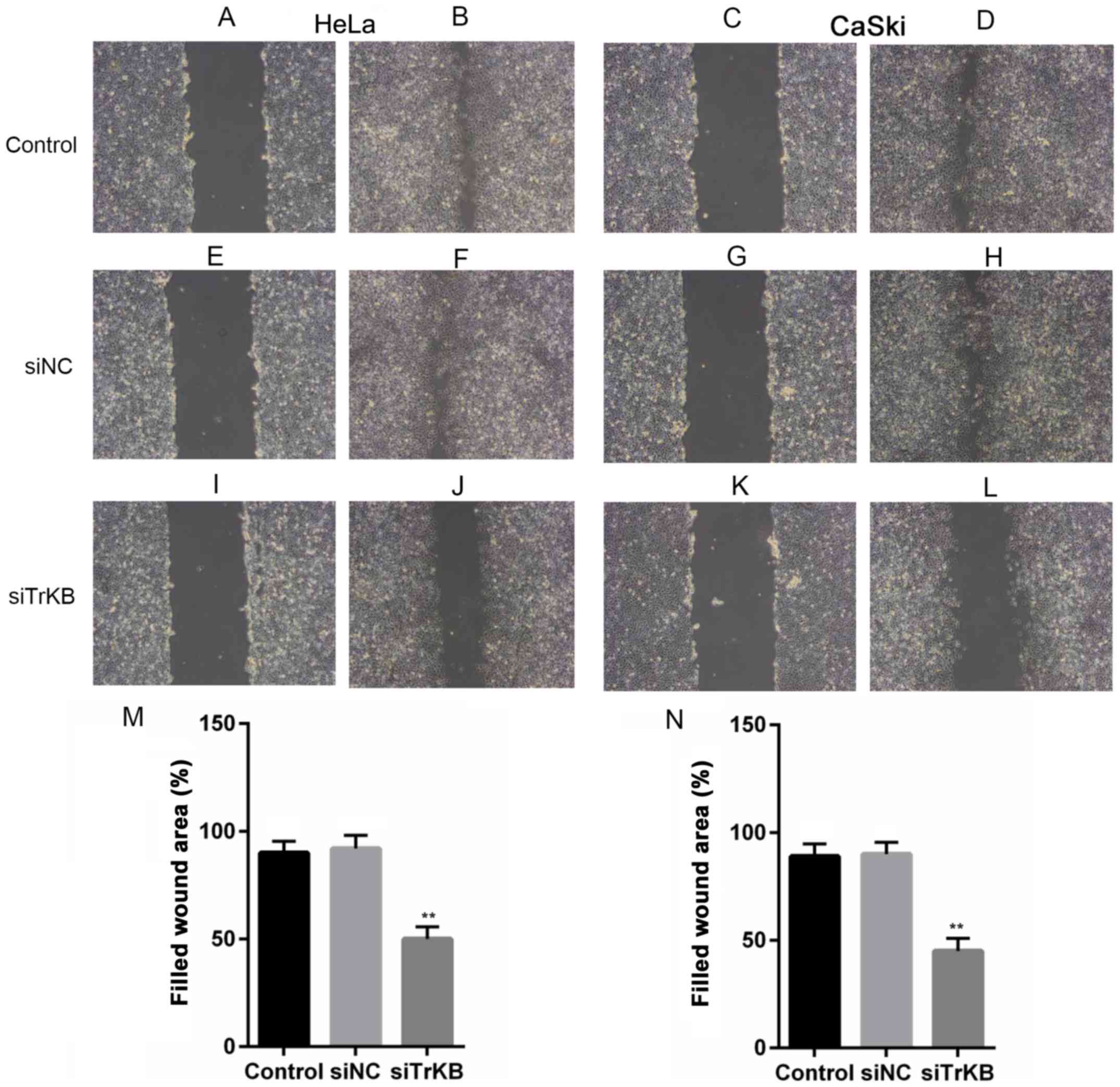
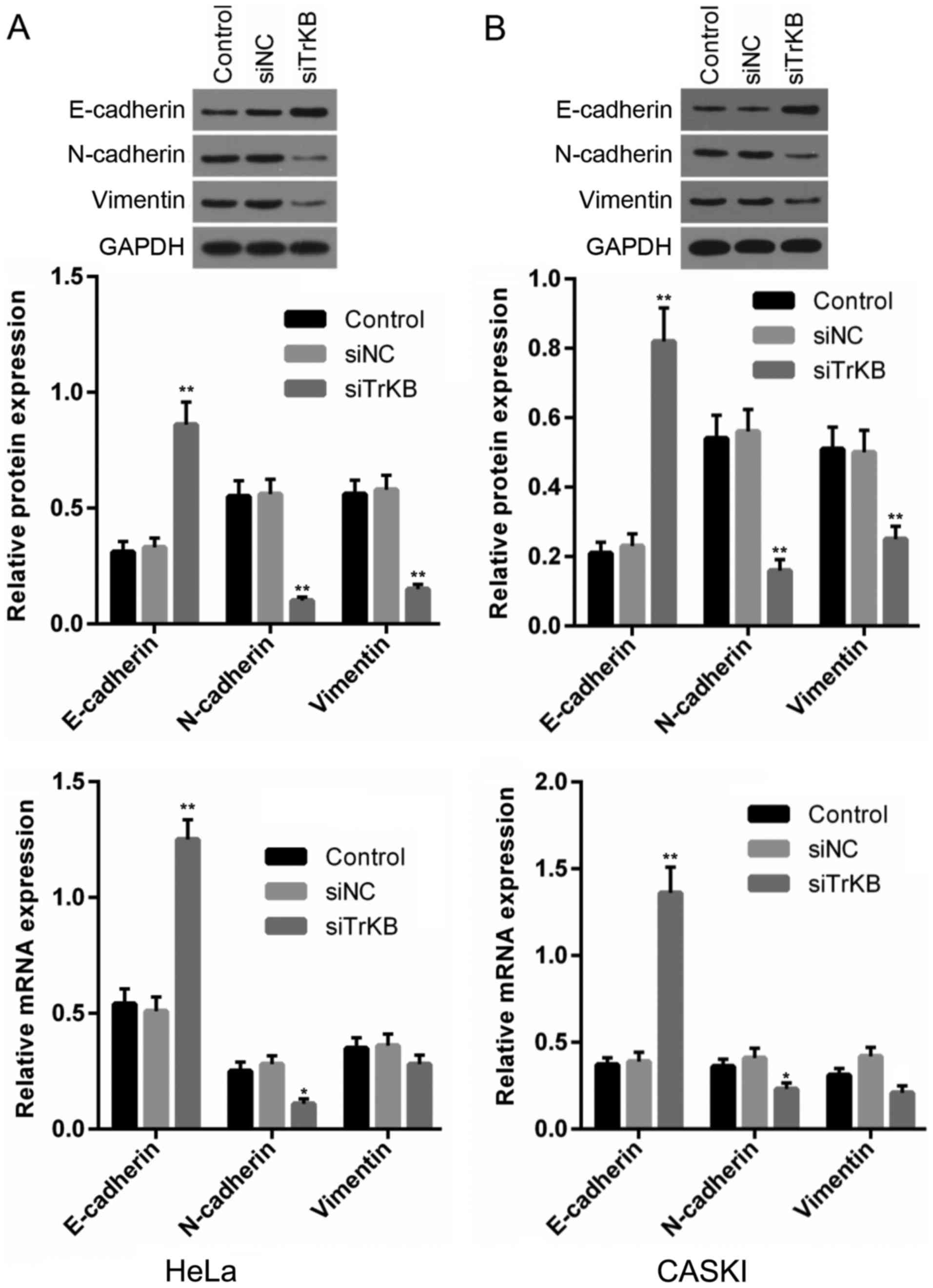
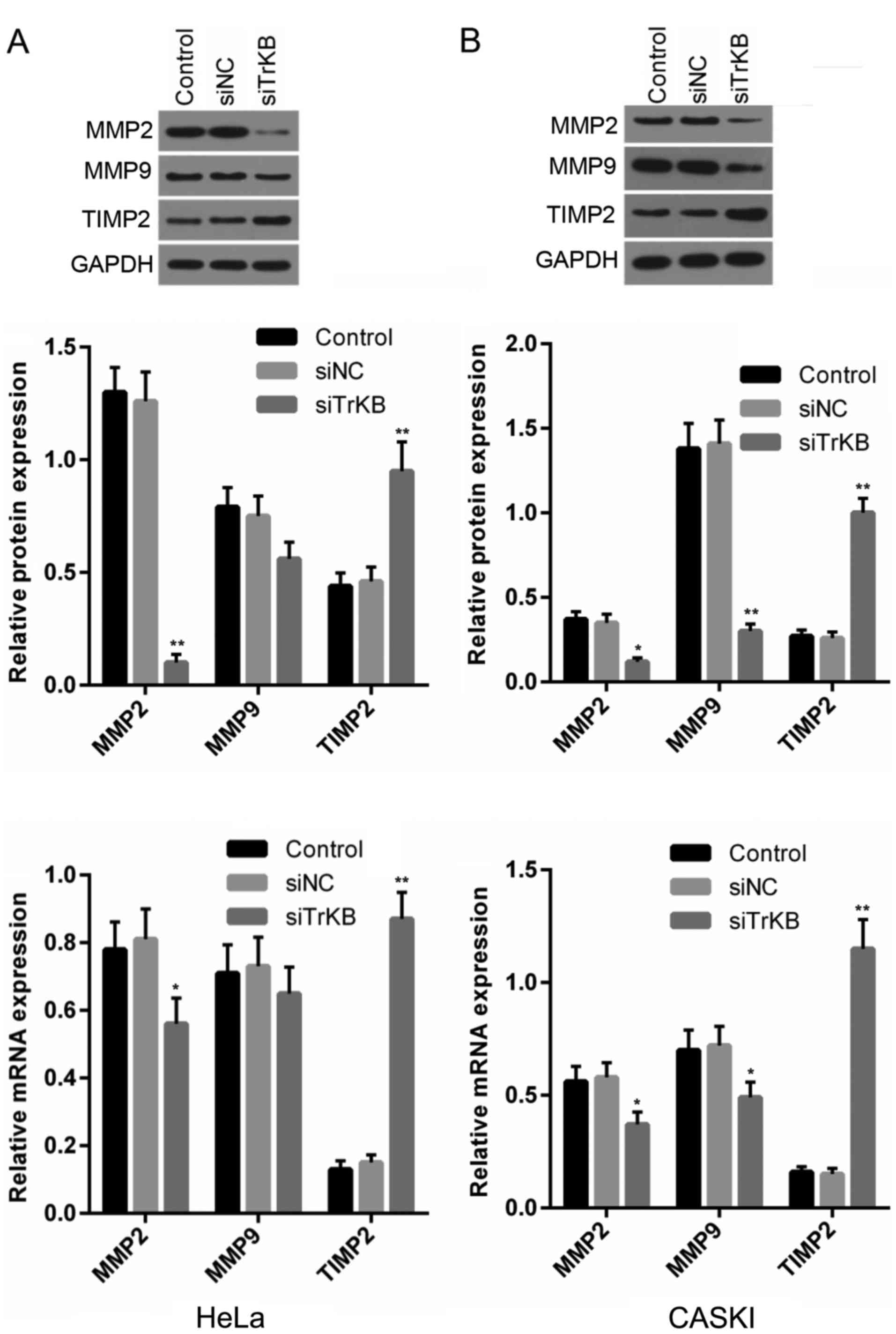
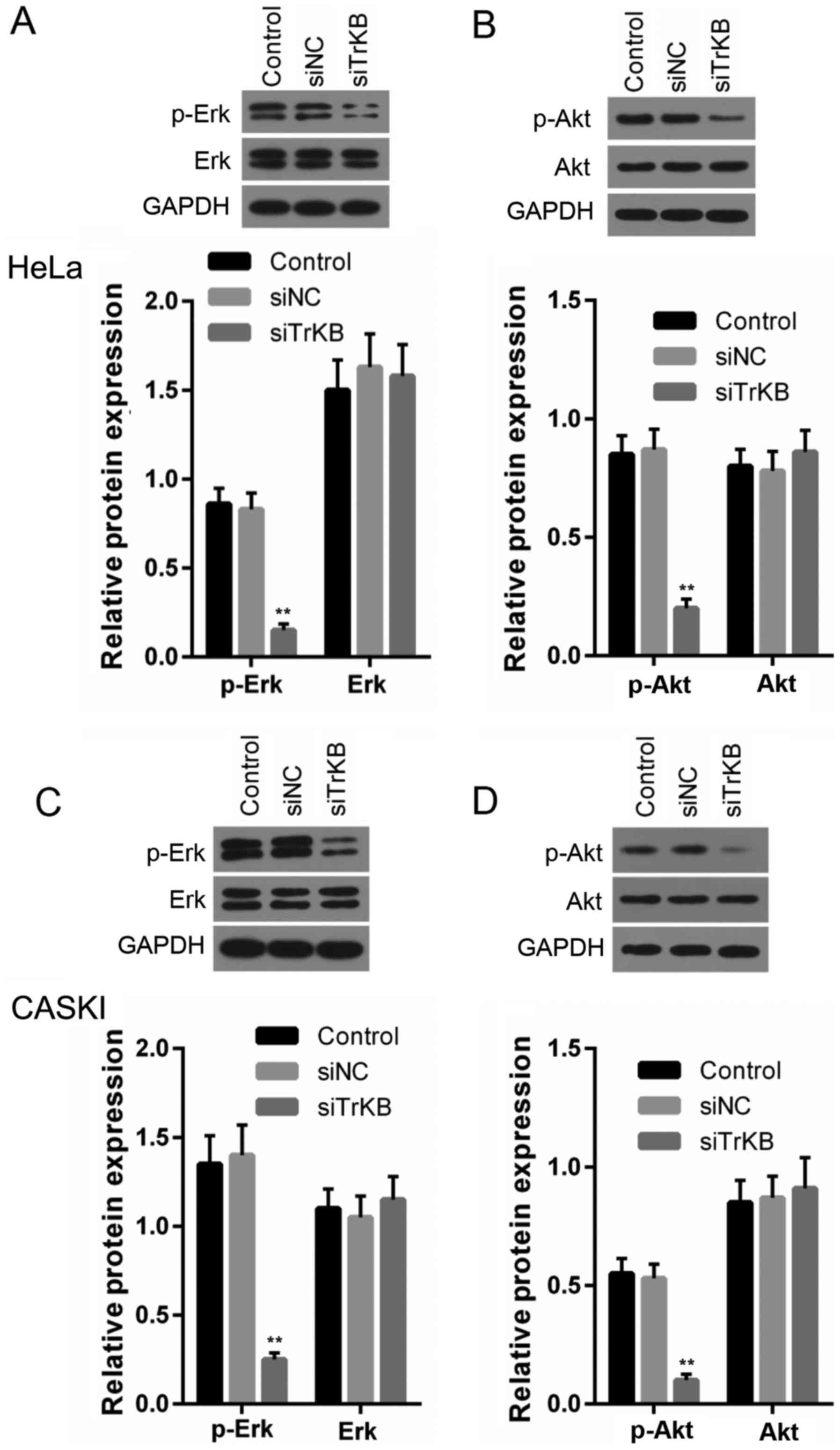
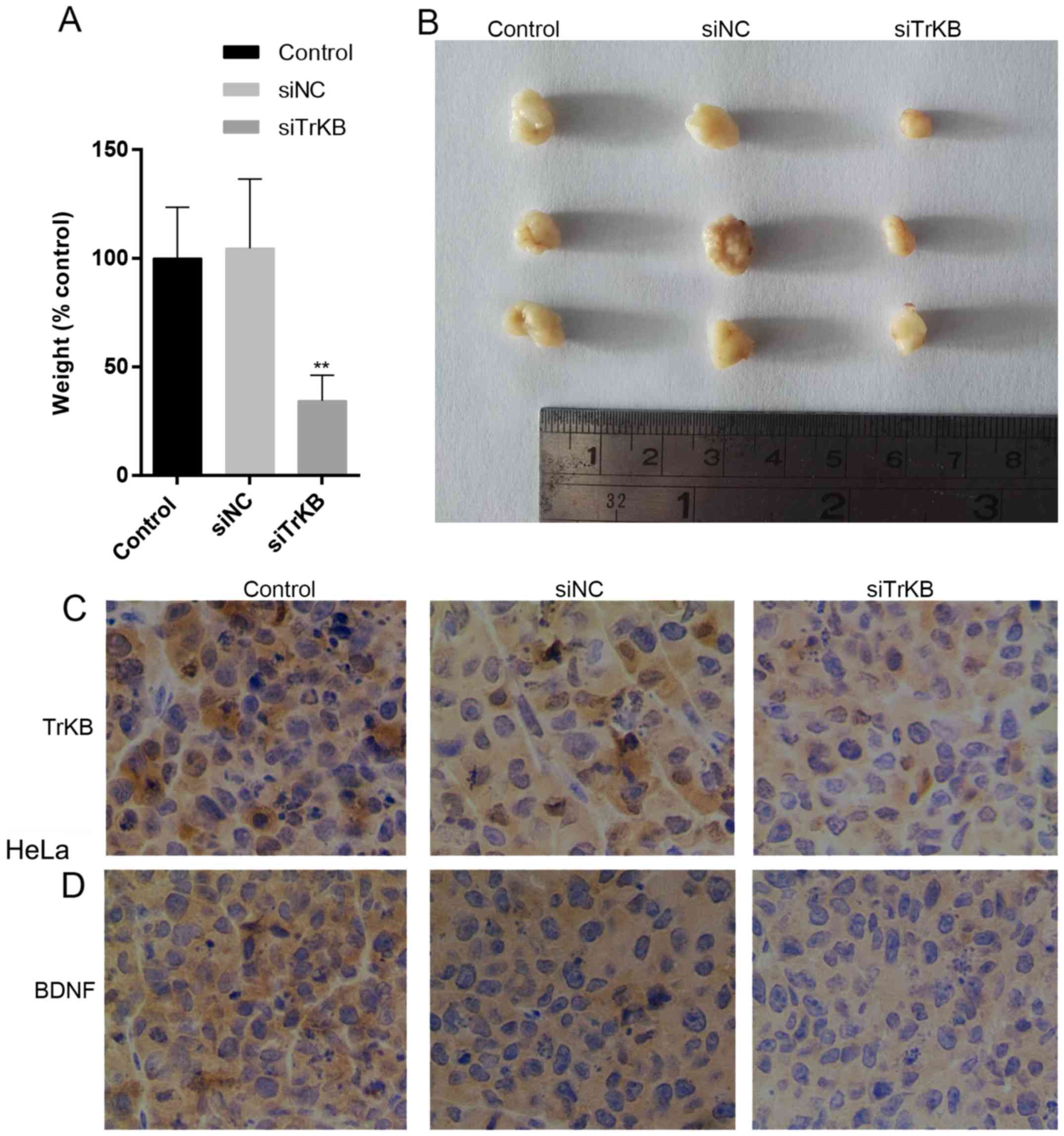
|
1
|
Singhal P, Hussain S, Thakur N, Batra S,
Salhan S, Bhambani S and Bharadwaj M: Association of MDM2 and p53
polymorphisms with the advancement of cervical carcinoma. DNA Cell
Biol. 32:19–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fukushima K, Ogawa S, Tsukimori K,
Kobayashi H and Wake N: Can we diagnose invasive cervical cancer
during pregnancy as precise as in nonpregnant women? Maternal and
perinatal outcome in pregnancies complicated with cervical cancers.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:1439–1445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qu J, Lu W, Li B, Lu C and Wan X: WWOX
induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in cervical cancer and
cell lines. Int J Mol Med. 31:1139–1147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao Y, Shen L, Chen X, Qian Y, Zhou Q,
Wang Y, Li K, Liu M, Zhang S and Huang X: High expression of PKM2
as a poor prognosis indicator is associated with radiation
resistance in cervical cancer. Histol Histopathol. 30:1313–1320.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okugawa Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kawamura M,
Kawamoto A, Hiro J, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Ohi M, Uchida K, et al:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B
