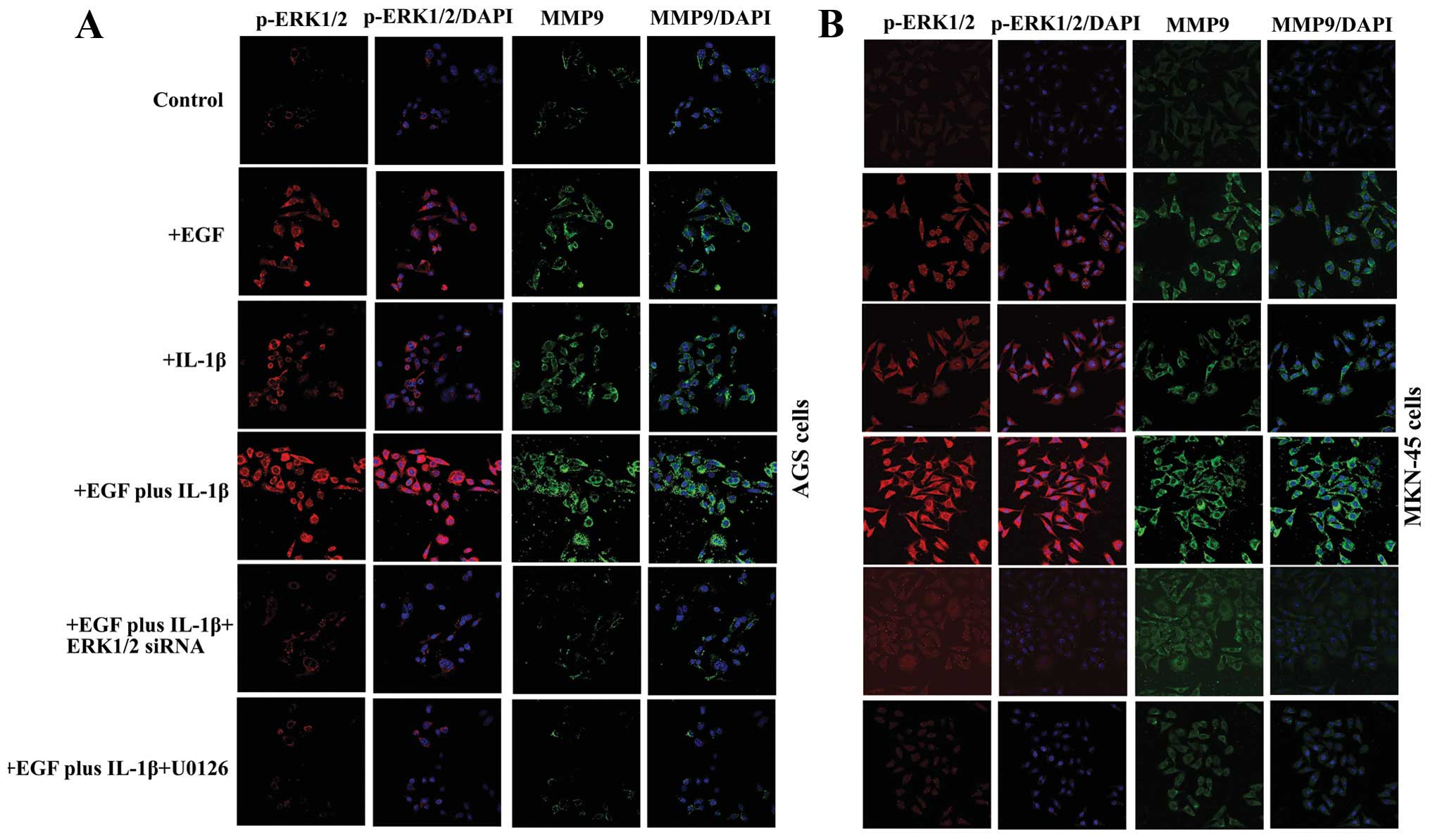
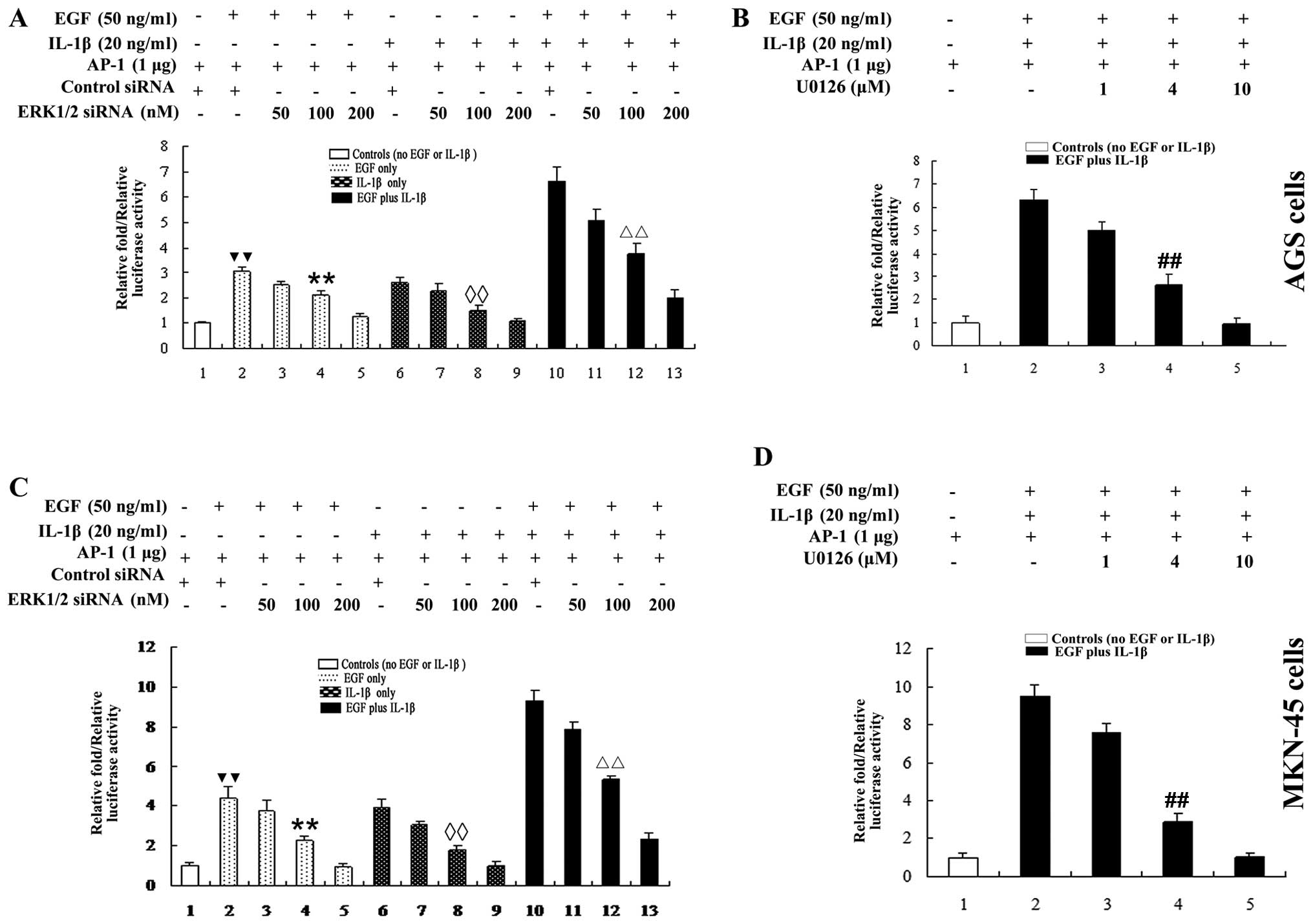
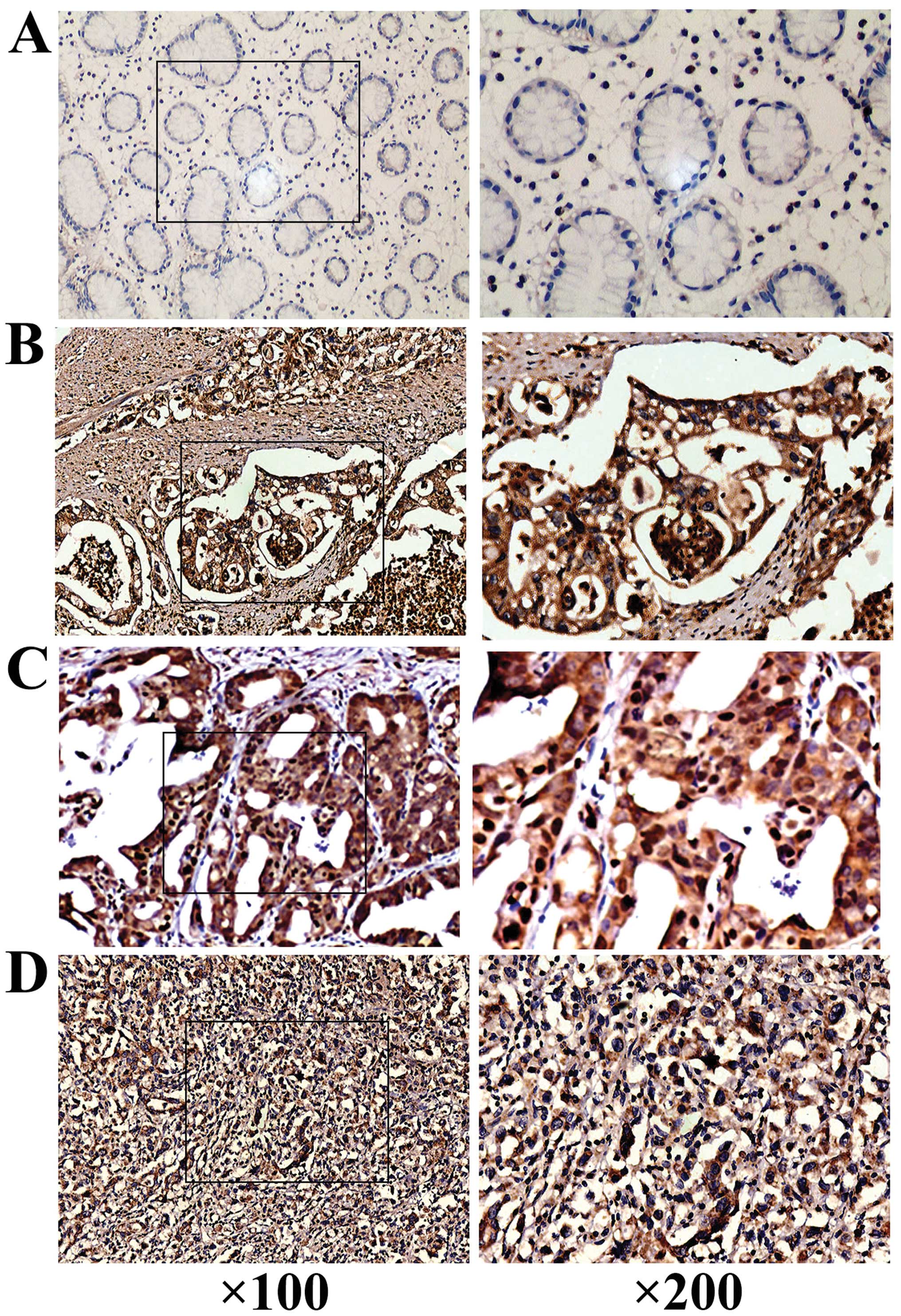
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Ajani JA: Optimizing docetaxel
chemotherapy in patients with cancer of the gastric and
gastroesophageal junction evolution of the docetaxel, cisplatin,
and 5-fluorouracil regimen. Cancer. 113:945–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, et al: Sonic
hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via
activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer
Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumour cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Abe MK, Saelzler MP, Espinosa R III, et
al: ERK8, a new member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase
family. J Biol Chem. 277:16733–16743. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Xu YM, Zhu F, Cho YY, et al: Extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 8-mediated c-Jun phosphorylation increases
