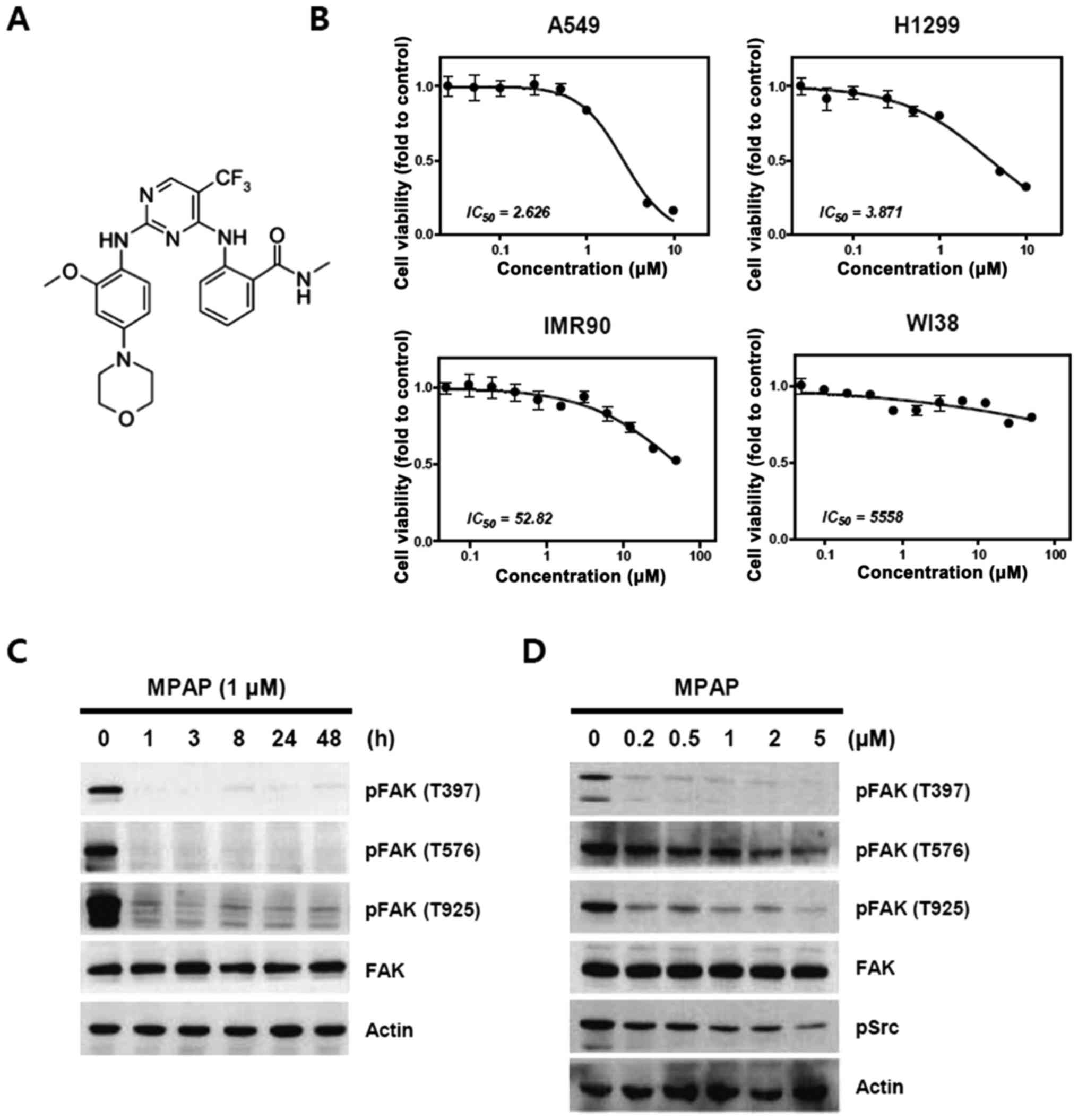
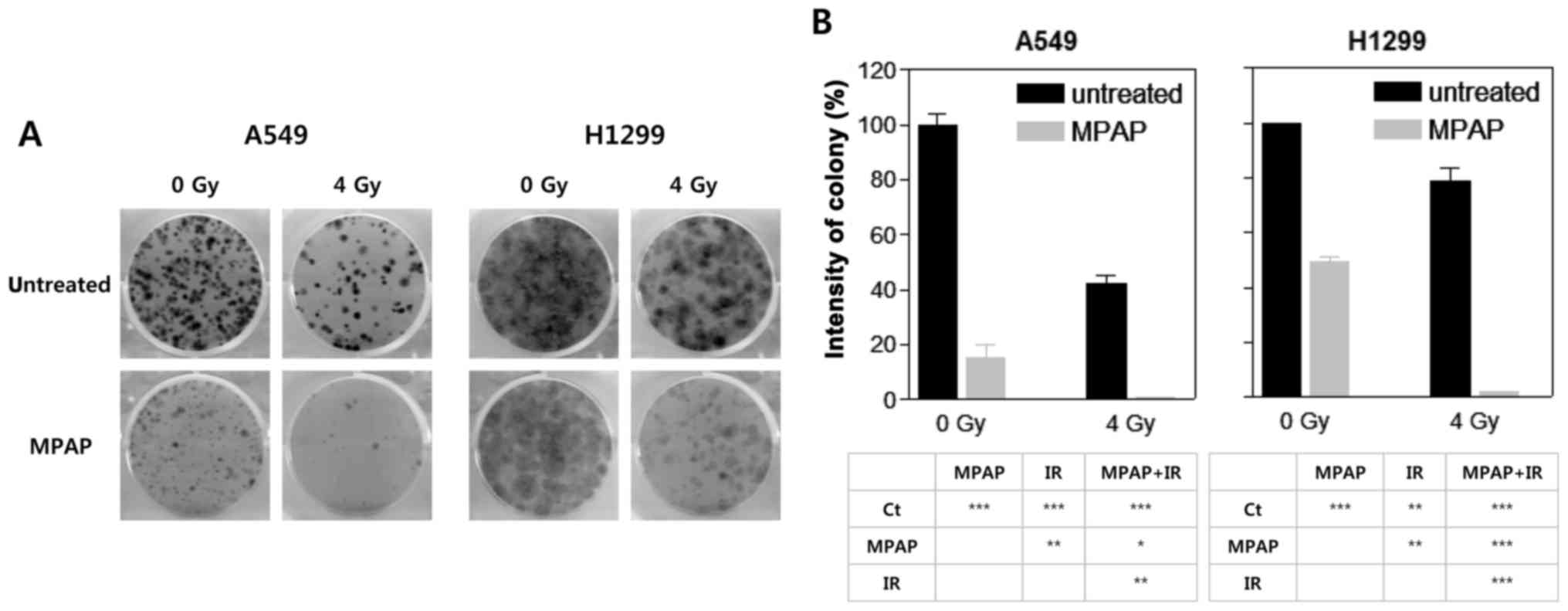
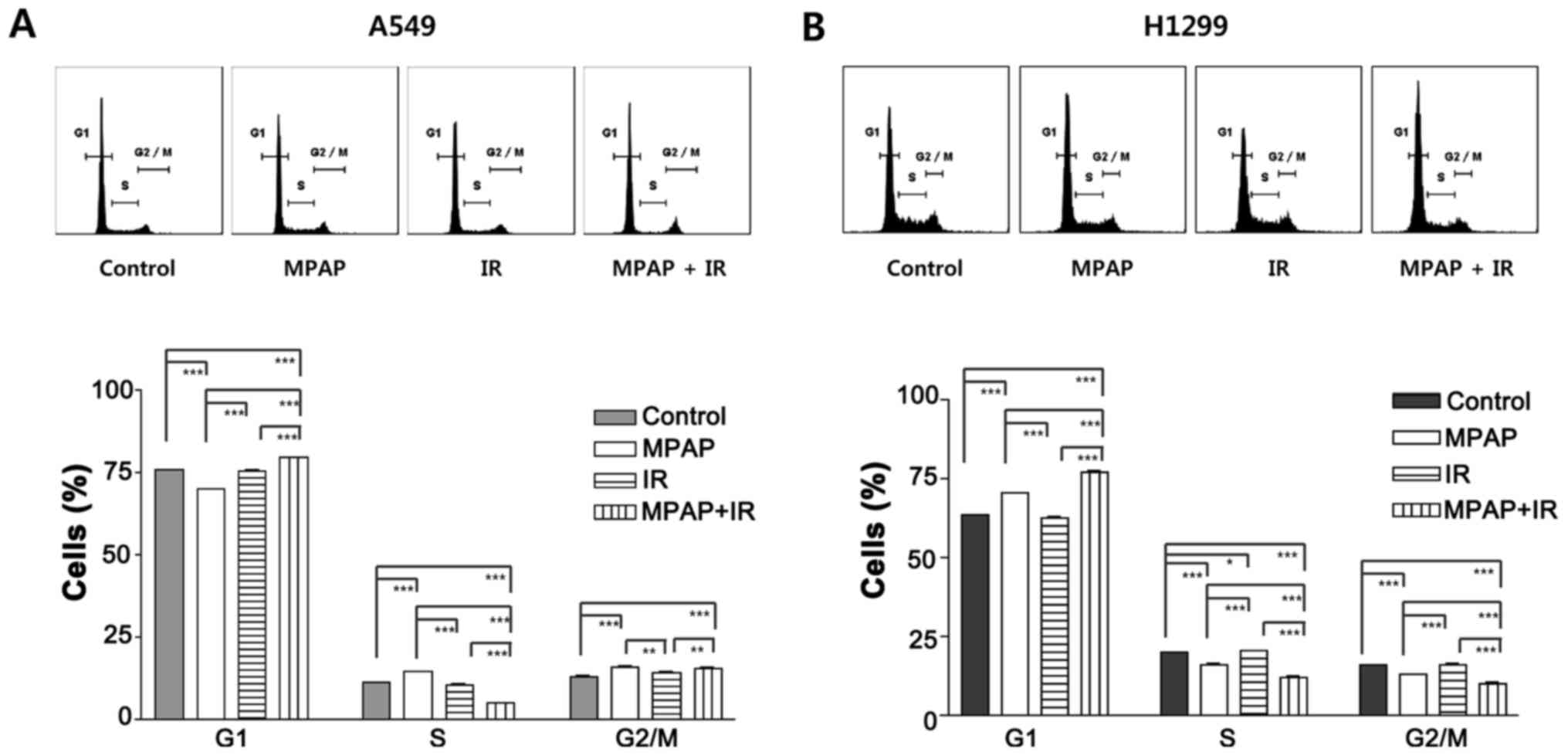
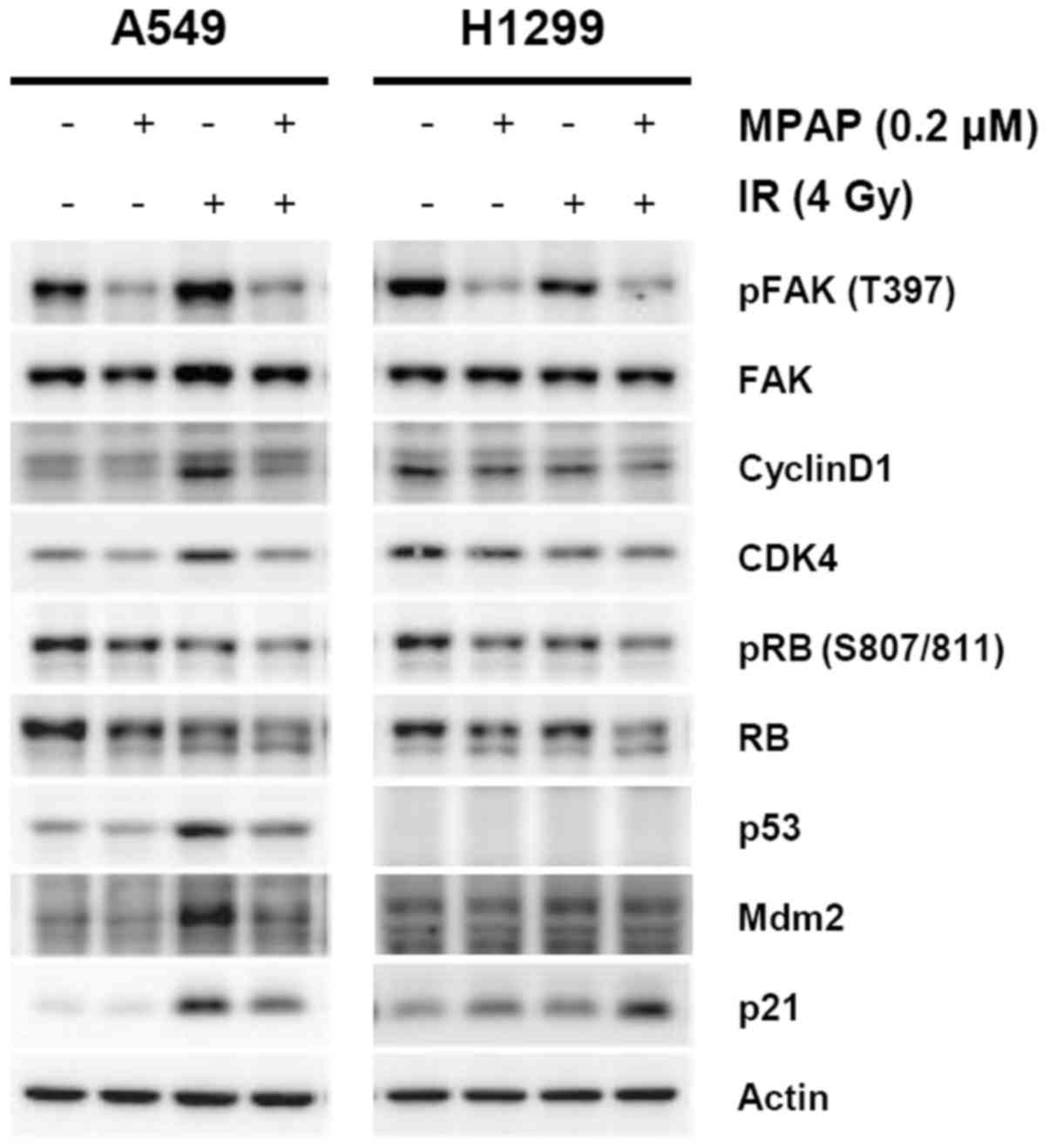
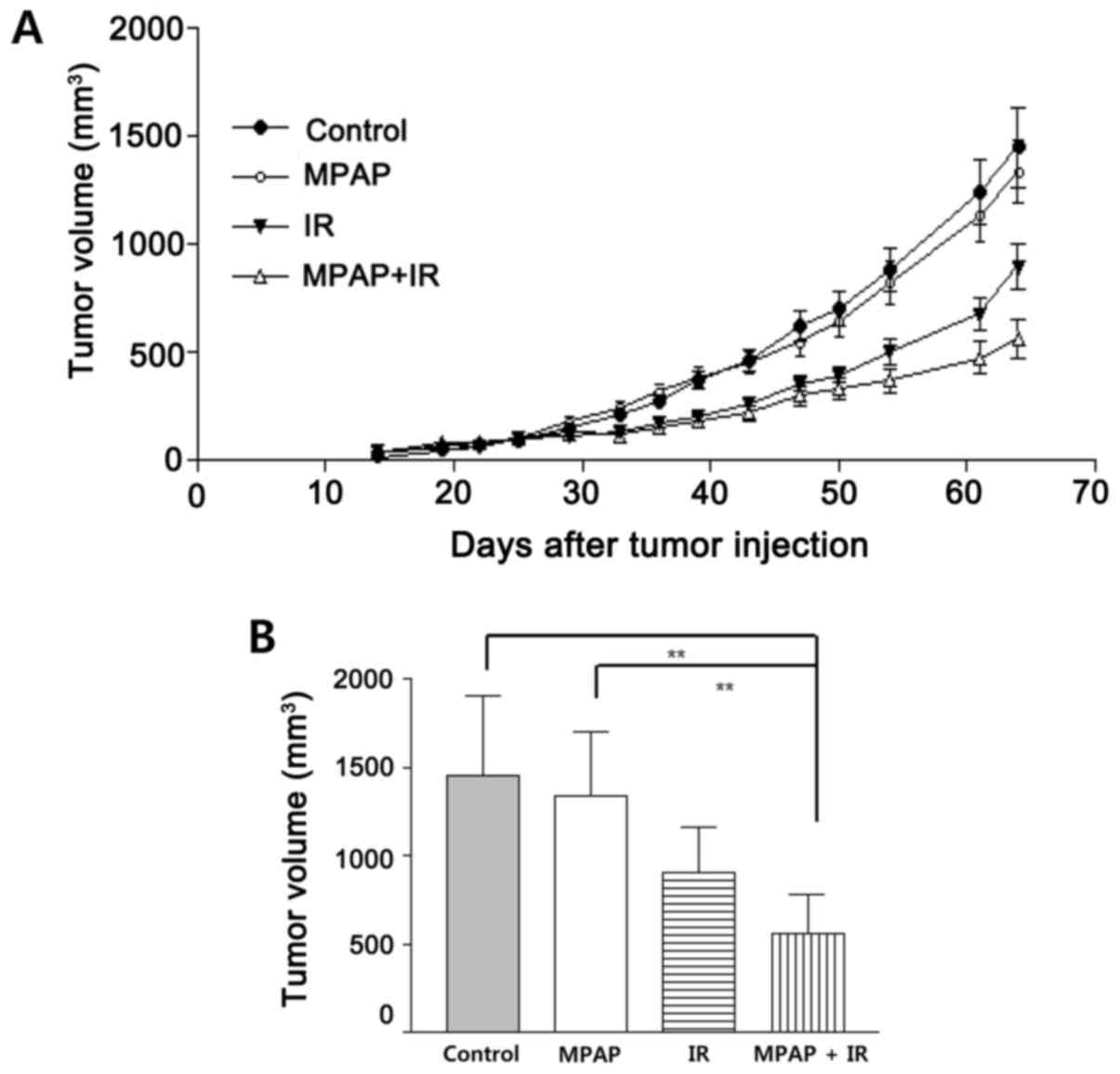
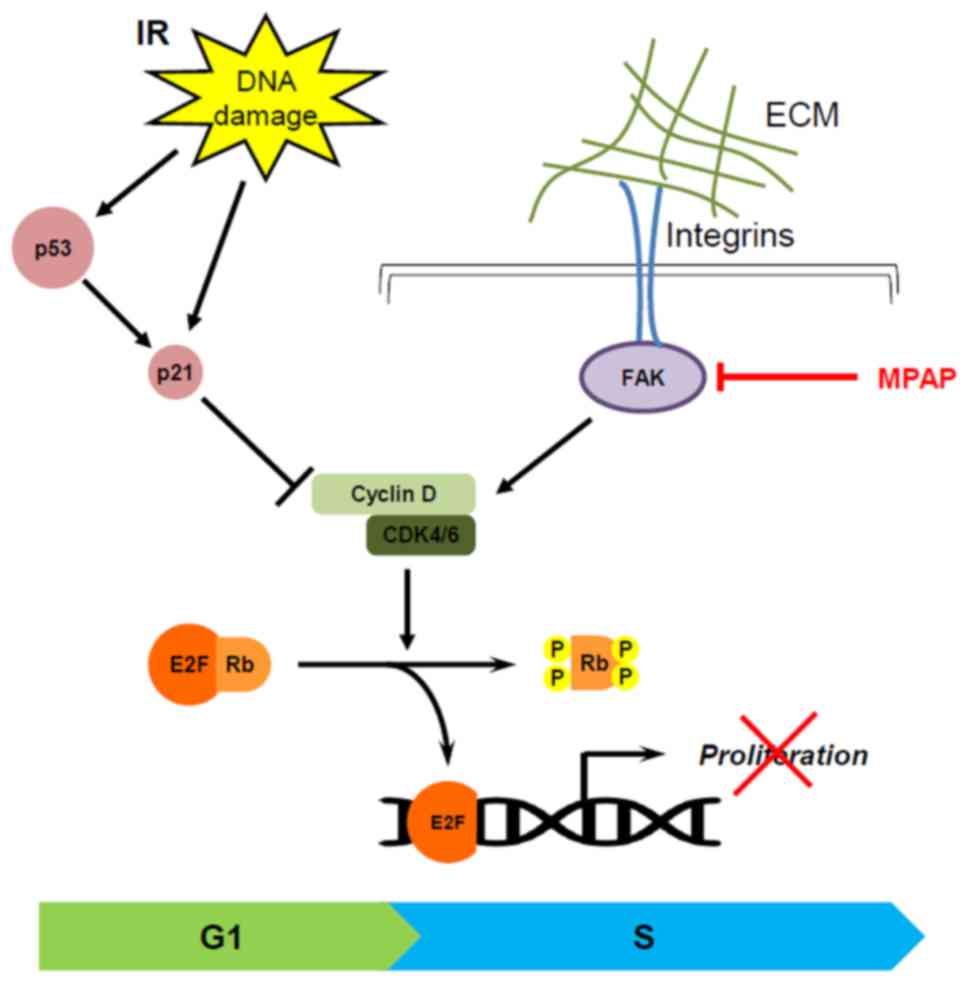
|
1
|
Parsons JT: Focal adhesion kinase: The
first ten years. J Cell Sci. 116:1409–1416. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mitra SK, Hanson DA and Schlaepfer DD:
Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:56–68. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanks SK, Calalb MB, Harper MC and Patel
