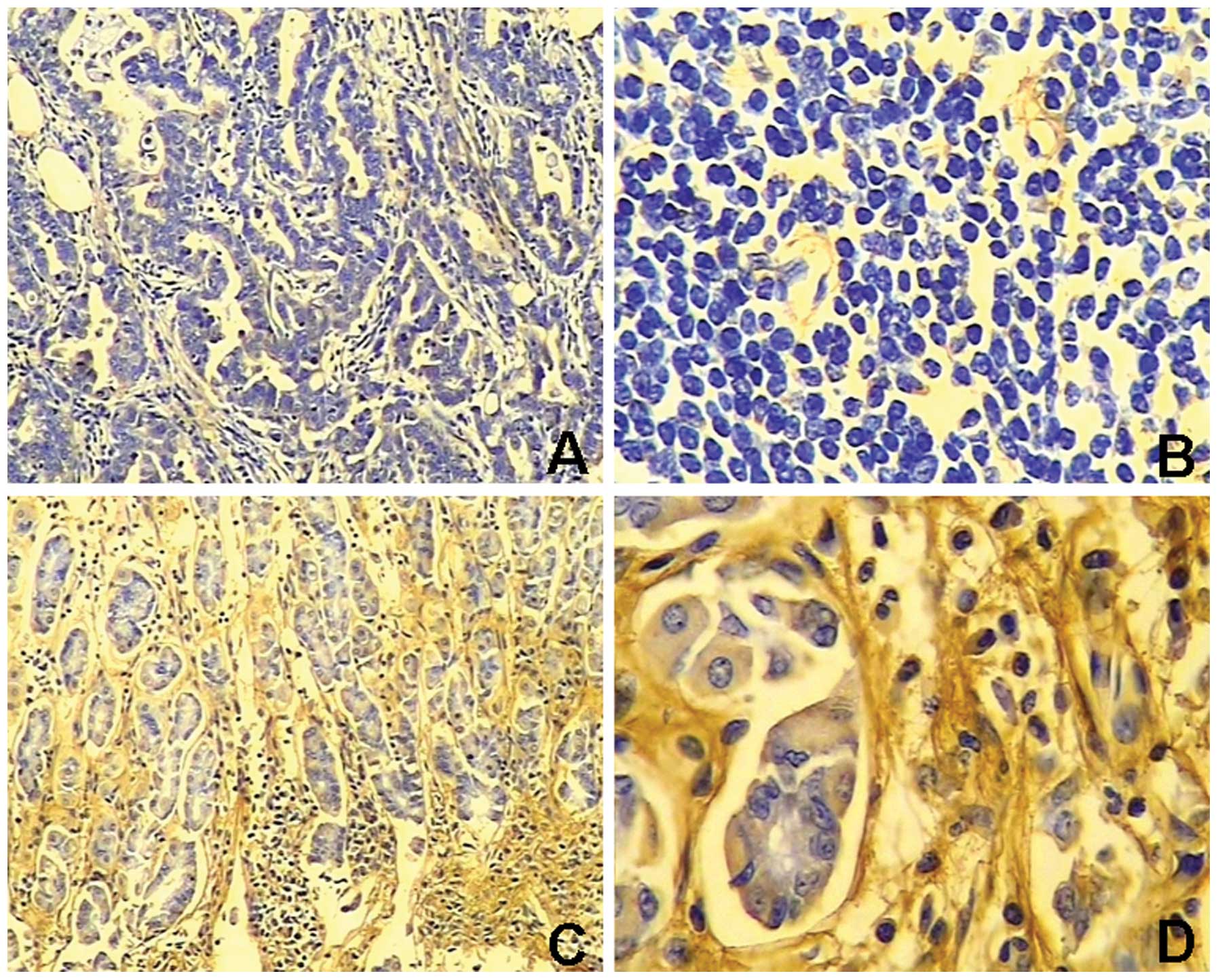
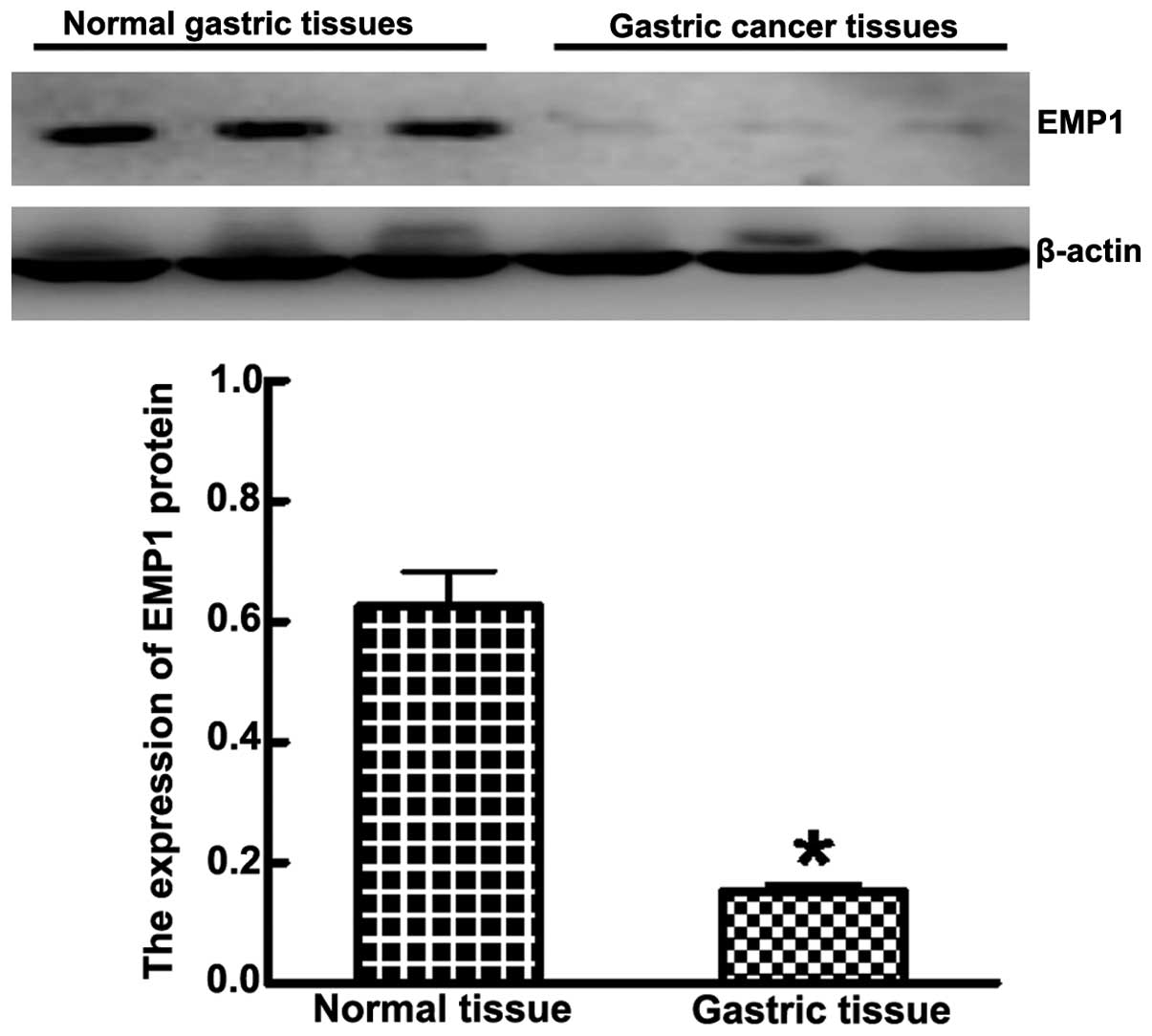
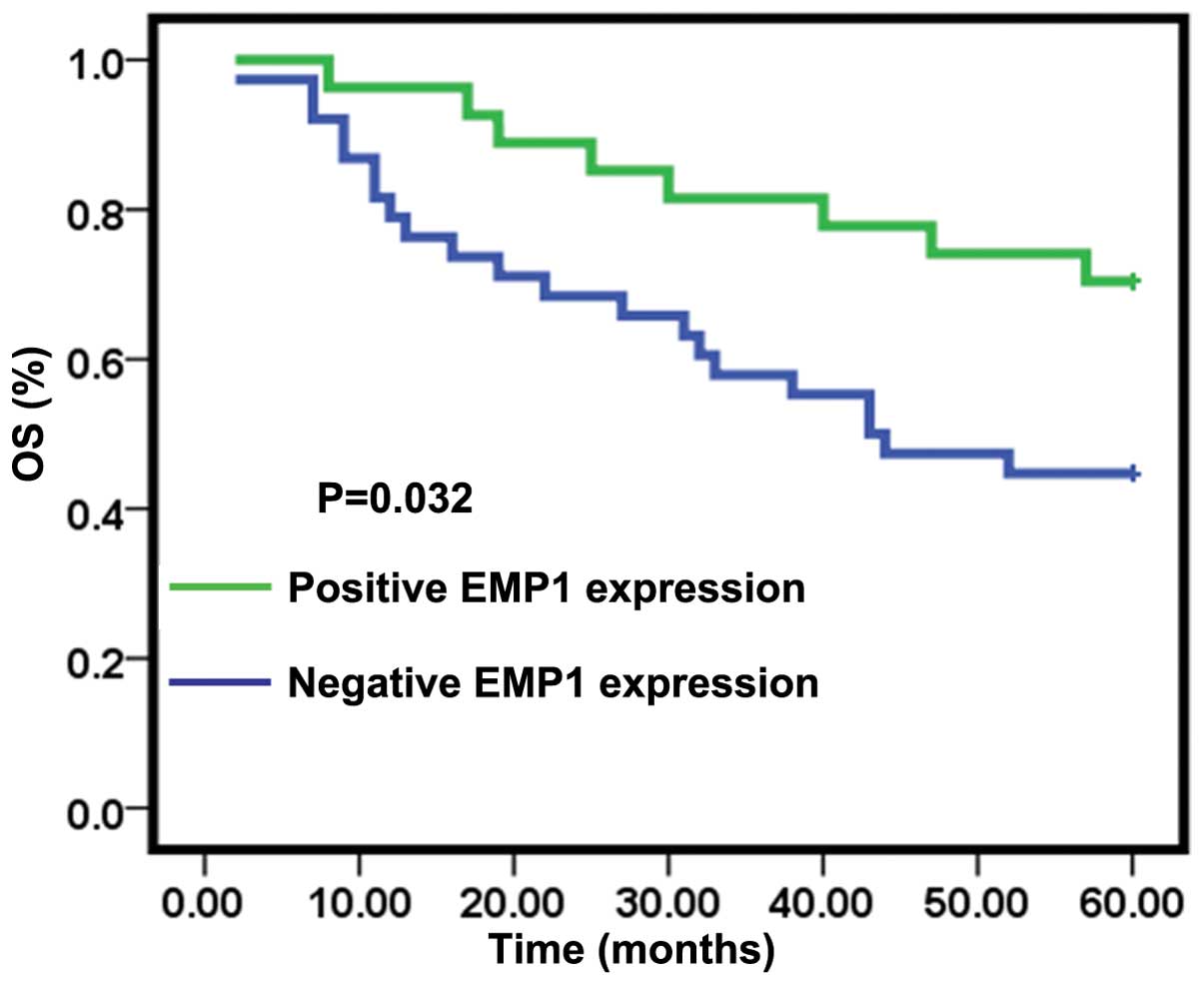
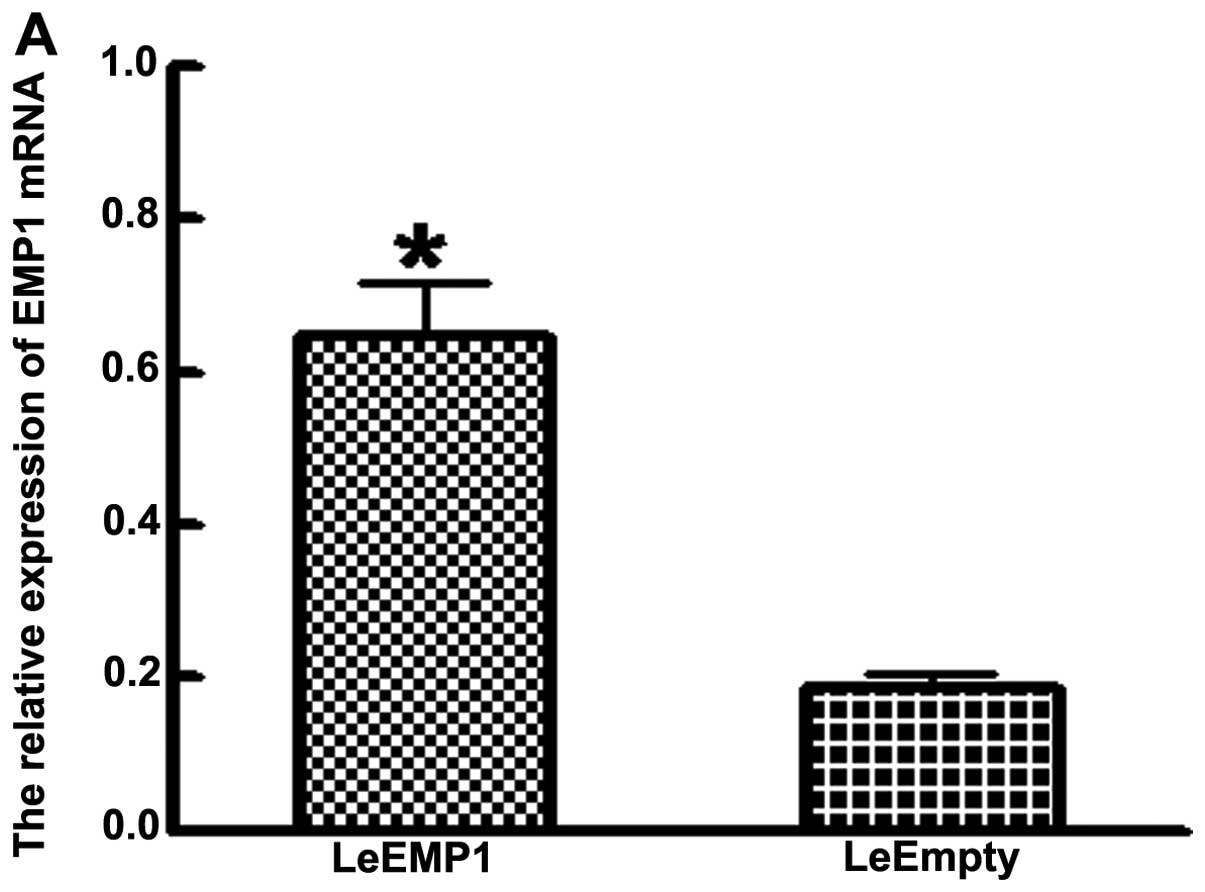
|
1
|
Hofmockel G: Molecular genetic principles
of tumor development and progression. Urologe A. 39:212–213.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Martel C, Forman D and Plummer M:
Gastric cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin
North Am. 42:219–240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dimofte G, Tarcoveanu E, Taraşi M, Panait
C, Lozneanu G, Nicolescu S, Porumb V and Grigoraş O: Mean number of
lymph nodes in colonic cancer specimen: possible quality control
index for surgical performance. Chirurgia (Bucur). 106:759–764.
