Introduction
Malignant gliomas are the most common primary brain
tumors in adults. Most patients present with glioblastoma
multiforme (GBM), WHO grade IV tumor at diagnosis. The prognosis
for these patients is poor; the median survival is 15 months, even
with the current standard of care, surgical resection of the tumor
followed by concomitant radio-chemotherapy and sequential
temozolomide administration (1–3). The
invasion and migration of the tumor is one of the intrinsic
characteristics of GBM, demonstrated by both local recurrence and
metastasis and it is a major cause of death in GBM patients
(4). Ironically, the aggressive
potential of GBM may also be increased by radiotherapy and
chemotherapy in vivo (5,6). It
is believed that the initial acquisition of migratory and invasive
capabilities by glioma cells is the rate-limiting step of the
invasion cascade, and the progression from a non-migratory to a
migratory cellular phenotype is a critical step in the invasive
progression of GBM (7,8).
It has been shown that phenotypic progression of
malignant cells from a proliferating to a migrating state is
initially driven by the harsh microenvironment where the cells
propagate. Generally, this process is controlled by a complex
signaling network with different regulatory levels. In glioma
cells, mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin), a highly conserved
serine/threonine kinase found in all eukaryotic cells, is
considered to be a central regulator of cell growth (9). In contrast, Ras-related C3 botulinum
toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), a member of the Rho family of GTPases,
promotes cell migration by regulating actin polymerization at the
front of migrating cells and induces the formation of membrane
ruffles and lamellipodia (10,11).
It is reasonable to assume that the switching of cellular phenotype
from proliferation to migration might be alternatively regulated by
mTOR or Rac1 activation. Therefore, the master regulator of mTOR
and Rac1 is a compelling subject for further investigation.
Endogenous microRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) are 18- to
24-nucleotide (nt) single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) molecules that
function in the regulation of gene expression (12). Translation of the targeted mRNAs is
inhibited post-transcriptionally by the binding of miRs to
sequences in the 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) (13–15).
It has been demonstrated that miRs play critical roles in
biological processes including positive and negative effects on
tumor cell development, differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis,
invasion and pluripotency in various cancers (16–18).
In malignant gliomas, the dysregulation of a number of miRs has
been confirmed, including miR-21, miR-451, miR-23a, miR-145,
miR-155, miR-218, miR329 and others (19,20).
Of these dysregulated miRs, miR-451 is peculiar in that its
expression is responsive to metabolic stress in the
microenvironment. A recent study suggested that elevated miR-451
suppresses the expression of calcium-binding protein 39 (CAB39,
also known as MO25α), leading to repression of LKB1 activity and
its downstream substrate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). This
repression facilitates unrestrained mTOR activation and maintains
high cellular proliferation rates (21). However, it is still unknown whether
reduced expression of miR-451, in contrast, would induce AMPK
activity, thereby activating Rac1 and promoting cell motility.
Further investigation is also essential to determine whether AMPK
is, in fact, the master regulator through which miR-451 functions
to regulate the switch between mTOR or Rac1 activation.
Materials and methods
Human tissue
Human tissue specimens were obtained at the General
Hospital of Tianjin Medical University (Tianjin, China). Forty GBM
specimens and 25 control brain tissue specimens were collected from
surgeries for tumor resection or temporal lobe epilepsy,
respectively. Tissue samples were immediately frozen in liquid
nitrogen and stored at −80°C. All procedures used in the present
study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical
University and informed consents were obtained from all patients
included in the study.
Cells and cell culture
The human GBM cell lines U-87, SNB-19 and U-251 were
purchased from the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology,
Chinese Academy of Science. All cell lines were cultured in
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA)
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Invitrogen,
Carlsbad, CA, USA) in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator.
miRNA overexpression and knockdown
Simulated overexpres-sion of miR-451 was
accomplished using the oligonucleotide
5′-AAACCGUUACCAUUACUGAGUU-3′, whereas its knockdown was achieved
with the complementary oligonucleotide
5′-AACUCAGUAAUGGUAACGGUUU-3′. Synthetic miR-451, miR-451 inhibitor
and scrambled negative control ssRNA were purchased from Shanghai
GenePharma, Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). U-87, U-251 or SNB-19
cells were seeded into 6-well culture plates and transfected with
100 pmol of miR oligonucleotides using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
(Invitrogen) when the cells reached 70% confluency. After 6 h, the
medium was changed to DMEM or McCoy's 5A supplemented with 1%
phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cells were harvested 24 or 48 h
after transfection. The expression level of miR-451 was analyzed by
quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR).
AMPKα1 knockdown
The lentiviral vectors expressing an AMPKα1 shRNA or
fluorescence protein (as a negative control) were synthesized by
Shanghai GenePharma. AMPKα1 shRNA and the control vector (1
µg/ml medium) was transfected into the human U-87, SNB-19 or
U-251 cells according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Real-time PCR analysis
Total RNA extractions were performed using TRIzol
(Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Integrity of the isolated RNA quality was determined by
electrophoresis in a 1% agarose-formaldehyde gel. First strand cDNA
was generated by reverse transcription. Subsequent PCR
amplification was performed using a real-time PCR cycler (ABI 7500;
Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Expression levels of
mature miR-451 were quantified by miR-qRT-PCR using Hairpin-it™
miRNA qPCR Quantitation kit (Shanghai GenePharma). The
amplification reaction (40 µl) included 2X real-time buffer,
5 µM miR-specific primer set (0.80 µl),
ddH2O (15 µl), cDNA (4 µl), and 0.2
µl Taq DNA polymerase (5 U/µl). The reaction
conditions were as follows: an initial denaturation at 95°C for 3
min; 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 12 sec followed by
extension at 62°C for 60 sec; and a final ramping from 62°C up to
95°C followed by cooling to 0.2°C for 2 sec. The results of the
real-time PCR were analyzed using the ΔΔCt method: ΔCt =
Ctselected gene − Ctu6, ΔΔCt =
ΔCttherapy group − ΔCtcontrol group, RQ
(Relative Quantitation)therapy group =
2−ΔΔCT, RQcontrol group = 1. The results of
the real-time PCR were presented as the ratio between the selected
genes and U6 transcripts.
Annexin V/PI analysis
The apoptosis induced by VP-16 was assessed by
staining cells with an Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)
apoptosis detection kit (556547; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA,
USA). Cells were treated similarly as in the cell cycle assay. The
cells were collected and then washed with cold PBS twice. Then,
they were resuspended in 100 µl of Annexin V binding buffer
and incubated with 5 µl of FITC-conjugated Annexin V and 5
µl of propidium iodide for 15 min in the dark. Annexin V
binding buffer (200 µl) was then added to each tube.
Finally, the cells were examined using a BD FACSCanto II flow
cytometer (BD Biosciences).
MTT assay
Transfected and control cells in the log-phase of
growth were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of
0.4×104 cells/well in 0.1 ml supplemented DMEM. Each
day, for seven consecutive days, 20 µl of MTT (5 mg/ml) was
added to the corresponding well, and cells were incubated at 37°C
for an additional 4 h. The reaction was stopped by lysing the cells
with 200 µl of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 20 min. Optical
density was measured at 570 nm, and the data were expressed as a
percentage of the control well.
Transwell migration assay
Transwell filters (Corning Costar, Corning, NY, USA)
were coated with Matrigel (3.9 µg/µl, 60–80
µl) on the upper surface of the polycarbonic membrane
(diameter 6.5 mm, pore size 8 µm). Following incubation for
30 min at 37°C, the Matrigel solidified and served as the
extracellular matrix for tumor cell invasion analysis. Harvested
cells (1×105) of the transfected or control groups in
100 µl of serum-free DMEM were added into the upper
compartment of the chamber, and 200 µl of conditioned medium
from U-87, SNB-19 or U-251 cells was used as the chemoattractant
and placed in the bottom chamber. After incubation for 24 h at 37°C
and 5% CO2, the medium was removed from the upper
chamber. The non-invaded cells on the upper side of the chamber
were scraped off with a cotton swab. The cells that had migrated
from the Matrigel into the pores of the inserted filter were fixed
with 100% methanol, stained with hematoxylin, mounted and dried at
80°C for 30 min. The number of cells invading the Matrigel was
counted from three randomly selected visual fields, each from the
central and peripheral portions of the filter, using an inverted
microscope at ×200 magnification. Each test was performed in
triplicate.
Immunofluorescence
The glioma cells under different treatments were
grown on glass coverslips for 24 h. The cells were washed and then
fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 25 min. Fixed cells were
permeabilized by treatment with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 min and
blocked by incubation with 5% BSA in PBS for 1 h. The cells were
then incubated overnight at 4°C with p-cofilin (rabbit) antibodies
at a dilution of 1:100. The cells were washed three times with PBS
and then incubated for 1 h with Alexa 488-conjugated goat
anti-rabbit secondary antibody at a dilution of 1:1,000 for 1 h at
37°C. The cells were washed with PBS and then counterstained with
rhodamine phalloidin for 20 min to stain actin filaments and DAPI
to stain DNA. The cells were imaged under a confocal microscope
(Olympus FV1000; Research Center of Basic Medical Science of Tanjin
Medical University; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Rac1 activation assay
Rac1 activation assays were conducted as previously
described to test the activation of Rac1 in cells (22). Briefly, cells were rinsed with cold
PBS and lysed in ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA)
buffer. Lysates were cleared by centrifugation and the protein
concentration in the clarified supernatant was measured. Equal
amounts of protein (400–600 µg) were incubated with 50
µg of PAK1 agarose beads (Assay Designs, Farmingdale, NY,
USA), and the reaction mixture was gently rocked at 4°C for 60 min.