tumorigenesis of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3218–3227.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Adams DG, Coffee RL Jr, Zhang H, et al:
Positive regulation of Raf1-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling by protein
serine/threonine phosphatase 2A holoenzymes. J Biol Chem.
280:42644–42654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Bai Y, Luo Y, Liu S, et al: PRL-1 protein
promotes ERK1/2 and RhoA protein activation through a non-canonical
interaction with the Src homology 3 domain of p115 Rho
GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 286:42316–42324. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Guturi KK, Mandal T, Chatterjee A, et al:
Mechanism of β-catenin-mediated transcriptional regulation of
epidermal growth factor receptor expression in glycogen synthase
kinase 3 β-inactivated prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
287:18287–18296. 2012.
|
|
11.
|
Takeuchi A, Eto M, Shiota M, Tatsugami K,
et al: Sunitinib enhances antitumor effects against
chemotherapy-resistant bladder cancer through suppression of ERK1/2
phosphorylation. Int J Oncol. 40:1691–1696. 2012.
|
|
12.
|
Nakata W, Hayakawa Y, Nakagawa H, et al:
Anti-tumor activity of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in
gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 39:1529–1536. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M, et al:
The tumor micro-environment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 40:1733–1747. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Soria G, Ofri-Shahak M, Haas I, et al:
Inflammatory mediators in breast cancer: coordinated expression of
TNFα and IL-1β with CCL2 and CCL5 and effects on
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer.
