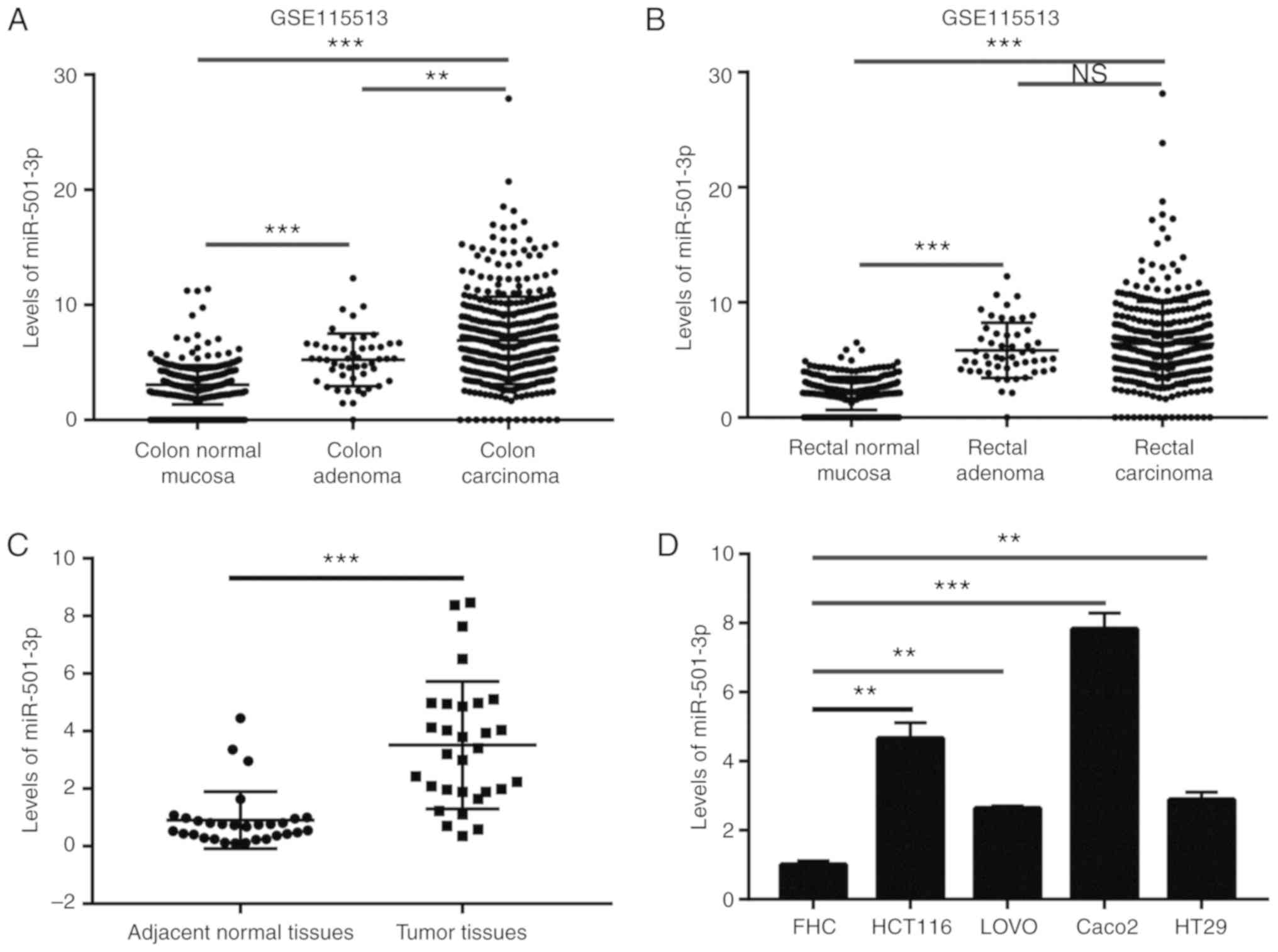
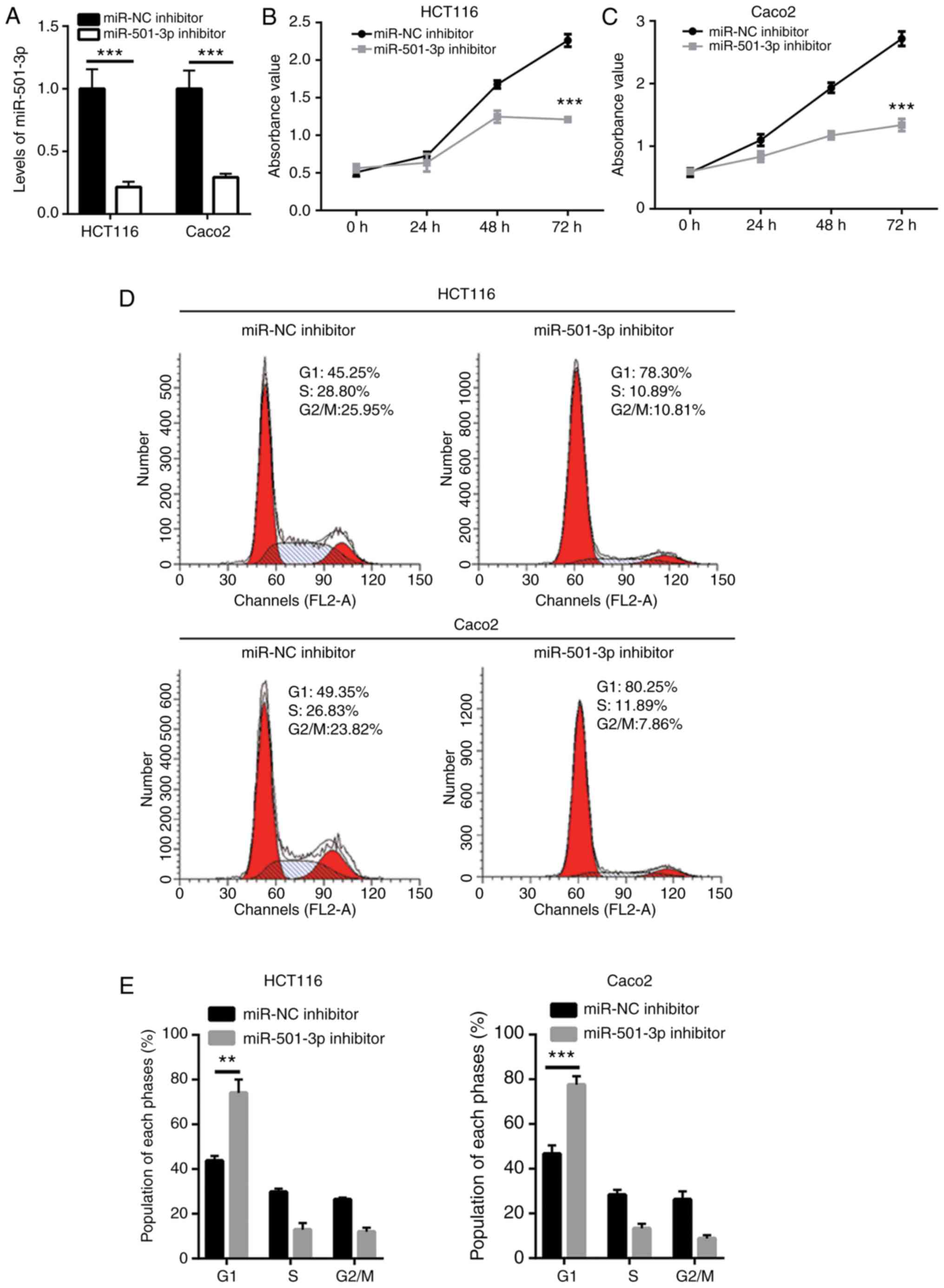
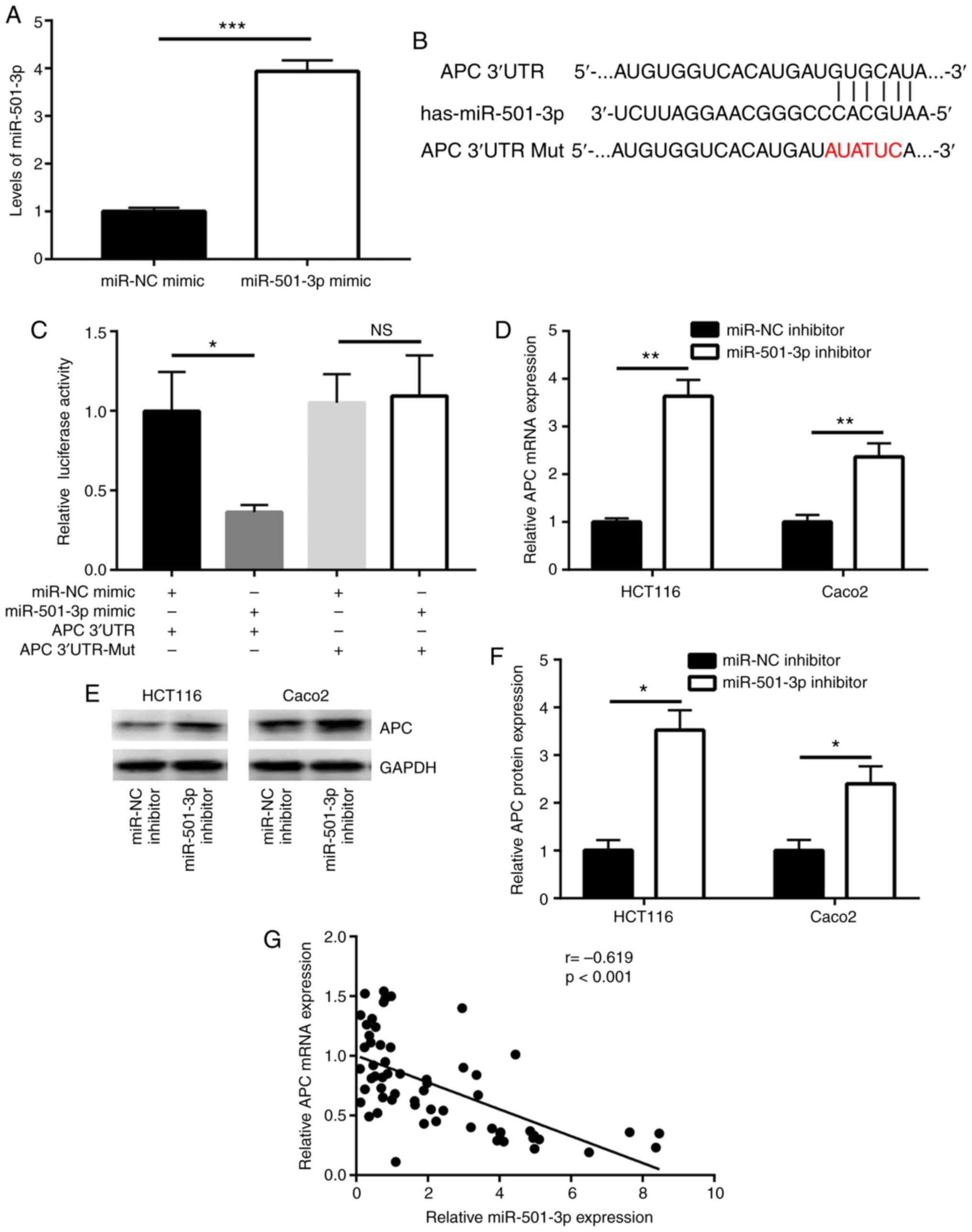
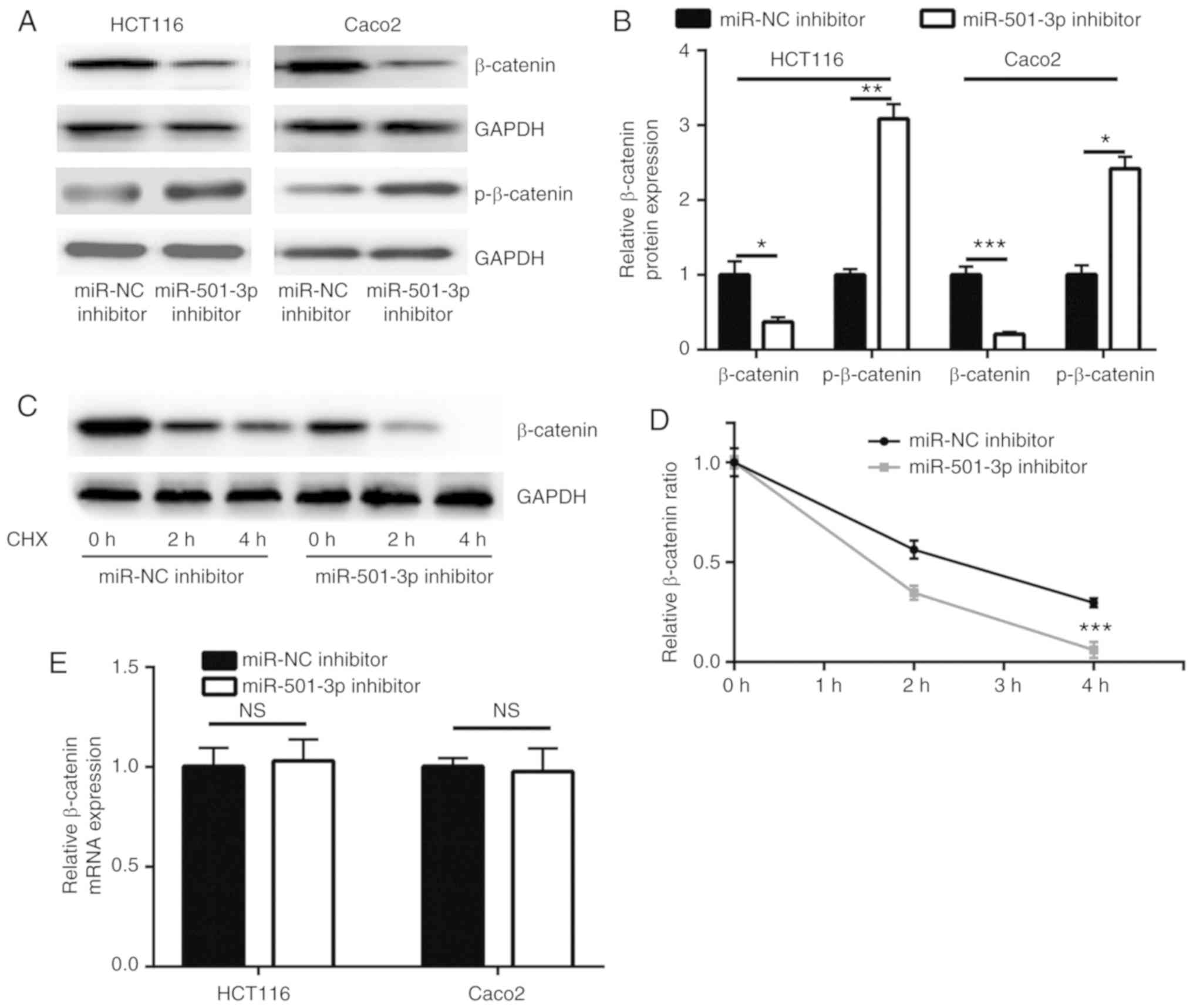
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Araghi M, Soerjomataram I, Jenkins M,
Brierley J, Morris E, Bray F and Arnold M: Global trends in
colorectal cancer mortality: Projections to the year 2035. Int J
Cancer. 144:2992–3000. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jiang S, Miao D, Wang M, Lv J, Wang Y and
Tong J: MiR-30-5p suppresses cell chemoresistance and stemness in
colorectal cancer through USP22/Wnt/β-catenin signaling axis. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:630–640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Claessen MM, Schipper ME, Oldenburg B,
Siersema PD, Offerhaus GJ and Vleggaar FP: WNT-pathway activation
in IBD-associated colorectal carcinogenesis: Potential biomarkers
for colonic surveillance. Cell Oncol. 32:303–310. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng H, Sun X, Li J, He P, Liu W and Meng
X: Knockdown of Uba2 inhibits colorectal cancer cell invasion and
migration through downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:6914–6925. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bienz M and Clevers H: Linking colorectal
cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell. 103:311–320. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Emons G, Spitzner M, Reineke S, Möller J,
Auslander N, Kramer F, Hu Y, Beissbarth T, Wolff HA, Rave-Fränk M,
