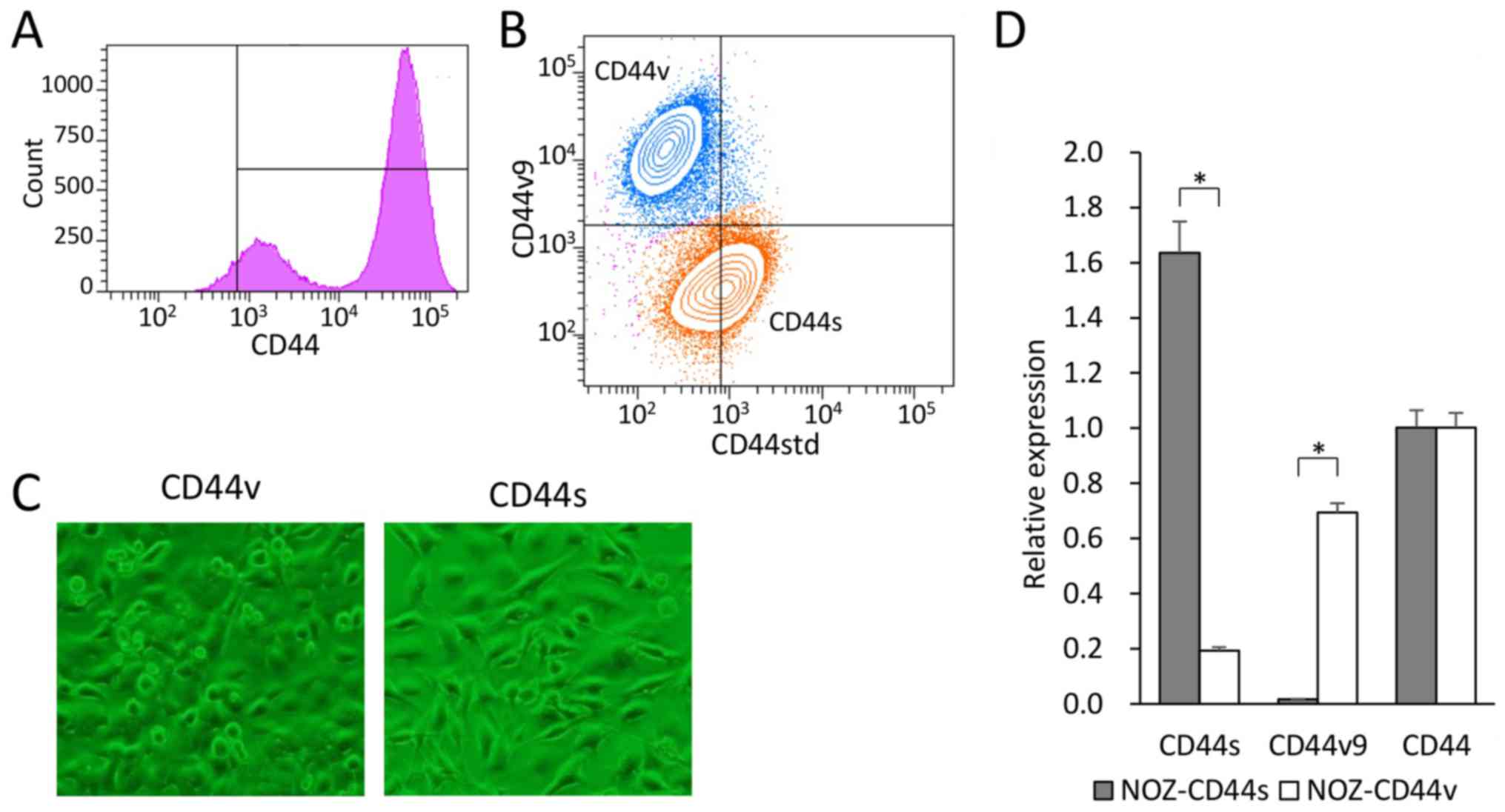
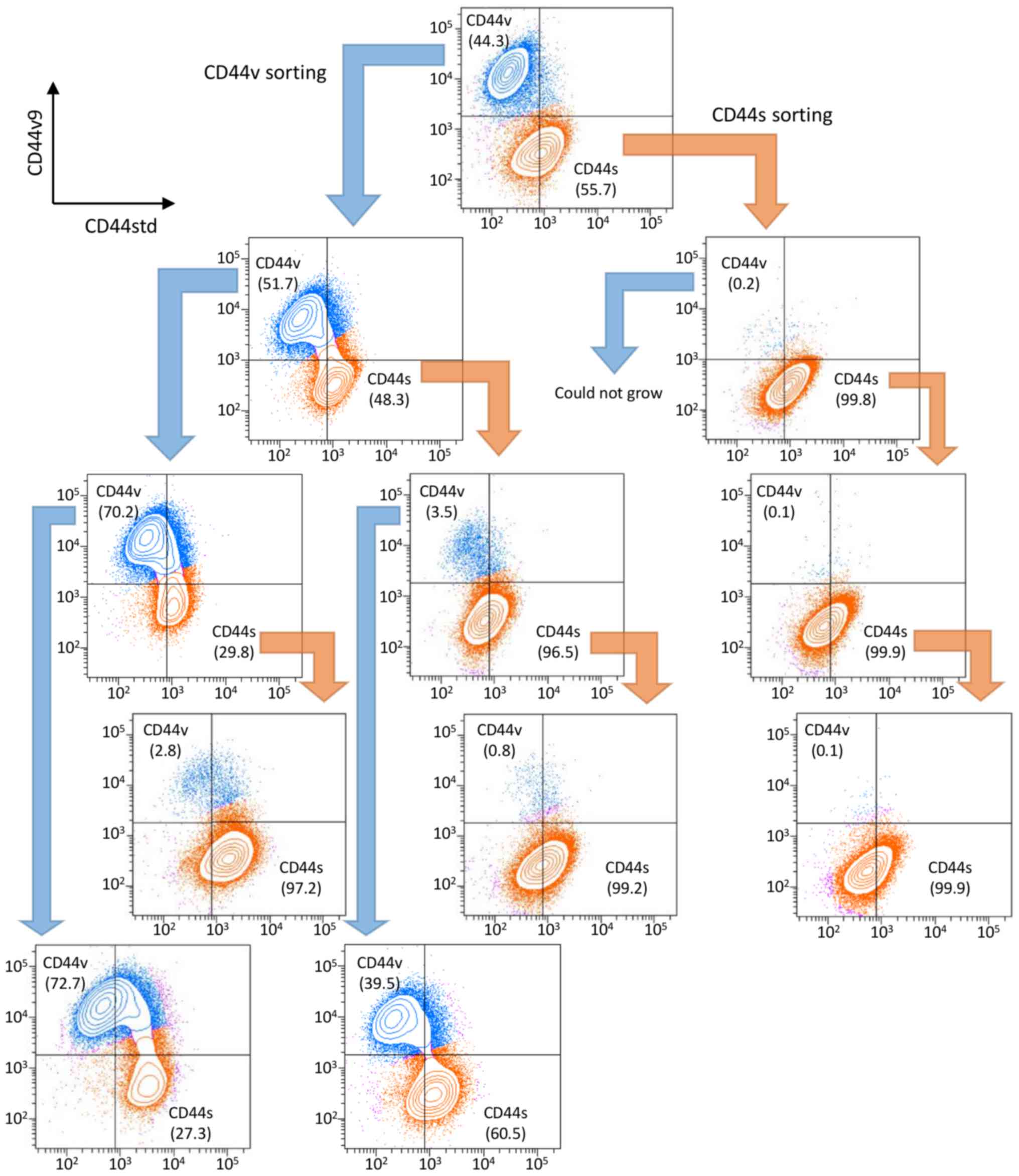
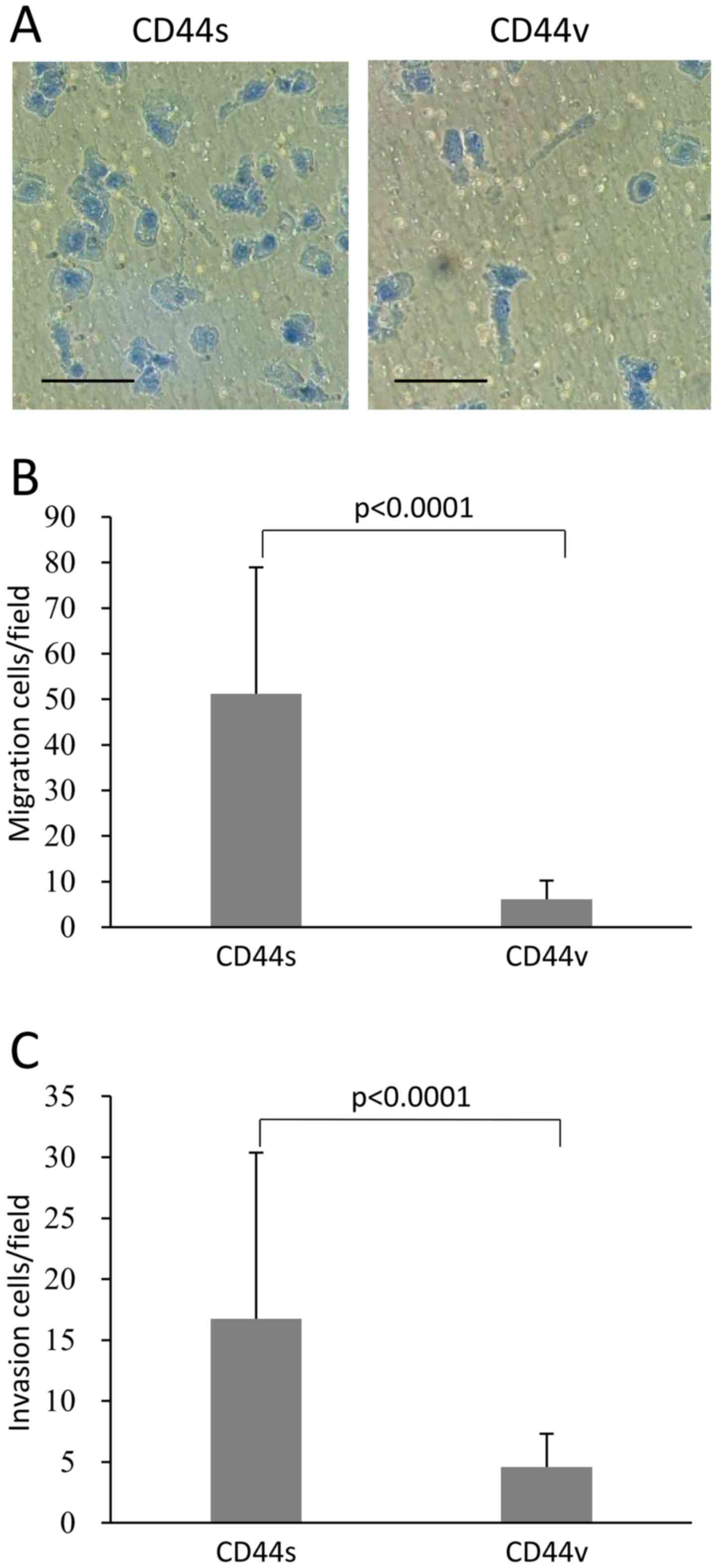
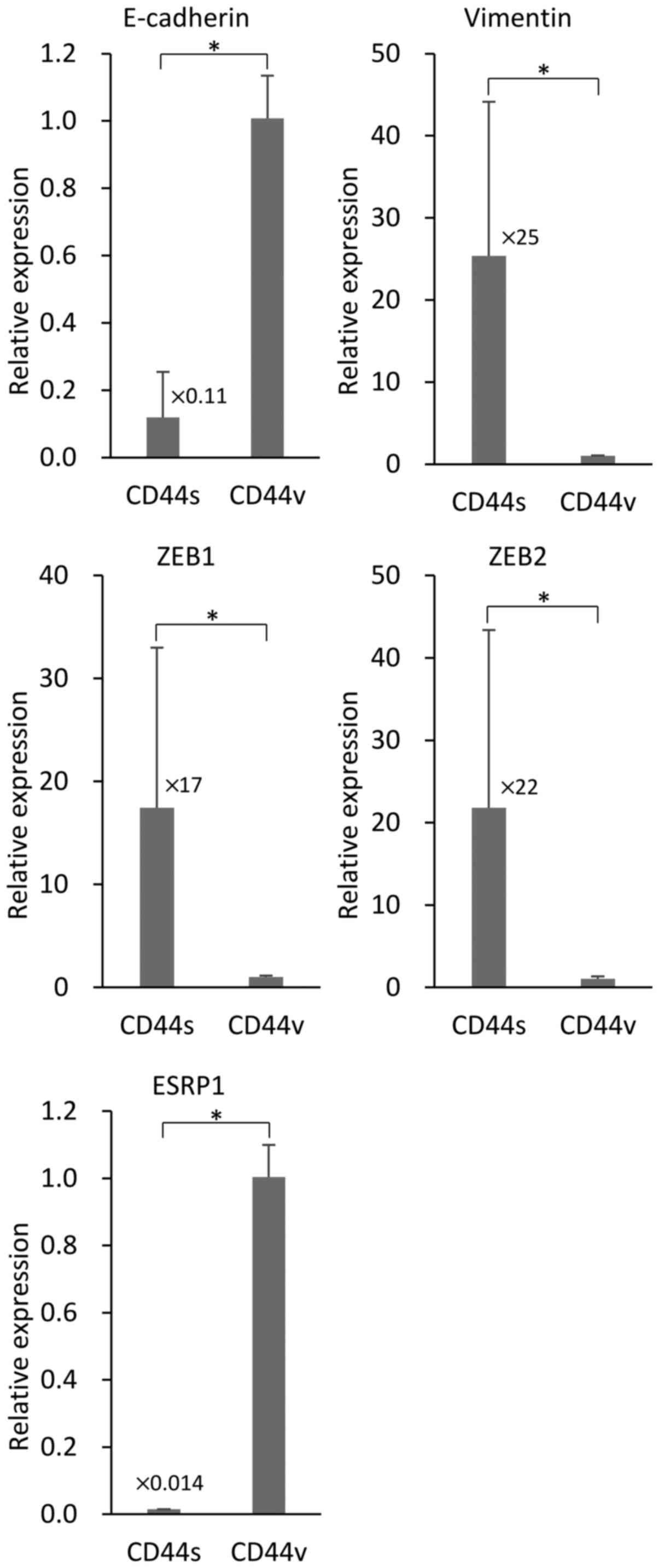
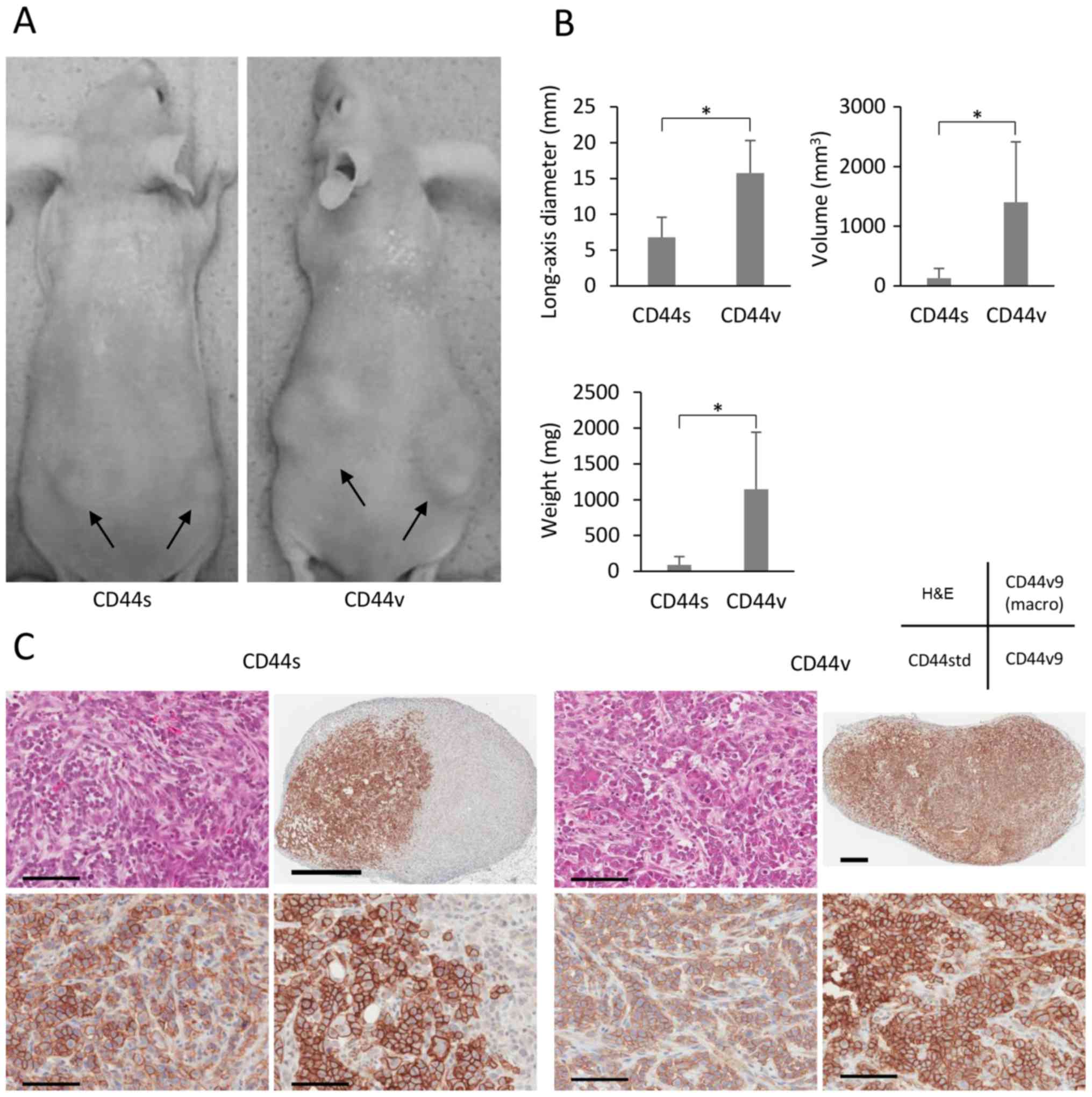
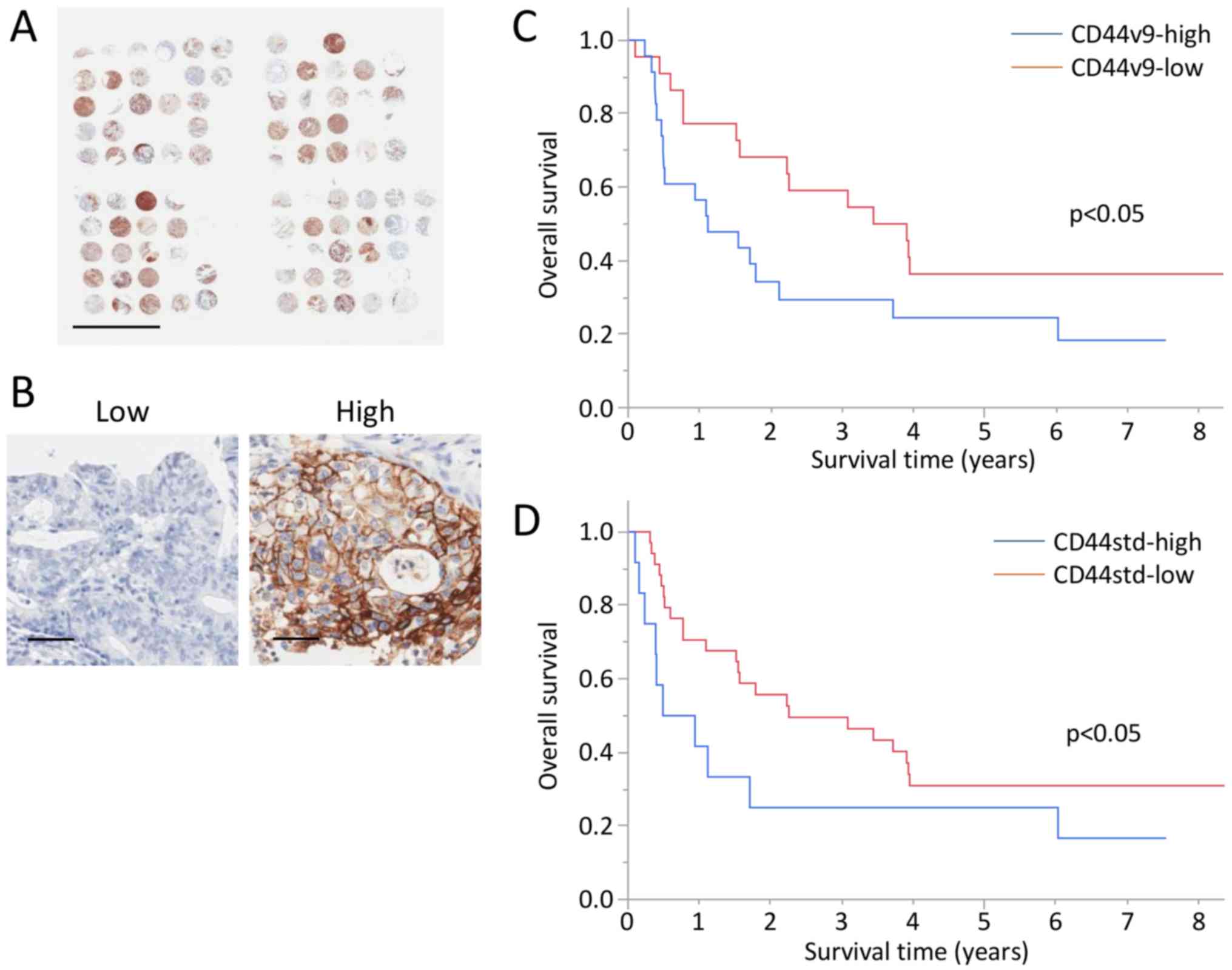
|
1
|
Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC and Sharma
ID: Carcinoma of the gallbladder. Lancet Oncol. 4:167–176. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gourgiotis S, Kocher HM, Solaini L,
Yarollahi A, Tsiambas E and Salemis NS: Gallbladder cancer. Am J
Surg. 196:252–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hofmann M, Rudy W, Zöller M, Tölg C, Ponta
H, Herrlich P and Günthert U: CD44 splice variants confer