The agarose beads were collected by pulsing for 5 sec in a
microcentrifuge at 14,000 × g and the supernatant was removed and
discarded. The beads were washed thrice with lysis buffer, and the
agarose beads were resuspended in 40 µl of 2× Laemmli buffer
and boiled for 10 min to elute the bound proteins. Eluted proteins
were resolved in 12% polyacrylamide gels, transferred to
polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes, and immunoblotted with
the anti-Rac1 antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK).
Western blot analysis
U-87, SNB-19 and U-251 cells were lysed in 1%
Nonidet P-40 lysis buffer 48 h after transfection with negative
control ssRNA, miR-451, or miR-451 inhibitor oligonucleotide.
Homogenates were clarified by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 15
min at 4°C, and protein concentration was measured by the Lowry
method. SDS-PAGE gels were loaded with 40 µg of protein from
each sample, and resolved proteins were transferred to PVDF
membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and incubated with
primary antibodies against Rac1 (1:1,000 dilution; Abcam), AMPKα1,
p-AMPKα1, mTORC1, p-mTORC1, confilin or p-confilin (1:1,000
dilution; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), followed by
incubation with an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1,000
dilution; Zymed, San Diego, CA). The specific protein was detected
using the SuperSignal protein detection kit (Pierce, Waltham, MA,
USA). After washing with stripping buffer, the membrane was
reprobed with antibody against GAPDH (1:1000 dilution; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA).
Results
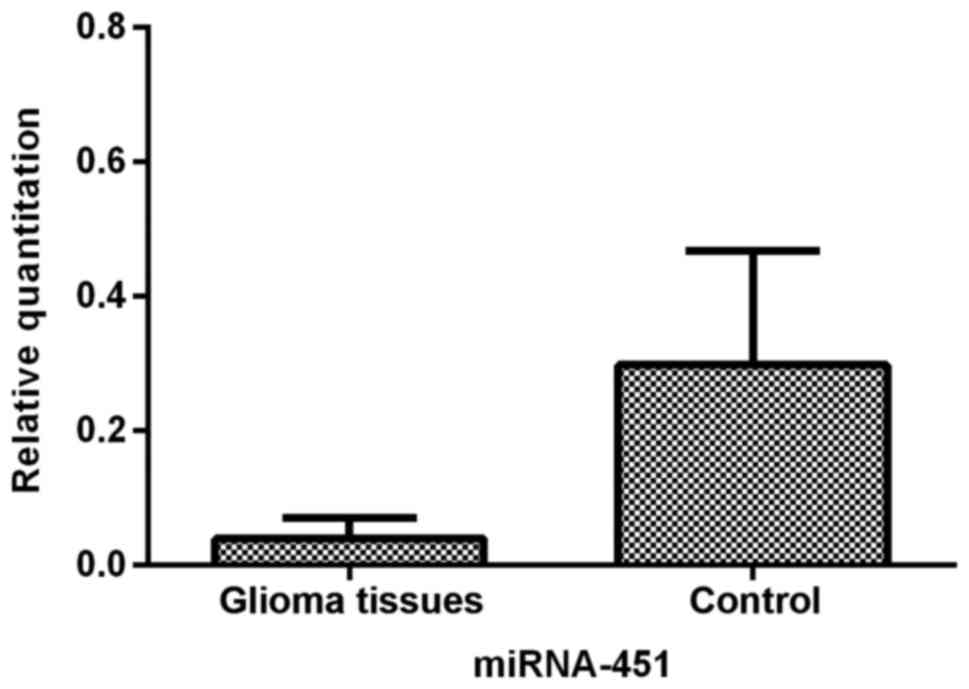
miR-451 is downregulated in glioma
tissues, especially in the central portions of tumors
We first determined the relative expression of
miR-451 in human glioma tissues and control brain tissues by
qRT-PCR analysis. The data demonstrated that the level of miR-451
was significantly suppressed (P<0.01) in glioma tissues when
compared to the control brain tissues (Fig. 1).
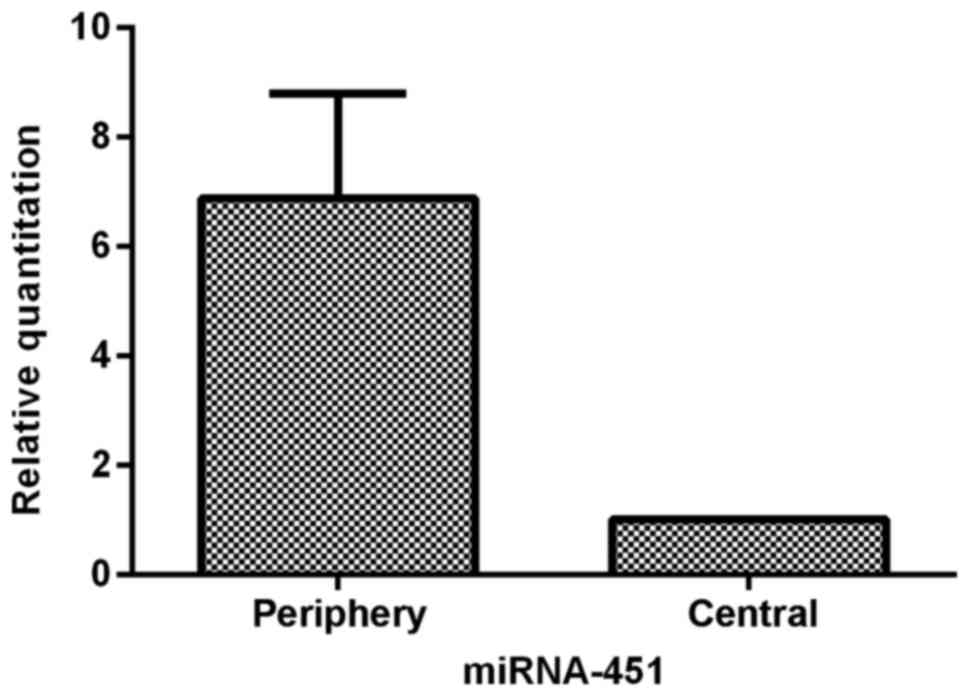
To characterize miR-451 expression in glioma tissues
further, we analyzed the heterogeneous expression of miR-451
between the central and periphery regions of sixteen glioma
tissues. The data showed that cells in the periphery region of
glioma tissues expressed 6.88-fold (±1.91) greater levels of
miR-451 than cells in the central region (P<0.05; Fig. 2). The tumor cells in the central
region of the glioma tissues appeared to express much less miR-451,
indicating that downregulation of miR-451 expression is sensitive
to hypoxic-hypoglycemic microenvironments.
