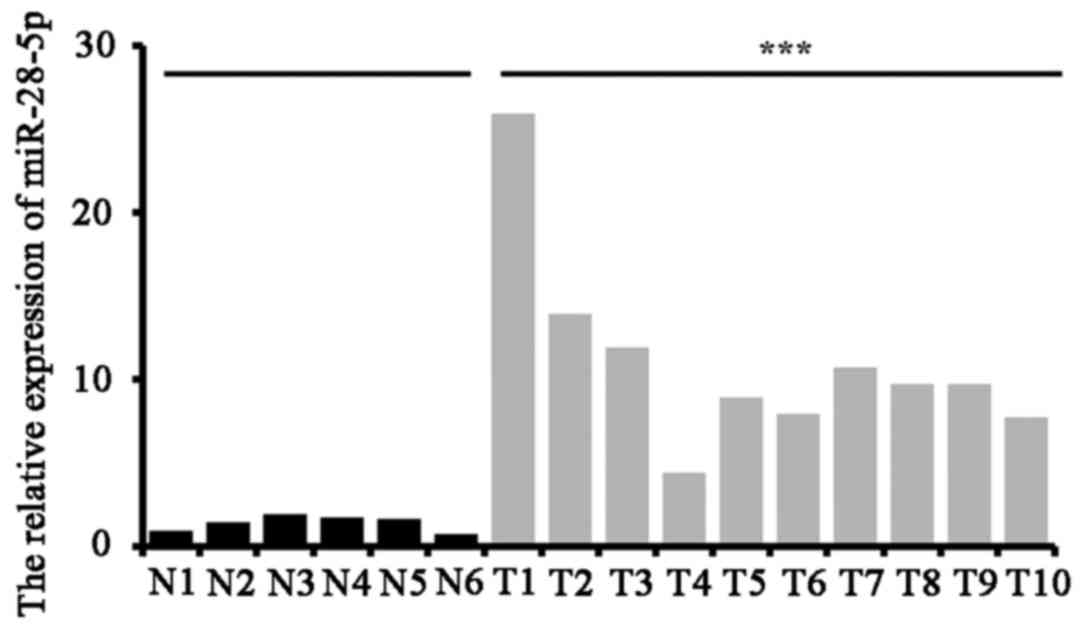
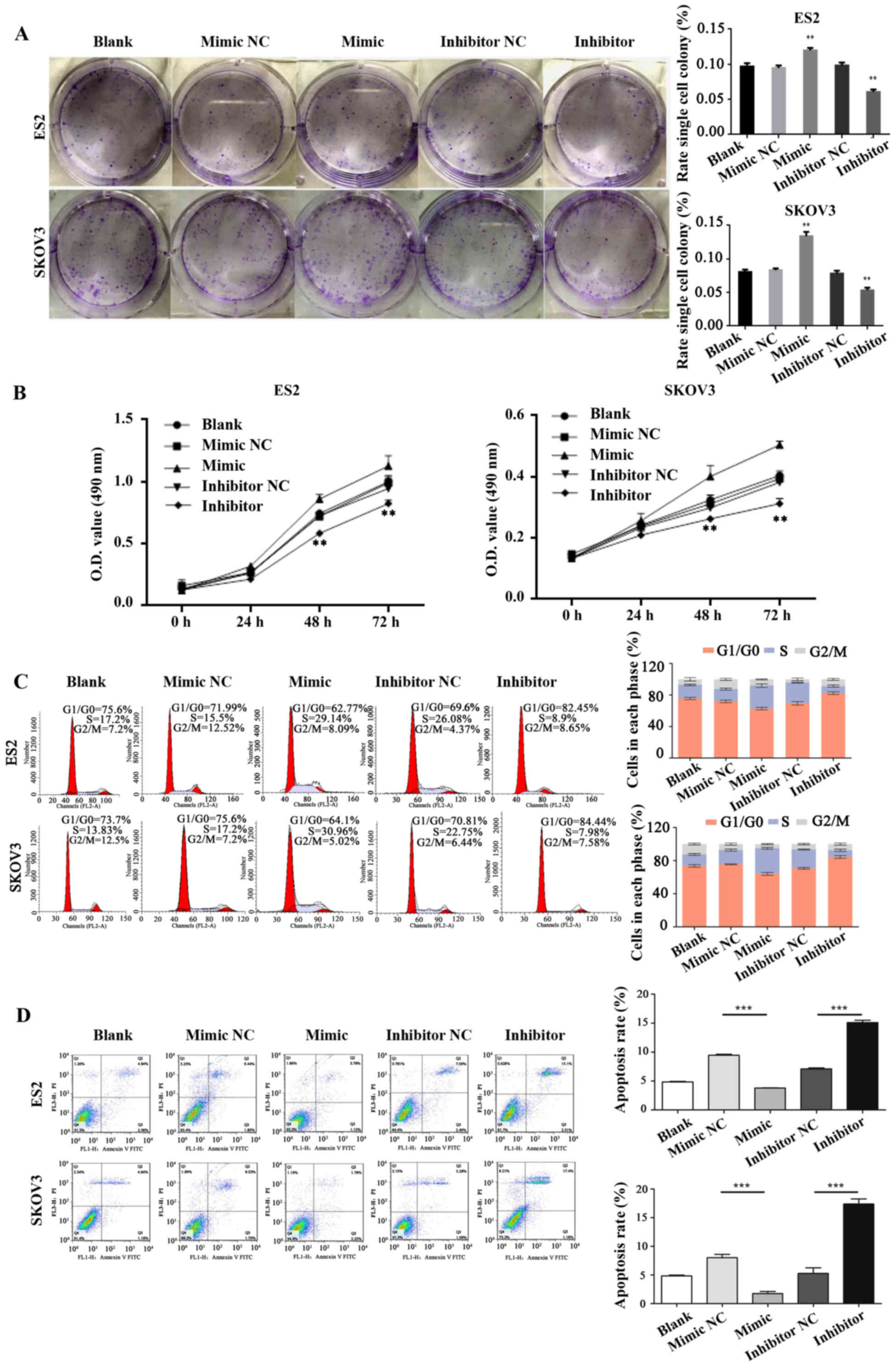
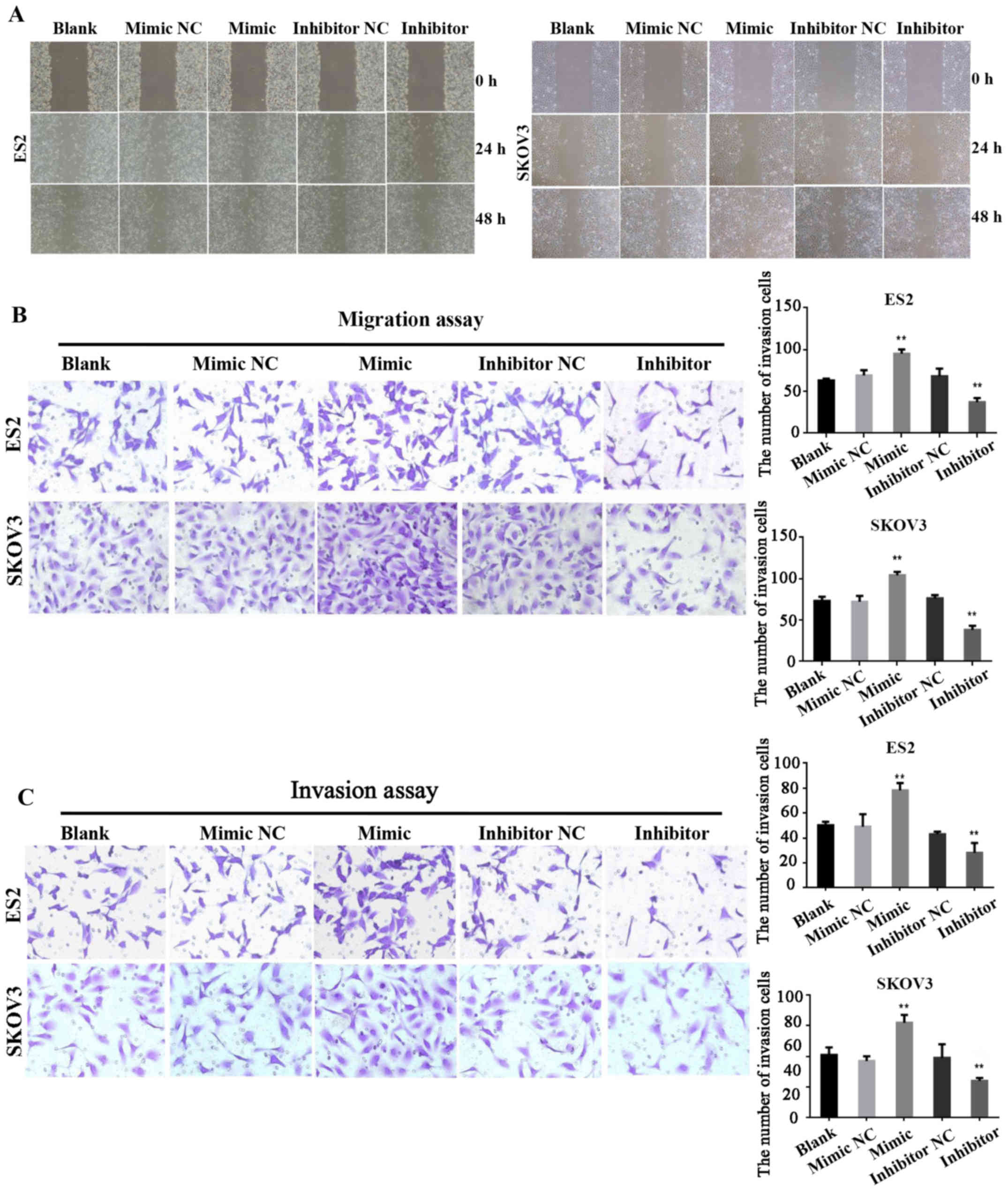
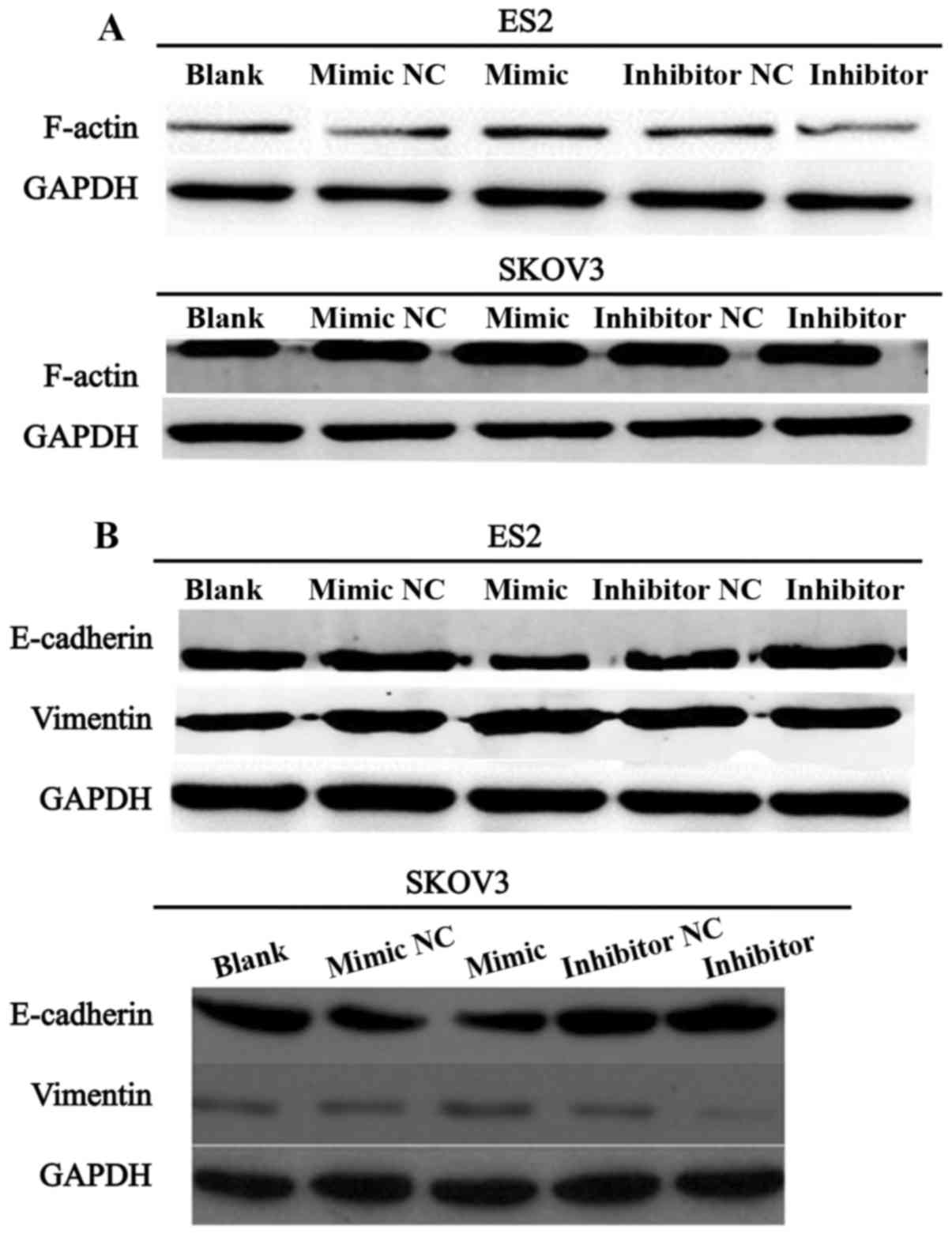
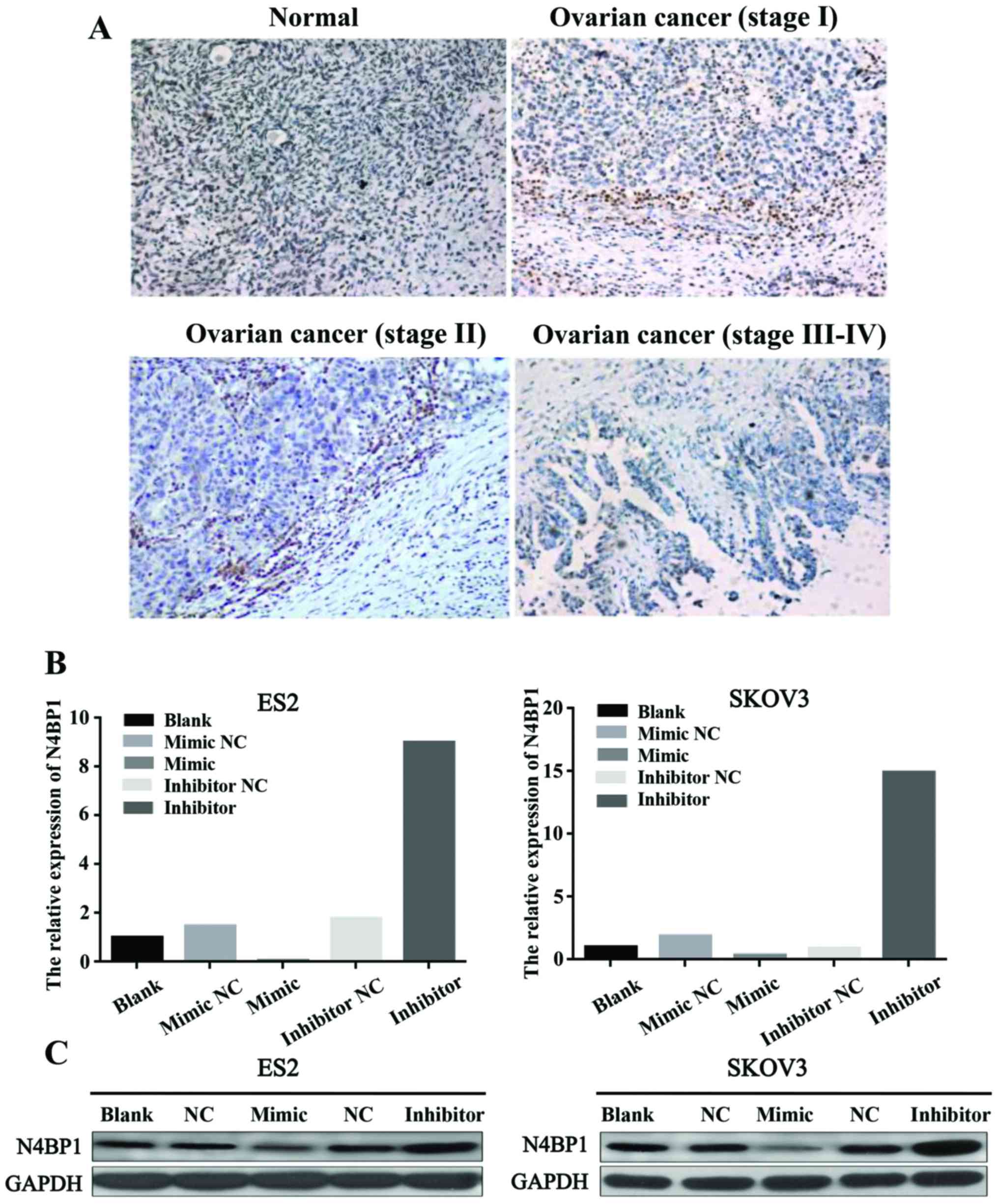
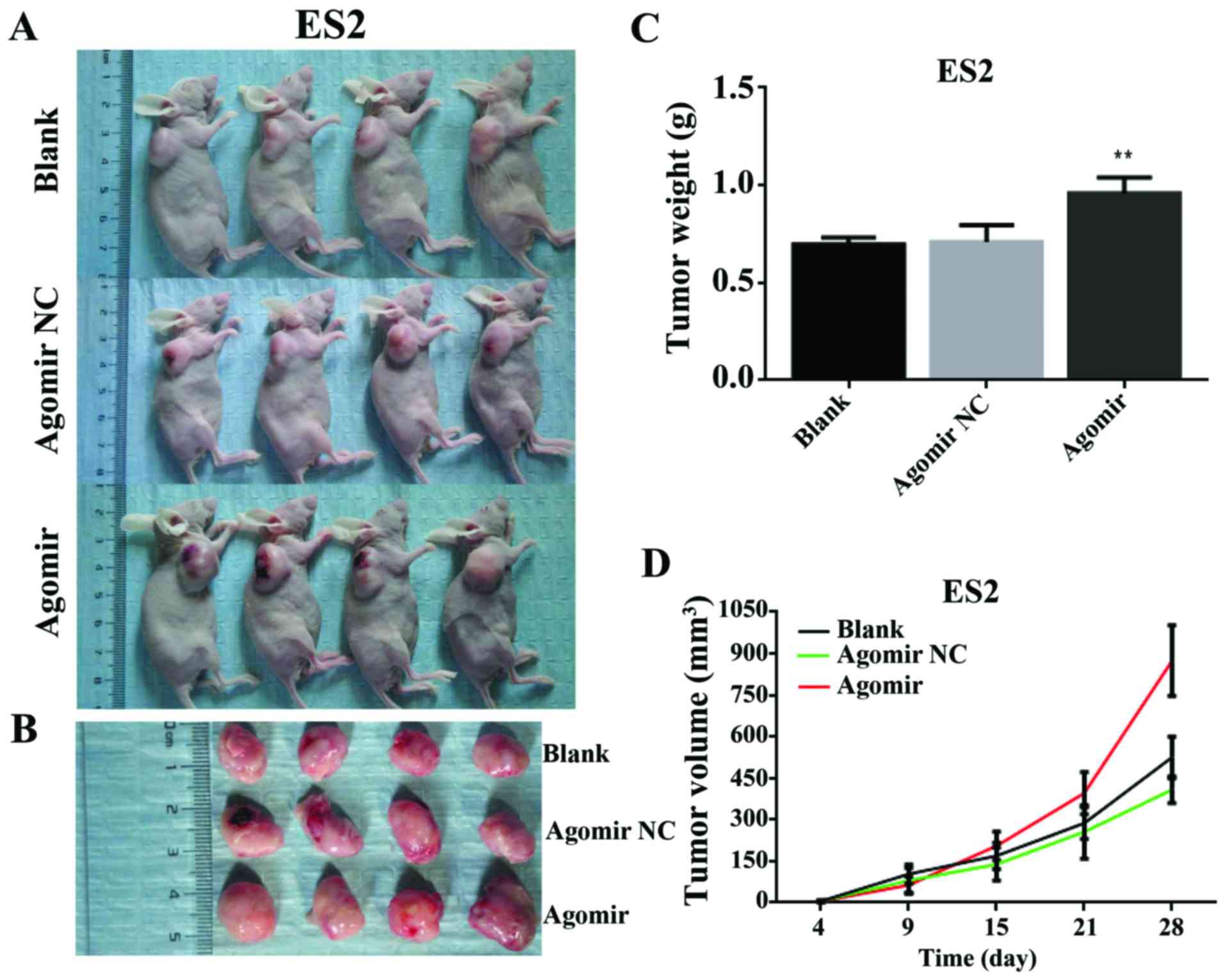
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zaman MS, Maher DM, Khan S, Jaggi M and
Chauhan SC: Current status and implications of microRNAs in ovarian
cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Ovarian Res. 