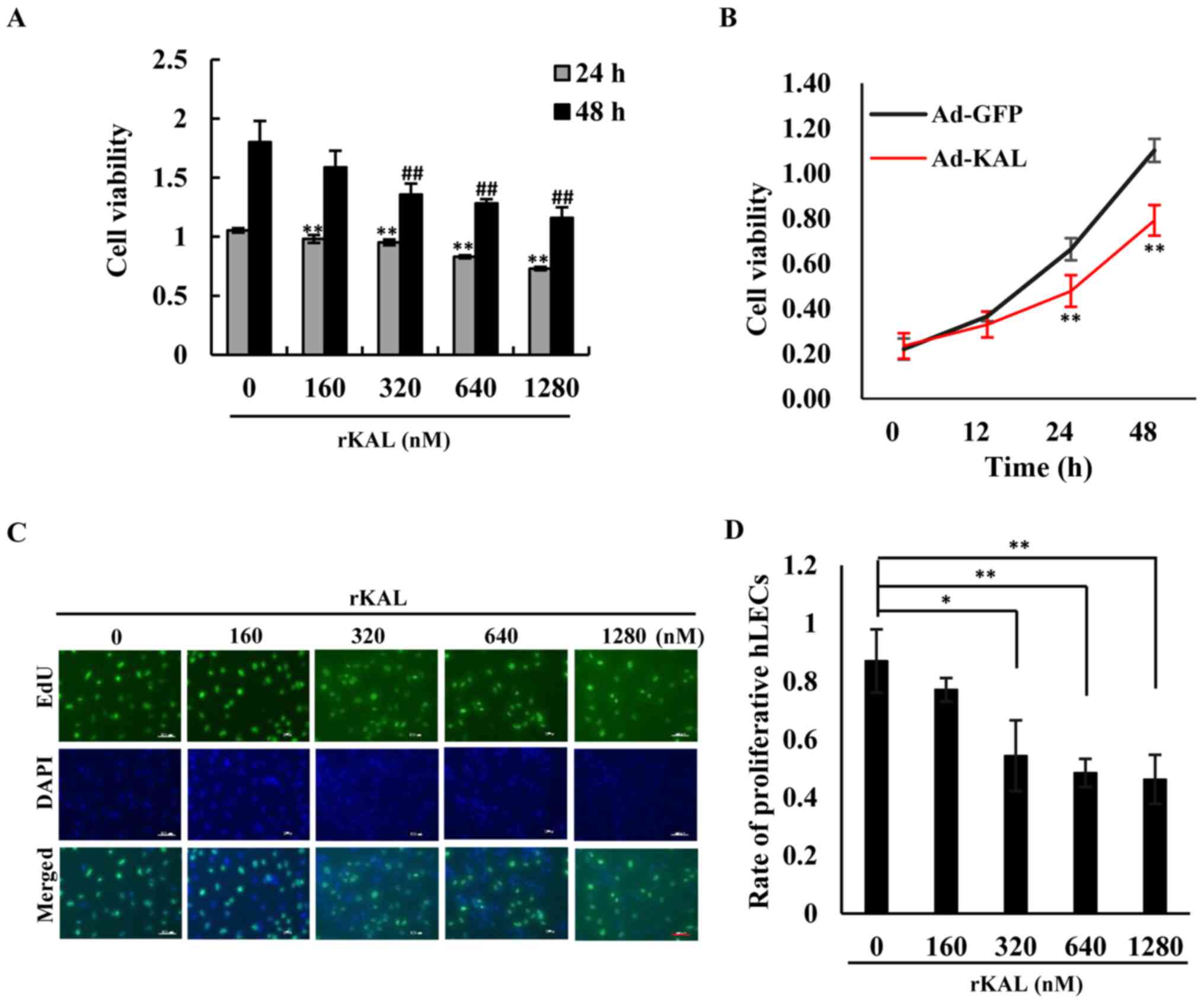
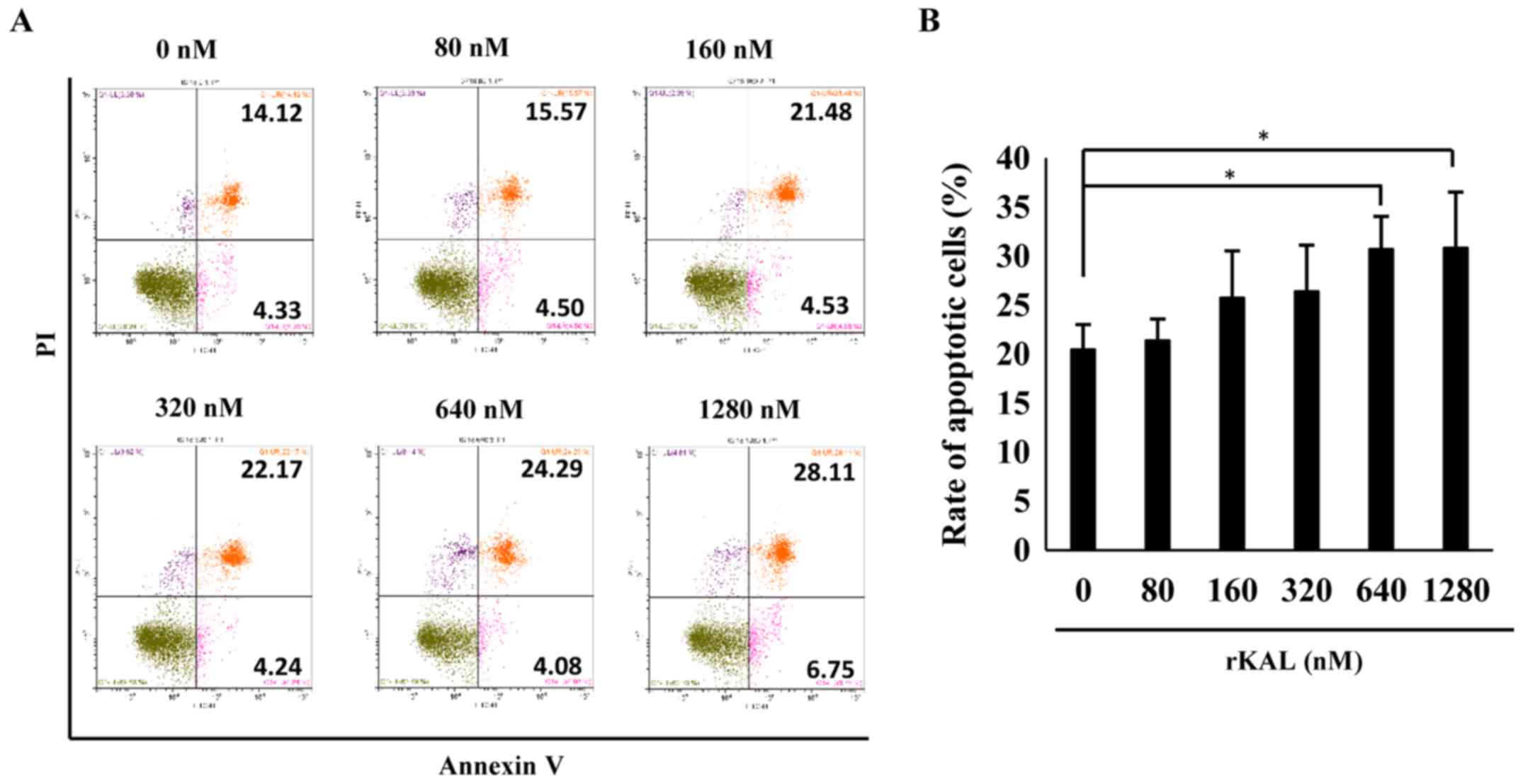
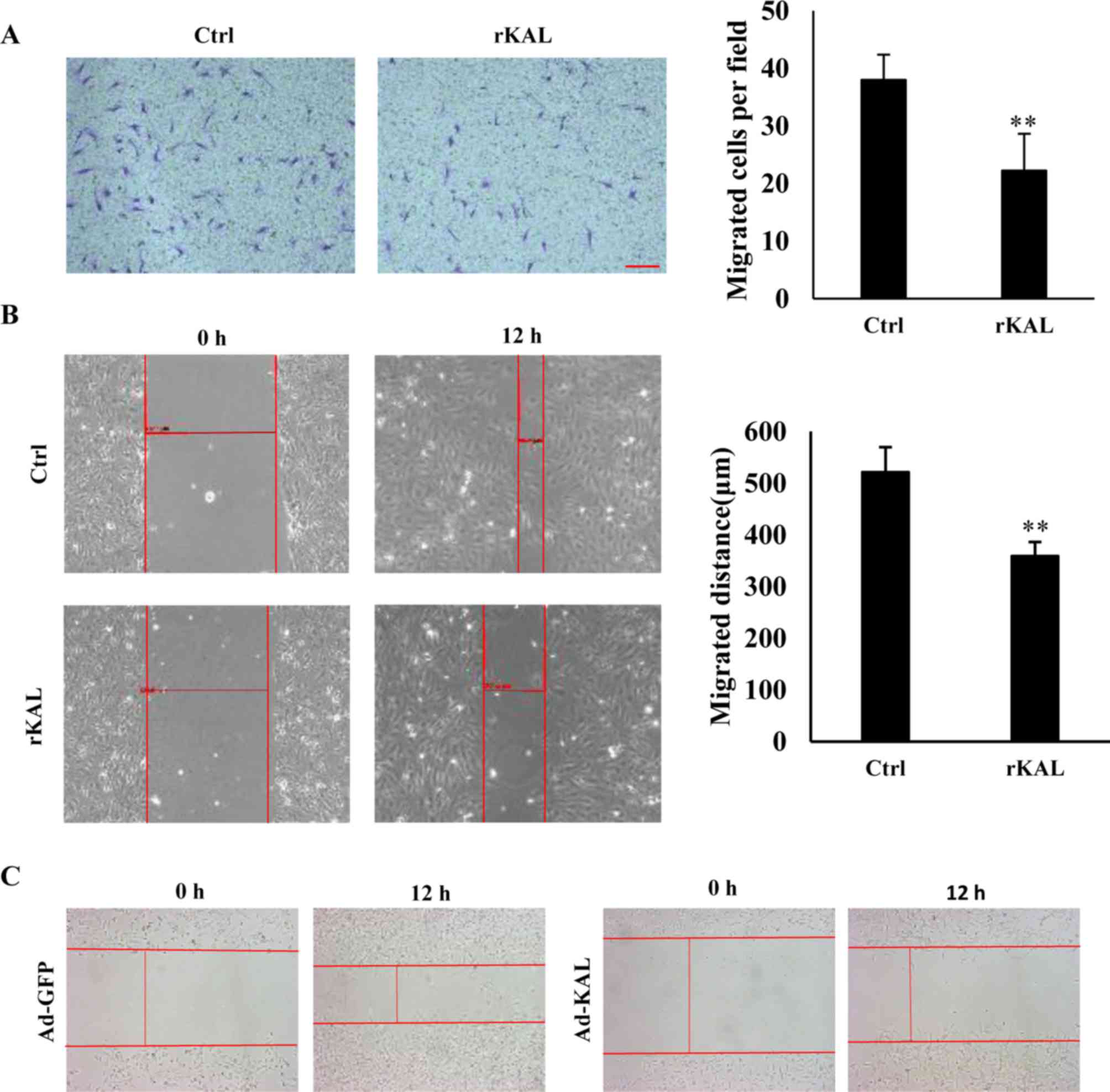
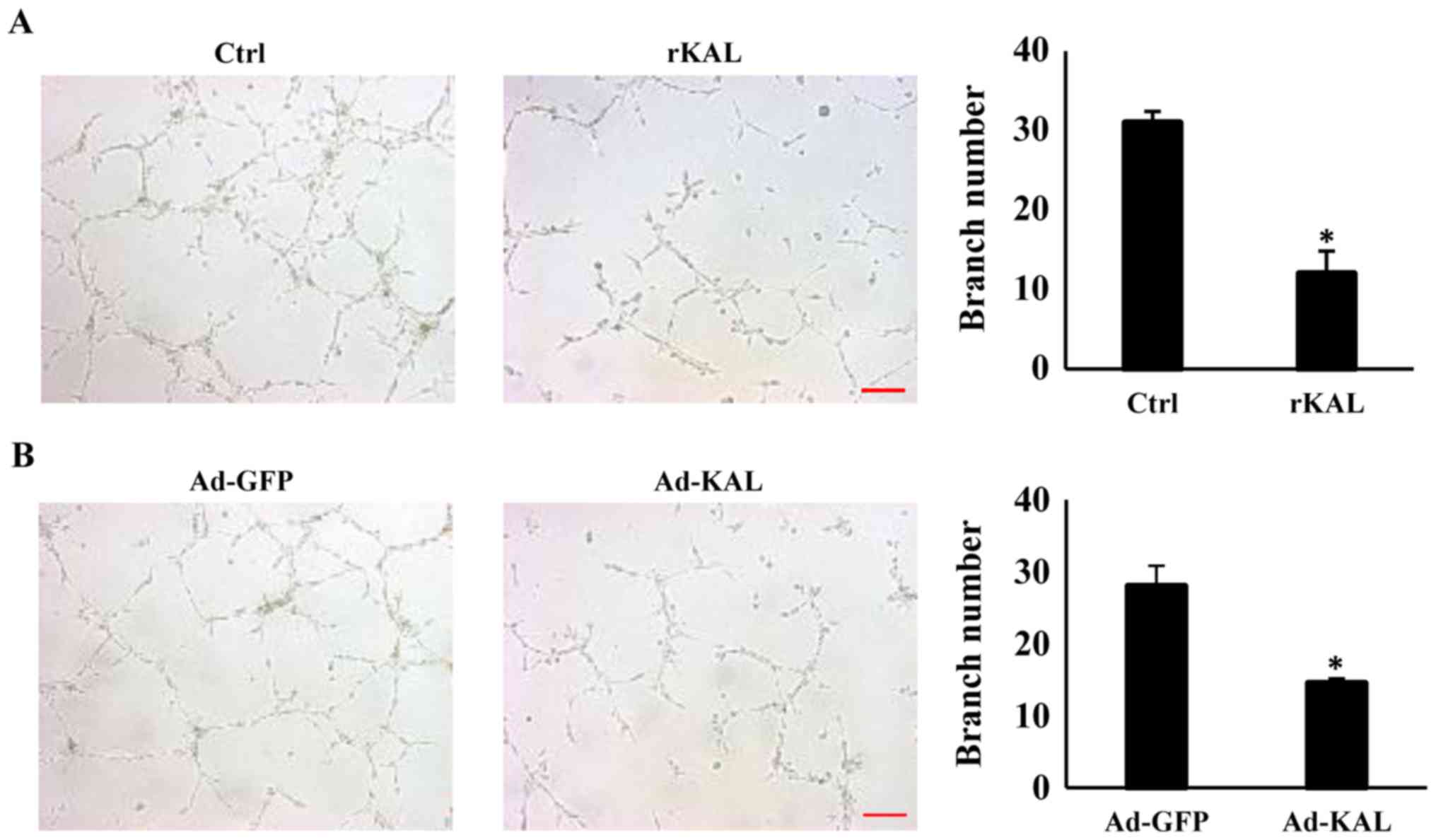
|
1
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stacker SA, Williams SP, Karnezis T,
Shayan R, Fox SB and Achen MG: Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic
vessel remodelling in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:159–172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoshimatsu Y, Miyazaki H and Watabe T:
Roles of signaling and transcriptional networks in pathological
lymphangiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99B:161–171. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Lin C, Liang W, Wu S, Liu A, Wu J,
Zhang X, Ren P, Li M and Song L: TBL1XR1 promotes lymphangiogenesis
and lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gut. 64:26–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hirakawa S: From tumor lymphangiogenesis
to lymphvascular niche. Cancer Sci. 100:983–989. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dadras SS, Paul T, Bertoncini J, Brown LF,
Muzikansky A, Jackson DG, Ellwanger U, Garbe C, Mihm MC and Detmar
M: Tumor lymphangiogenesis: A novel prognostic indicator for
cutaneous melanoma metastasis and survival. Am J Pathol.
162:1951–1960. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He Y, Rajantie I, Pajusola K, Jeltsch M,
Holopainen T, Yla-Herttuala S, Harding T, Jooss K, Takahashi T and
Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor
3-mediated activation of lymphatic endothelium is crucial for tumor
cell entry and spread via lymphatic vessels. Cancer Res.
