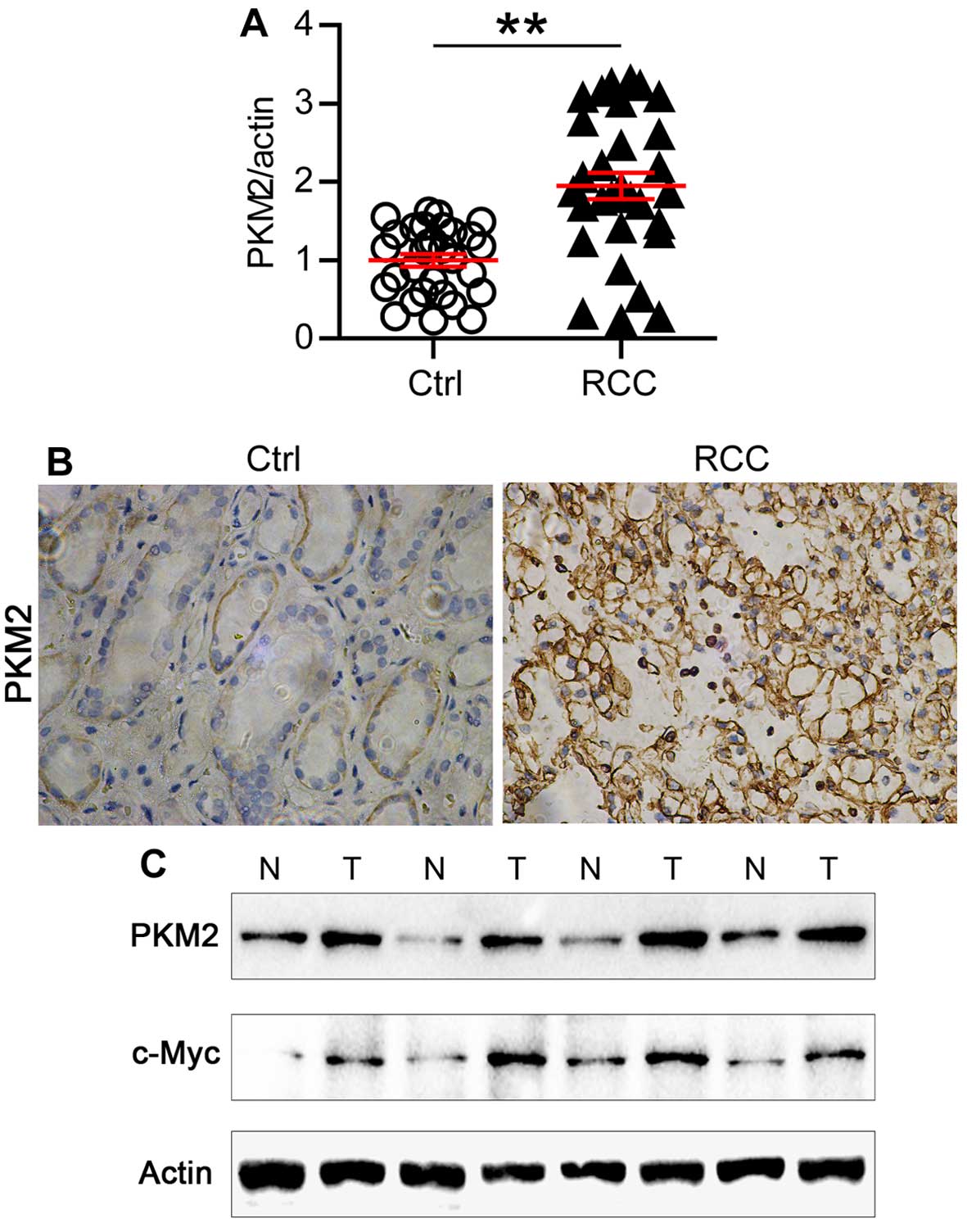
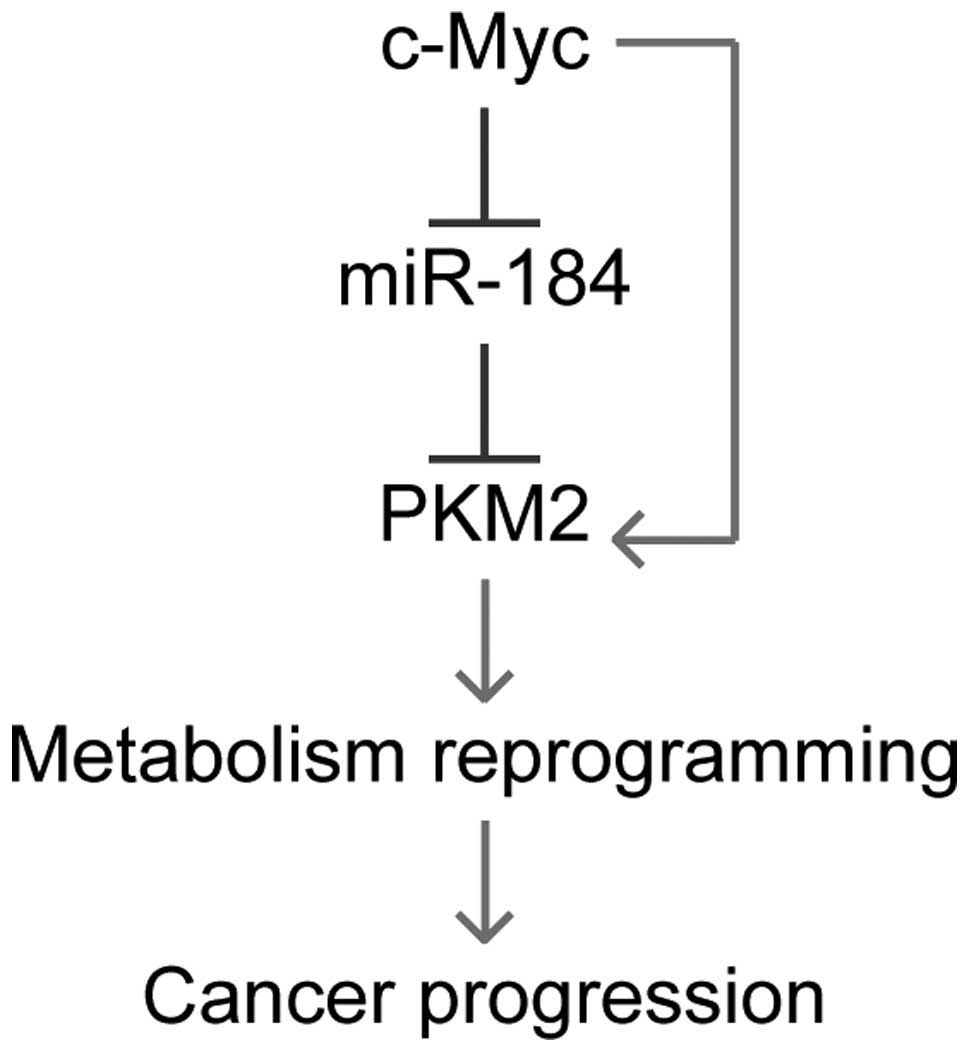
|
1
|
Chow WH, Dong LM and Devesa SS:
Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
7:245–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Majer W, Kluzek K, Bluyssen H and Wesoły
J: Potential approaches and recent advances in biomarker discovery
in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 6:1105–1113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohen HT and McGovern FJ: Renal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 353:2477–2490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amato RJ: Chemotherapy for renal cell
carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 27:177–186. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beck SD, Patel MI, Snyder ME, Kattan MW,
Motzer RJ, Reuter VE and Russo P: Effect of papillary and
chromophobe cell type on disease-free survival after nephrectomy
for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 11:71–77. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Massari F, Ciccarese C, Santoni M,
Brunelli M, Piva F, Modena A, Bimbatti D, Fantinel E, Santini D,
Cheng L, et al: Metabolic alterations in renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Treat Rev. 41:767–776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Linehan WM, Srinivasan R and Schmidt LS:
The genetic basis of kidney cancer: A metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Urol. 7:277–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gossage L, Eisen T and Maher ER: VHL, the
story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:55–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network.
Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Nature. 499:43–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang SW, Chang WH, Su YC, Chen YC, Lai YH,
Wu PT, Hsu CI, Lin WC, Lai MK and Lin JY: MYC pathway is activated
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and essential for proliferation
of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 273:35–43.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ma L and Qu L: The function of microRNAs
in renal development and pathophysiology. J Genet Genomics.
40:143–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP
and Wei WI: Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of
squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2588–2592.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Foley NH, Bray IM, Tivnan A, Bryan K,
Murphy DM, Buckley PG, Ryan J, O’Meara A, O’Sullivan M and
Stallings RL: MicroRNA-184 inhibits neuroblastoma cell survival
through targeting the serine/threonine kinase AKT2. Mol Cancer.
9:832010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhen Y, Liu Z, Yang H, Yu X, Wu Q, Hua S,
Long X, Jiang Q, Song Y, Cheng C, et al: Tumor suppressor PDCD4
modulates miR-184-mediated direct suppression of C-MYC and BCL2
blocking cell growth and survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e8722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu GG, Li WH, He WG, Jiang N, Zhang GX,
Chen W, Yang HF, Liu QL, Huang YN, Zhang L, et al: Mir-184
post-transcriptionally regulates SOX7 expression and promotes cell
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e887962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leng HM, Qian WP, Zhou L, Zhai QN, Li XX,
Guan ZC, Gui YT and Cai ZM: Abnormal expression and significance of
MIR-184 in human renal carcinoma. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.
43:509–513. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su Z, Chen D, Li Y, Zhang E, Yu Z, Chen T,
Jiang Z, Ni L, Yang S, Gui Y, et al: microRNA-184 functions as
tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 9:961–966.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lebofsky R and Walter JC: New Myc-anisms
for DNA replication and tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell. 12:102–103.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin TC, Lin PL, Cheng YW, Wu TC, Chou MC,
Chen CY and Lee H: MicroRNA-184 deregulated by the microRNA-21
promotes tumor malignancy and poor outcomes in non-small cell lung
cancer via targeting CDC25A and c-Myc. Ann Surg Oncol. 22(Suppl 3):
1532–1539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu Z, Mai C, Yang H, Zhen Y, Yu X, Hua S,
Wu Q, Jiang Q, Zhang Y, Song X, et al: Candidate tumour suppressor
CCDC19 regulates miR-184 direct targeting of C-Myc thereby
suppressing cell growth in non-small cell lung cancers. J Cell Mol
Med. 18:1667–1679. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shroff EH, Eberlin LS, Dang VM, Gouw AM,
Gabay M, Adam SJ, Bellovin DI, Tran PT, Philbrick WM, Garcia-Ocana
A, et al: MYC oncogene overexpression drives renal cell carcinoma
in a mouse model through glutamine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:6539–6544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu W, Cao H, Ye C, Chang C, Lu M, Jing Y,
Zhang D, Yao X, Duan Z, Xia H, et al: Hepatic miR-378 targets p110α
and controls glucose and lipid homeostasis by modulating hepatic
insulin signalling. Nat Commun. 5:56842014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jo HS, Kang KH, Joe CO and Kim JW: Pten
coordinates retinal neurogenesis by regulating Notch signalling.
EMBO J. 31:817–828. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jia LF, Wei SB, Gong K, Gan YH and Yu GY:
Prognostic implications of micoRNA miR-195 expression in human
tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e566342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Y and Stallings RL: Differential
patterns of microRNA expression in neuroblastoma are correlated
with prognosis, differentiation, and apoptosis. Cancer Res.
67:976–983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iqbal MA, Gupta V, Gopinath P, Mazurek S
and Bamezai RN: Pyruvate kinase M2 and cancer: An updated
assessment. FEBS Lett. 588:2685–2692. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta V and Bamezai RN: Human pyruvate
kinase M2: a multi-functional protein. Protein Sci. 19:2031–2044.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong N, Ojo D, Yan J and Tang D: PKM2
contributes to cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett. 356:184–191. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lane BR, Rini BI, Novick AC and Campbell
SC: Targeted molecular therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Urology.
69:3–10. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Redova M, Svoboda M and Slaby O: MicroRNAs
and their target gene networks in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 405:153–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|