miR-451 enhances the proliferation in
glioma cells regulating CAB39/AMPK/mTOR pathway
To clarify the role of miR-451 and downstream
molecular targets in glioma cells, we prepared synthetic miR-451
and miR-451 inhibitor and used them to alter the expression levels
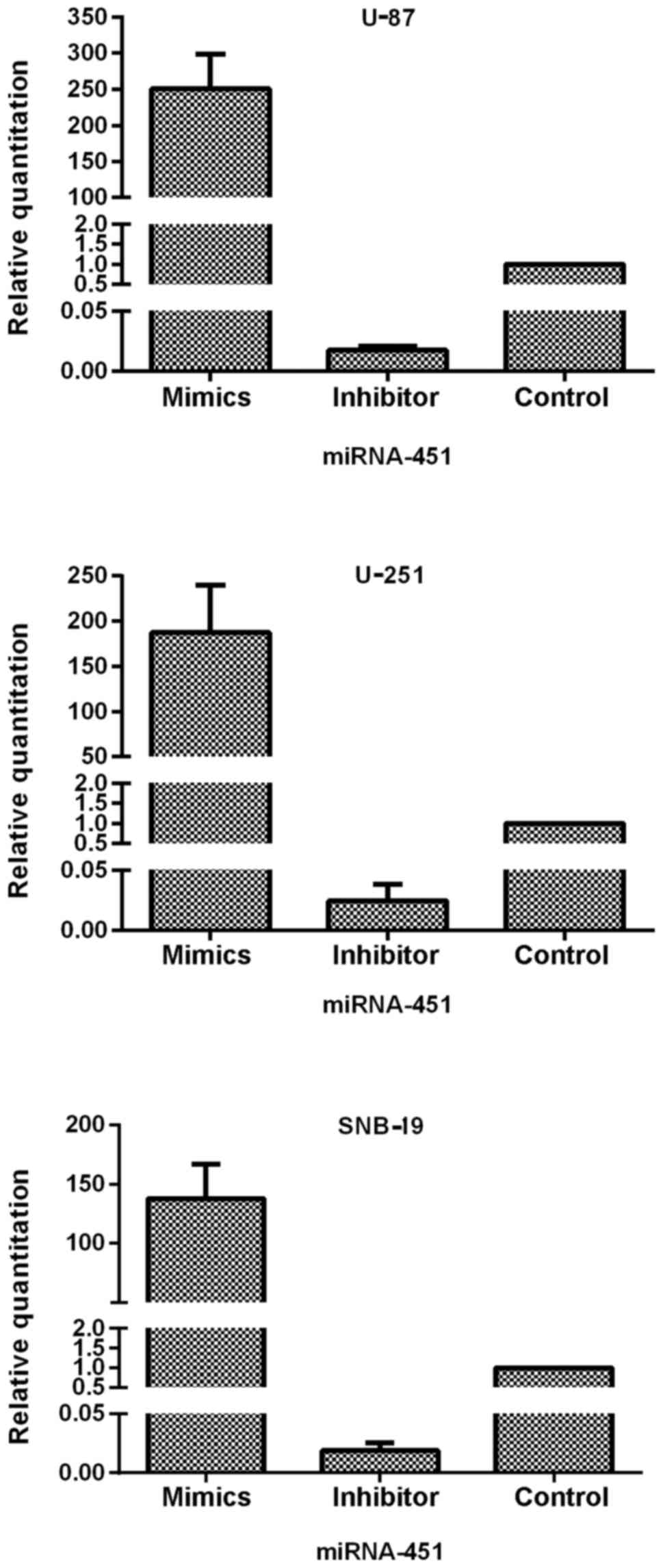
of miR-451 in three glioma cell lines: U-87, U-251 and SNB-19.
After transfection of the oligonucleotides into the cells, qRT-PCR
was performed to test the efficiency of expression dysregulation.
Compared to the control groups, the miR-451 level was increased in
the synthetic miR-451-treated U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells with an
RQ of 250.60±47.53, 187.46±52.64 and 137.63±29.14, respectively. In
contrast, expression decreased in the miR-451 inhibitor-treated
U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells with an RQ of 0.017±0.003, 0.025±0.013
and 0.019±0.007 (each of the three cell lines P<0.01),
respectively (Fig. 3).
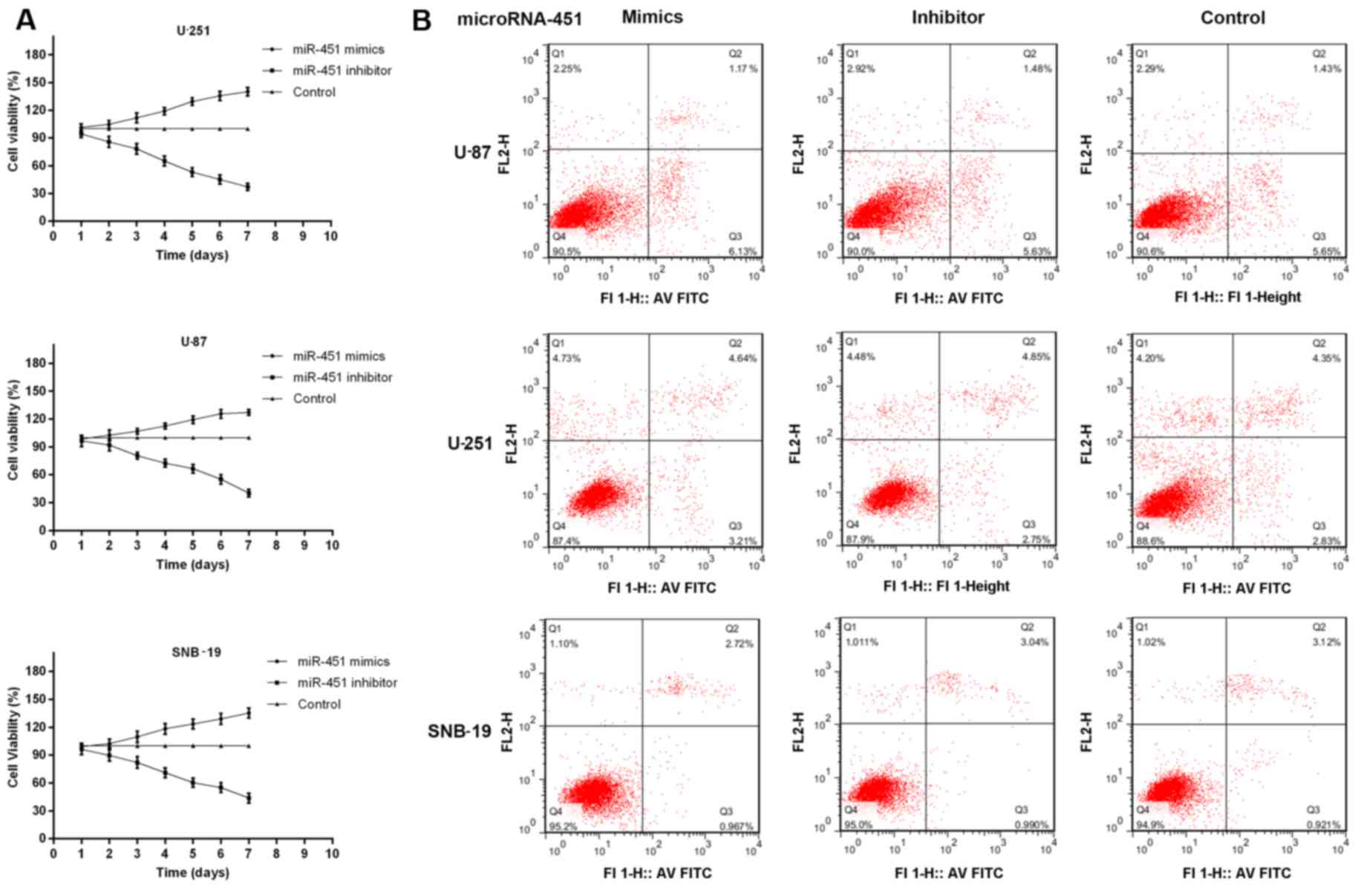
Furthermore, MTT assays and Annexin V/PI analysis
were performed to measure the role of miR-451 in cellular
proliferation. Cell growth was followed on days 2 through 7
following transfection with miR-451 or the inhibitor in all three
cell lines compared with the control group. Transfection of U-87,
U-251 and SNB-19 cells with synthetic miR-451 resulted in
127.21±3.06, 140.20±4.61 and 135.46±5.21% increased cell growth
rates, respectively. In contrast, miR-451 inhibitor-treated cells
showed a slower growth rate of 40.23±3.97, 37.31±4.13 and
43.97±5.37%, respectively, compared to the control group (each cell
line P<0.01) (Fig. 4A).
Whereas, miR-451 had no effect on apoptosis in oligonucleotides
treated and non-treated glioma cells. The percentage of viable
cells had no significant difference among the three groups in each
cell line (P>0.05; Fig. 4B).
The cells with highest expression levels of miR-451 showed the
fastest rates of cellular proliferation.
To investigate the downstream molecular targets
affected by miR-451 upregulation or downregulation in glioma cells,
we transfected synthetic miR-451 or miR-451 inhibitor into U-87,
U-251 and SNB-19 cells. The levels of CAB39, p-AMPK and AMPK
expression were assessed semi-quantitatively by western blotting.
The data showed no significant difference in AMPKα1 expression
(P>0.05), while CAB39 expression (40.53±4.61, 39.91±4.23 and
41.06±9.87 in U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells, respectively) and
p-AMPKα1 expression (36.44±3.76, 35.63±2.06 and 29.47±6.59% in
U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells, respectively) declined after
treatment with synthetic miR-451. These results indicate that
elevated miR-451 inhibits the expression of the immediate
downstream target CAB39, which subsequently leads to decreased AMPK
activation.
To determine the activation state of mTOR after
miR-451 upregulation in glioma cells, mTOR and p-mTOR expression
levels were evaluated by western blotting. No significant
difference was found in mTOR expression levels, while p-mTOR
expression was elevated (207.62±19.64, 228.85±23.10 and
188.97±16.73% in U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells, respectively). In
short, increased expression of miR-451 enhances mTOR activation
regulating the dominance of downstream mTOR-dependent pathways
(Fig. 5).