2011.
|
|
4
|
Fleming M, Ravula S, Tatishchev SF and
Wang HL: Colorectal carcinoma: pathologic aspects. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 3:153–173. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Lai S, Wang G, Cao X, Li Z, Hu J and Wang
J: EMP-1 promotes tumorigenesis of NSCLC through PI3K/AKT pathway.
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 32:834–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang HT, Liu ZH, Wang XQ and Wu M: Effect
of EMP-1 gene on human esophageal cancer cell line. Ai Zheng.
21:229–232. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee HS, Sherley JL, Chen JJ, Chiu CC,
Chiou LL, Liang JD, Yang PC, Huang GT and Sheu JC: EMP-1 is a
junctional protein in a liver stem cell line and in the liver.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:996–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kasher R, Bajayo A, Gabet Y, Nevo N,
Fridkin M, Katchalski-Katzir E, Kohen F and Bab I: Restrain of bone
growth by estrogen-mimetic peptide-1 (EMP-1): a micro-computed
tomographic study. Peptides. 30:1181–1186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bozec A, Peyrade F and Milano G: Molecular
targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 13:389–402. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suzuki K, Nakamura K, Kato K, Hamada H and
Tsukamoto T: Exploration of target molecules for prostate cancer
gene therapy. Prostate. 67:1163–1173. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Ehrmann J,
Fridman E, Skarda J and Kolar Z: Novel immunohistochemical markers
for the differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast
carcinomas. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub.
151:59–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Muller PY, Janovjak H, Miserez AR and
Dobbie Z: Processing of gene expression data generated by
quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques. 32:1372–1379.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ranganathan V and De PK: Western blot of
proteins from Coomassie-stained poly-acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem.