et al: Chemoradiotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer cells is
mediated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1481–1490.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Myant KB, Cammareri P, McGhee EJ, Ridgway
RA, Huels DJ, Cordero JB, Schwitalla S, Kalna G, Ogg EL, Athineos
D, et al: ROS production and NF-κB activation triggered by RAC1
facilitate WNT-driven intestinal stem cell proliferation and
colorectal cancer initiation. Cell Stem Cell. 12:761–773. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peifer M and Polakis P: Wnt signaling in
oncogenesis and embryogenesis-a look outside the nucleus. Science.
287:1606–1609. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sparks AB, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and
Kinzler KW: Mutational analysis of the APC/beta-catenin/Tcf pathway
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 58:1130–1134. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sawa M, Masuda M and Yamada T: Targeting
the Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 20:419–429. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Olsen AK, Coskun M, Bzorek M, Kristensen
MH, Danielsen ET, Jørgensen S, Olsen J, Engel U, Holck S and
Troelsen JT: Regulation of APC and AXIN2 expression by intestinal
tumor suppressor CDX2 in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
34:1361–1369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shu Z, Chen L and Ding D: miR-582-5P
induces colorectal cancer cell proliferation by targeting
adenomatous polyposis coli. World J Surg Oncol. 14:2392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heter-ochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thomas J, Ohtsuka M, Pichler M and Ling H:
MicroRNAs: Clinical relevance in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
16:28063–28076. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iwaya T, Yokobori T, Nishida N, Kogo R,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Sawada G, Takahashi Y, Ishibashi M, et
al: Downregulation of miR-144 is associated with colorectal cancer
progression via activation of mTOR signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 33:2391–2397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Slattery ML, Herrick JS, Pellatt DF,
Stevens JR, Mullany LE, Wolff E, Hoffman MD, Samowitz WS and Wolff
RK: MicroRNA profiles in colorectal carcinomas, adenomas and normal
colonic mucosa: Variations in miRNA expression and disease
progression. Carcinogenesis. 37:245–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sanches JGP, Xu Y, Yabasin IB, Li M, Lu Y,
Xiu X, Wang L, Mao L, Shen J, Wang B, et al: miR-501 is upregulated
in cervical cancer and promotes cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by targeting CYLD. Chem Biol Interact. 285:85–95. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Y, Chai Y, Zhang J and Tang J: A
Function variant at miR-501 alters susceptibility to hepatocellular
carcinoma in a Chinese Han population. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:2500–2508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Hardisson D, Sánchez C,
