|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Belmont LD and Mitchison TJ:
Identification of a protein that interacts with tubulin dimers and
increases the catastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell. 84:623–631.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Curmi PA, Gavet O, Charbaut E, Ozon S,
Lachkar-Colmerauer S, Manceau V, Siavoshian S, Maucuer A and Sobel
A: Stathmin and its phosphoprotein family: General properties,
biochemical and functional interaction with tubulin. Cell Struct
Funct. 24:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cassimeris L: The oncoprotein 18/stathmin
family of microtubule destabilizers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:18–24.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Curmi PA, Andersen SS, Lachkar S, Gavet O,
Karsenti E, Knossow M and Sobel A: The stathmin/tubulin interaction
in vitro. J Biol Chem. 272:25029–25036. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Curmi PA, Noguès C, Lachkar S, Carelle N,
Gonthier MP, Sobel A, Lidereau R and Bièche I: Overexpression of
stathmin in breast carcinomas points out to highly proliferative
tumours. Br J Cancer. 82:142–150. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arnedos M, Drury S, Afentakis M, A'Hern R,
Hills M, Salter J, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS and Dowsett M: Biomarker
changes associated with the development of resistance to aromatase
inhibitors (AIs) in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 25:605–610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, Albain KS, André F,
Bergh J, et al Panel members: Personalizing the treatment of women
with early breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International
Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer
2013. Ann Oncol. 24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A and
Koukourakis MI: The CD44+/CD24− phenotype
relates to 'triple-negative' state and unfavorable prognosis in
breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 28:745–752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Idowu MO, Kmieciak M, Dumur C, Burton RS,
Grimes MM, Powers CN and Manjili MH:
CD44+/CD24−/low cancer stem/progenitor cells
are more abundant in triple-negative invasive breast carcinoma
phenotype and are associated with poor outcome. Hum Pathol.
43:364–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shafee N, Smith CR, Wei S, Kim Y, Mills
GB, Hortobagyi GN, Stanbridge EJ and Lee EY: Cancer stem cells
contribute to cisplatin resistance in Brca1/p53-mediated mouse
mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 68:3243–3250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
To K, Fotovati A, Reipas KM, Law JH, Hu K,
Wang J, Astanehe A, Davies AH, Lee L, Stratford AL, et al: Y-box
binding protein-1 induces the expression of CD44 and CD49f leading
to enhanced self-renewal, mammosphere growth, and drug resistance.
Cancer Res. 70:2840–2851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saal LH, Johansson P, Holm K,
Gruvberger-Saal SK, She QB, Maurer M, Koujak S, Ferrando AA,
Malmström P, Memeo L, et al: Poor prognosis in carcinoma is
associated with a gene expression signature of aberrant PTEN tumor
suppressor pathway activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7564–7569.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Golouh R, Cufer T, Sadikov A, Nussdorfer
P, Usher PA, Brünner N, Schmitt M, Lesche R, Maier S, Timmermans M,
et al: The prognostic value of Stathmin-1, S100A2, and SYK proteins
in ER-positive primary breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant
tamoxifen monotherapy: An immunohistochemical study. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 110:317–326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Baquero MT, Hanna JA, Neumeister V, Cheng
H, Molinaro AM, Harris LN and Rimm DL: Stathmin expression and its
relationship to microtubule-associated protein tau and outcome in
breast cancer. Cancer. 118:4660–4669. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alli E, Bash-Babula J, Yang JM and Hait
WN: Effect of stathmin on the sensitivity to antimicrotubule drugs
in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62:6864–6869. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7th edition.
Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
25
|
Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Kurosumi M, Sakamoto G
and Watanabe T; Japan National Surgical Adjuvant Study of Breast
Cancer(NSAS-BC) Pathology Section: Establishment of histological
criteria for high-risk node-negative breast carcinoma for a
multi-institutional randomized clinical trial of adjuvant therapy.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 28:486–491. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M,
McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M,
Fitzgibbons P, et al American Society of Clinical Oncology; College
of American Pathologists: Recommendations for human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society
of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical
practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 31:3997–4013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A'Hern R, Bartlett
J, Coombes RC, Cuzick J, Ellis M, Henry NL, Hugh JC, Lively T, et
al International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group: Assessment
of Ki-67 in breast cancer: Recommendations from the International
Ki-67 in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:1656–1664. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung
S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, et al: Ki67
index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:736–750. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M and Clark
GM: Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by
immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 11:155–168.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
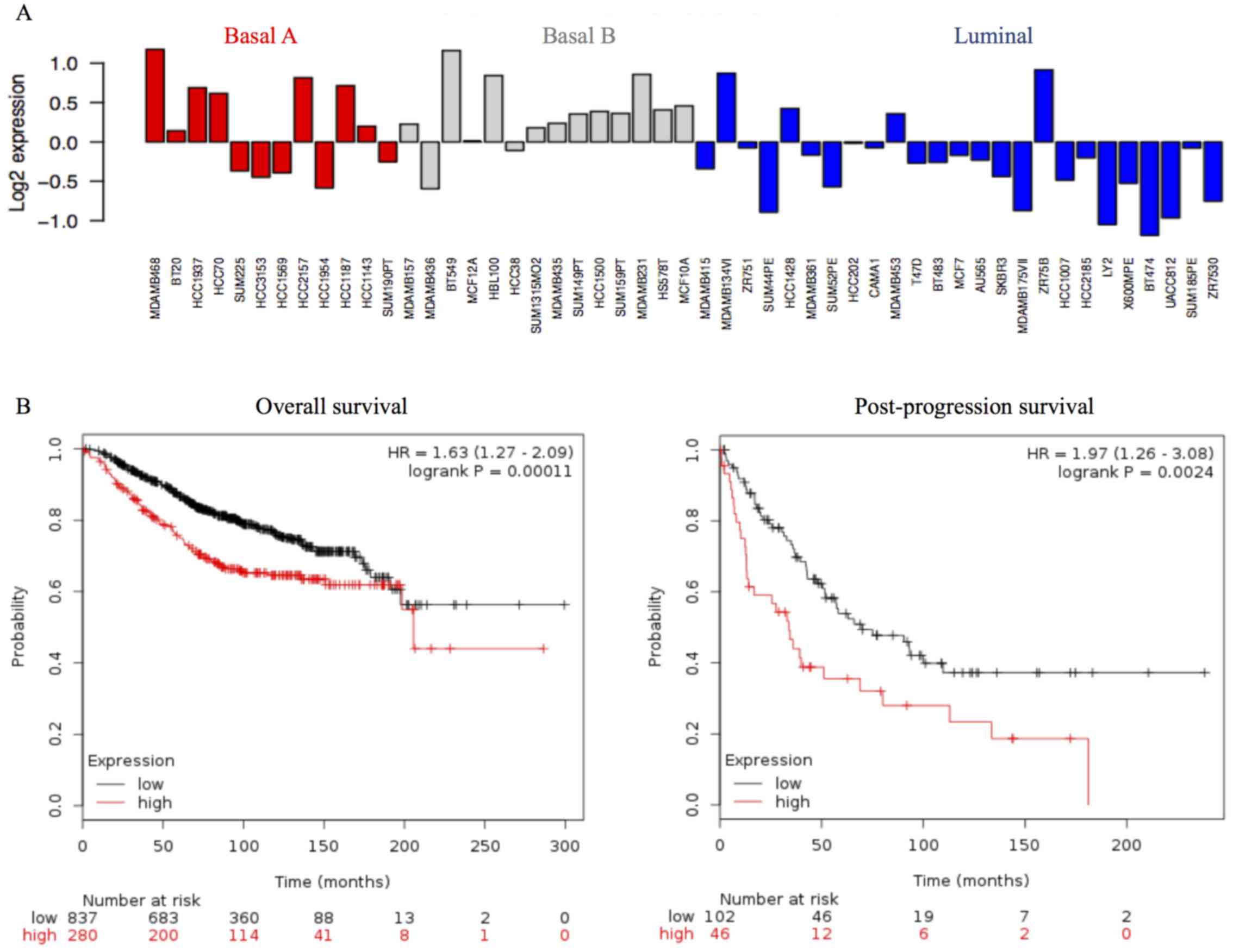
Ringnér M, Fredlund E, Häkkinen J, Borg Å
and Staaf J; GOBO: Gene expression-based outcome for breast cancer
online. PLoS One. 6:e179112011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN and
McCann A: Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:96–132. 2008.
|
|
33
|
Meng XL, Su D, Wang L, Gao Y, Hu YJ, Yang
HJ and Xie SN: Low expression of stathmin in tumor predicts high
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel-containing
regimens in locally advanced breast cancer. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 16:689–694. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alli E, Yang JM, Ford JM and Hait WN:
Reversal of stathmin-mediated resistance to paclitaxel and
vinblastine in human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol.
71:1233–1240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iancu C, Mistry SJ, Arkin S and Atweh GF:
Taxol and anti-stathmin therapy: A synergistic combination that
targets the mitotic spindle. Cancer Res. 60:3537–3541.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao J: Cancer stem cells and
chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol Ther.
160:145–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Biddle A, Liang X, Gammon L, Fazil B,
Harper LJ, Emich H, Costea DE and Mackenzie IC: Cancer stem cells
in squamous cell carcinoma switch between two distinct phenotypes
that are preferentially migratory or proliferative. Cancer Res.
71:5317–5326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Cong Y, Wang D, Sun Y, Deng L, Liu
Y, Martin-Trevino R, Shang L, McDermott SP, Landis MD, et al:
Breast cancer stem cells transition between epithelial and
mesenchymal states reflective of their normal counterparts. Stem
Cell Rep. 2:78–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li N, Jiang P, Du W, Wu Z, Li C, Qiao M,
Yang X and Wu M: Siva1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and metastasis of tumor cells by inhibiting stathmin and
stabilizing microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12851–12856.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu M, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Stott SL, Smas
ME, Ting DT, Isakoff SJ, Ciciliano JC, Wells MN, Shah AM, et al:
Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in
epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science. 339:580–584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abell AN and Johnson GL: Implications of
mesenchymal cells in cancer stem cell populations: Relevance to
EMT. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2:21–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Depowski PL, Rosenthal SI and Ross JS:
Loss of expression of the PTEN gene protein product is associated
with poor outcome in breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 14:672–676. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Saal LH, Holm K, Maurer M, Memeo L, Su T,
Wang X, Yu JS, Malmström PO, Mansukhani M, Enoksson J, et al:
PIK3CA mutations correlate with hormone receptors, node metastasis,
and ERBB2, and are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in human
breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:2554–2559. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Perren A, Weng LP, Boag AH, Ziebold U,
Thakore K, Dahia PL, Komminoth P, Lees JA, Mulligan LM, Mutter GL,
et al: Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in
primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol.
155:1253–1260. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|