65:4739–4746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo
H, Ylä-Herttuala S, Jäättelä M and Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial
growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and
intra-lymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 61:1786–1790.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karnezis T, Shayan R, Caesar C, Roufail S,
Harris NC, Ardipradja K, Zhang YF, Williams SP, Farnsworth RH, Chai
MG, et al: VEGF-D promotes tumor metastasis by regulating
prostaglandins produced by the collecting lymphatic endothelium.
Cancer Cell. 21:181–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang MY, Day J, Chao L and Chao J: Human
kallistatin, a new tissue kallikrein-binding protein: Purification
and characterization. Adv Exp Med Biol. 247B:1–8. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chao J and Chao L: Biochemistry,
regulation and potential function of kallistatin. Biol Chem Hoppe
Seyler. 376:705–713. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao RQ, Murakami H, Song Q, Chao L and
Chao J: Kallistatin stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration in vitro and neointima formation in
balloon-injured rat artery. Circ Res. 86:418–424. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao J, Miao RQ, Chen V, Chen LM and Chao
L: Novel roles of kallistatin, a specific tissue kallikrein
inhibitor, in vascular remodeling. Biol Chem. 382:15–21. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miao RQ, Agata J, Chao L and Chao J:
Kallistatin is a new inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth.
Blood. 100:3245–3252. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stadnicki A, Mazurek U, Plewka D and
Wilczok T: Intestinal tissue kallikrein-kallistatin profile in
inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 3:939–944. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chao J, Yin H, Yao YY, Shen B, Smith RS Jr
and Chao L: Novel role of kallistatin in protection against
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing apoptosis and
inflammation. Hum Gene Ther. 17:1201–1213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shen B, Hagiwara M, Yao YY, Chao L and
Chao J: Salutary effect of kallistatin in salt-induced renal
injury, inflammation, and fibrosis via antioxidative stress.
Hypertension. 51:1358–1365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen B, Gao L, Hsu YT, Bledsoe G, Hagiwara
M, Chao L and Chao J: Kallistatin attenuates endothelial apoptosis
through inhibition of oxidative stress and activation of Akt-eNOS
signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 299:H1419–H1427. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu SL, Tsai CY, Luo YH, Kuo CF, Lin WC,
Chang YT, Wu JJ, Chuang WJ, Liu CC, Chao L, et al: Kallistatin
modulates immune cells and confers anti-inflammatory response to
protect mice from group A streptococcal infection. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 57:5366–5372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li P, Bledsoe G, Yang ZR, Fan H, Chao L
and Chao J: Human kallistatin administration reduces organ injury
and improves survival in a mouse model of polymicrobial sepsis.
Immunology. 142:216–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li P, Guo Y, Bledsoe G, Yang Z, Chao L and
Chao J: Kallistatin induces breast cancer cell apoptosis and
autophagy by modulating Wnt signaling and microRNA synthesis. Exp
Cell Res. 340:305–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yiu WH, Wong DW, Wu HJ, Li RX, Yam I, Chan
LY, Leung JC, Lan HY, Lai KN and Tang SC: Kallistatin protects
against diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by suppressing
AGE-RAGE-induced oxidative stress. Kidney Int. 89:386–398. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Diao Y, Ma J, Xiao WD, Luo J, Li XY, Chu
KW, Fung P, Habib N, Farzaneh F and Xu RA: Inhibition of
angiogenesis and HCT-116 xenograft tumor growth in mice by
kallistatin. World J Gastroenterol. 13:4615–4619. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang KF, Huang XP, Xiao GQ, Yang HY, Lin
JS and Diao Y: Kallistatin, a novel anti-angiogenesis agent,
inhibits angiogenesis via inhibition of the NF-κB signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:455–461. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang KF, Yang HY, Xing YM, Lin JS and
Diao Y: Recombinant human kallistatin inhibits angiogenesis by
blocking VEGF signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 115:575–584. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun HM, Mi YS, Yu FD, Han Y, Liu XS, Lu S,
Zhang Y, Zhao SL, Ye L, Liu TT, et al: SERPINA4 is a novel
independent prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target
for colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1636–1649.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Scavelli C, Weber E, Aglianò M, Cirulli T,
Nico B, Vacca A and Ribatti D: Lymphatics at the crossroads of
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. J Anat. 204:433–449. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scavelli C, Vacca A, Di Pietro G, Dammacco
F and Ribatti D: Crosstalk between angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis in tumor progression. Leukemia. 18:1054–1058.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Van den Eynden GG, Van der Auwera I, Van
Laere SJ, Trinh XB, Colpaert CG, van Dam P, Dirix LY, Vermeulen PB
and Van Marck EA: Comparison of molecular determinants of
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in lymph node metastases and in
primary tumours of patients with breast cancer. J Pathol.