Sarrió D, Cassia R, García-Rostán G, Prat J, Guo M, Herman JG,
Matías-Guiu X, et al: Abnormalities of the APC/beta-catenin pathway
in endometrial cancer. Oncogene. 21:7981–7990. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gumbiner BM: Carcinogenesis: A balance
between beta-catenin and APC. Curr Biol. 7:R443–R446. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gomase VS and Parundekar AN: MicroRNA:
Human disease and development. Int J Bioinform Res Appl. 5:479–500.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bailey ST, Westerling T and Brown M: Loss
of estrogen-regulated microRNA expression increases HER2 signaling
and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 75:436–445. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Gu J, Roth JA, Hildebrandt MA,
Lippman SM, Ye Y, Minna JD and Wu X: Pathway-based serum microRNA
profiling and survival in patients with advanced stage non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 73:4801–4809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yokoi A, Matsuzaki J, Yamamoto Y, Yoneoka
Y, Takahashi K, Shimizu H, Uehara T, Ishikawa M, Ikeda SI, Sonoda
T, et al: Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian
cancer screening. Nat Commun. 9:43192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu C, Liu R, Zhang D, Deng Q, Liu B, Chao
HP, Rycaj K, Takata Y, Lin K, Lu Y, et al: MicroRNA-141 suppresses
prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by targeting a cohort of
