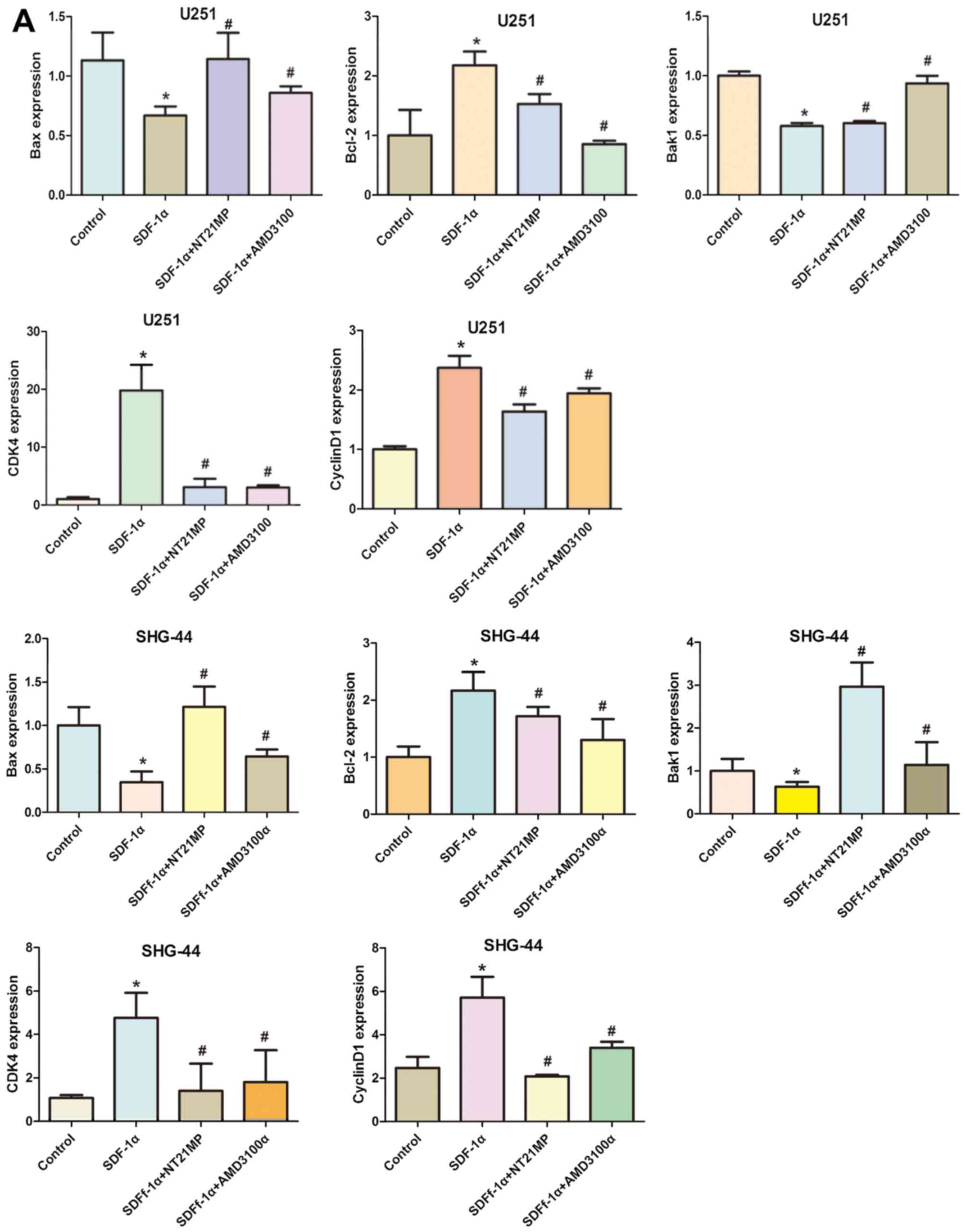
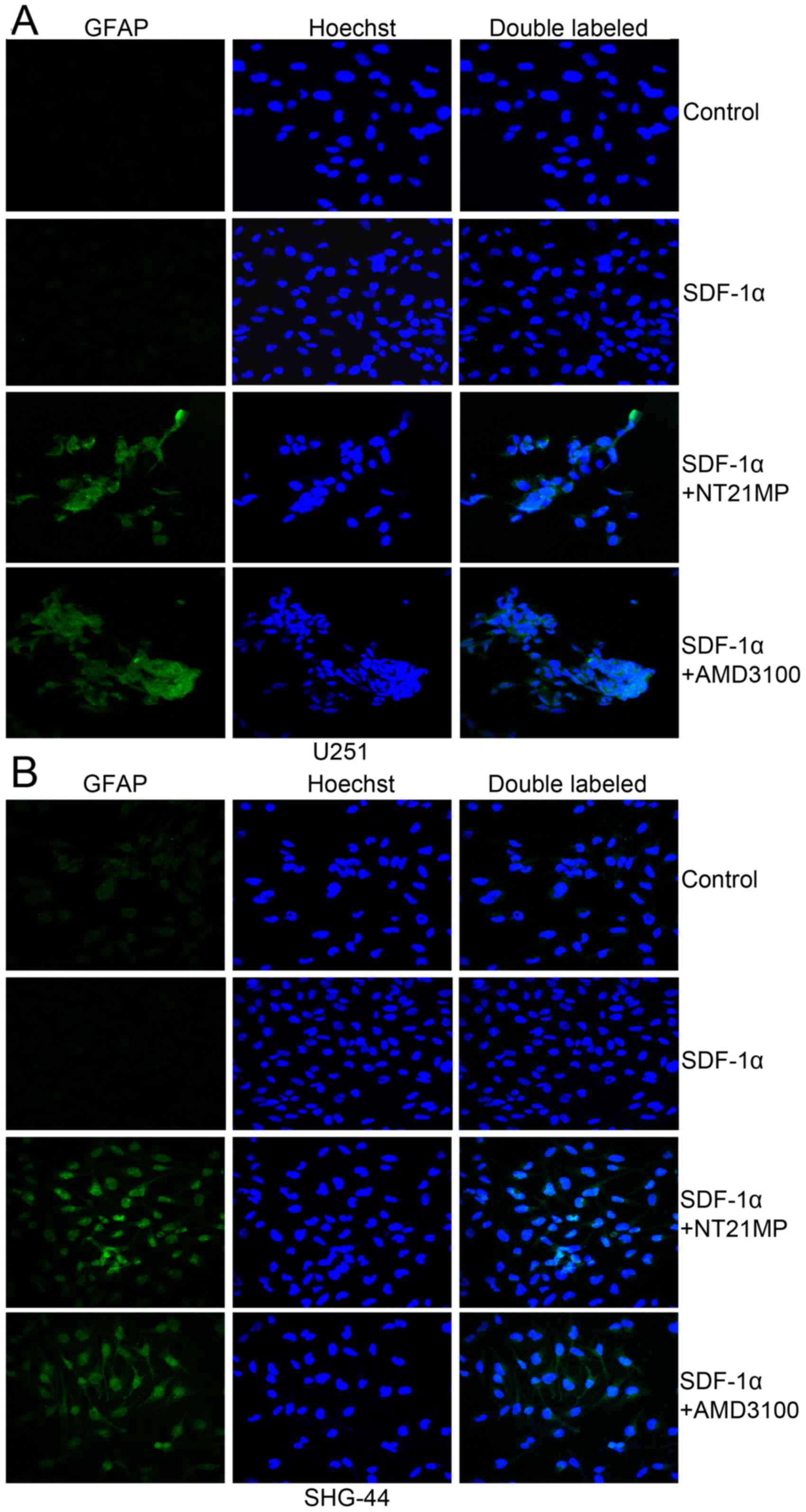
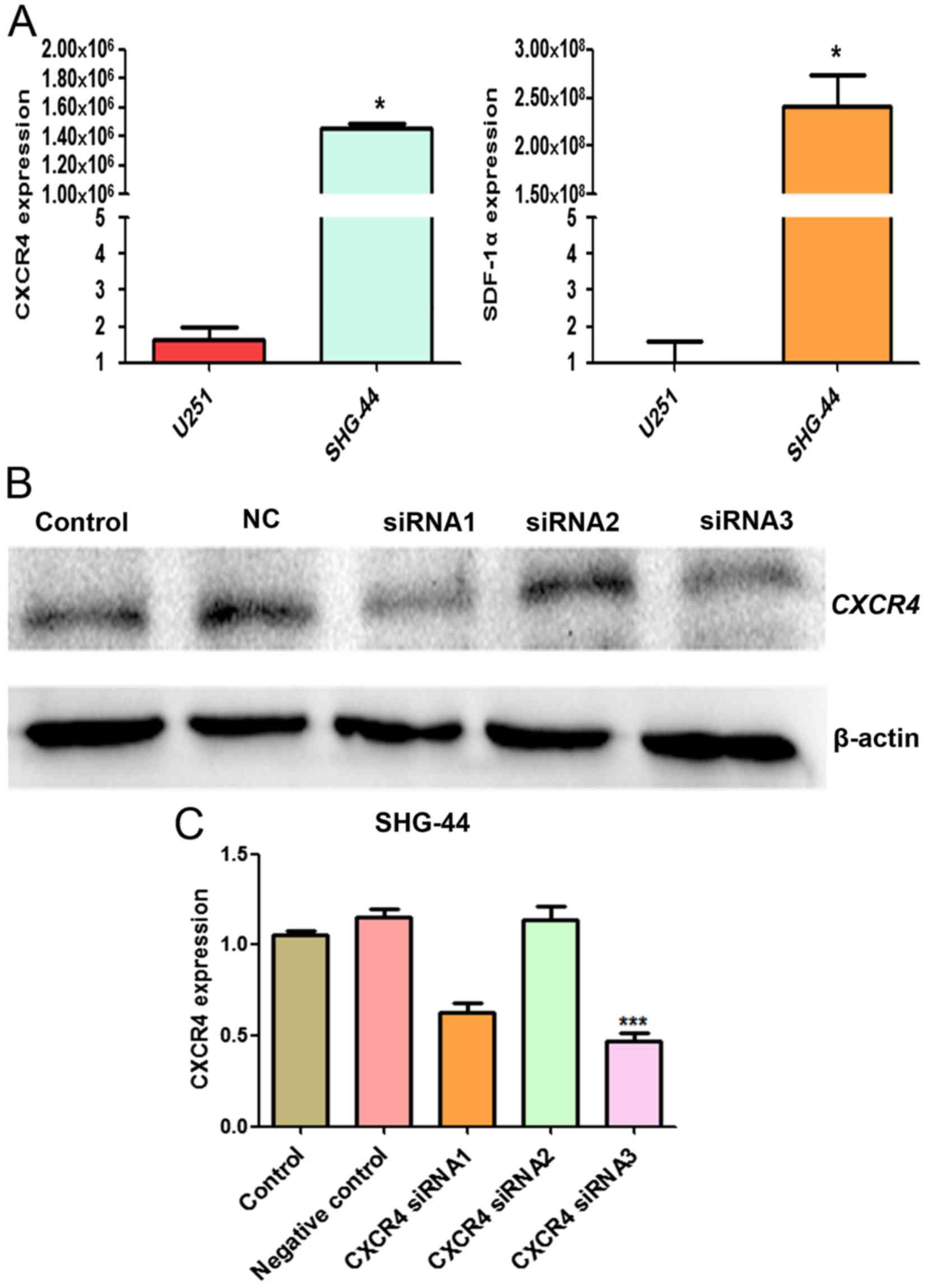
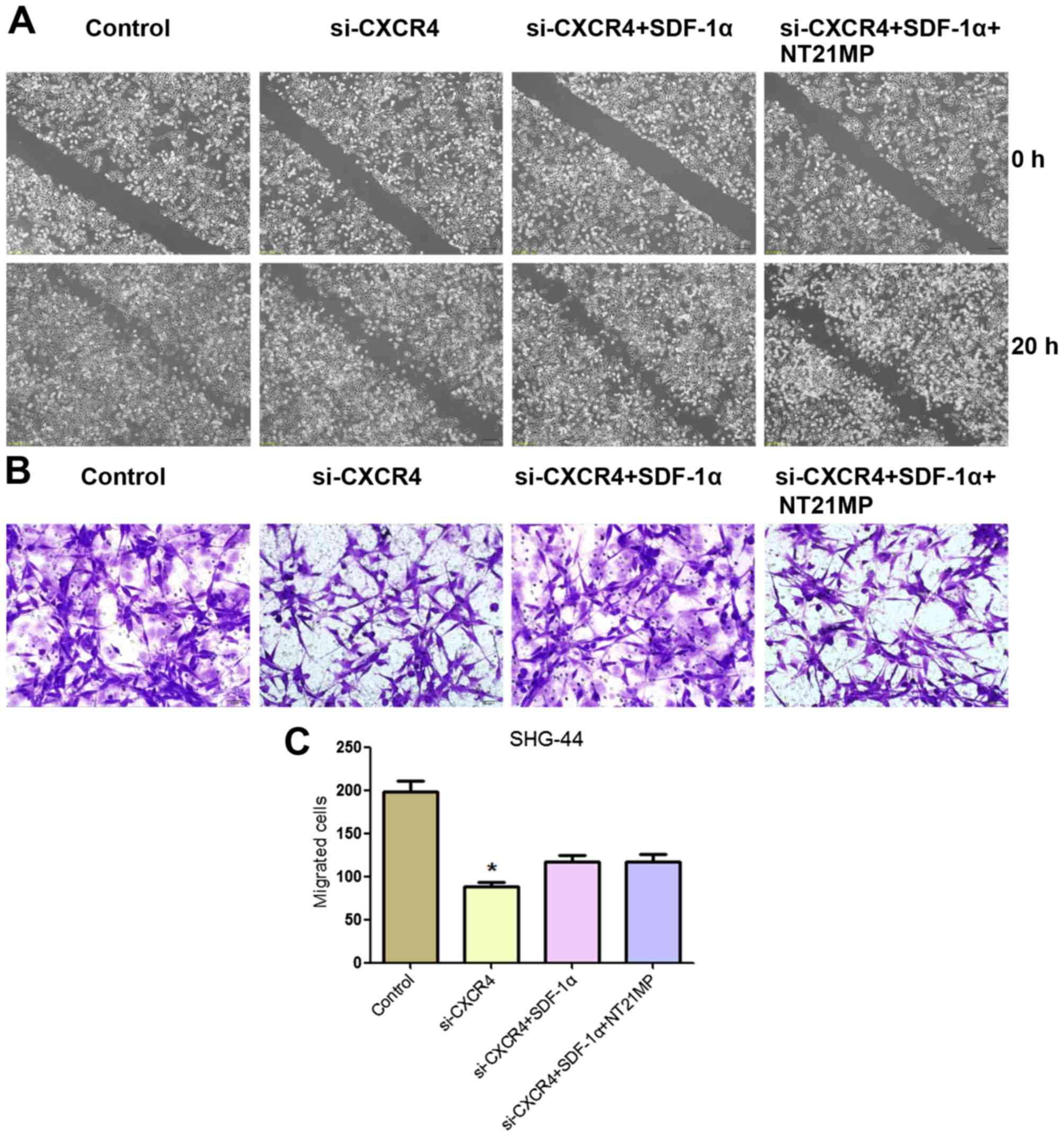
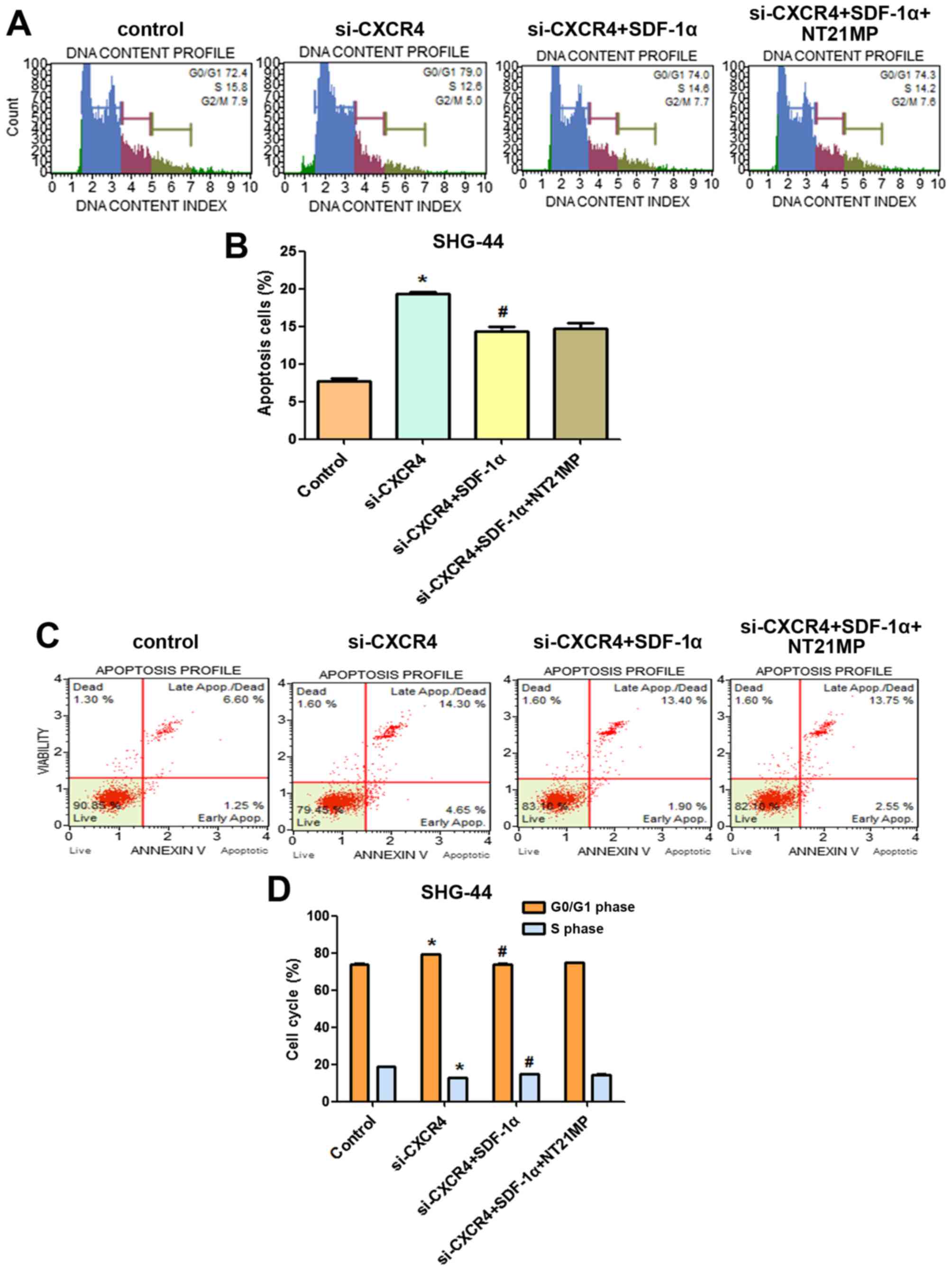
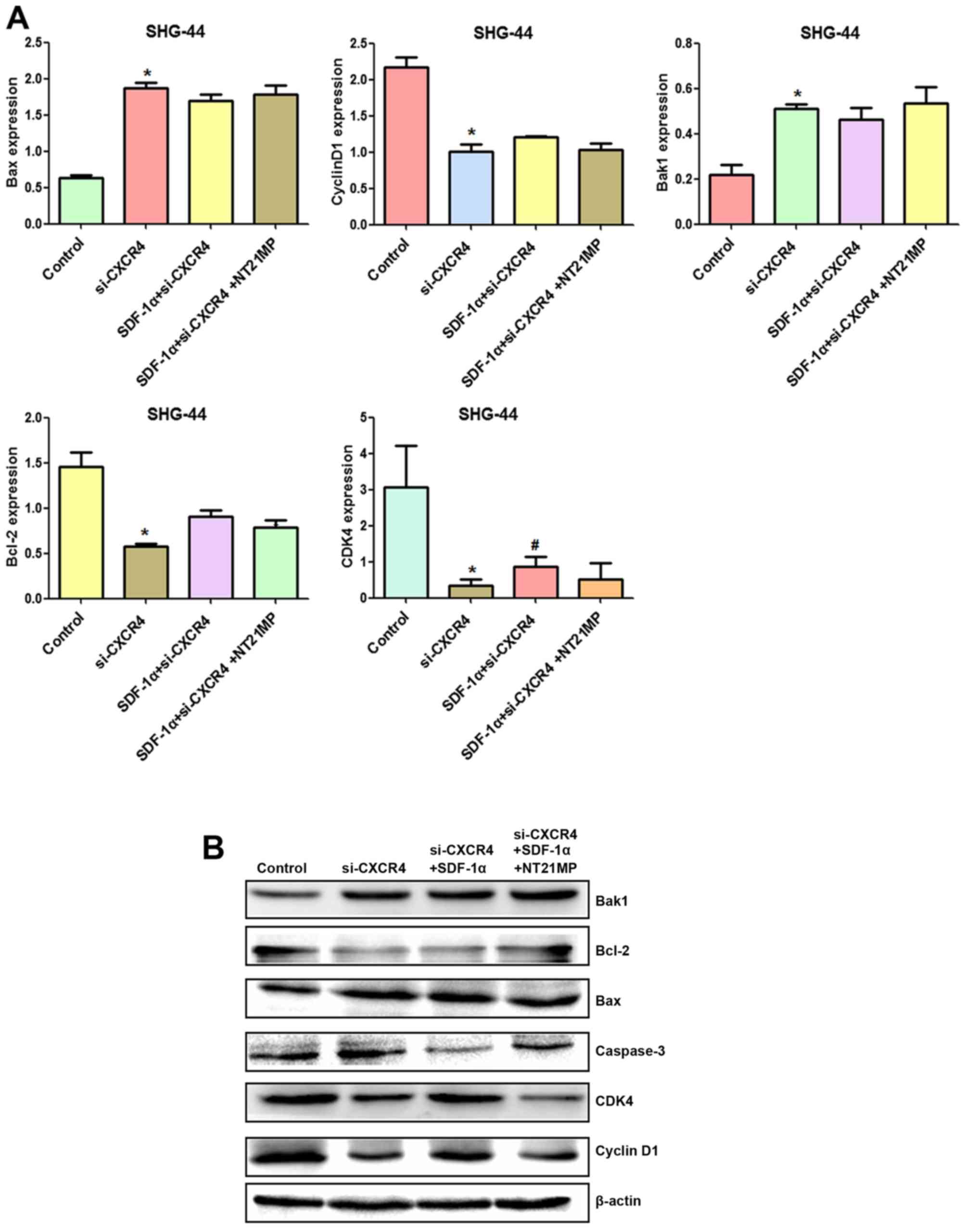
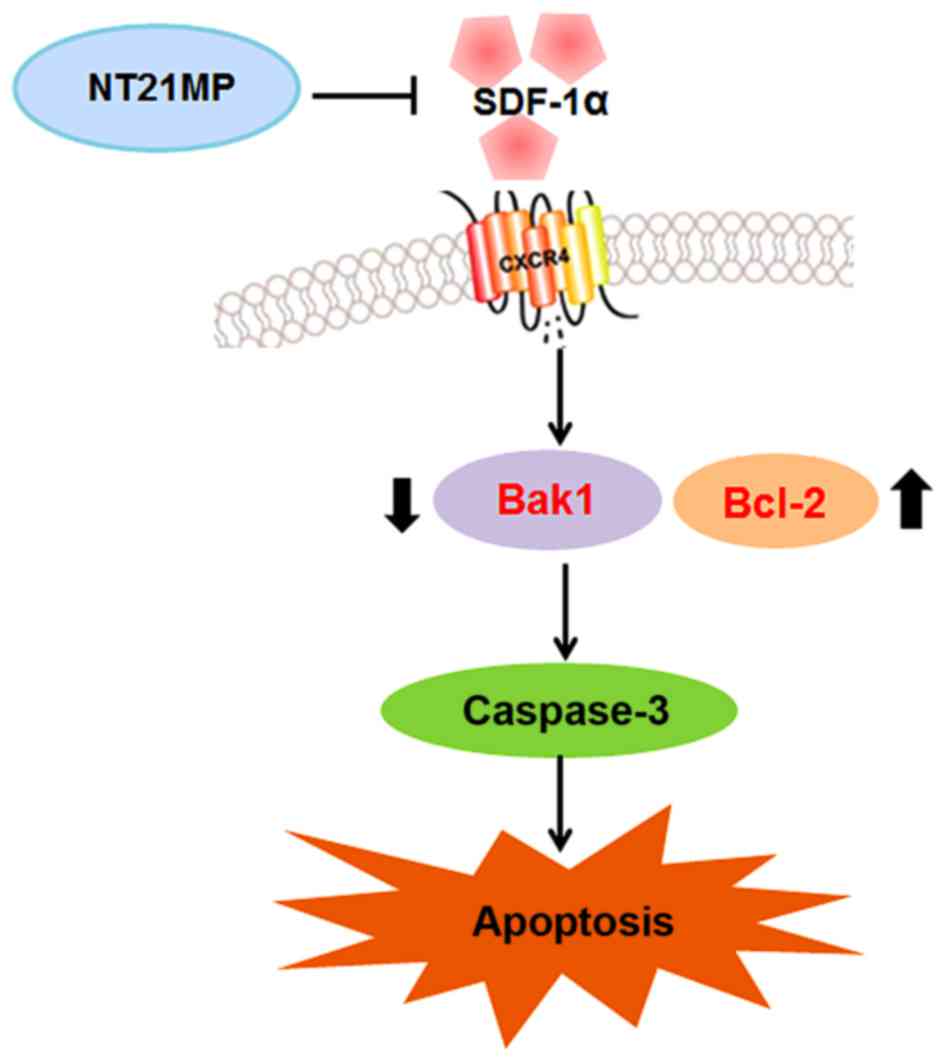
|
1
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fishman M and Seigne J: Immunotherapy of
metastatic renal cell cancer. Cancer Control. 9:293–304.