5:442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heintz AP, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P, Quinn
MA, Benedet JL, Creasman WT, Ngan HY, Pecorelli S and Beller U:
Carcinoma of the ovary. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the Results of
Treatment in Gynecological Cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 95(Suppl
1): S161–S192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: Epigenetics and
genetics. MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: Progress in validating
and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:849–864. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Di Leva G and Croce CM: The role of
microRNAs in the tumori-genesis of ovarian cancer. Front Oncol.
3:1532013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dahiya N and Morin PJ: MicroRNAs in
ovarian carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F77–F89. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Mateescu B, Batista L, Cardon M, Gruosso
T, de Feraudy Y, Mariani O, Nicolas A, Meyniel JP, Cottu P,
Sastre-Garau X, et al: miR-141 and miR-200a act on ovarian
tumorigenesis by controlling oxidative stress response. Nat Med.
17:1627–1635. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dahiya N, Sherman-Baust CA, Wang TL,
Davidson B, Shih IeM, Zhang Y, Wood W III, Becker KG and Morin PJ:
MicroRNA expression and identification of putative miRNA targets in
ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 3:e24362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hell MP, Thoma CR, Fankhauser N,
Christinat Y, Weber TC and Krek W: miR-28–5p promotes chromosomal
instability in VHL-associated cancers by inhibiting Mad2
translation. Cancer Res. 74:2432–2443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Almeida MI, Nicoloso MS, Zeng L, Ivan C,
Spizzo R, Gafà R, Xiao L, Zhang X, Vannini I, Fanini F, et al:
Strand-specific miR-28-5p and miR-28-3p have distinct effects in
colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 142:886–896.e9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Zhu F and Chen P: miR-7 and miR-218
epigenetically control tumor suppressor genes RASSF1A and Claudin-6
by targeting HoxB3 in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
424:28–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Creighton CJ, Gibbons DL and Kurie JM: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition programming in invasion
and metastasis: A clinical perspective. Cancer Manag Res.