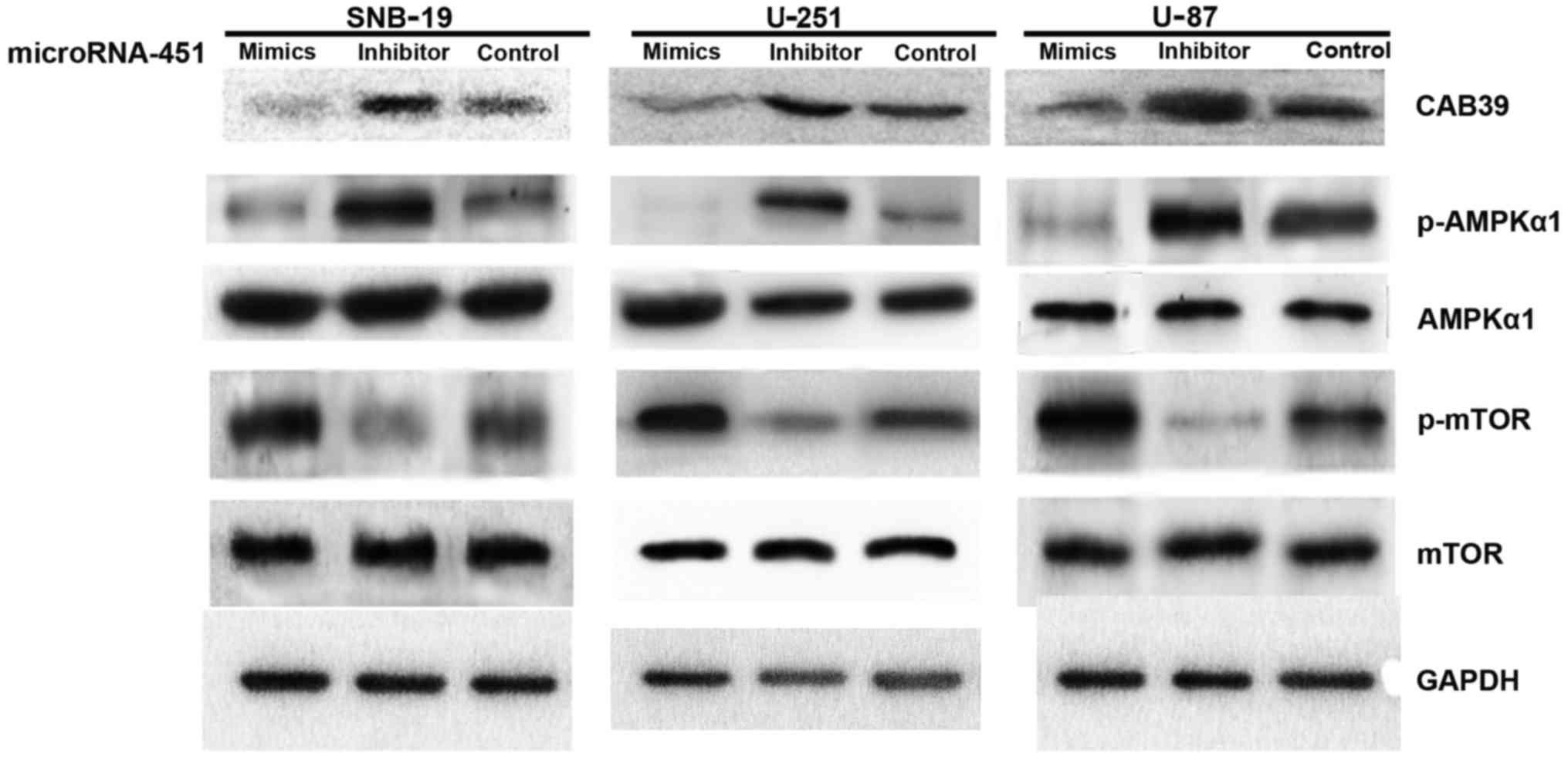 | Figure 5The effect of miR-451 downstream of
CAB39/AMPK/mTOR pathway in glioma cell lines determined by western
blot analysis. Impact of miR-451 mimics and inhibitor
oligonucleotides on the expression of CAB39, p-AMPK, AMPK, mTOR and
p-mTOR. U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells were treated with
oligonucleotides, as described. CAB39, p-AMPK, AMPK, mTOR, p-mTOR
and GAPDH expression was determined following treatment by western
blot analysis. Expression of CAB39 was declined in miR-451 mimics
group. No statistical difference of total AMPKα1 and mTOR was
found. When we evaluated the activation of p-AMPKα1 and p-mTOR
expression level, representing activation of AMPK and mTOR, was
elevated in miR-451 mimics-treated cells. Data are from one of
three representative experiments in U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cell
lines. |
Decreased miR-451 triggers the enhanced
cell motility in glioma cells
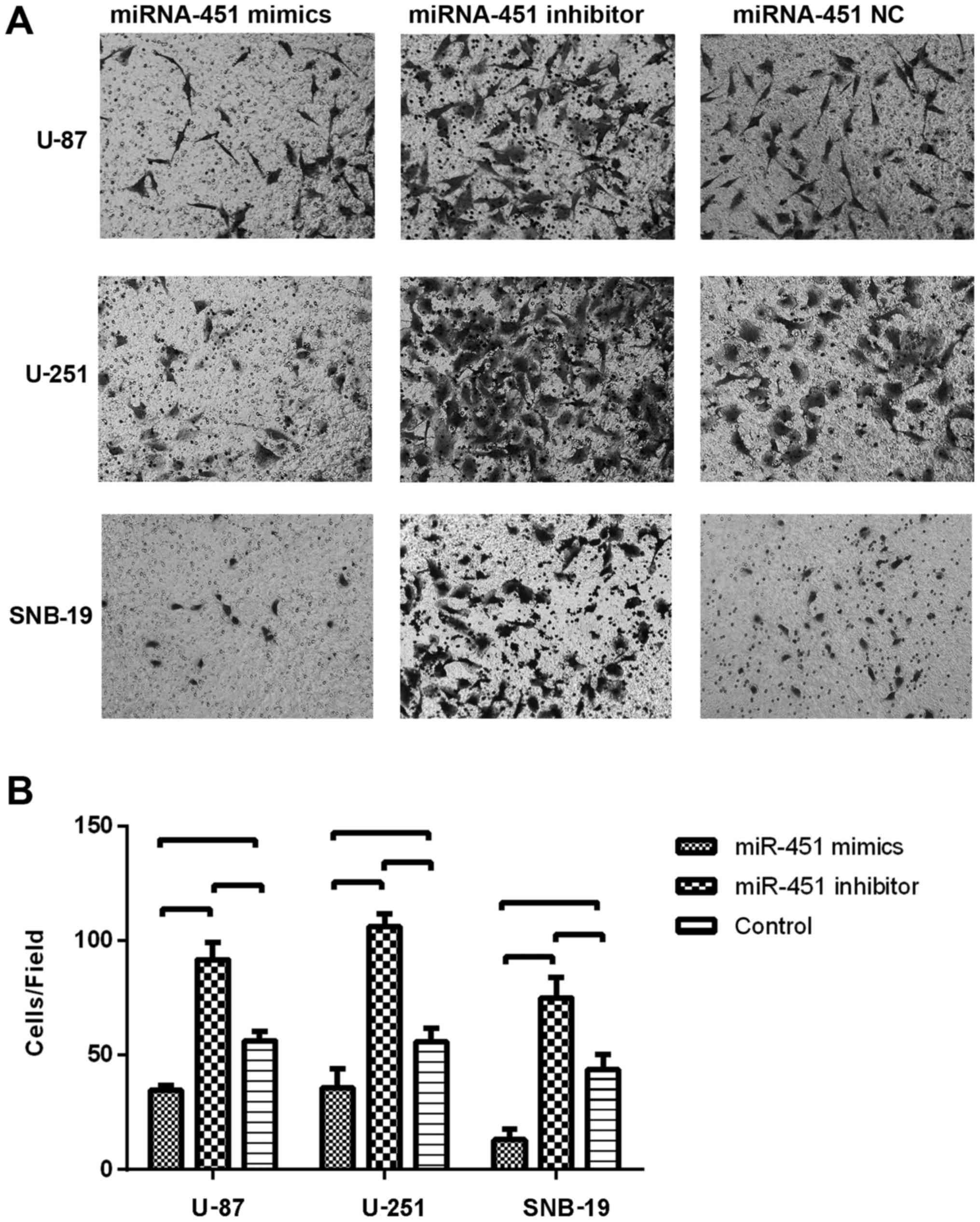
To evaluate the impact of miR-451 expression on cell
migration, the Transwell migration assay was conducted. Glioma
cells were seeded 6 h after the transfection with the miR-451
oligonucleotides. In the Transwell migration assay, we counted the
number of cells that migrated onto the Transwell chamber membrane.
The cell number counted in the synthetic miR-451-treated U-87
(34.67±2.08), U-251 (35.67±8.50) and SNB-19 (13±4.58) groups were
less than in the respective control groups (P<0.01), whereas,
the number of cells on the Transwell chamber membrane in the
miR-451 inhibitor-treated groups of U-87 (91.67±7.51), U-251
(106.00±5.57) and SNB-19 (75.00±8.89) were much greater than in the
respective control groups (P<0.01; Fig. 6B).
These results suggest that elevated miR-451 levels
in cultured glioma cells might promote cell proliferation in
vitro, while decreased miR-451 levels might trigger enhanced
cell motility.
Consequently, the fluctuation of miR-451 expression
in glioma cells appears to be associated with the phenotypic switch
between cellular proliferation and migration.