pathway in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 108:121–130. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Tanaka K, Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y,
Saigusa S, Kawamura M, Araki T, Uchida K, Mohri Y and Kusunoki M:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced
tropomyosin-related kinase B (Trk B) signaling is a potential
therapeutic target for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from
colorectal cancer. PLoS One 9: e96410. 2014
|
|
7
|
Kelly-Spratt KS, Klesse LJ and Parada LF:
BDNF activated TrkB/IRR receptor chimera promotes survival of
sympathetic neurons through Ras and PI-3 kinase signaling. J
Neurosci Res. 69:151–159. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kimura A, Namekata K, Guo X, Harada C and
Harada T: Neuroprotection, growth factors and BDNF-TrkB signalling
in retinal degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 17:15842016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Okamura K, Harada T, Wang S, Ijichi K,
Furuyama K, Koga T, Okamoto T, Takayama K, Yano T and Nakanishi Y:
Expression of TrkB and BDNF is associated with poor prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 78:100–106. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choi B, Lee EJ, Shin MK, Park YS, Ryu MH,
Kim SM, Kim EY, Lee HK and Chang EJ: Upregulation of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in advanced gastric cancer contributes to bone
metastatic osteolysis by inducing long pentraxin 3. Oncotarget.
7:55506–55517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Au CW, Siu MK, Liao X, Wong ES, Ngan HY,
Tam KF, Chan DC, Chan QK and Cheung AN: Tyrosine kinase B receptor
and BDNF expression in ovarian cancers - Effect on cell migration,
angiogenesis and clinical outcome. Cancer Lett. 281:151–161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bronzetti E, Artico M, Forte F,
Pagliarella G, Felici LM, D'Ambrosio A, Vespasiani G and Bronzetti
B: A possible role of BDNF in prostate cancer detection. Oncol Rep.
19:969–974. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang YT, Lai PC, Wu CC, Hsu SH, Cheng CC,
Lan YF and Chiu TH: BDNF mediated TrkB activation is a survival
signal for transitional cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
36:1469–1476. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiang J, Pan J, Chen F, Zheng L, Chen Y,
Zhang S and Feng W: L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive
impairment of APP/ PS1 mice by BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 7:1706–1713. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Taube JH, Herschkowitz JI, Komurov K, Zhou
AY, Gupta S, Yang J, Hartwell K, Onder TT, Gupta PB, Evans KW, et
al: Core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interactome
gene-expression signature is associated with claudin-low and
metaplastic breast cancer subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:15449–15454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang CC, Zhu LF, Xu XH, Ning TY, Ye JH and
