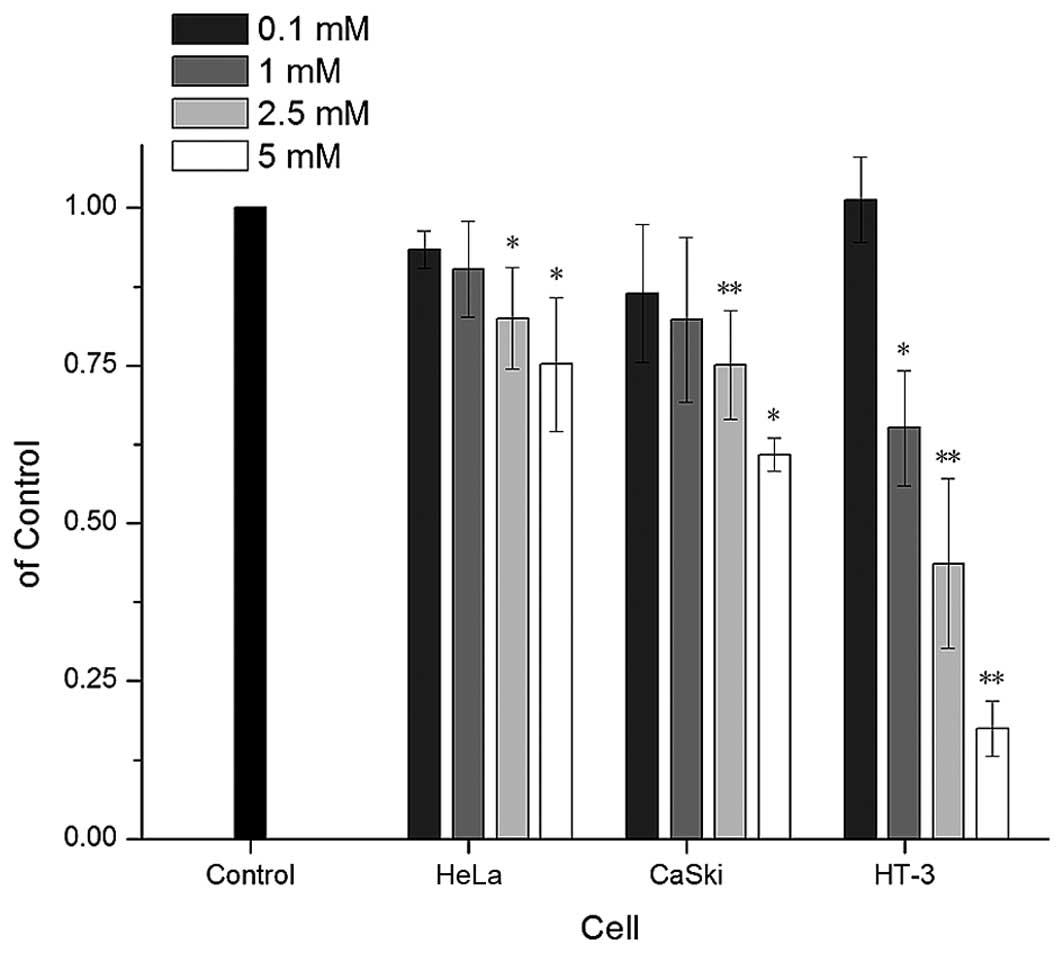
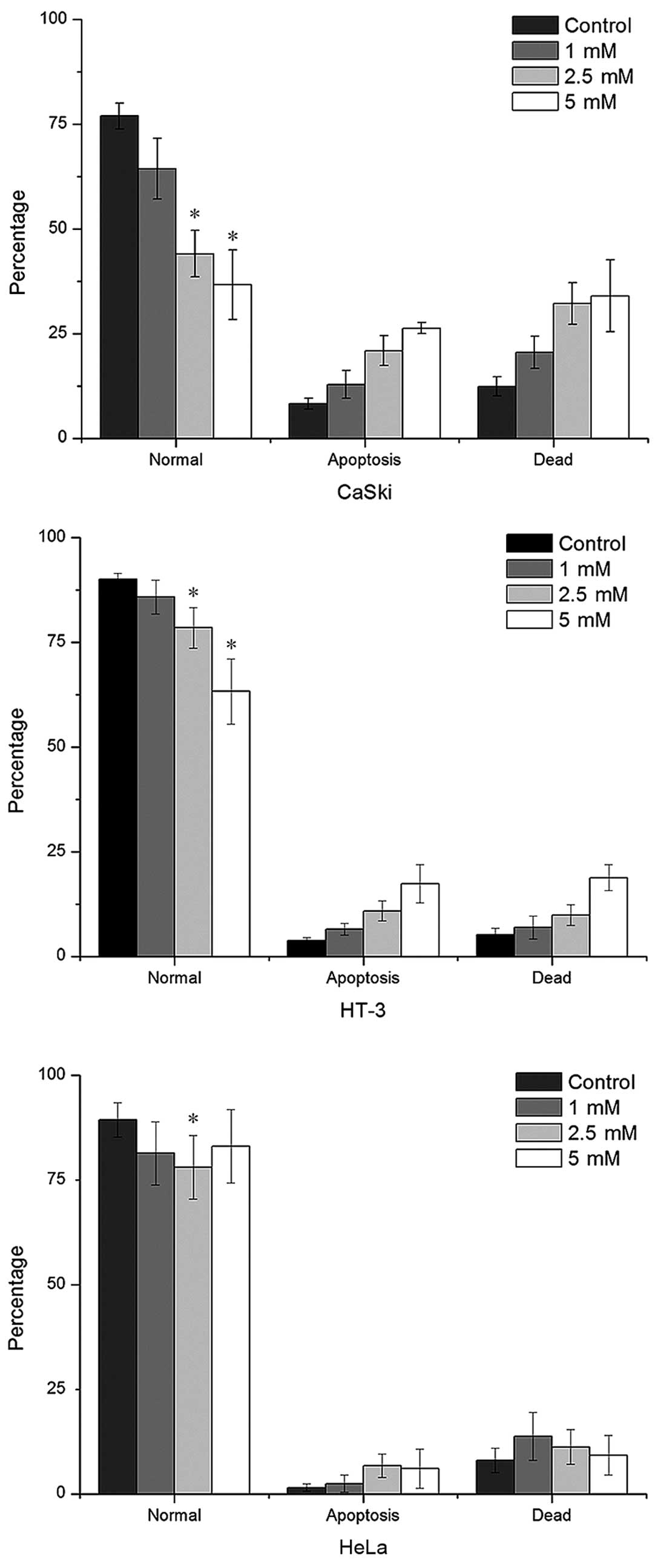
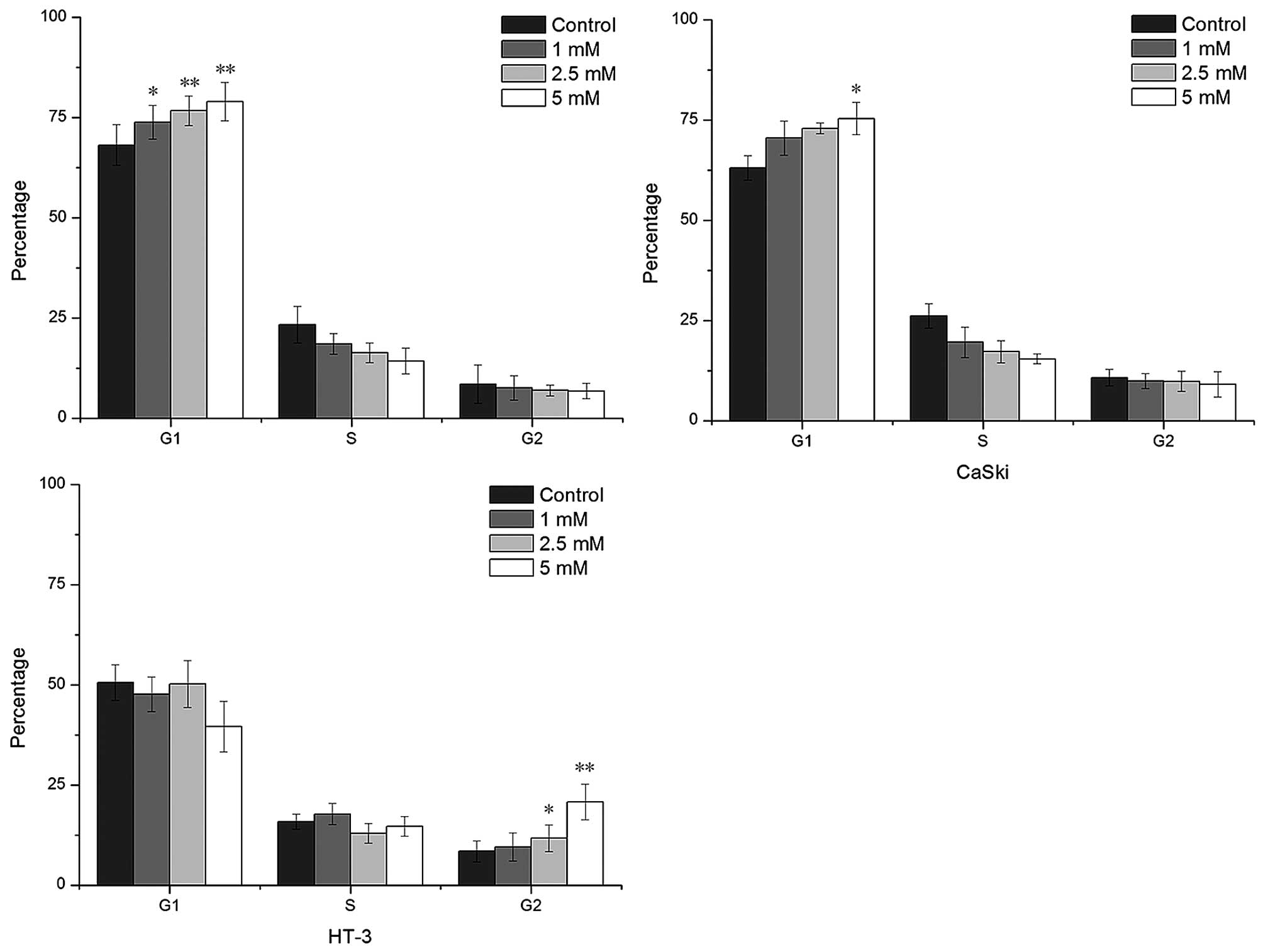
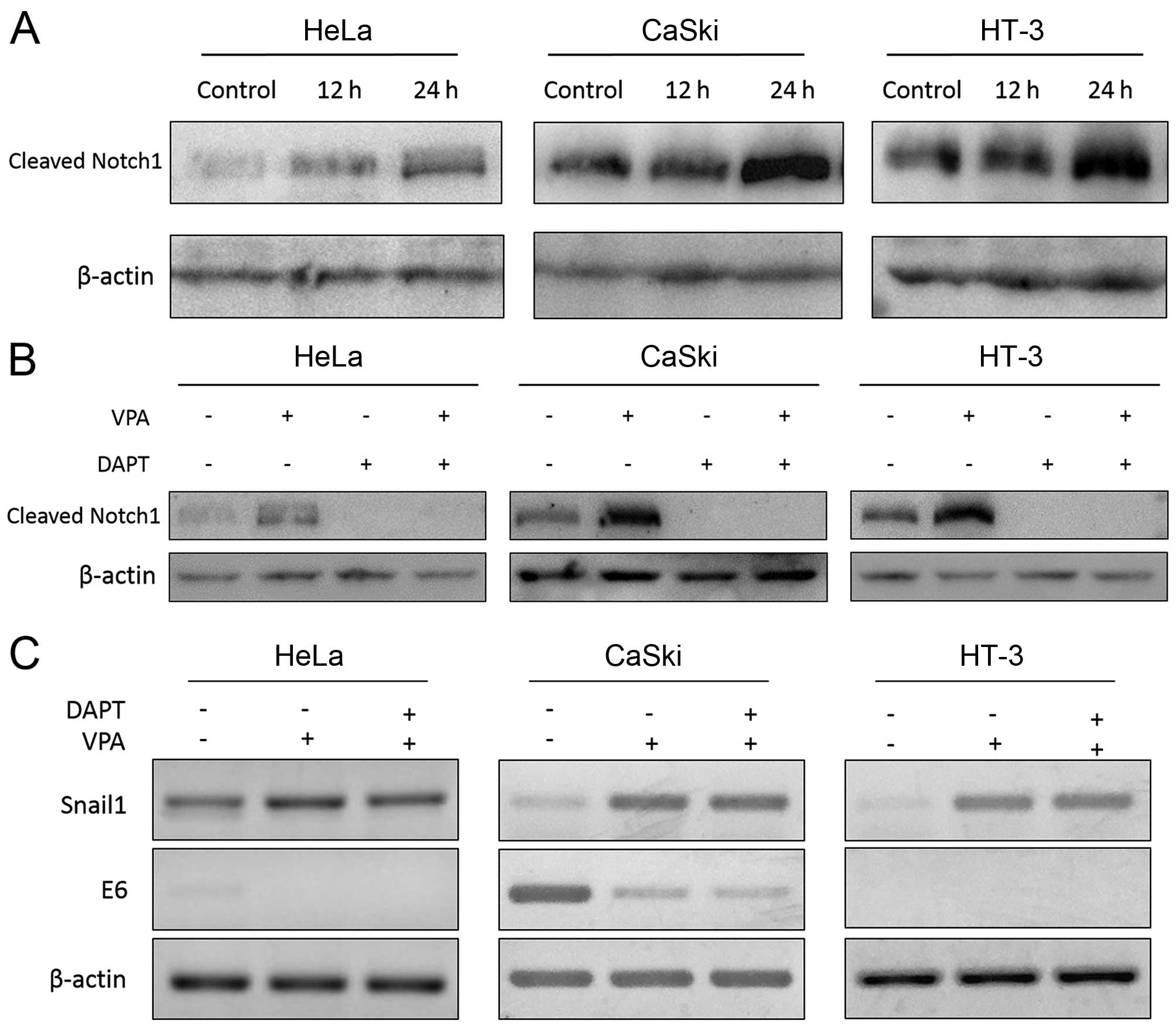
|
1
|
Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch
FX, Kummer JA, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Peto J, Meijer CJ and Muñoz N:
Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical
cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 189:12–19. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu L and Griffin JD: Modulation of Notch
signaling by mastermind-like (MAML) transcriptional co-activators
and their involvement in tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:348–356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weijzen S, Zlobin A, Braid M, Miele L and
Kast WM: HPV16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins regulate Notch-1 expression
and cooperate to induce transformation. J Cell Physiol.