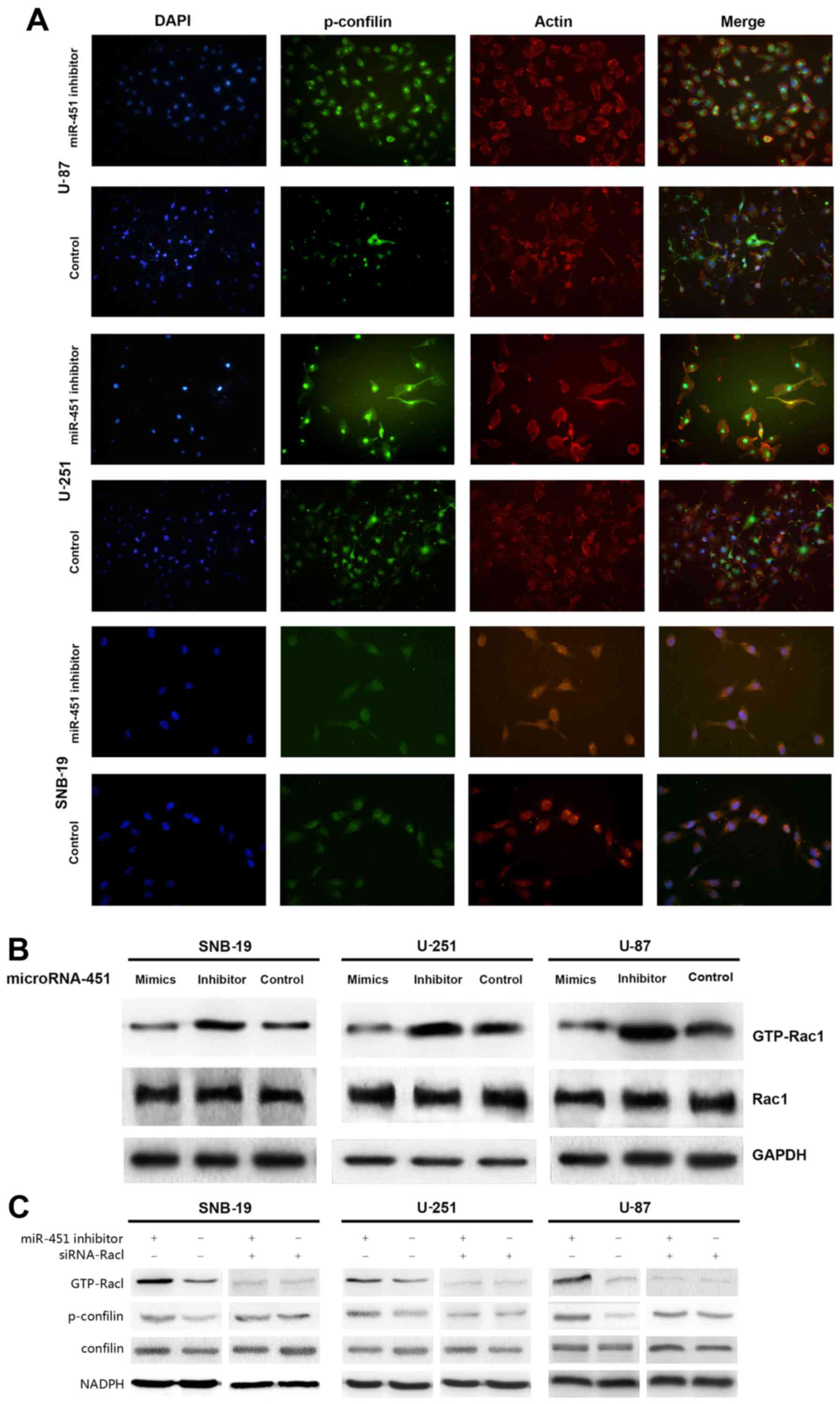
Activation of Rac1/cofilin pathway is
required for the enhanced migration of miR-451 decreased glioma
cells
We recruited the immunofluorescence and western blot
analysis to investigate lamellipodia and Rac1/confilin activation
in decreased miR-451 glioma cells. miR-451 inhibitor enhanced the
formation of lamellipodia in glioma cells increasing the
fluorescence intensity (Fig.
7A).
To determine the activation state of Rac1 after
miR-451 upregulation in glioma cells, Rac1 expression levels were
evaluated by western blotting, and the Rac1 activation assay was
utilized to analyze GTP-Rac1 expression. No significant difference
was found in Rac1 expression levels, while GTP-Rac1 expression
decreased in the synthetic miR-451-treated cells (32.76±6.31,
32.19±3.84 and 24.76±1.69% in U-87, U-251 and SNB-19 cells,
respectively) compared to the control groups (P<0.01; Fig. 7B).
siRNA-Rac1 were then transfected into the miR-451
inhibitor-treated group and control group cells separately. The
data of western blot analysis suggested that the inhibition of
miR-451 increased the the expression of p-confilin with the
activation of Rac1, whereas, siRNA-Rac1 suppressed the enhanced
activation of confilin in glioma cells with lower miR-451
expression (Fig. 7B).
In short, increased expression of miR-451 decreases
Rac1 activation, thereby regulating the dominance of downstream
Rac1-dependent pathways.
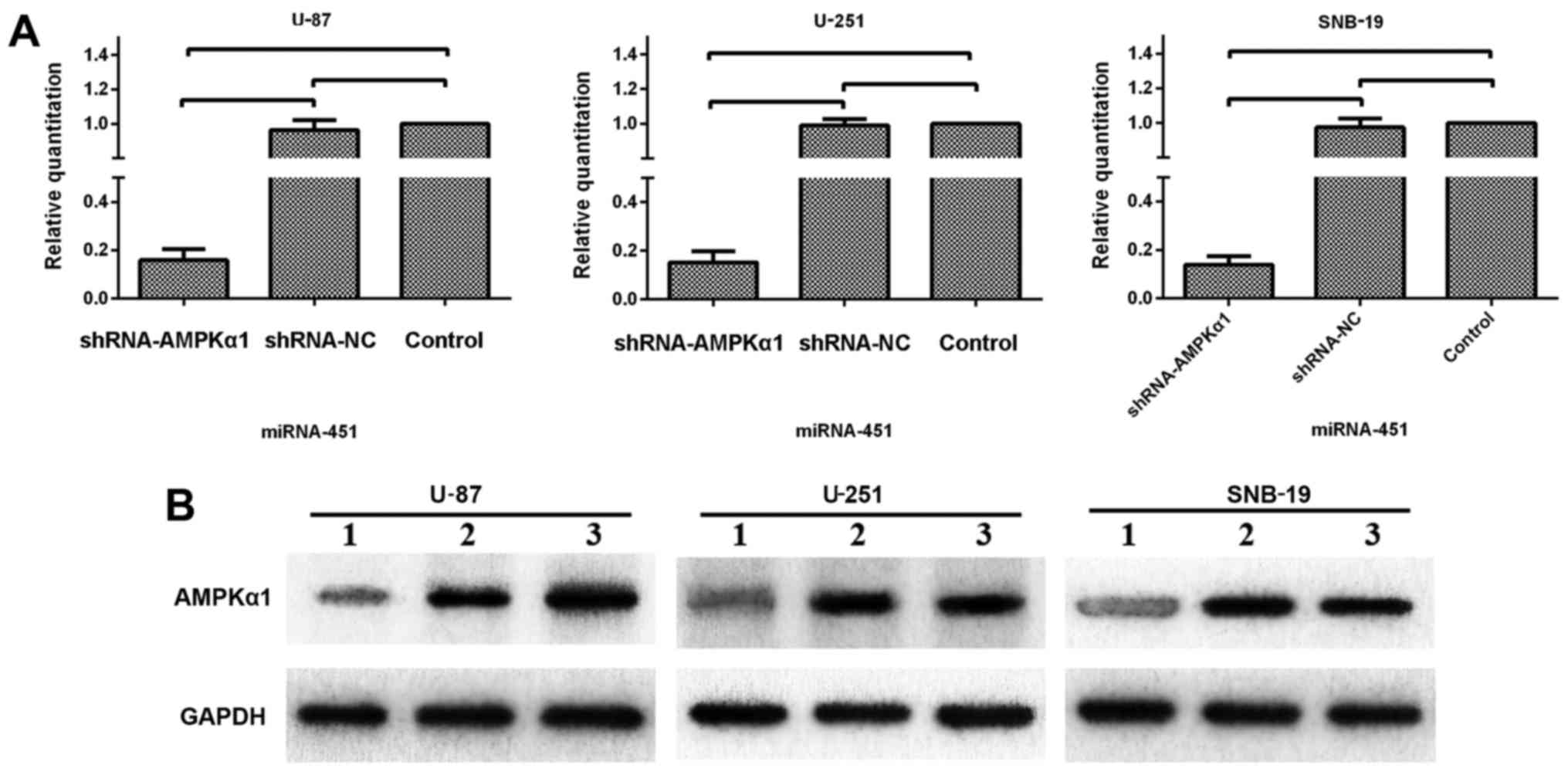
AMPK is essential for miR-451 regulation
of proliferation and migration
Considering the previous results, AMPK activation
appears to be deeply involved in the miR-451-dependent phenotypic
switch between cellular proliferation and migration in glioma
