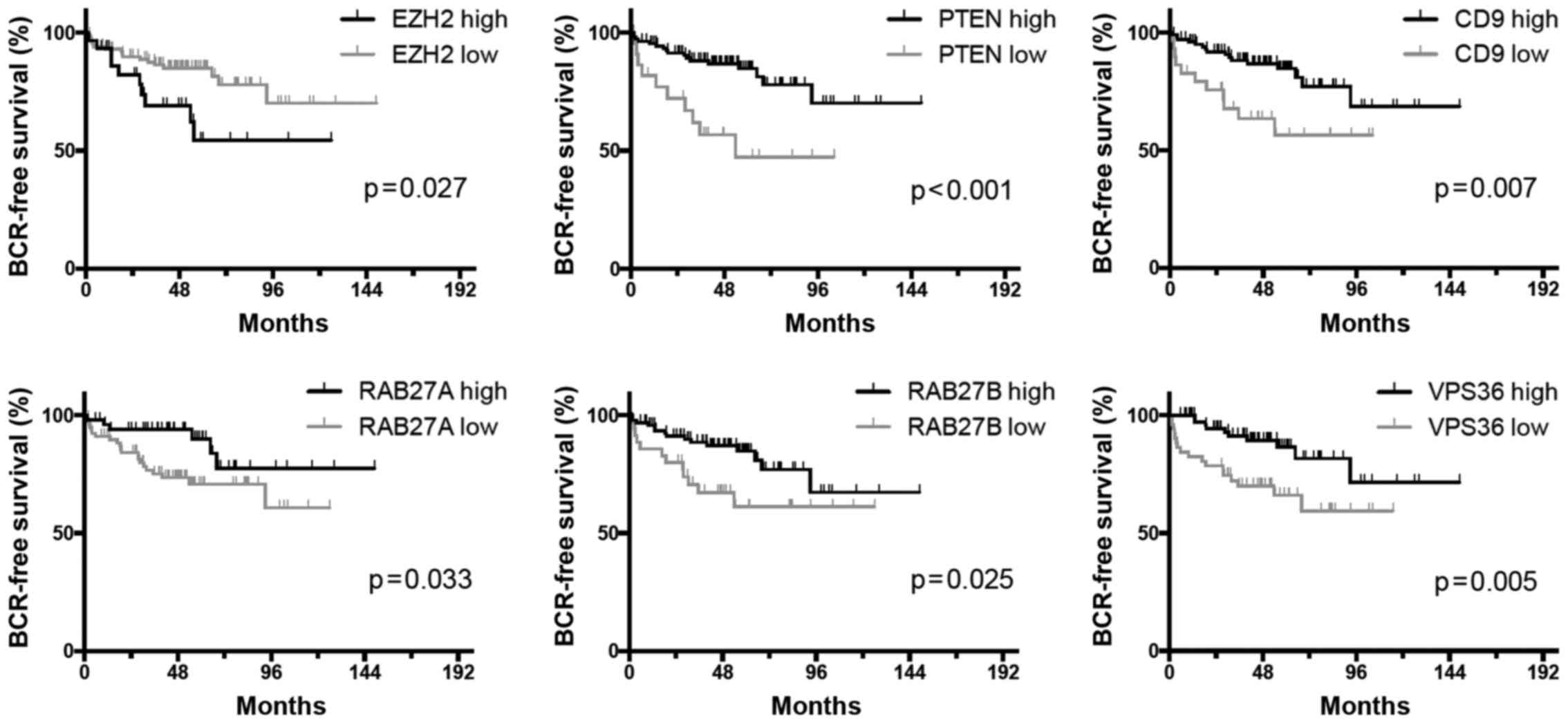
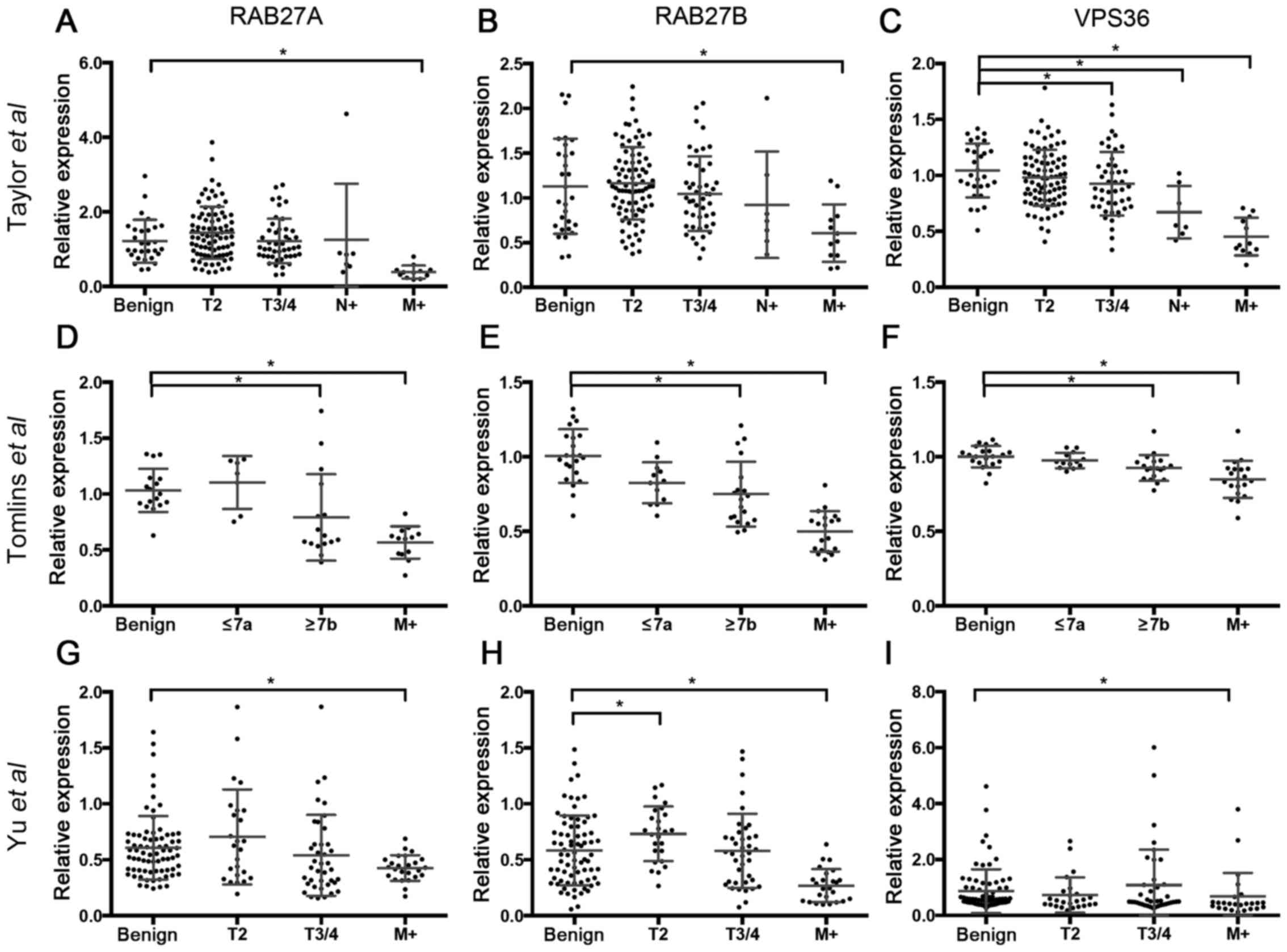
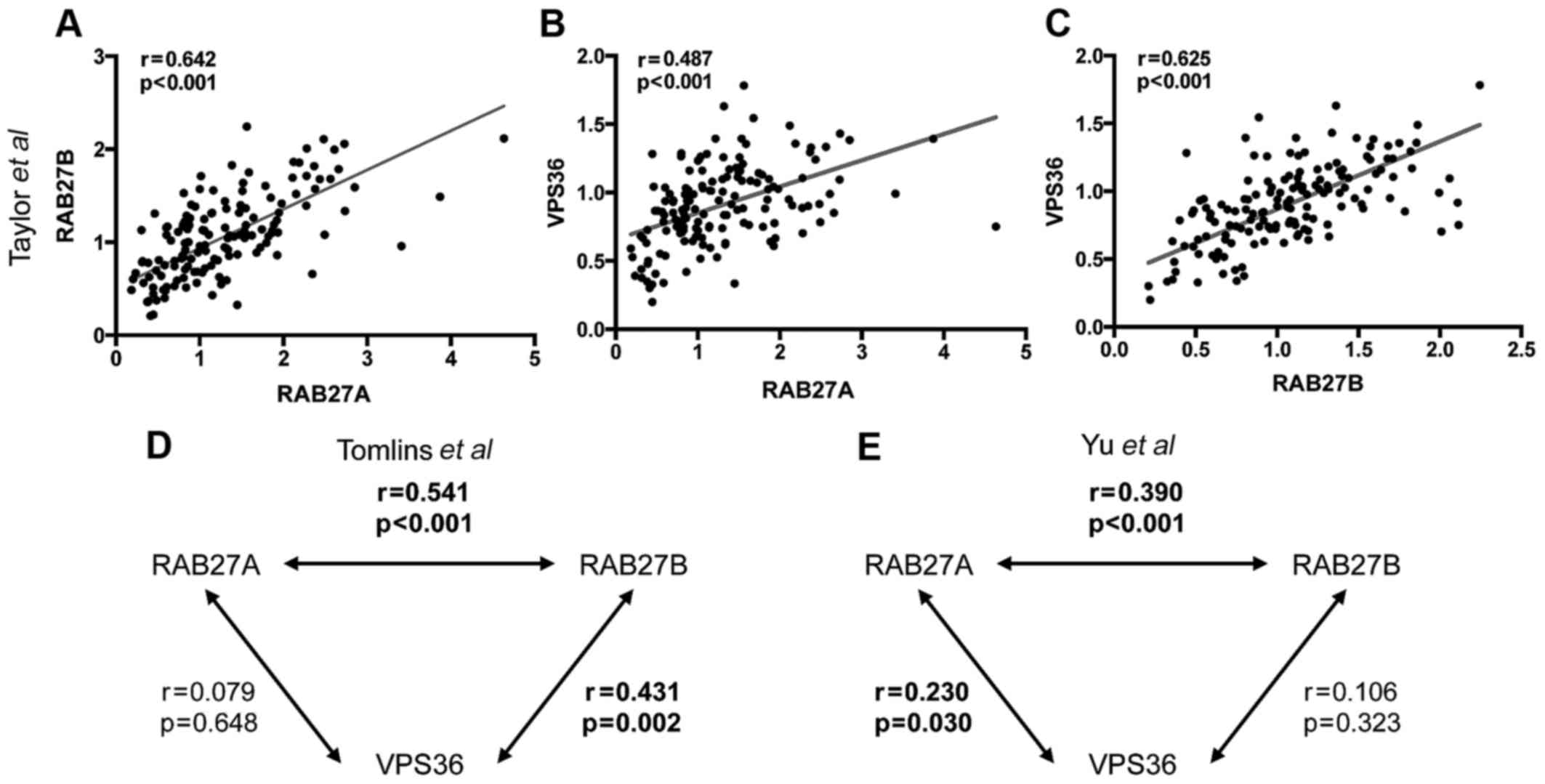
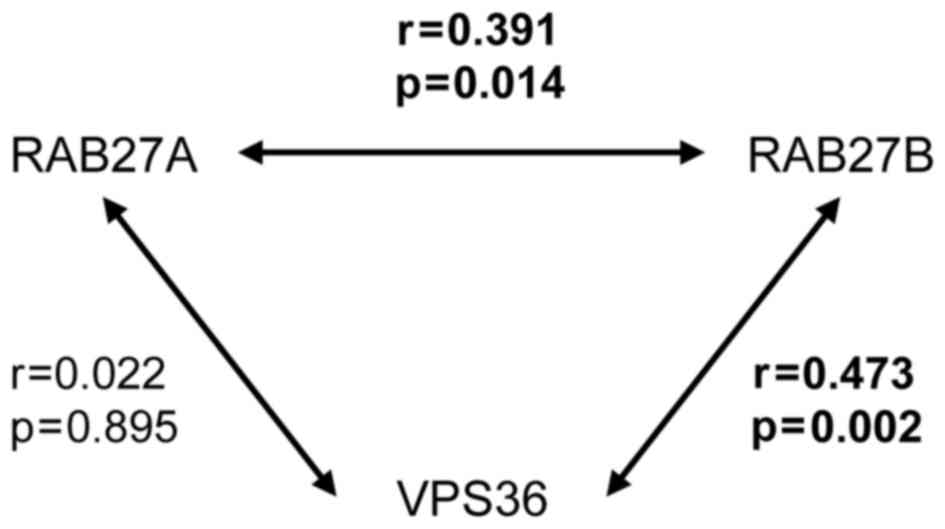