SK: Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in
response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:8487–8491. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calalb MB, Polte TR and Hanks SK: Tyrosine
phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at sites in the catalytic
domain regulates kinase activity: A role for Src family kinases.
Mol Cell Biol. 15:954–963. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Owen JD, Ruest PJ, Fry DW and Hanks SK:
Induced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) expression in FAK-null cells
enhances cell spreading and migration requiring both auto- and
activation loop phosphorylation sites and inhibits
adhesion-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Pyk2. Mol Cell Biol.
19:4806–4818. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sulzmaier FJ, Jean C and Schlaepfer DD:
FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat
Rev Cancer. 14:598–610. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490:61–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bell D, Berchuck A, Birrer M, Chien J,
Cramer DW, Dao F, Dhir R, DiSaia P, Gabra H, Glenn P, et al Cancer
Genome Atlas Research Network: Integrated genomic analyses of
ovarian carcinoma. Nature. 474:609–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sood AK, Armaiz-Pena GN, Halder J, Nick
AM, Stone RL, Hu W, Carroll AR, Spannuth WA, Deavers MT, Allen JK,
et al: Adrenergic modulation of focal adhesion kinase protects
human ovarian cancer cells from anoikis. J Clin Invest.
120:1515–1523. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Nimwegen MJ and van de Water B: Focal
adhesion kinase: A potential target in cancer therapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:597–609. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Siesser PMF and Hanks SK: The signaling
and biological implications of FAK overexpression in cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:3233–3237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ward KK, Tancioni I, Lawson C, Miller NL,
Jean C, Chen XL, Uryu S, Kim J, Tarin D, Stupack DG, et al:
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity prevents
anchorage-independent ovarian carcinoma cell growth and tumor
progression. Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:579–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen XL, Nam JO, Jean C, Lawson C, Walsh
CT, Goka E, Lim ST, Tomar A, Tancioni I, Uryu S, et al:
VEGF-induced vascular permeability is mediated by FAK. Dev Cell.
22:146–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Walsh C, Tanjoni I, Uryu S, Tomar A, Nam
JO, Luo H, Phillips A, Patel N, Kwok C, McMahon G, et al: Oral
delivery of PND-1186 FAK inhibitor decreases tumor growth and
spontaneous breast to lung metastasis in pre-clinical models.