11:1302011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yang HT, Cohen P and Rousseau S:
IL-1beta-stimulated activation of ERK1/2 and p38 alpha MAPK
mediates the transcriptional up-regulation of IL-6, IL-8 and
GRO-alpha in HeLa cells. Cell Signal. 20:375–380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Tsai CY, Lee TS, Kou YR, et al:
Glucosamine inhibits IL-1beta-mediated IL-8 production in prostate
cancer cells by MAPK attenuation. J Cell Biochem. 108:489–498.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Huang Q, Yang J, Lin Y, et al:
Differential regulation of interleukin 1 receptor and Toll-like
receptor signaling by MEKK3. Nat Imm. 5:98–103. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Huang Q, Lan F, Zheng Z, et al: Akt2
suppresses GAPDH mediated-apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via
phosphorylating gapdh at threonine 237 and decreasing its nuclear
translocation. J Biol Chem. 286:42211–42220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Sumida T, Itahana Y, Hamakawa H, et al:
Reduction of human metastatic breast cancer cell aggressiveness on
introduction of either form A or B of the progesterone receptor and
then treatment with progestins. Cancer Res. 64:7886–7892. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Huang QJ, Huang QL, Chen WN, et al:
Identification of transgelin as a potential novel biomarker for
gastric adenocarcinoma based on proteomics technology. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 134:1219–1227. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ebert M, Yokoyama M, Kobrin MS, et al:
Induction and expression of amphiregulin in human pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Res. 54:3959–3962. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ju XZ, Yang JM, Zhou XY, et al: Emmprin
expression as a prognostic factor in radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res.
12:494–501. 2008.
|
|
23.
|
Chen MF, Lu MS, Chen PT, et al: Role of
interleukin 1 beta in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med
(Berl). 90:89–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Park S, Jung HH, Park YH, et al: ERK/MAPK
pathways play critical roles in EGFR ligands-induced MMP1
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 407:680–686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Komurov K, Padron D, Cheng T, et al:
Comprehensive mapping of the human kinome to epidermal growth
factor receptor signal. J Biol Chem. 285:21134–21142. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Angst E, Reber HA, Hines OJ, et al:
Mononuclear cell-derived interleukin-1 beta confers chemoresistance
in pancreatic cancer cells by upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2.
Surgery. 144:57–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Arakawa T, Hayashi H, Itoh S, et al:
IL-1-induced ERK1/2 activation up-regulates p21(Waf1/Cip1) protein
by inhibition of degradation via ubiquitin-independent pathway in
human melanoma cells A375. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:369–372.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Yadav VR, Prasad S, Gupta SC, et al:
3-Formylchromone interacts with cysteine 38 in p65 protein and with
cysteine 179 in IκBα kinase, leading to down-regulation of nuclear
factor-κB (NF-κB)-regulated gene products and sensitization of
tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 287:245–256. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Han H, Du B, Pan X, et al: CADPE inhibits
PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma cell invasion and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by FAK/MEK/ERK mediated AP-1
activation. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1477–1488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Babykutty S, Suboj P, Srinivas P, et al:
Insidious role of nitric oxide in migration/invasion of colon
cancer cells by upregulating MMP-2/9 via activation of cGMP-PKG-ERK
signaling pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:471–492. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Fujisawa T, Joshi BH and Puri RK: IL-13
regulates cancer invasion and metastasis through IL-13Rα2 via
ERK/AP-1 pathway in mouse model of human ovarian cancer. Int J
Cancer. 131:344–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Han W and Lo HW: Landscape of EGFR
signaling network in human cancers: biology and therapeutic
response in relation to receptor subcellular locations. Cancer
Lett. 318:124–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yotsumoto F, Sanui A, Fukami T, et al:
Efficacy of ligand-based targeting for the EGF system in cancer.
Anticancer Res. 29:4879–4885. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Schäfer B, Gschwind A and Ullrich A:
Multiple G-protein-coupled receptor signals converge on the
epidermal growth factor receptor to promote migration and invasion.
Oncogene. 23:991–999. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Cragg MS, Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, et al:
Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant
EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. Plos Med.
4:1681–1689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Kaler P, Godasi BN, Augenlicht L, et al:
The NF-kappaB/AKT-dependent induction of Wnt signaling in colon
cancer cells by macrophages and IL-1beta. Cancer Microenviron.
2:69–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Rucci N, Sanità P and Angelucci A: Roles
of metalloproteases in metastatic niche. Curr Mol Med. 11:609–622.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Luo Y, Liang F and Zhang ZY: PRL1 promotes
cell migration and invasion by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression
through Src and ERK1/2 pathways. Biochemistry. 48:1838–1846. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Huang C, Ma WY and Dong Z: The
extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinases (Erks) are required
for UV-induced AP-1 activation in JB6 cells. Oncogene.
18:2828–2835. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|