metastatic behavior in rats: Homologous sequences are expressed in
human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 51:5292–5297. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sneath RJS and Mangham DC: The normal
structure and function of CD44 and its role in neoplasia. Mol
Pathol. 51:191–200. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goodison S, Urquidi V and Tarin D: CD44
cell adhesion molecules. Mol Pathol. 52:189–196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zöller M: CD44: Can a cancer-initiating
cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer.
11:254–267. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okabe H, Ishimoto T, Mima K, Nakagawa S,
Hayashi H, Kuroki H, Imai K, Nitta H, Saito S, Hashimoto D, et al:
CD44s signals the acquisition of the mesenchymal phenotype required
for anchorage-independent cell survival in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 110:958–966. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hirata K, Suzuki H, Imaeda H, Matsuzaki J,
Tsugawa H, Nagano O, Asakura K, Saya H and Hibi T: CD44 variant 9
expression in primary early gastric cancer as a predictive marker
for recurrence. Br J Cancer. 109:379–386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Z, Chen K, Jiang P, Zhang X, Li X and
Li Z: CD44v/CD44s expression patterns are associated with the
survival of pancreatic carcinoma patients. Diagn Pathol. 9:792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kakehashi A, Ishii N, Sugihara E, Gi M,
Saya H and Wanibuchi H: CD44 variant 9 is a potential biomarker of
tumor initiating cells predicting survival outcome in hepatitis C
virus-positive patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Sci. 107:609–618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishimoto T, Nagano O, Yae T, Tamada M,
Motohara T, Oshima H, Oshima M, Ikeda T, Asaba R, Yagi H, et al:
CD44 variant regulates redox status in cancer cells by stabilizing
the xCT subunit of system xc(-) and thereby promotes tumor growth.
Cancer Cell. 19:387–400. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mielgo A, van Driel M, Bloem A, Landmann L
and Günthert U: A novel antiapoptotic mechanism based on
interference of Fas signaling by CD44 variant isoforms. Cell Death
Differ. 13:465–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nagano O, Okazaki S and Saya H: Redox
regulation in stem-like cancer cells by CD44 variant isoforms.
Oncogene. 32:5191–5198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kiuchi S, Ikeshita S, Miyatake Y and
Kasahara M: Pancreatic cancer cells express CD44 variant 9 and
multidrug resistance protein 1 during mitosis. Exp Mol Pathol.
98:41–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kimura Y, Goi T, Nakazawa T, Hirono Y,
Katayama K, Urano T and Yamaguchi A: CD44 variant exon 9 plays an
important role in colon cancer initiating cells. Oncotarget.
4:785–791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalekou H and Miliaras D:
Immunohistochemical study of microvessel density, CD44 (standard
form), p53 protein and c-erbB2 in gallbladder carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:812–818. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yanagisawa N, Mikami T, Mitomi H, Saegusa
M, Koike M and Okayasu I: CD44 variant overexpression in
gallbladder carcinoma associated with tumor dedifferentiation.