Liu LK: Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces an
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like
properties in SCC9 cells. BMC Cancer. 13:1712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cufí S, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Martin-Castillo B, Joven J and Menendez JA:
Metformin against TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT): From cancer stem cells to aging-associated fibrosis. Cell
Cycle. 9:4461–4468. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bao W, Qiu H, Yang T, Luo X, Zhang H and
Wan X: Upregulation of TrkB promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and anoikis resistance in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS
One. 8:e706162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ricci A, De Vitis C, Noto A, Fattore L,
Mariotta S, Cherubini E, Roscilli G, Liguori G, Scognamiglio G,
Rocco G, et al: TrkB is responsible for EMT transition in malignant
pleural effusions derived cultures from adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Cell Cycle. 12:1696–1703. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, Wang Y,
Tong L, Chen X, Ji Y, Shang Q, Xu B, et al: Metadherin confers
chemoresistance of cervical cancer cells by inducing autophagy and
activating ERK/NF-κB pathway. Tumour Biol. 34:2433–2440. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ming P, Cai T, Li J, Ning Y, Xie S, Tao T
and Tang F: A novel arylbenzofuran induces cervical cancer cell
apoptosis and G1/S arrest through ERK-mediated Cdk2/cyclin-A
signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:41843–41856. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Q, Liang Y, Zhang T, Wang K and Yang
X: ER-α36 mediates estrogen-stimulated MAPK/ERK activation and
regulates migration, invasion, proliferation in cervical cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:625–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Im SR and Jang YJ: Aspirin enhances
TRAIL-induced apoptosis via regulation of ERK1/2 activation in
human cervical cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:65–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Yang Z, Song W, Zhou L, Li Q, Tao K,
Zhou J, Wang X, Zheng Z, You N, et al: Overexpression of Bmi-1
contributes to the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2, MMP-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor via the
PTEN/I3K/Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:793–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li B, Tsao SW, Li YY, Wang X, Ling MT,
Wong YC, He QY and Cheung ALM: Id-1 promotes tumorigenicity and
metastasis of human esophageal cancer cells through activation of
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Cancer. 125:2576–2585. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cornelio DB, DE Farias CB, Prusch DS,
Heinen TE, Dos Santos RP, Abujamra AL, Schwartsmann G and Roesler