194:356–362. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwarz JK, Payton JE, Rashmi R, Xiang T,
Jia Y, Huettner P, Rogers BE, Yang Q, Watson M, Rader JS, et al:
Pathway-specific analysis of gene expression data identifies the
PI3K/Akt pathway as a novel therapeutic target in cervical cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:1464–1471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perez-Plasencia C, Duenas-Gonzalez A and
Alatorre-Tavera B: Second hit in cervical carcinogenesis process:
Involvement of wnt/beta catenin pathway. Int Arch Med. 1:102008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yousif NG, Sadiq AM, Yousif MG,
Al-Mudhafar RH, Al-Baghdadi JJ and Hadi N: Notch1 ligand signaling
pathway activated in cervical cancer: Poor prognosis with
high-level JAG1/Notch1. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 292:899–904. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maliekal TT, Bajaj J, Giri V, Subramanyam
D and Krishna S: The role of Notch signaling in human cervical
cancer: Implications for solid tumors. Oncogene. 27:5110–5114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu L, Aster JC, Blacklow SC, Lake R,
Artavanis-Tsakonas S and Griffin JD: MAML1, a human homologue of
Drosophila mastermind, is a transcriptional co-activator for NOTCH
receptors. Nat Genet. 26:484–489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wael H, Yoshida R, Kudoh S, Hasegawa K,
Niimori-Kita K and Ito T: Notch1 signaling controls cell
proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in lung carcinoma.
Lung Cancer. 85:131–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brakenhoff RH: Cancer. Another NOTCH for
cancer. Science. 333:1102–1103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
del Campo JM, Prat A, Gil-Moreno A, Pérez
J and Parera M: Update on novel therapeutic agents for cervical
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110(Suppl 2): S72–S76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pant S, Jones SF, Kurkjian CD, Infante JR,
Moore KN, Burris HA, McMeekin DS, Benhadji KA, Patel BK, Frenzel
MJ, et al: A first-in-human phase I study of the oral Notch
inhibitor, LY900009, in patients with advanced cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 56:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kong R, Feng J, Ma Y, Zhou B, Li S, Zhang
W, Jiang J, Zhang J, Qiao Z, Zhang T, et al: Silencing NACK by
siRNA inhibits tumorigenesis in non-small cell lung cancer via
targeting Notch1 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:2306–2314.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M,
Perez-Plascencia C, Perez-Cardenas E, de la Cruz-Hernandez E and
Herrera LA: Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical,
clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat
Rev. 34:206–222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zagouras P, Stifani S, Blaumueller CM,
Carcangiu ML and Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Alterations in Notch
signaling in neoplastic lesions of the human cervix. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 92:6414–6418. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tewari KS, Taylor JA, Liao SY, DiSaia PJ,
Burger RA, Monk BJ, Hughes CC and Villarreal LP: Development and
assessment of a general theory of cervical carcinogenesis utilizing
a severe combined immunodeficiency murine-human xenograft model.
Gynecol Oncol. 77:137–148. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Talora C, Sgroi DC, Crum CP and Dotto GP:
Specific down-modulation of Notch1 signaling in cervical cancer
cells is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression and late steps
of malignant transformation. Genes Dev. 16:2252–2263. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Talora C, Cialfi S, Segatto O, Morrone S,
Kim Choi J, Frati L, Paolo Dotto G, Gulino A and Screpanti I:
Constitutively active Notch1 induces growth arrest of HPV-positive
cervical cancer cells via separate signaling pathways. Exp Cell
Res. 305:343–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu H, Zhao X, Huang S, Jian L, Qian G and
Ge S: Blocking Notch1 signaling by RNA interference can induce
growth inhibition in HeLa cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:511–516.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khan O and La Thangue NB: HDAC inhibitors
in cancer biology: Emerging mechanisms and clinical applications.
Immunol Cell Biol. 90:85–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang BH, Laban M, Leung CH, Lee L, Lee
CK, Salto-Tellez M, Raju GC and Hooi SC: Inhibition of histone
deacetylase 2 increases apoptosis and p21Cip1/WAF1 expression,
independent of histone deacetylase 1. Cell Death Differ.