5:187–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sheppard D: Epithelial-mesenchymal
interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β
activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Ann Am Thorac Soc.
12(Suppl 1): S21–S23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fraga CH, True LD and Kirk D: Enhanced
expression of the mesenchymal marker, vimentin, in hyperplastic
versus normal human prostatic epithelium. J Urol. 159:270–274.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
McGough A, Pope B, Chiu W and Weeds A:
Cofilin changes the twist of F-actin: Implications for actin
filament dynamics and cellular function. J Cell Biol. 138:771–781.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Murillas R, Simms KS, Hatakeyama S,
Weissman AM and Kuehn MR: Identification of developmentally
expressed proteins that functionally interact with Nedd4 ubiquitin
ligase. J Biol Chem. 277:2897–2907. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Oberst A, Malatesta M, Aqeilan RI, Rossi
M, Salomoni P, Murillas R, Sharma P, Kuehn MR, Oren M, Croce CM, et
al: The Nedd4-binding partner 1 (N4BP1) protein is an inhibitor of
the E3 ligase Itch. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:11280–11285. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sharma P, Murillas R, Zhang H and Kuehn
MR: N4BP1 is a newly identified nucleolar protein that undergoes
SUMO-regulated polyubiquitylation and proteasomal turnover at
promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies. J Cell Sci. 123:1227–1234.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anantharaman V and Aravind L: The NYN
domains: Novel predicted RNAses with a PIN domain-like fold. RNA
Biol. 3:18–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang L, Lai YK, Zhang J, Wang H, Lin MC,
He ML and Kung HF: Targeting S100P inhibits colon cancer growth and
metastasis by Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and proteomic
analysis. Mol Med. 17:709–716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Madhyastha HK, Radha KS, Nakajima Y, Omura
S and Maruyama M: uPA dependent and independent mechanisms of wound
healing by C-phycocyanin. J Cell Mol Med. 12B:2691–2703. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl
J Med. 351:2519–2529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T and
Thun M: Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin. 51:15–36. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Paris PL, Chen J, Ngo V, Yao H,
Frazier ML, Killary AM, Liu CG, Liang H, Mathy C, et al: Next
generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid microRNAs from low
grade-benign and high grade-invasive lesions. Cancer Lett.
356B:404–409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Stahlhut C and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs and the
cancer phenotype: Profiling, signatures and clinical implications.
Genome Med. 5:1112013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cheng W, Liu T, Wan X, Gao Y and Wang H:
MicroRNA-199a targets CD44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and
multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells. FEBS J.
279:2047–2059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagaraja AK, Creighton CJ, Yu Z, Zhu H,
Gunaratne PH, Reid JG, Olokpa E, Itamochi H, Ueno NT, Hawkins SM,
et al: A link between mir-100 and FRAP1/mTOR in clear cell ovarian
cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 24:447–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu X, Tian J, Zhang L, Chen Y and Hao Q:
Involvement of microRNA-93, a new regulator of PTEN/Akt signaling
pathway, in regulation of chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin
chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 586:1279–1286.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou SL, Hu ZQ, Zhou ZJ, Dai Z, Wang Z,
Cao Y, Fan J, Huang XW and Zhou J: miR-28–5p-IL-34-macrophage
feedback loop modulates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.
Hepatology. 63:1560–1575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shi X and Teng F: Down-regulated miR-28-5p
in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlated with tumor
proliferation and migration by targeting insulin-like growth
factor-1 (IGF-1). Mol Cell Biochem. 408:283–293. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesen-chymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
De Wever O, Demetter P, Mareel M and
Bracke M: Stromal myofibroblasts are drivers of invasive cancer
growth. Int J Cancer. 123:2229–2238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lauffenburger DA and Horwitz AF: Cell
migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell.
84:359–369. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|