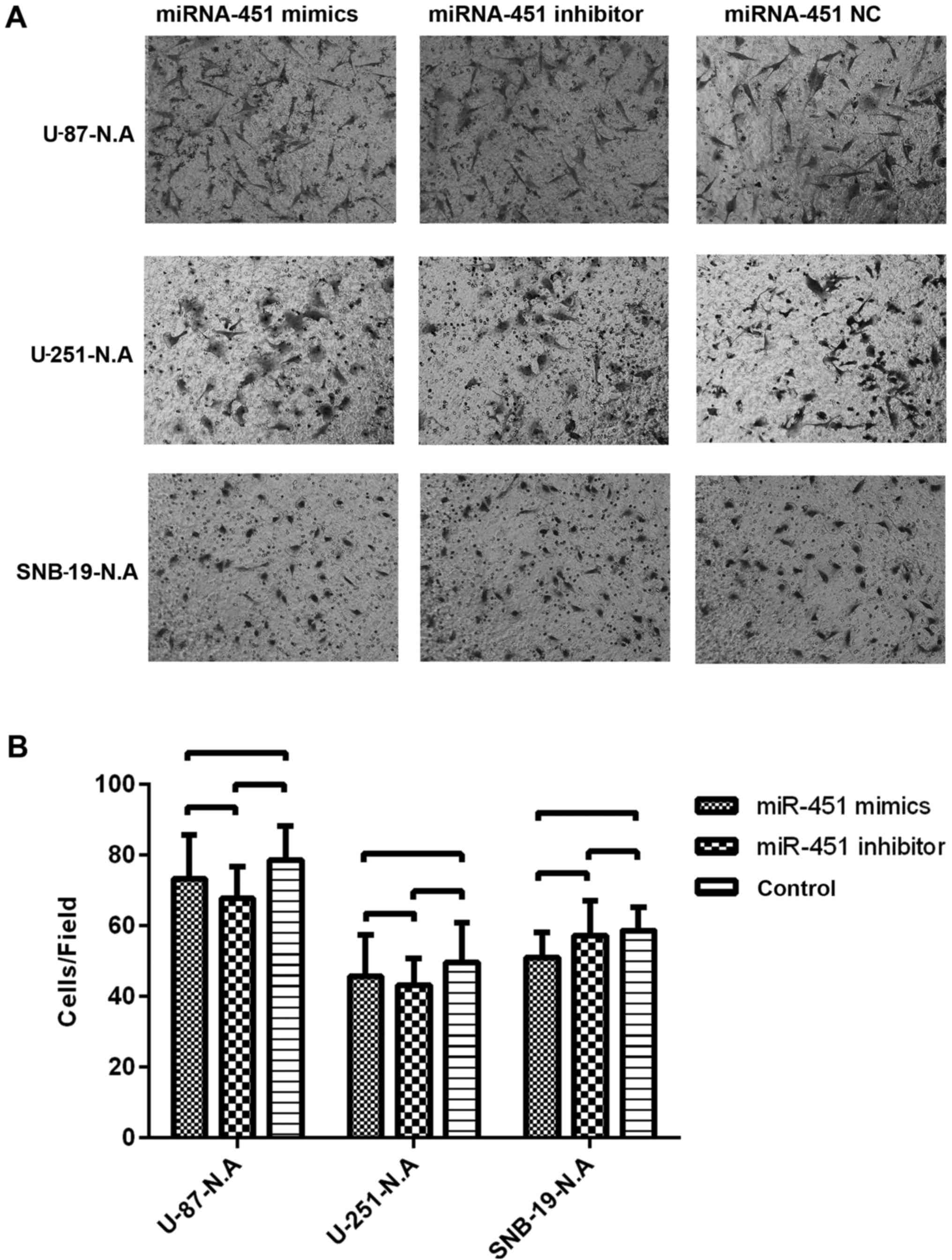
cells. As shown in Fig. 8, we used
a synthetic shRNA to knock down AMPKα1, and established three cell
line derivatives; U-87-N.A, U-251-N.A and SNB-19-N.A. qRT-PCR and
western blotting were used to test the efficiency of AMPKα1
knockdown. The mRNA expression levels of AMPKα1 in the U-87-N.A
(15.91±4.50), U-251-N.A (15.16±6.69) and SNB-19-N.A (13.81±3.75%)
cell lines were markedly decreased, as were the levels of AMPKα1
protein (26.72±5.93, 24.87±3.28 and 21.97±6.72% in U-87-N.A,
U-251-N.A and SNB-19-N.A cells, respectively), compared to the
control groups (P<0.01; Fig.
8).
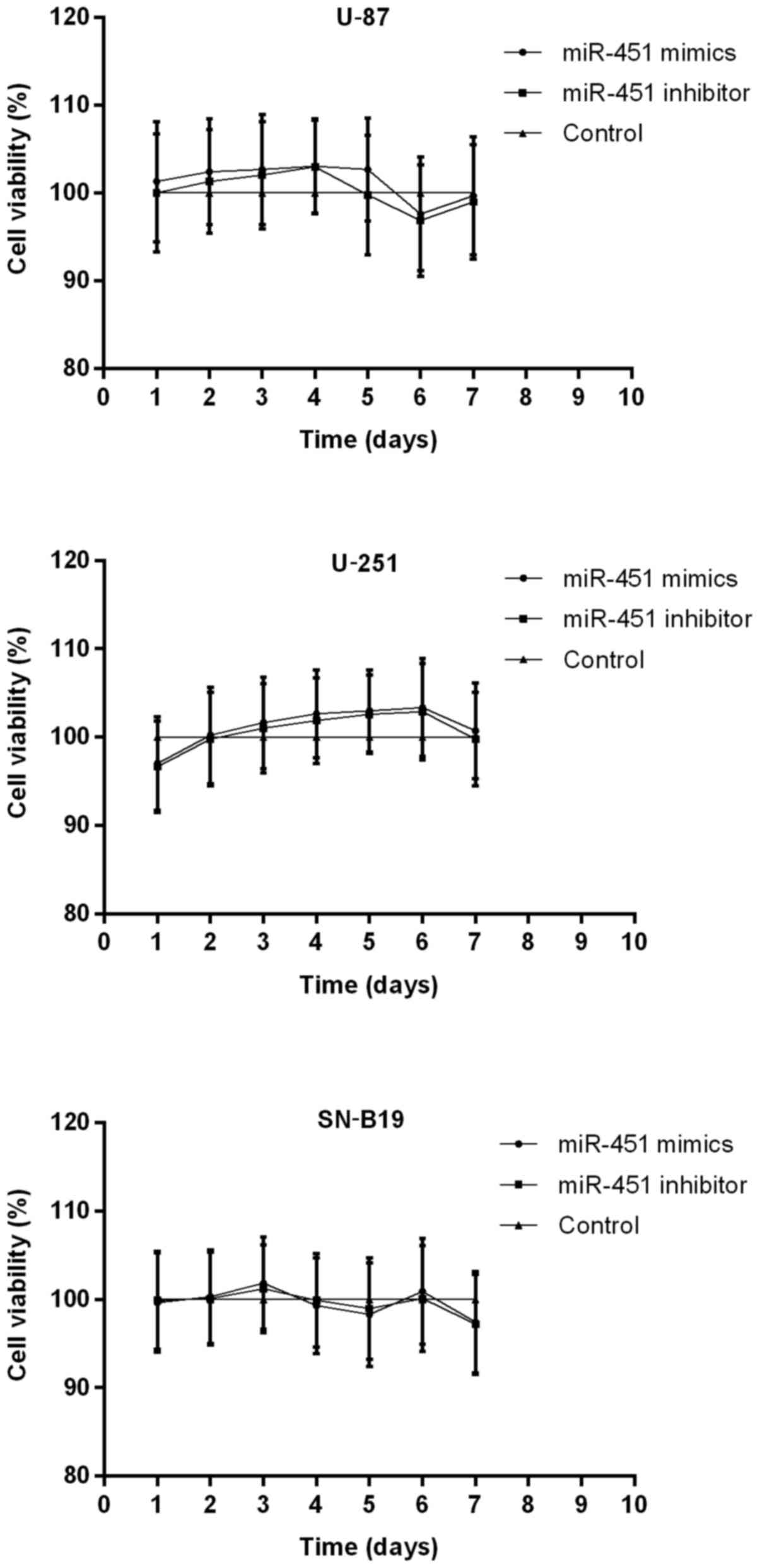
The glioma cell line derivatives were subsequently
transfected with the synthetic miR-451 or the miR-451 inhibitor
oligonucleotides. MTT assays were performed to determine the rates
of cell growth. Following treatment with synthetic miR-451, the
proliferation rate was 109.67±6.71, 104.71±5.43, and 110.46±5.73%
in U-87-N.A, U-251-N.A and SNB-19-N.A cells, respectively, compared
to the parental glioma cell lines. Moreover, following transfection
with the miR-451 inhibitor, the proliferation rate was 108.99±6.55,
103.78±5.32 and 110.21±5.68% in U-87-N.A, U-251-N.A and SNB-19-N.A
cells, respectively. These data clearly show that no significant
difference was found in the cellular growth rates between synthetic
miR-451-treated AMPKα1 knockdown cells and the respective parental
glioma cells, nor between miR-451 inhibitor-treated AMPKα1
knockdown cells and the respective parental glioma cells
(P>0.05; Fig. 9). These results
imply that miR-451 fails to regulate glioma cell proliferation in
the absence of AMPKα1, regardless of the level of miR-451
expression.