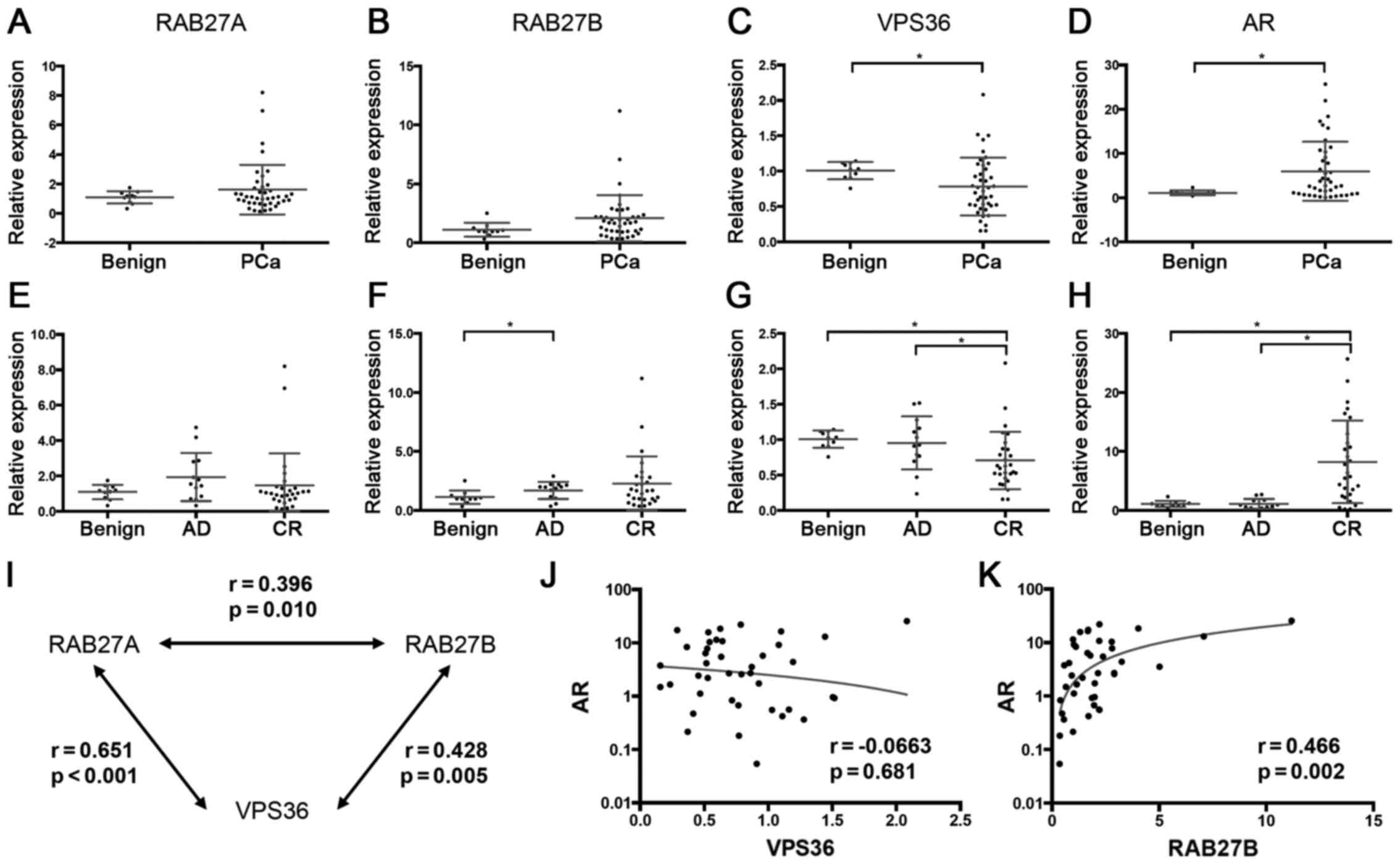
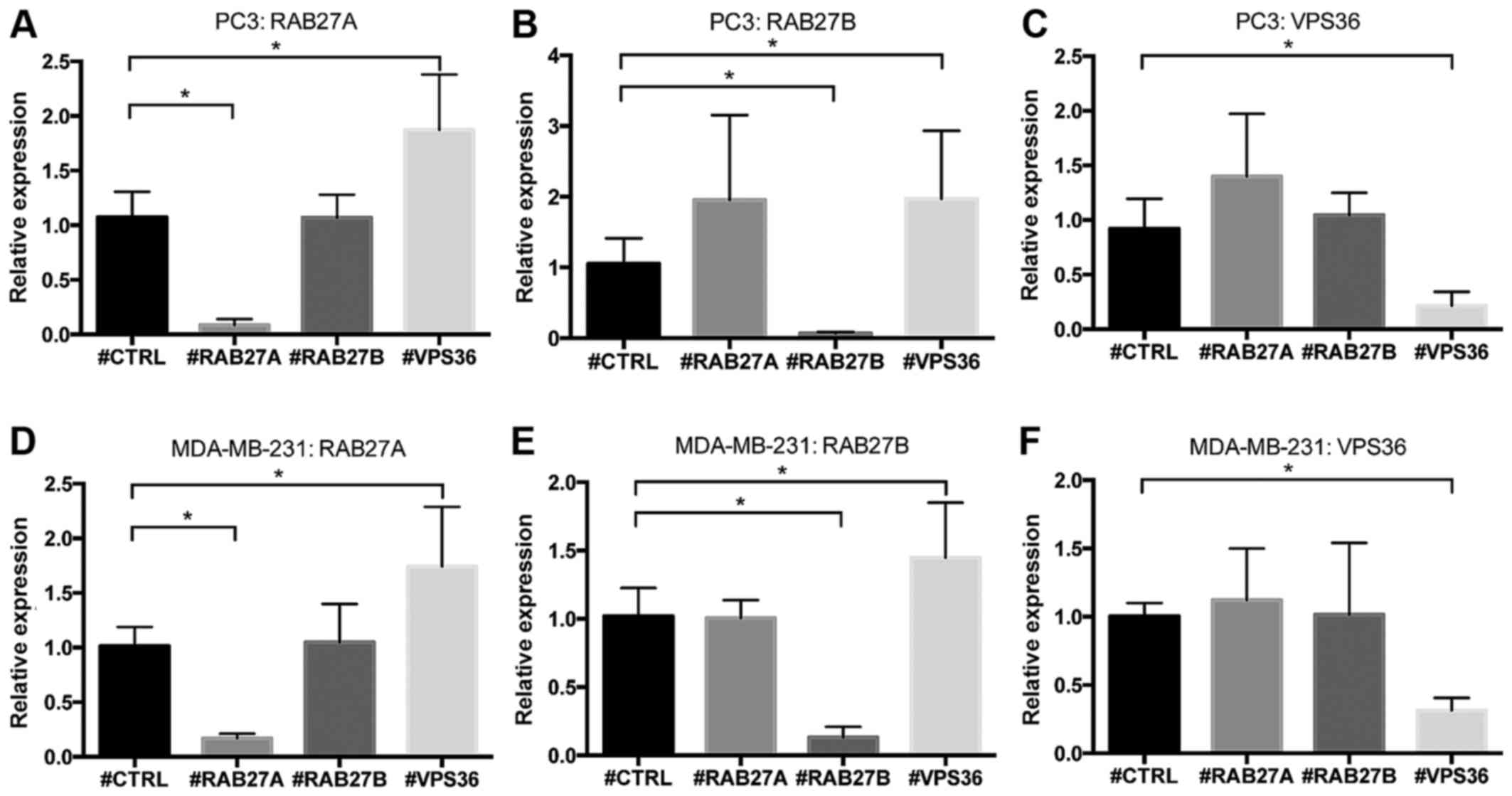
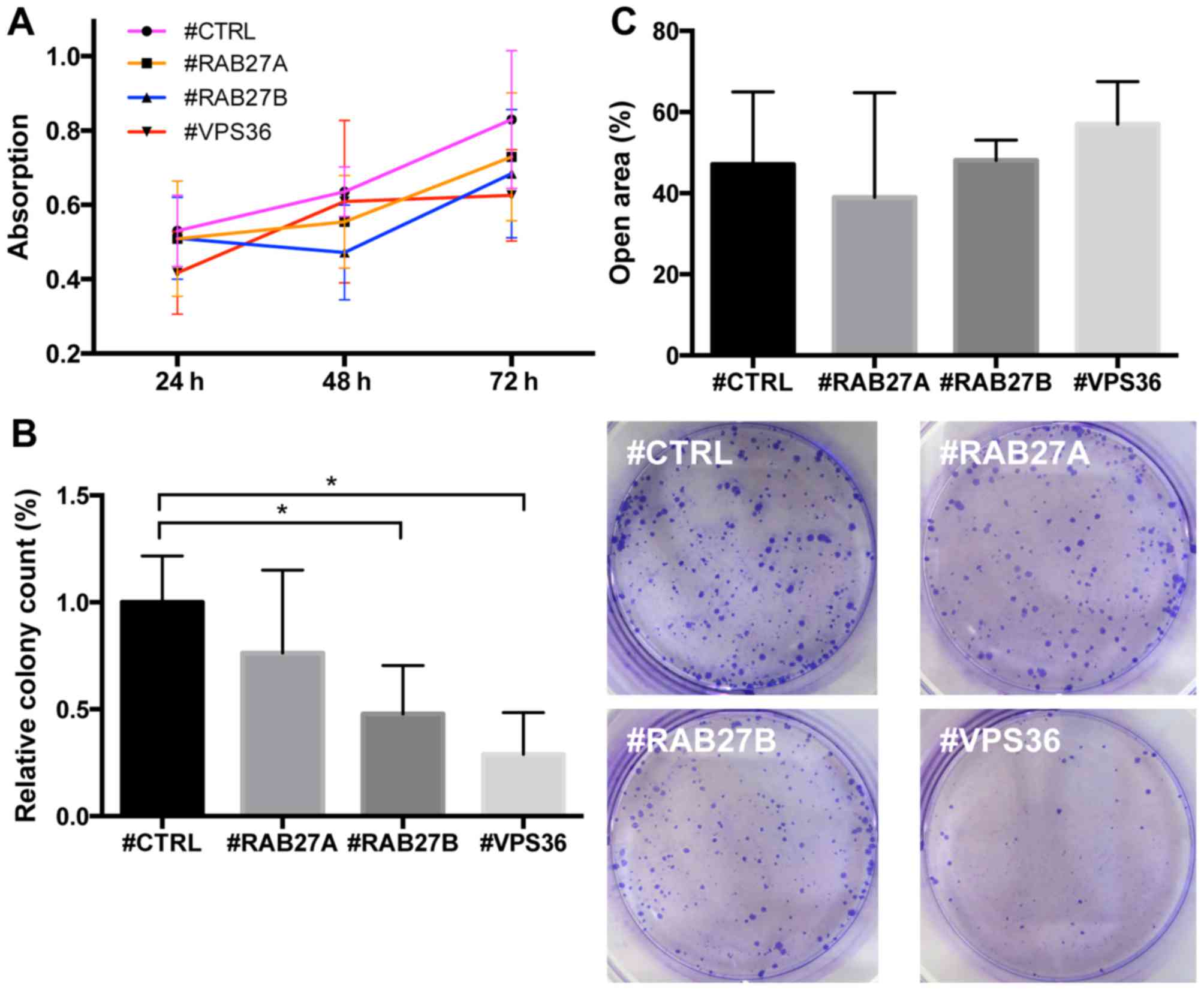
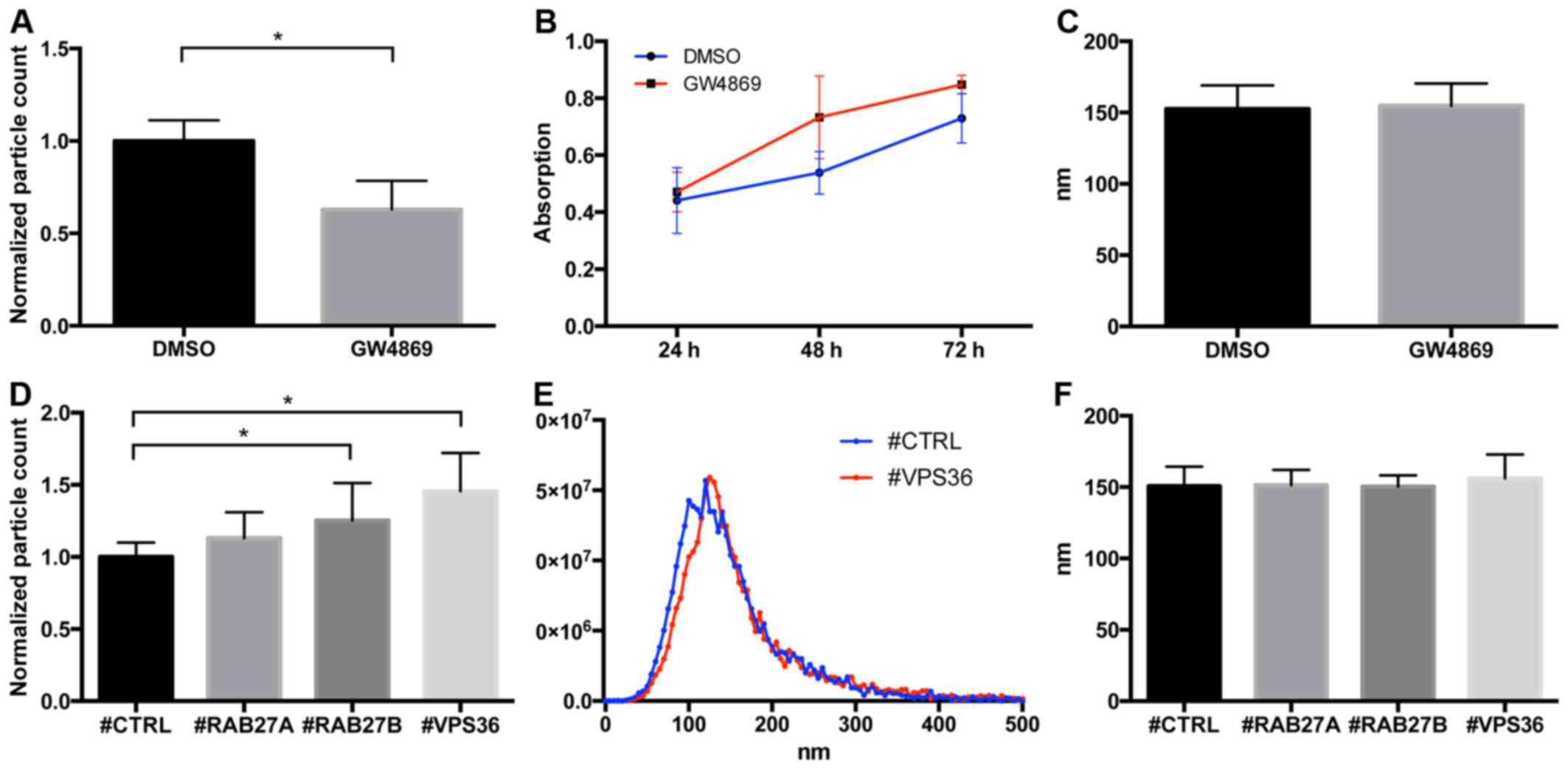
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and
Conrad R: Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition,
biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:940–948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Junker K, Heinzelmann J, Beckham C, Ochiya
T and Jenster G: Extracellular vesicles and their role in urologic
malignancies. Eur Urol. 70:323–331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bobrie A, Krumeich S, Reyal F, Recchi C,
Moita LF, Seabra MC, Ostrowski M and Théry C: Rab27a supports
exosome-dependent and -independent mechanisms that modify the tumor
microenvironment and can promote tumor progression. Cancer Res.