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vicari AP and Caux C: Chemokines in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:143–154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li W and Graeber MB: The molecular profile
of microglia under the influence of glioma. Neuro Oncol.
14:958–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Flüh C, Hattermann K, Mehdorn HM, Synowitz
M and Held-Feindt J: Differential expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7
with various stem cell markers in paired human primary and
recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Oncol. 48:1408–1416. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho KS, Yoon SJ, Lee JY, Cho NH, Choi YD,
Song YS and Hong SJ: Inhibition of tumor growth and
histopathological changes following treatment with a chemokine
receptor CXCR4 antagonist in a prostate cancer xenograft model.
Oncol Lett. 6:933–938. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maddirela DR, Kesanakurti D, Gujrati M and
Rao JS: MMP-2 suppression abrogates irradiation-induced microtubule
formation in endothelial cells by inhibiting αvβ3-mediated
SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling. Int J Oncol. 42:1279–1288. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sekuła M, Miekus K and Majka M:
Downregulation of the CXCR4 receptor inhibits cervical carcinoma
metastatic behavior in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol.
44:1853–1860. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Broxmeyer HE, Orschell CM, Clapp DW,
Hangoc G, Cooper S, Plett PA, Liles WC, Li X, Graham-Evans B,
Campbell TB, et al: Rapid mobilization of murine and human
hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells with AMD3100, a CXCR4
antagonist. J Exp Med. 201:1307–1318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Labrosse B, Brelot A, Heveker N, Sol N,
Schols D, De Clercq E and Alizon M: Determinants for sensitivity of
human immunodeficiency virus coreceptor CXCR4 to the bicyclam
AMD3100. J Virol. 72:6381–6388. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalatskaya I, Berchiche YA, Gravel S,
Limberg BJ, Rosenbaum JS and Heveker N: AMD3100 is a CXCR7 ligand
with allosteric agonist properties. Mol Pharmacol. 75:1240–1247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan A, Greenman J and Archibald SJ: Small
molecule CXCR4 chemokine receptor antagonists: Developing drug
candidates. Curr Med Chem. 14:2257–2277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kledal TN, Rosenkilde MM, Coulin F,
Simmons G, Johnsen AH, Alouani S, Power CA, Lüttichau HR, Gerstoft
J, Clapham PR, et al: A broad-spectrum chemokine antagonist encoded
by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Science. 277:1656–1659.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang QL, Ding YQ, Chen CJ, Tang J, Zhang J
and Yang ZF: Suppression of murine breast cancer metastasis by
selective inhibition of CXCR4 by synthetic polypeptide derived from
viral macrophage inflammatory protein II. Chin Sci Bull.