213:56–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Adams RH and Alitalo K: Molecular
regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:464–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garmy-Susini B and Varner JA: Roles of
integrins in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Lymphat Res
Biol. 6:155–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gomes FG, Nedel F, Alves AM, Nör JE and
Tarquinio SB: Tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis:
Tumor/endothelial crosstalk and cellular/microenvironmental
signaling mechanisms. Life Sci. 92:101–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Sasahira T, Ueda N, Yamamoto K, Kurihara
M, Matsushima S, Bhawal UK, Kirita T and Kuniyasu H: Prox1 and
FOXC2 act as regulators of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e925342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Riabov V, Gudima A, Wang N, Mickley A,
Orekhov A and Kzhyshkowska J: Role of tumor associated macrophages
in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Front Physiol.
5:752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Escobedo N and Oliver G:
Lymphangiogenesis: Origin, specification, and cell fate
determination. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 32:677–691. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Corliss BA, Azimi MS, Munson JM, Peirce SM
and Murfee WL: Macrophages: An inflammatory link between
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Microcirculation. 23:95–121.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Paduch R: The role of lymphangiogenesis
and angiogenesis in tumor metastasis. Cell Oncol. 39:397–410. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Orellana C: Is lymphangiogenesis as
important as angiogenesis? Lancet Oncol. 6:2652005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu B, Lu L, Cai W, Yang X, Li C, Yang Z,
Zhan W, Ma JX and Gao G: Kallikrein-binding protein inhibits growth
of gastric carcinoma by reducing vascular endothelial growth factor
production and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:3297–3306. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tammela T and Alitalo K:
Lymphangiogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell.
140:460–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Morabito A, De Maio E, Di Maio M, Normanno
N and Perrone F: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors of vascular endothelial
growth factor receptors in clinical trials: Current status and
future directions. Oncologist. 11:753–764. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA,
et al TARGET Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu S, Chen JJ, Kudelka A, Lu J and Zhu X:
Incidence and risk of hypertension with sorafenib in patients with
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol.
9:117–123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Demetri GD, Reichardt P, Kang YK, Blay JY,
Rutkowski P, Gelderblom H, Hohenberger P, Leahy M, von Mehren M,
Joensuu H, et al GRID study investigators: Efficacy and safety of
regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after
failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): An international,
multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
381:295–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, Siena
S, Falcone A, Ychou M, Humblet Y, Bouché O, Mineur L, Barone C, et
al CORRECT Study Group: Regorafenib monotherapy for previously
treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international,
multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
381:303–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang W, Sukamotoh E, Xiao H and Zhang G:
Curcumin inhibits lymphangiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 59:2345–2354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W,
Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH and Cheng JQ: Advances of AKT pathway in
human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:2–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tan L, Song X, Sun X, Wang N, Qu Y and Sun
Z: ART3 regulates triple-negative breast cancer cell function via
activation of Akt and ERK pathways. Oncotarget. 7:46589–46602.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kaliszczak M, Trousil S, Ali T and Aboagye
EO: AKT activation controls cell survival in response to HDAC6
inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D'Alessio A,
Pergameno M and Normanno N: The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT
signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications
for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16(Suppl 2):
S17–S27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gao L, Li P, Zhang J, Hagiwara M, Shen B,
Bledsoe G, Chang E, Chao L and Chao J: Novel role of kallistatin in
vascular repair by promoting mobility, viability, and function of
endothelial progenitor cells. J Am Heart Assoc. 3:e0011942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gao G, Shao C, Zhang SX, Dudley A, Fant J
and Ma JX: Kallikrein-binding protein inhibits retinal
neovascularization and decreases vascular leakage. Diabetologia.
46:689–698. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|