72:4920–4930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beckham CJ, Olsen J, Yin P-N, Wu CH, Ting
HJ, Hagen FK, Scosyrev E, Messing EM and Lee YF: Bladder cancer
exosomes contain EDIL-3/Del1 and facilitate cancer progression. J
Urol. 192:583–592. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alderton GK: Metastasis. Exosomes drive
premetastatic niche formation. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:4472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peinado H, Alečković M, Lavotshkin S,
Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, Hergueta-Redondo M,
Williams C, García-Santos G, Ghajar C, et al: Melanoma exosomes
educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic
phenotype through MET. Nat Med. 18:883–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Webber MM, Trakul N, Thraves PS,
Bello-DeOcampo D, Chu WW, Storto PD, Huard TK, Rhim JS and Williams
DE: A human prostatic stromal myofibroblast cell line WPMY-1: A
model for stromal-epithelial interactions in prostatic neoplasia.
Carcinogenesis. 20:1185–1192. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z and
Clayton A: Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast
differentiation. Cancer Res. 70:9621–9630. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G, Kowal J,
Vigneron J, Benaroch P, Manel N, Moita LF, Théry C and Raposo G:
Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and
secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J
Cell Sci. 126:5553–5565. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adell MA and Teis D: Assembly and
disassembly of the ESCRT-III membrane scission complex. FEBS Lett.
585:3191–3196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brinton LT, Sloane HS, Kester M and Kelly
KA: Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:659–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget
I, Raposo G, Savina A, Moita CF, Schauer K, Hume AN, Freitas RP, et
al: Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome
secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 12:19–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G and Clayton
A: Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture
supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Chapter
3: Unit 3.22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Théry C, Zitvogel L and Amigorena S:
Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol.
2:569–579. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C,
Sánchez-Cabo F, Pérez-Hernández D, Vázquez J, Martin-Cofreces N,
Martinez-Herrera DJ, Pascual-Montano A, Mittelbrunn M and
Sánchez-Madrid F: Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of
miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat
Commun. 4:29802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koppers-Lalic D, Hackenberg M, Bijnsdorp
IV, van Eijndhoven MA, Sadek P, Sie D, Zini N, Middeldorp JM,
Ylstra B, de Menezes RX, et al: Nontemplated nucleotide additions
distinguish the small RNA composition in cells from exosomes. Cell
Rep. 8:1649–1658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van der Pol E, Böing AN, Harrison P, Sturk
A and Nieuwland R: Classification, functions, and clinical
relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 64:676–705.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H,
Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva
B, et al: Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer.
Cancer Cell. 18:11–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Rhodes DR, Cao X,
Wang L, Dhanasekaran SM, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Wei JT, Rubin MA,
Pienta KJ, et al: Integrative molecular concept modeling of
prostate cancer progression. Nat Genet. 39:41–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yu YP, Landsittel D, Jing L, Nelson J, Ren
B, Liu L, McDonald C, Thomas R, Dhir R, Finkelstein S, et al: Gene
expression alterations in prostate cancer predicting tumor
aggression and preceding development of malignancy. J Clin Oncol.
22:2790–2799. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Specht E, Kaemmerer D, Sänger J, Wirtz RM,
Schulz S and Lupp A: Comparison of immunoreactive score, HER2/neu
score and H score for the immunohistochemical evaluation of
somatostatin receptors in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine
neoplasms. Histopathology. 67:368–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaemmerer D, Reimann C, Specht E, Wirtz
RM, Sayeg M, Baum RP, Schulz S and Lupp A: Differential expression
and prognostic value of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in
bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Oncotarget. 6:3346–3358.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T,
Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M and Rozen SG: Primer3 - new capabilities
and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:e1152012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−∆∆C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ashby WJ and Zijlstra A: Established and
novel methods of interrogating two-dimensional cell migration.