55:2152–2159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang Q, Chen C, Yang Z, Gao Y and Tang J:
Suppression of breast cancer proliferation and induction of
apoptosis via AKT and ERK1/2 signal transduction pathways by
synthetic polypeptide derived from viral macrophage inflammatory
protein II. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 31:497–503.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang QL, Ding YX, Chen CJ, Yang ZF and Gao
YJ: The mechanism of polypeptide derived from viral macrophage
inflammatory protein II modulates SDF-1α/CXCR4-induced migration.
Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:137–140. 2012.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Domanska UM, Kruizinga RC, Nagengast WB,
Timmer-Bosscha H, Huls G, de Vries EG and Walenkamp AM: A review on
CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: No place to hide. Eur J Cancer.
49:219–230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Epstein RJ: The CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic
pathway as a target of adjuvant breast cancer therapies. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:901–909. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Portella L, Vitale R, De Luca S, D'Alterio
C, Ieranò C, Napolitano M, Riccio A, Polimeno MN, Monfregola L,
Barbieri A, et al: Preclinical development of a novel class of
CXCR4 antagonist impairing solid tumors growth and metastases. PLoS
One. 8:e745482013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Berghuis D, Schilham MW, Santos SJ, Savola
S, Knowles HJ, Dirksen U, Schaefer KL, Vakkila J, Hogendoorn PC and
Lankester AC: The CXCR4-CXCL12 axis in Ewing sarcoma: Promotion of
tumor growth rather than metastatic disease. Clin Sarcoma Res.
2:24–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peled A, Wald O and Burger J: Development
of novel CXCR4-based therapeutics. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
21:341–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Skommer J, Wlodkowic D and Pelkonen J:
CXCR4 expression during tumour cell death. Leuk Res. 31:1155–1156.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR 4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barbero S, Bonavia R, Bajetto A, Porcile
C, Pirani P, Ravetti JL, Zona GL, Spaziante R, Florio T and
Schettini G: Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha stimulates human
glioblastoma cell growth through the activation of both
extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and Akt. Cancer Res.
63:1969–1974. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tu H, Zhou Z, Liang Q, Li Z, Li D, Qing J,
Wang H and Zhang L: CXCR4 and SDF-1 production are stimulated by
hepatocyte growth factor and promote glioma cell invasion.
Onkologie. 32:331–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ehtesham M, Winston JA, Kabos P and
Thompson RC: CXCR4 expression mediates glioma cell invasiveness.
Oncogene. 25:2801–2806. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koepp DM, Schaefer LK, Ye X, Keyomarsi K,
Chu C, Harper JW and Elledge SJ: Phosphorylation-dependent
ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase.
Science. 294:173–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamamori-Adachi M, Ito H,
Sumrejkanchanakij P, Adachi S, Hiroe M, Shimizu M, Kawauchi J,
Sunamori M, Marumo F, Kitajima S, et al: Critical role of cyclin D1
nuclear import in cardiomyocyte proliferation. Circ Res. 92:9–12.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen S, Zhu L, Huang J, Cai Y, Lu X, Yang
Q, Wu Q, Chen C and Wang Z: Arsenic trioxide targets miR-125b in
glioma cells. Curr Pharm Des. 20:5354–5361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Middeldorp J and Hol EM: GFAP in health
and disease. Prog Neurobiol. 93:421–443. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou J, Liu Q, Wang J, Guo X and Song L:
Expressions of peroxiredoxin 1, peroxiredoxin 6 and GFAP in human
brain astrocytoma and their clinical significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke
Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:1255–1259. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sehgal A, Keener C, Boynton AL, Warrick J
and Murphy GP: CXCR-4, a chemokine receptor, is overexpressed in
and required for proliferation of glioblastoma tumor cells. J Surg
Oncol. 69:99–104. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|