R: Influence of GRPR and BDNF/TrkB signaling on the viability of
breast and gynecologic cancer cells. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:148–152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
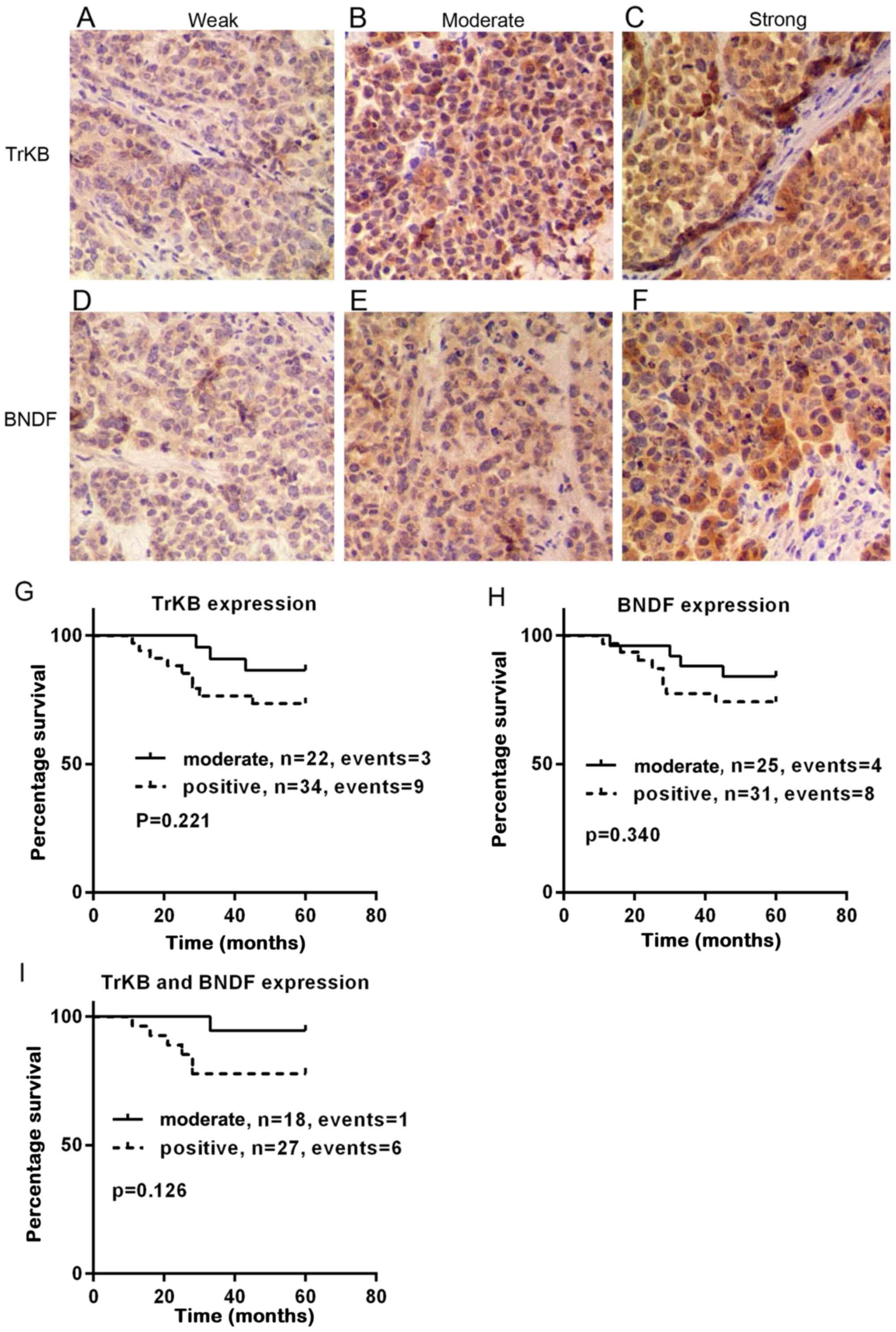
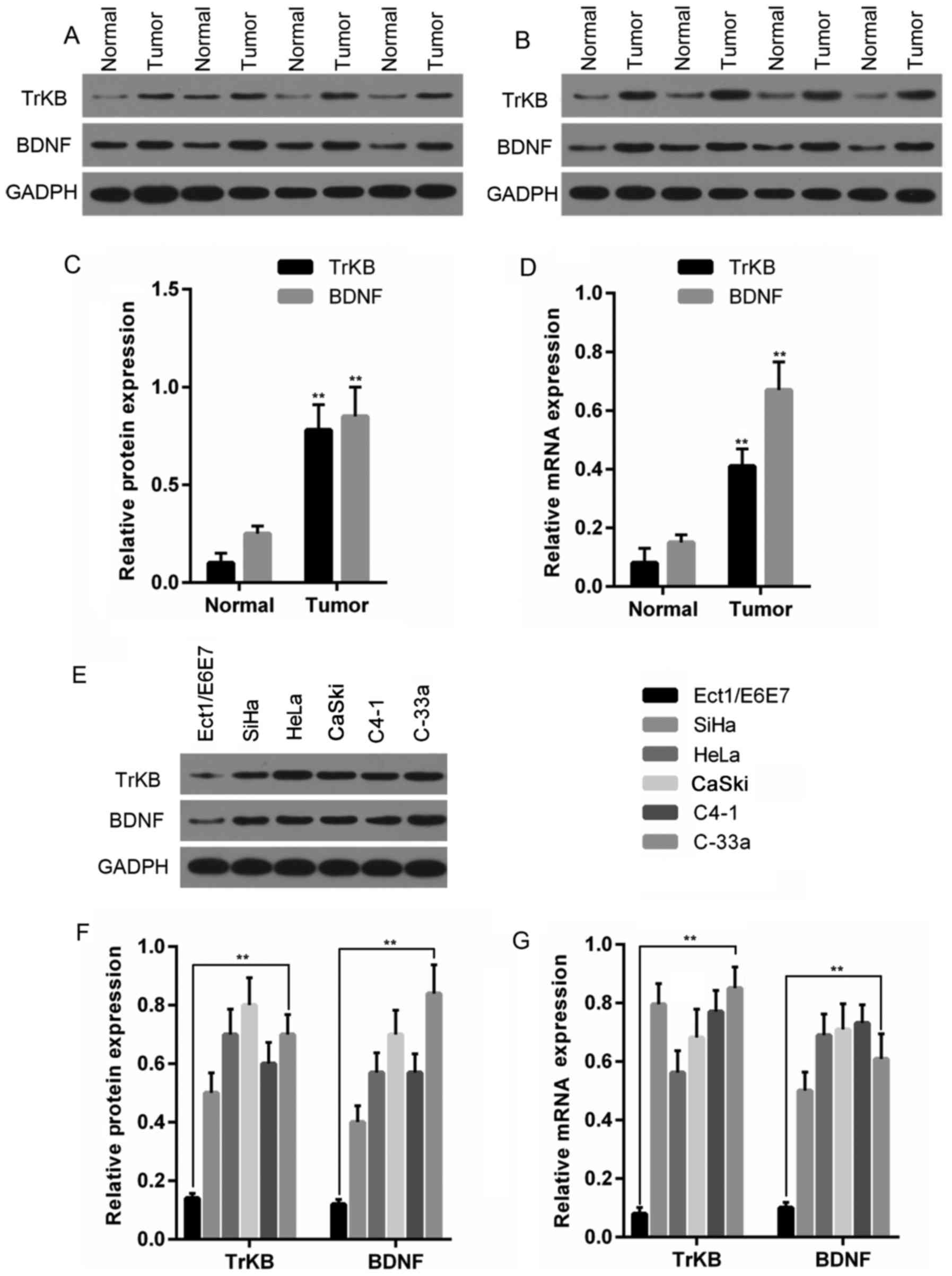
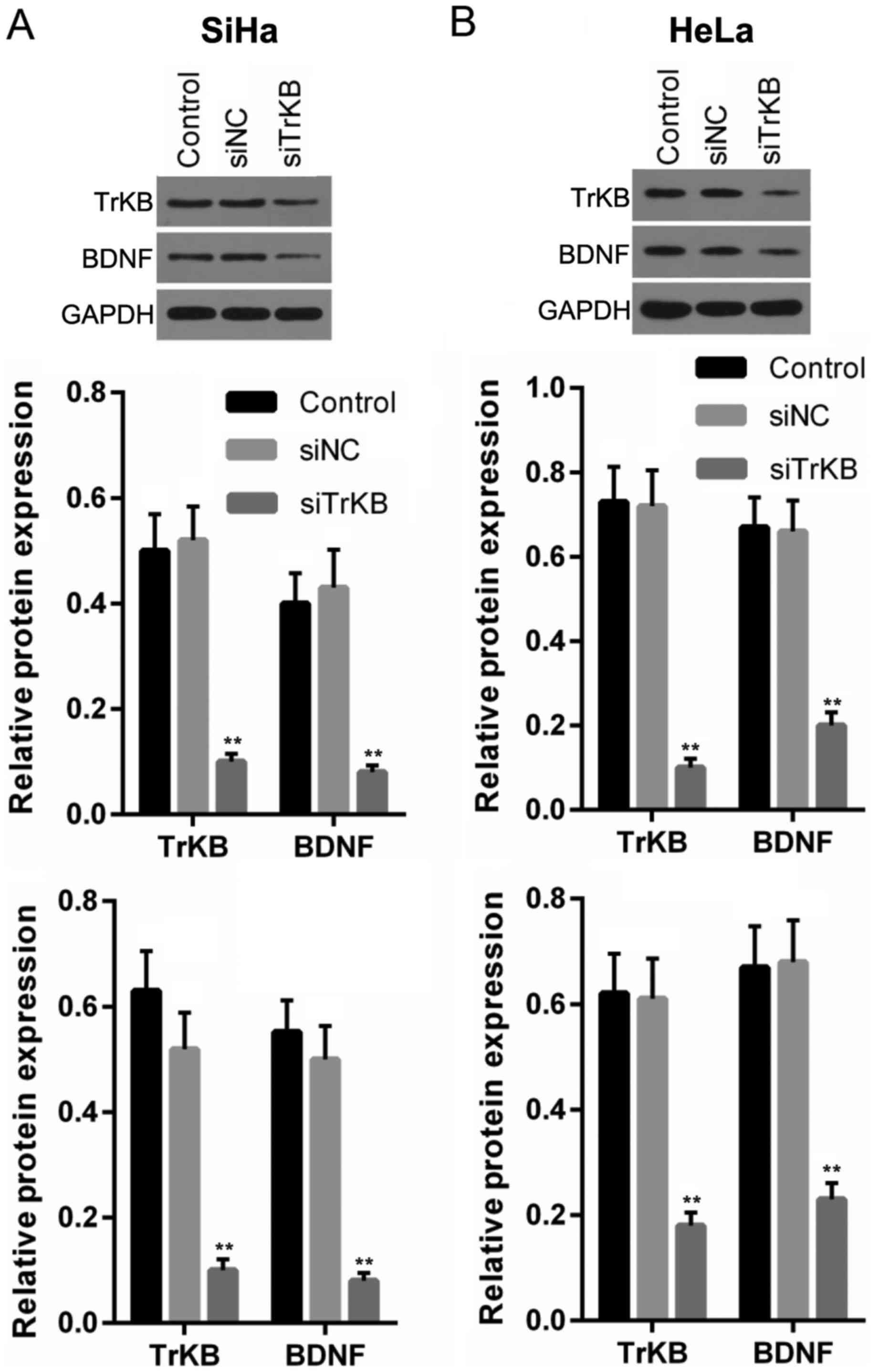
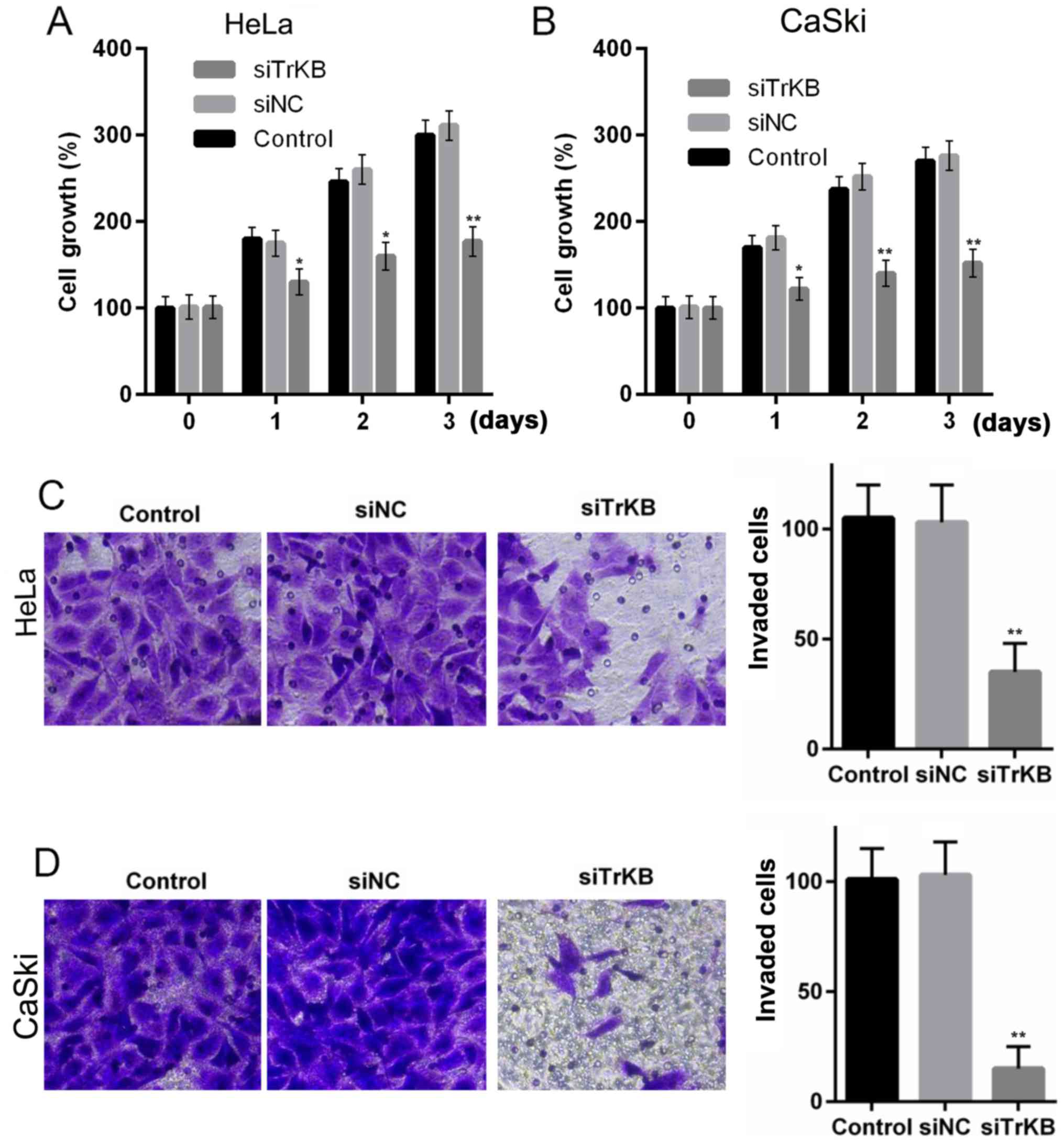
Moon A, Won KY, Lee JY, Kang I, Lee SK and
Lee J: Expression of BDNF, TrkB, and p53 in early-stage squamous
cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Pathology. 43:453–458. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Benedet JL, Bender H, Jones H III and Ngan
HY: FIGO staging classifications and clinical practice guidelines
in the management of gynecologic cancers. Int J Gynaecol Obstet.
70:209–262. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alonso-Alconada L, Eritja N, Muinelo-Romay
L, Barbazan J, Lopez-Lopez R, Matias-Guiu X, Gil-Moreno A, Dolcet X
and Abal M: ETV5 transcription program links BDNF and promotion of
EMT at invasive front of endometrial carcinomas. Carcinogenesis.
35:2679–2686. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jia S, Wang W, Hu Z, Shan C, Wang L, Wu B,
Yang Z, Yang X and Lei D: BDNF mediated TrkB activation contributes
to the EMT progression and the poor prognosis in human salivary
adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 51:64–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee J, Jiffar T and Kupferman ME: A novel