Cancer. 91:408–416. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi A, Zhang M, Goi T, Fujita T,
Niimoto S, Katayama K and Hirose K: Expression of variant CD44
containing variant exon v8-10 in gallbladder cancer. Oncol Rep.
7:541–544. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Homma S, Hasumura S, Nagamori S and Kameda
H: Establishment and characterization of a human gall bladder
carcinoma cell line NOZ. Hum Cell. 1:95–97. 1988.In Japanese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kramer N, Walzl A, Unger C, Rosner M,
Krupitza G, Hengstschläger M and Dolznig H: In vitro cell migration
and invasion assays. Mutat Res. 752:10–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Valster A, Tran NL, Nakada M, Berens ME,
Chan AY and Symons M: Cell migration and invasion assays. Methods.
37:208–215. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Long J, Luo G, Liu C, Cui X, Satoh K, Xiao
Z, Zhang B, Xu J, Ni Q, Li M, et al: Development of a unique mouse
model for pancreatic cancer lymphatic metastasis. Int J Oncol.
41:1662–1668. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren
K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D and van Roy
F: The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1
downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell.
7:1267–1278. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishii H, Saitoh M, Sakamoto K, Kondo T,
Katoh R, Tanaka S, Motizuki M, Masuyama K and Miyazawa K:
Epithelial splicing regulatory proteins 1 (ESRP1) and 2 (ESRP2)
suppress cancer cell motility via different mechanisms. J Biol
Chem. 289:27386–27399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mashita N, Yamada S, Nakayama G, Tanaka C,
Iwata N, Kanda M, Kobayashi D, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Koike M, et al:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition might be induced via CD44
isoform switching in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 110:745–751.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sekine S, Shimada Y, Nagata T, Moriyama M,
Omura T, Watanabe T, Hori R, Yoshioka I, Okumura T, Sawada S, et
al: Prognostic significance of aquaporins in human biliary tract
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 27:1741–1747. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sekine S, Shimada Y, Nagata T, Sawada S,
Yoshioka I, Matsui K, Moriyama M, Omura T, Osawa S, Shibuya K, et
al: Role of aquaporin-5 in gallbladder carcinoma. Eur Surg Res.
51:108–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fukuoka J, Fujii T, Shih JH, Dracheva T,
Meerzaman D, Player A, Hong K, Settnek S, Gupta A, Buetow K, et al:
Chromatin remodeling factors and BRM/BRG1 expression as prognostic
indicators in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:4314–4324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mima K, Okabe H, Ishimoto T, Hayashi H,
Nakagawa S, Kuroki H, Watanabe M, Beppu T, Tamada M, Nagano O, et
al: CD44s regulates the TGF-β-mediated mesenchymal phenotype and is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:3414–3423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brown RL, Reinke LM, Damerow MS, Perez D,
Chodosh LA, Yang J and Cheng C: CD44 splice isoform switching in
human and mouse epithelium is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest.
121:1064–1074. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yae T, Tsuchihashi K, Ishimoto T, Motohara
T, Yoshikawa M, Yoshida GJ, Wada T, Masuko T, Mogushi K, Tanaka H,
et al: Alternative splicing of CD44 mRNA by ESRP1 enhances lung
colonization of metastatic cancer cell. Nat Commun. 3:8832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu MJ and Jang BI: Clinicopathologic
significance of Sox2, CD44 and CD44v6 expression in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 20:655–660. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han Z, Chen Z, Zheng R, Cheng Z, Gong X
and Wang D: Clinicopathological significance of CD133 and CD44
expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma and their relationship
to angiogenesis. World J Surg Oncol. 13:562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang M, Xiao J, Shen M, Yahong Y, Tian R,
Zhu F, Jiang J, Du Z, Hu J, Liu W, et al: Isolation and
characterization of tumorigenic extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
cells with stem cell-like properties. Int J Cancer. 128:72–81.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang SJ and Bourguignon LYW: Role of
hyaluronan-mediated CD44 signaling in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. Am J Pathol.
178:956–963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akasaka J, Uekuri C, Shigetomi H, Koike M
and Kobayashi H: Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-1β and its
physiological importance in endometriosis. Biomed Rep. 1:13–17.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|