As reported previously, the migration ability of the
newly established U-87-N.A, U-251-N.A and SNB-19-N.A cell lines was
investigated. After treatment with synthetic miR-451, the number of
glioma cells migrating onto the Transwell membrane was 73.33±12.50
in U-87-N.A, 45.67±11.72 in U-251-N.A, and 51.00±7.21 in SNB-19-N.A
cells. After treatment with miR-451 inhibitor, the number of glioma
cells migrating onto the Transwell membrane was 67.67±9.07 in
U-87-N.A, 43.33±7.51 in U-251-N.A and 57.33±9.71 in SNB-19-N.A
cells. By comparison, in the control groups the number of glioma
cells migrating onto the Transwell membrane was 78.67±9.61 in
U-87-N.A, 49.67±11.24 in U-251-N.A and 58.67±6.51 in SNB-19-N.A
cells. Thus, the number of cells migrating onto the Transwell
chamber membrane showed no significant difference among the
treatment conditions (P>0.05) (Fig. 10). These results imply that
miR-451 fails to regulate glioma cell migration in the absence of
AMPKα1, regardless of the level of miR-451 expression.
miR-451 regulates activation of mTOR and
Rac1 via AMPK
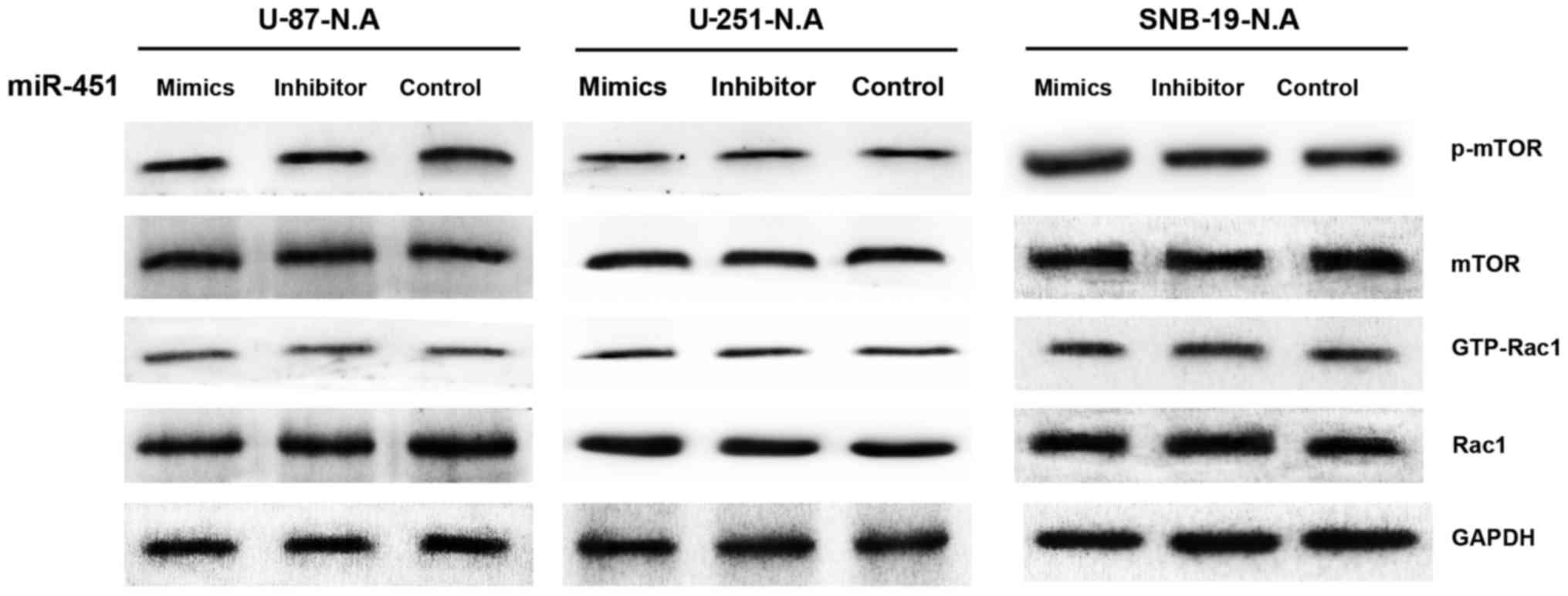
To further investigate the downstream molecular
targets in AMPK-knockdown glioma cells in response to miRNA-451
dysregulation, we examined mTOR, p-mTOR, Rac1 and GTP-Rac1
expression by western blotting in the knockdown derivative cell
lines treated with synthetic miR-451, miR-451 inhibitor, or the
control oligonucleotide. Neither mTOR nor p-mTOR protein expression
showed a significant difference in the three AMPKα1-knockdown
glioma cell lines under any treatment condition, nor did Rac1 or
GTP-Rac1 (Fig. 11). These results
imply that miR-451 fails to regulate mTOR and Rac1 activation in
glioma cells lacking AMPKα1, regardless of miR-451 expression
levels.
Discussion
The microenvironment within and around tumors is an
important determinant in the phenotype of tumor cells. The 'go or
grow' hypothesis, first described in 1996, suggests that a
dichotomy exists between cellular proliferation and motility, and
such hypothesis has been corroborated by several in vitro
studies and through mathematical modeling (8,23).
In the stereotypical environment, tumor cells have higher
proliferation rates, but when the conditions become unfavorable
(e.g., acidic pH, decreased nutrient availability, or decreased
oxygen level), cells begin to migrate away in search of better
conditions at the expense of their proliferation ability (24,25).
Thus, it seems that the preference between proliferation or
migration is driven by microenvironmental conditions and is an
intrinsic property of tumor cells, largely complying with the law
of macroecology, similar to the migration of human beings.
Antiangiogenic GBM therapy with bevacizumab is a good example to
demonstrate the relationship between a harsh microenvironment and
the migration of tumor cells. de Groot et al (26) noted an apparent phenotypic shift to
a predominantly infiltrative pattern of tumor progression after
treatment with bevacizumab.
Because miR-451 was reported to have a prominent
role in glioma, a study of miR profiles in glioblastoma cell lines,
GBM tissue, and brain tissue showed that miR-451 had reduced
expression levels in GBM compared to normal brain tissues (11). In fact, the microenvironment is
also heterogeneous within a tumor. Microenvironmental conditions in
the center of a GBM tumor are harsher compared to the periphery of
the tumor. In the central hypoxic-hypoglycemic microenvironment,
the growth of tumor cells is inhibited, and necrosis is apparent,
while in the peripheral portions of the tumor, the survival of
tumor cells is enhanced, and the tumor cells actively proliferate
and infiltrate into the surrounding parenchyma. In the present
study, we compared miR-451 expression not only between tumor tissue
and control brain tissue but also between central and peripheral
tissues of GBM tumors. We found that miR-451 expression was lower
in central regions and higher in peripheral regions through the
qRT-PCR analysis, a result indicating that miR-451 expression is
also heterogeneous, acting in coordination with the
microenvironmental heterogeneity. The results further emphasized
that miR451 expression is regulated by the microenvironmental
conditions and is related to the phenotypic switch between cellular
proliferation and migration.
In our in vitro study, miR-451 levels were
elevated or reduced in GBM cell lines following transfection with
synthetic miR-451 or miR-451 inhibitor, respectively. We confirmed
that the higher miR-451 level in the glioma cells could facilitate
cellular proliferation while suppressing migration; in contrast,
lower miR-451 levels promoted cell migration while suppressing
cellular proliferation. In fact, miR-451 regulates the 'go or grow'
biological behavior of tumor cells by epigenetic mechanisms.
Understanding the downstream signaling pathways and identifying the
master regulator controlling the phenotypic switch is essential to
determine the utility of these therapeutic targets in clinical
applications.
AMPK is a highly conserved sensor of cellular energy
status in eukaryotes and is known as a regulator of cellular
metabolism (27). It consists of a
hetero-trimetric complex of two regulatory β/γ subunits and a
single catalytic α subunit (28,29).
AMPK is activated in response to an increase in the ratio of AMP to
ATP within the cell and is phosphorylated at Thr172 within the
activation domain of the α subunit by upstream kinases LKB1
(30–32) and calmodulin dependent protein
kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ) (6,33–35).