pro-metastasis genes. Nat Commun. 8:142702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu J, Lei R, Zhuang X, Li X, Li G, Lev S,
Segura MF, Zhang X and Hu G: MicroRNA-182 targets SMAD7 to
potentiate TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis of cancer cells. Nat Commun. 7:138842016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hara N, Kikuchi M, Miyashita A, Hatsuta H,
Saito Y, Kasuga K, Murayama S, Ikeuchi T and Kuwano R: Serum
microRNA miR-501-3p as a potential biomarker related to the
progression of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun.
5:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
James MI, Iwuji C, Irving G, Karmokar A,
Higgins JA, Griffin-Teal N, Thomas A, Greaves P, Cai H, Patel SR,
et al: Curcumin inhibits cancer stem cell phenotypes in ex vivo
models of colorectal liver metastases, and is clinically safe and
tolerable in combination with FOLFOX chemotherapy. Cancer Lett.
364:135–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boman BM, Fields JZ, Bonham-Carter O and
Runquist OA: Computer modeling implicates stem cell overproduction
in colon cancer initiation. Cancer Res. 61:8408–8411.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Novellasdemunt L, Antas P and Li VS:
Targeting Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. A review in the
theme: Cell signaling: Proteins, pathways and mechanisms. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 309:C511–C521. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang N, Li X, Wu CW, Dong Y, Cai M, Mok
MT, Wang H, Chen J, Ng SS, Chen M, et al: microRNA-7 is a novel
inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis.
Oncogene. 32:5078–5088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang H, Hao Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Li J, Yin
S, Sun C, Ma M, Huang Y and Xi JJ: Genome-wide functional screening
of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer
metastasis. Nat Commun. 2:5542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nagel R, le Sage C, Diosdado B, van der
Waal M, Oude Vrielink JA, Bolijn A, Meijer GA and Agami R:
Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135
family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 68:5795–5802. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin Y, Gu Q, Sun Z, Sheng B, Qi C, Liu B,
Fu T, Liu C and Zhang Y: Upregulation of miR-3607 promotes lung
adenocar-cinoma proliferation by suppressing APC expression. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:497–503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu L, Zhang H, Shi L, Zhang W, Yuan J,
Chen X, Liu J, Zhang Y and Wang Z: Inhibition of Rac1 activity
induces G1/S phase arrest through the GSK3/cyclin D1 pathway in
human cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 32:1395–1400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee SH, Chen TY, Dhar SS, Gu B, Chen K,
Kim YZ, Li W and Lee MG: A feedback loop comprising PRMT7 and
miR-24-2 interplays with Oct4, Nanog, Klf4 and c-Myc to regulate
stemness. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:10603–10618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|