role for BDNF-TrkB in the regulation of chemotherapy resistance in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e302462012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fujikawa H, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Saigusa
S, Inoue Y, Uchida K and Kusunoki M: High TrkB expression levels
are associated with poor prognosis and EMT induction in colorectal
cancer cells. J Gastroenterol. 47:775–784. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wong J: Neurotrophin Signaling and
Alzheimer's Disease Neurodegeneration - Focus on BDNF/TrkB
Signaling, Trends in Cell Signaling Pathways in Neuronal Fate
Decision. Wislet-Gendebien Dr Sabine: InTech. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar : Available from:
https://www.intechopen.com/books/trends-in-cell-signaling-pathways-in-neuronal-fate-decision/neurotrophin-signaling-and-alzheimer-s-disease-neurodegeneration-focus-on-bdnf-trkb-signaling.
|
|
34
|
Eberhardt KA, Irintchev A, Al-Majed AA,
Simova O, Brushart TM, Gordon T and Schachner M: BDNF/TrkB
signaling regulates HNK-1 carbohydrate expression in regenerating
motor nerves and promotes functional recovery after peripheral
nerve repair. Exp Neurol. 198:500–510. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Berner A, Reichert JC, Müller MB, Zellner
J, Pfeifer C, Dienstknecht T, Nerlich M, Sommerville S, Dickinson
IC, Schütz MA, et al: Treatment of long bone defects and
non-unions: From research to clinical practice. Cell Tissue Res.