12:395–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Teng HF, Li PN, Hou DR, Liu SW, Lin CT,
Loo MR, Kao CH, Lin KH and Chen SL: Valproic acid enhances Oct4
promoter activity through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway activated nuclear
receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 383:147–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shan Z, Feng-Nian R, Jie G and Ting Z:
Effects of valproic acid on proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis
and metastasis of ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 13:3977–3982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dotto GP: Notch tumor suppressor function.
Oncogene. 27:5115–5123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Franko-Tobin LG, Mackey LV, Huang W, Song
X, Jin B, Luo J, Morris LM, Liu M, Fuselier JA, Coy DH, et al:
Notch1-mediated tumor suppression in cervical cancer with the
involvement of SST signaling and its application in enhanced
SSTR-targeted therapeutics. Oncologist. 17:220–232. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsai C, Leslie JS, Franko-Tobin LG,
Prasnal MC, Yang T, Vienna Mackey L, Fuselier JA, Coy DH, Liu M, Yu
C, et al: Valproic acid suppresses cervical cancer tumor
progression possibly via activating Notch1 signaling and enhances
receptor-targeted cancer chemotherapeutic via activating
somatostatin receptor type II. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 288:393–400.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Greenblatt DY, Cayo MA, Adler JT, Ning L,
Haymart MR, Kunnimalaiyaan M and Chen H: Valproic acid activates
Notch1 signaling and induces apoptosis in medullary thyroid cancer
cells. Ann Surg. 247:1036–1040. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Greenblatt DY, Vaccaro AM, Jaskula-Sztul
R, Ning L, Haymart M, Kunnimalaiyaan M and Chen H: Valproic acid
activates notch-1 signaling and regulates the neuroendocrine
phenotype in carcinoid cancer cells. Oncologist. 12:942–951. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Platta CS, Greenblatt DY, Kunnimalaiyaan M
and Chen H: Valproic acid induces Notch1 signaling in small cell
lung cancer cells. J Surg Res. 148:31–37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuncharin Y, Sangphech N, Kueanjinda P,
Bhattarakosol P and Palaga T: MAML1 regulates cell viability via
the NF-κB pathway in cervical cancer cell lines. Exp Cell Res.
317:1830–1840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng J, Cen J, Li J, Zhao R, Zhu C, Wang
Z, Xie J and Tang W: Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid
(VPA) promotes the epithelial mesenchymal transition of colorectal
cancer cells via up regulation of Snail. Cell Adhes Migr.
9:495–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mawatari T, Ninomiya I, Inokuchi M, Harada
S, Hayashi H, Oyama K, Makino I, Nakagawara H, Miyashita T, Tajima
H, et al: Valproic acid inhibits proliferation of HER2-expressing
breast cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through Hsp70 acetylation. Int J Oncol. 47:2073–2081.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kostrouchová M, Kostrouch Z and
Kostrouchová M: Valproic acid, a molecular lead to multiple
regulatory pathways. Folia Biol (Praha). 53:37–49. 2007.
|
|
37
|
Qing H, He G, Ly PT, Fox CJ, Staufenbiel
M, Cai F, Zhang Z, Wei S, Sun X, Chen CH, et al: Valproic acid
inhibits Abeta production, neuritic plaque formation, and
behavioral deficits in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. J Exp Med.
205:2781–2789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dueñas-González A, Lizano M, Candelaria M,
Cetina L, Arce C and Cervera E: Epigenetics of cervical cancer. An
overview and therapeutic perspectives. Mol Cancer. 4:382005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang L, Qin H, Chen B, Xin X, Li J and Han
H: Overexpressed active Notch1 induces cell growth arrest of HeLa
cervical carcinoma cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:1283–1292. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yuan CH, Filippova M, Krstenansky JL and
Duerksen-Hughes PJ: Flavonol and imidazole derivatives block HPV16
E6 activities and reactivate apoptotic pathways in HPV(+) cells.
Cell Death Dis. 7:20602016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cai Q, Lv L, Shao Q, Li X and Dian A:
Human papillomavirus early proteins and apoptosis. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 287:541–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|