Under suitable conditions, normal or upregulated levels of miR-451
suppress the activation of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via downregulation
of CAB39 expression. As a consequence, cellular proliferation is
promoted because of unrestricted activity from mTORC1, an essential
factor linking growth factor abundance to cell growth and
proliferation (36). Godlewski
et al (21) showed that the
concentration of glucose in the microenvironment of glioma tumors
is one of the triggers of this cascade.
In the present study, we found that upregulation of
miR-451 suppressed the activation of the AMPK/mTOR pathway via
downregulation of CAB39 expression, while downregulation of miR-451
facilitated the activation of the AMPK/mTOR pathway via increased
expression of CAB39. The mechanism of miR-451/AMPK-mediated
migration in glioma cells is not fully understood and is evident in
the finding of Rac1 activation in both upregulated or downregulated
miR-451 scenarios in the present study.
Cell migration begins with an initial protrusion or
extension of the plasma membrane at the leading edge of the cell.
The protrusion is driven by the polymerization of a network of
cytoskeletal actin filaments and is stabilized through the
formation of an adhesive complex (37). Rac1, a highly expressed protein in
glioma and glioma stem cells, promotes cell spreading, lamellipodia
formation and cell migration. Its activation and phosphorylation,
the regulatory mechanism of Rho GTPase activation, are independent
of GDP-GTP cycling (38,39). It is therefore possible that the
activation of small GTPases or regulatory proteins of small
GTPases, such as guanine nucleotide exchange factors, GDP
dissociation inhibitors, and GTPase activating proteins could be
promoted by the phosphorylation or activation of AMPK. Our data
indicate a role for the miR-451/AMPK/Rac1 pathway in glioma cell
migration.
At this time, we propose that miR-451 may function
in glioma cells to control the phenotypic switch between
proliferation and migration through AMPK/mTOR or AMPK/Rac1
activation. Whether AMPK plays the pivotal role in this process,
activating mTOR and stimulating cellular proliferation or
activating Rac1 and stimulating migration required further
investigation. We found that RNAi knockdown of AMPK expression in
glioma cells prevented miR-451-mediated regulation of mTOR and Rac1
activation, and also prevented the typical pattern of cellular
proliferation or migration of glioma cells. These findings indicate
that AMPKα1 involvement is essential in the miR-451-mediated
regulation of proliferation and migration of glioma cells in
response to the tumor micro-environment.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that miR-451 is
down-regulated in GBM tissues, especially in the central regions of
glioma tissues, compared to control brain tissues. The inclination
toward proliferation or migration of glioma cells is influenced by
the expression level of miR-451. By regulating the activity of
AMPK, the master regulator in the downstream pathway, miR-451,
reconfigures the activation of mTOR and Rac1, which play key roles
in cellular proliferation and migration in glioma cells,
respectively and enables cells to adapt to microenvironmental
conditions in the tumor. This study demonstrates that any
therapeutic target aimed to suppress proliferation of tumor cells
should be carefully examined for potential roles in cell
infiltration. In the case of GMB, reducing AMPK expression,
compared to simply inhibiting AMPK activity, produces more
desirable global effects that disrupt the regulation of mTOR and
Rac1 activation.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by grants from the
National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81472352, no.
81272782 and no. 81502171), Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin
City (no. 15JCZDJC36200) and Science Projects of Logistics
University of The Chinese People's Armed Police Force
(WHJ2016027).
References
|
1
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK,
Kernie SG and Parada LF: A restricted cell population propagates
glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 488:522–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Westermark B: Glioblastoma: a moving
target. Ups J Med Sci. 117:251–256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME and
Westphal M: Cost of migration: Invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 21:1624–1636. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans
J and Wick W: Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and
invasiveness of glioma cells: Implications for radiotherapy of
human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 61:2744–2750. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Nicolantonio F, Mercer SJ, Knight LA,
Gabriel FG, Whitehouse PA, Sharma S, Fernando A, Glaysher S, Di
Palma S, Johnson P, et al: Cancer cell adaptation to chemotherapy.
BMC Cancer. 5:782005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: New insights of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 40:643–650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hatzikirou H, Basanta D, Simon M, Schaller
K and Deutsch A: 'Go or grow': the key to the emergence of invasion
in tumour progression? Math Med Biol. 29:49–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Zhang X, Xiang J, Lv Y and Shi J:
miR-451: Potential role as tumor suppressor of human hepatoma cell
growth and invasion. Int J Oncol. 45:739–745. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nan Y, Han L, Zhang A, Wang G, Jia Z, Yang
Y, Yue X, Pu P, Zhong Y and Kang C: MiRNA-451 plays a role as tumor
suppressor in human glioma cells. Brain Res. 1359:14–21. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK,
Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP and Bartel DP: MicroRNA targeting
specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell.
27:91–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hatziapostolou M and Iliopoulos D:
Epigenetic aberrations during oncogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
68:1681–1702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: microRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Dutta A and Abounader R: The role
of microRNAs in glioma initiation and progression. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 17:700–712. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gits CM, van Kuijk PF, Jonkers MB, Boersma
AW, Smid M, van Ijcken WF, Coindre JM, Chibon F, Verhoef C,
Mathijssen RH, et al: MicroRNA expression profiles distinguish
liposarcoma subtypes and implicate miR-145 and miR-451 as tumor
suppressors. Int J Cancer. 135:348–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu D, Liu C, Wang X, Ingvarsson S and
Chen H: MicroRNA-451 suppresses tumor cell growth by
down-regulating IL6R gene expression. Cancer Epidemiol. 38:85–92.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A, Nuovo
G, Palatini J, De Lay M, Van Brocklyn J, Ostrowski MC, Chiocca EA
and Lawler SE: MicroRNA-451 regulates LKB1/AMPK signaling and
allows adaptation to metabolic stress in glioma cells. Mol Cell.
37:620–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Azab AK, Azab F, Blotta S, Pitsillides CM,
Thompson B, Runnels JM, Roccaro AM, Ngo HT, Melhem MR, Sacco A, et
al: RhoA and Rac1 GTPases play major and differential roles in
stromal cell-derived factor-1-induced cell adhesion and chemo-taxis
in multiple myeloma. Blood. 114:619–629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giese A, Loo MA, Tran N, Haskett D, Coons
SW and Berens ME: Dichotomy of astrocytoma migration and
proliferation. Int J Cancer. 67:275–282. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tamaki M, McDonald W, Amberger VR, Moore E
and Del Maestro RF: Implantation of C6 astrocytoma spheroid into
collagen type I gels: Invasive, proliferative, and enzymatic
char-acterizations. J Neurosurg. 87:602–609. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu SP, Yang XJ, Zhang B, Ming HL, Chen C,
Ren BC, Liu ZF and Liu B: Enhanced invasion in vitro and the
distribution patterns in vivo of CD133+ glioma stem
cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:2599–2604. 2011.
|
|
26
|
de Groot JF, Fuller G, Kumar AJ, Piao Y,
Eterovic K, Ji Y and Conrad CA: Tumor invasion after treatment of
glioblastoma with bevacizumab: Radiographic and pathologic
correlation in humans and mice. Neuro Oncol. 12:233–242. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated/SNF1 protein
kinases: Conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:774–785. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hardie DG and Carling D: The AMP-activated
protein kinase: Fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem.
246:259–273. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hardie DG, Scott JW, Pan DA and Hudson ER:
Management of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase
system. FEBS Lett. 546:113–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carling D: The AMP-activated protein
kinase cascade - a unifying system for energy control. Trends
Biochem Sci. 29:18–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hardie DG: The AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway - new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci.
117:5479–5487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hawley SA, Pan DA, Mustard KJ, Ross L,
Bain J, Edelman AM, Frenguelli BG and Hardie DG:
Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta is an alternative
upstream kinase for AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Metab.
2:9–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hurley RL, Anderson KA, Franzone JM, Kemp
BE, Means AR and Witters LA: The
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinases are
AMP-activated protein kinase kinases. J Biol Chem. 280:29060–29066.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Woods A, Dickerson K, Heath R, Hong SP,
Momcilovic M, Johnstone SR, Carlson M and Carling D:
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta
acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells.
Cell Metab. 2:21–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan QW, Cheng C, Knight ZA, Haas-Kogan D,
Stokoe D, James CD, McCormick F, Shokat KM and Weiss WA: EGFR
signals to mTOR through PKC and independently of Akt in glioma. Sci
Signal. 2:ra42009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Horwitz AR and Parsons JT: Cell migration:
'movin' on. Science. 286:1102–1103. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Forget MA, Desrosiers RR, Gingras D and
Béliveau R: Phosphorylation states of Cdc42 and RhoA regulate their
interactions with Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor and their
extraction from biological membranes. Biochem J. 361:243–254. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang B, Sun J, Yu SP, Chen C, Liu B, Liu
ZF, Ren BC, Ming HL and Yang XJ: Rac1 cells distributed in
accordance with CD 133 cells in glioblastomas and the elevated
invasiveness of CD 133 glioma cells with higher Rac1 activity. Chin
Med J. 125:4344–4348. 2012.
|