347:501–519. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Li Y and Chopp M: Intracerebral
transplantation of bone marrow with BDNF after MCAo in rat.
Neuropharmacology. 39:711–716. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fulgenzi G, Tomassoni-Ardori F, Babini L,
Becker J, Barrick C, Puverel S and Tessarollo L: BDNF modulates
heart contraction force and long-term homeostasis through truncated
TrkBT1 receptor activation. J Cell Biol. 210:1003–1012. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pouneh Kermani BH: BDNF: A newly described
mediator of angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 17:1402007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hong JH, Park HM, Byun KH, Lee BH, Kang WC
and Jeong GB: BDNF expression of macrophages and angiogenesis after
myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 176:1405–1408. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jerónimo-Santos A, Vaz SH, Parreira S,
Rapaz-Lérias S, Caetano AP, Buée-Scherrer V, Castrén E, Valente CA,
Blum D, Sebastião AM, et al: Dysregulation of TrkB receptors and
BDNF function by amyloid-β peptide is mediated by calpain. Cereb
Cortex. 25:3107–3121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Feng N, Huke S, Zhu G, Tocchetti CG, Shi
S, Aiba T, Kaludercic N, Hoover DB, Beck SE, Mankowski JL, et al:
Constitutive BDNF/ TrkB signaling is required for normal cardiac
contraction and relaxation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:1880–1885.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Brodeur GM, Nakagawara A, Yamashiro DJ,
Ikegaki N, Liu XG, Azar CG, Lee CP and Evans AE: Expression of
TrkA, TrkB and TrkC in human neuroblastomas. J Neurooncol.
31:49–55. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Zhao H, Brodeur GM
and Evans AE: Expression of the neurotrophin-receptor TrkB predicts
outcome in nephroblastomas: Results of a pilot-study. Klin Padiat .
213:191–196. 2001.In German.
|
|
44
|
Wang HY, Crupi D, Liu J, Stucky A,
Cruciata G, Di Rocco A, Friedman E, Quartarone A and Ghilardi MF:
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances BDNF-TrkB
signaling in both brain and lymphocyte. J Neurosci. 31:11044–11054.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siu MK, Wong OG and Cheung AN: TrkB as a
therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
13:1169–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang ZF, Ho DW, Lau CK, Tam KH, Lam CT,
Poon RTP and Fan ST: Platelet activation during tumor development,
the potential role of BDNF-TrkB autocrine loop. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 346:981–985. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Polakowski N, Terol M, Nash I, Hoang K,
Gazon H, Wurm T, Césaire R, Péloponèse JM, Mesnard JM and Lemasson
I: A BDNF/TrKB autocrine loop stimulated by HBZ is involved in
HTLV-1-infected cell-survival. Retrovirology. 11 (Suppl 1):
O572014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Bondow BJ, Faber ML, Wojta KJ, Walker EM
and Battle MA: E-cadherin is required for intestinal morphogenesis
in the mouse. Dev Biol. 371:1–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fournier MV, Fata JE, Martin KJ, Yaswen P
and Bissell MJ: Interaction of E-cadherin and PTEN regulates
morphogenesis and growth arrest in human mammary epithelial cells.
Cancer Res. 69:4545–4552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tamura G, Yin J, Wang S, Fleisher AS, Zou
T, Abraham JM, Kong D, Smolinski KN, Wilson KT, James SP, et al:
E-Cadherin gene promoter hypermethylation in primary human gastric
carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:569–573. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chetty RI, Serra S and Asa SL: Loss of
membrane localization and aberrant nuclear E-cadherin expression
correlates with invasion in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am J Surg
Pathol. 32:413–419. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang X, Liu G, Kang Y, Dong Z, Qian Q and
Ma X: N-cadherin expression is associated with acquisition of EMT
phenotype and with enhanced invasion in erlotinib-resistant lung
cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 8:e576922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nakajima S, Doi R, Toyoda E, Tsuji S, Wada
M, Koizumi M, Tulachan SS, Ito D, Kami K, Mori T, et al: N-cadherin
expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4125–4133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kumar B, Koul S, Petersen J, Khandrika L,
Hwa JS, Meacham RB, Wilson S and Koul HK: 38mitogen-activated
protein kinase-driven MAPKAPK2 regulates invasion of bladder cancer
by modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. Cancer Res. 70:832–841.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lu KV, Jong KA, Rajasekaran AK, Cloughesy
TF and Mischel PS: Upregulation of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases (TIMP)-2 promotes matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 activation and cell invasion in a human glioblastoma cell
line. Lab Invest. 84:8–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kumamaru E, Numakawa T, Adachi N and
Kunugi H: Glucocorticoid suppresses BDNF-stimulated MAPK/ERK
pathway via inhibiting interaction of Shp2 with TrkB. FEBS Lett.
585:3224–3228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Revest JM, Le Roux A, Roullot-Lacarrière
V, Kaouane N, Vallée M, Kasanetz F, Rougé-Pont F, Tronche F,
Desmedt A and Piazza PV: BDNF-TrkB signaling through Erk1/2 MAPK
phosphorylation mediates the enhancement of fear memory induced by
glucocorticoids. Mol Psychiatry. 19:1001–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Yao RQ, Qi DS, Yu HL, Liu J, Yang LH and
Wu XX: Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral
ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF-TrkB-I3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurochem Res. 37:2777–2786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|