Integr Biol. 4:1338–1350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li W, Hu Y, Jiang T, Han Y, Han G, Chen J
and Li X: Rab27A regulates exosome secretion from lung
adenocarcinoma cells A549: Involvement of EPI64. APMIS.
122:1080–1087. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng Y, Campbell EC, Lucocq J, Riches A
and Powis SJ: Monitoring the Rab27 associated exosome pathway using
nanoparticle tracking analysis. Exp Cell Res. 319:1706–1713. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Johnson JL, Ellis BA, Noack D, Seabra MC
and Catz SD: The Rab27a-binding protein, JFC1, regulates
androgen-dependent secretion of prostate-specific antigen and
prostatic-specific acid phosphatase. Biochem J. 391:699–710. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Catz SD: Characterization of Rab27a and
JFC1 as constituents of the secretory machinery of
prostate-specific antigen in prostate carcinoma cells. Methods
Enzymol. 438:25–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Webber JP, Spary LK, Sanders AJ, Chowdhury
R, Jiang WG, Steadman R, Wymant J, Jones AT, Kynaston H, Mason MD,
et al: Differentiation of tumour-promoting stromal myofibroblasts
by cancer exosomes. Oncogene. 34:290–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Catz SD: Regulation of vesicular
trafficking and leukocyte function by Rab27 GTPases and their
effectors. J Leukoc Biol. 94:613–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Singh RK, Mizuno K, Wasmeier C,
Wavre-Shapton ST, Recchi C, Catz SD, Futter C, Tolmachova T, Hume
AN and Seabra MC: Distinct and opposing roles for Rab27a/Mlph/MyoVa
and Rab27b/Munc13-4 in mast cell secretion. FEBS J. 280:892–903.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Elstak ED, Neeft M, Nehme NT, Voortman J,
Cheung M, Goodarzifard M, Gerritsen HC, van Bergen En Henegouwen
PM, Callebaut I, de Saint Basile G, et al: The munc13-4-rab27
complex is specifically required for tethering secretory lysosomes
at the plasma membrane. Blood. 118:1570–1578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hendrix A, Lambein K, Westbroek W, Seabra
MC, Cocquyt V, Pauwels P, Bracke M, Gespach C and De Wever O: An
immunohistochemical analysis of Rab27B distribution in fetal and
adult tissue. Int J Dev Biol. 56:363–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J-X, Huang X-X, Cai M-B, Tong ZT,
Chen JW, Qian D, Liao YJ, Deng HX, Liao DZ, Huang MY, et al:
Overexpression of the secretory small GTPase Rab27B in human breast
cancer correlates closely with lymph node metastasis and predicts
poor prognosis. J Transl Med. 10:2422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bao J, Ni Y, Qin H, Xu L, Ge Z, Zhan F,
Zhu H, Zhao J, Zhou X, Tang X, et al: Rab27b is a potential
predictor for metastasis and prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014:9131062014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dong W, Cui J, Yang J, Li W, Wang S, Wang
X, Li X, Lu Y and Xiao W: Decreased expression of Rab27A and Rab27B
correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Discov Med. 20:357–367. 2015.
|
|
40
|
Shaw GL, Whitaker H, Corcoran M, Dunning
MJ, Luxton H, Kay J, Massie CE, Miller JL, Lamb AD, Ross-Adams H,
et al: The early effects of rapid androgen deprivation on human
prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 70:214–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Schuh AL and Audhya A: The ESCRT
machinery: From the plasma membrane to endosomes and back again.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 49:242–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Woodfield SE, Graves HK, Hernandez JA and
Bergmann A: De-regulation of JNK and JAK/STAT signaling in ESCRT-II
mutant tissues cooperatively contributes to neoplastic
tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 8:e560212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Alam SL, Langelier C, Whitby FG, Koirala
S, Robinson H, Hill CP and Sundquist WI: Structural basis for
ubiquitin recognition by the human ESCRT-II EAP45 GLUE domain. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 13:1029–1030. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chairoungdua A, Smith DL, Pochard P, Hull
M and Caplan MJ: Exosome release of β-catenin: A novel mechanism
that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol. 190:1079–1091. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Gu Y and Cao X: The exosomes in
tumor immunity. OncoImmunology. 4:e10274722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lundholm M, Schröder M, Nagaeva O, Baranov
V, Widmark A, Mincheva-Nilsson L and Wikström P: Prostate
tumor-derived exosomes downregulate NKG2D expression on natural
killer cells and CD8+ T cells: Mechanism of immune
evasion. PLoS One. 9:e1089252014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li W, Mu D, Tian F, Hu Y, Jiang T, Han Y,
Chen J, Han G and Li X: Exosomes derived from Rab27a-overexpressing
tumor cells elicit efficient induction of antitumor immunity. Mol
Med Rep. 8:1876–1882. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|