234:102–104. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rasola A and Geuna M: A flow cytometry
assay simultaneously detects independent apoptotic parameters.
Cytometry. 45:151–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kramer N, Walzl A, Unger C, Rosner M,
Krupitza G, Hengstschläger M and Dolznig H: In vitro cell migration
and invasion assays. Mutat Res. 752:10–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Richards RJ: Responsibility for
statistical analyses. Endocr Pract. 9:3292003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taylor V, Welcher AA, Program AE and Suter
U: Epithelial membrane protein-1, peripheral myelin protein 22, and
lens membrane protein 20 define a novel gene family. J Biol Chem.
270:28824–28833. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lobsiger CS, Magyar JP, Taylor V, Wulf P,
Welcher AA, Program AE and Suter U: Identification and
characterization of a cDNA and the structural gene encoding the
mouse epithelial membrane protein-1. Genomics. 36:379–387. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wulf P and Suter U: Embryonic expression
of epithelial membrane protein 1 in early neurons. Brain Res Dev
Brain Res. 116:169–180. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zoidl G, Blass-Kampmann S, D’Urso D,
Schmalenbach C and Müller HW: Retroviral-mediated gene transfer of
the peripheral myelin protein PMP22 in Schwann cells: modulation of
cell growth. EMBO J. 14:1122–1128. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jetten AM and Suter U: The peripheral
myelin protein 22 and epithelial membrane protein family. Prog
Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 64:97–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu XM, Li CW, Li YY, Liu J, Lin ZB, Li TY,
Zhao L, Pan XL, Shi L and Wang de Y: Down-regulation of EMP1 is
associated with epithelial hyperplasia and metaplasia in nasal
polyps. Histopathology. 63:686–695. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gnirke AU and Weidle UH: Investigation of
prevalence and regulation of expression of progression associated
protein (PAP). Anticancer Res. 18:4363–4369. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Cao W, Xu Q and Chen WT: The
expression of EMP1 is downregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma
and possibly associated with tumour metastasis. J Clin Pathol.
64:25–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang HT, Kong JP, Ding F, Wang XQ, Wang
MR, Liu LX, Wu M and Liu ZH: Analysis of gene expression profile
induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA Microarray.
World J Gastroenterol. 9:392–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Isobe T, Hashimoto K, Kizaki J, Miyagi M,
Aoyagi K, Koufuji K and Shirouzu K: Characteristics and prognosis
of gastric cancer in young patients. Oncol Rep. 30:43–49.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee HS, Lee HK, Kim HS, Yang HK and Kim
WH: Tumour suppressor gene expression correlates with gastric
cancer prognosis. J Pathol. 200:39–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y and Mou L: A risk score system to
preoperatively predict TNM stages in gastric cancer. Am J Clin
Oncol. 34:130–134. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiexian J, Xiaoqin X, Lili D, Baoguo T,
Ting S, Xianwen Z and Cunzhi H: Clinical assessment and prognostic
evaluation of tumor markers in patients with gastric cancer. Int J
Biol Markers. 28:192–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sen S, Kawahara B and Chaudhuri G:
Mitochondrial-associated nitric oxide synthase activity inhibits
cytochrome c oxidase: implications for breast Cancer. Free Radic
Biol Med. 57:210–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang JM, Wang HC, Wang HX, Ruan LH, Zhang
YM, Li JT, Tian S and Zhang YC: Oxidative stress and activities of
caspase-8, -9, and -3 are involved in cryopreservation-induced
apoptosis in granulosa cells. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
166:52–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson CR and Jarvis WD: Caspase-9
regulation: an update. Apoptosis. 9:423–427. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fearnhead HO, Rodriguez J, Govek EE, Guo
W, Kobayashi R, Hannon G and Lazebnik YA: Oncogene-dependent
apoptosis is mediated by caspase-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:13664–13669. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie LX, Zhai TT, Yang LP, Yang E, Zhang
XH, Chen JY and Zhang H: Lymphangiogenesis and prognostic
significance of vascular endothelial growth factor C in
gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol.
94:39–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Meng X, Zeng H, Guan Y, Zhang Q,
Guo S, Liu X and Guo Q: Serum vascular endothelial growth factor-C
levels: a possible diagnostic marker for lymph node metastasis in
patients with primary non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett.
6:545–549. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|