Cancer Biol Ther. 9:778–790. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jean C, Chen XL, Nam JO, Tancioni I, Uryu
S, Lawson C, Ward KK, Walsh CT, Miller NL, Ghassemian M, et al:
Inhibition of endothelial FAK activity prevents tumor metastasis by
enhancing barrier function. J Cell Biol. 204:247–263. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cabrita MA, Jones LM, Quizi JL, Sabourin
LA, McKay BC and Addison CL: Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors are
potent antiangiogenic agents. Mol Oncol. 5:517–526. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Halder J, Lin YG, Merritt WM, Spannuth WA,
Nick AM, Honda T, Kamat AA, Han LY, Kim TJ, Lu C, et al:
Therapeutic efficacy of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor
TAE226 in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 67:10976–10983. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stokes JB, Adair SJ, Slack-Davis JK,
Walters DM, Tilghman RW, Hershey ED, Lowrey B, Thomas KS, Bouton
AH, Hwang RF, et al: Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by
PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer
Ther. 10:2135–2145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wendt MK and Schiemann WP: Therapeutic
targeting of the focal adhesion complex prevents oncogenic TGF-beta
signaling and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R682009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Slack-Davis JK, Hershey ED, Theodorescu D,
Frierson HF and Parsons JT: Differential requirement for focal
adhesion kinase signaling in cancer progression in the transgenic
adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:2470–2477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoon H, Dehart JP, Murphy JM and Lim ST:
Understanding the roles of FAK in cancer: Inhibitors, genetic
models, and new insights. J Histochem Cytochem. 63:114–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Liu TJ, LaFortune T, Honda T, Ohmori O,
Hatakeyama S, Meyer T, Jackson D, de Groot J and Yung WK:
Inhibition of both focal adhesion kinase and insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor kinase suppresses glioma proliferation in vitro
and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1357–1367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Keir ST, Song L,
Wickman S, Jackson D, Ohmori O, Bigner DD, Friedman HS and Rich JN:
A novel low-molecular weight inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase,
TAE226, inhibits glioma growth. Mol Carcinog. 46:488–496. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nam KY, Jin DH, No KT and Ahn SK:
Discovery of FAK inhibitors using structure based drug design. Bull
Korean Chem Soc. 35:3156–3157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Amin NP, Sher DJ and Konski AA: Systematic
review of the cost effectiveness of radiation therapy for prostate
cancer from 2003 to 2013. Appl Health Econ Health Policy.
12:391–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Begg AC, Stewart FA and Vens C: Strategies
to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:239–253. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hehlgans S, Lange I, Eke I and Cordes N:
3D cell cultures of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
cells are radiosensitized by the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor
TAE226. Radiother Oncol. 92:371–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Storch K, Sagerer A and Cordes N:
Cytotoxic and radiosensitizing effects of FAK targeting in human
glioblastoma cells in vitro. Oncol Rep. 33:2009–2016. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Golubovskaya VM and Cance WG: FAK and p53
protein interactions. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:617–619. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Pestell R and Guan JL:
Transcriptional activation of cyclin D1 promoter by FAK contributes
to cell cycle progression. Mol Biol Cell. 12:4066–4077. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gnani D, Romito I, Artuso S, Chierici M,
De Stefanis C, Panera N, Crudele A, Ceccarelli S, Carcarino E,
D'Oria V, et al: Focal adhesion kinase depletion reduces human
hepatocellular carcinoma growth by repressing enhancer of zeste
homolog 2. Cell Death Differ. 24:889–902. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Giacinti C and Giordano A: RB and cell
cycle progression. Oncogene. 25:5220–5227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Assoian RK: Anchorage-dependent cell cycle
progression. J Cell Biol. 136:1–4. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Assoian RK and Schwartz MA: Coordinate
signaling by integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases in the
regulation of G1 phase cell-cycle progression. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
11:48–53. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iliakis G, Wang Y, Guan J and Wang H: DNA
damage checkpoint control in cells exposed to ionizing radiation.
Oncogene. 22:5834–5847. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stewart N, Hicks GG, Paraskevas F and
Mowat M: Evidence for a second cell cycle block at G2/M by p53.
Oncogene. 10:109–115. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siles E, Villalobos M, Valenzuela MT,
Núñez MI, Gordon A, McMillan TJ, Pedraza V and Ruiz de Almodóvar
JM: Relationship between p53 status and radiosensitivity in human
tumour cell lines. Br J Cancer. 73:581–588. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Yu J,
Kinzler K, Vogelstein B and Williams J: Cell-cycle arrest versus
cell death in cancer therapy. Nat Med. 3:1034–1036. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|