Introduction
Bladder cancer is a common type of genitourinary
cancer. Radical cystectomy with urinary diversion is considered to
be the most effective local treatment for invasive bladder cancer
(1,2). As regards quality of life (QOL),
including urinary, sexual and social functioning, daily living
activities and body image satisfaction, orthotopic continent
diversions are considered the ‘gold standard’ among reconstructive
procedures (3–5). However, QOL has not been sufficiently
assessed in non-metastatic bladder cancer patients (NMBC) (6). Therefore, available data on the
comparison of the impact of different treatments on the QOL of NMBC
patients are limited (7). The MOS
36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) score is extensively used
worldwide and is considered to be accurate (8–11).
SF-36 has become a standard questionnaire and it may be applied to
patients as well as to healthy subjects. In addition, the questions
may be easily answered within a short time and they are limited to
the evaluation of basic issues regarding overall health. In this
study, we compared the functional results between patients with an
orthotopic and those with a non-orthotopic neobladder at 6, 12 and
24 months after surgery, using the SF-36 method.
Patients and methods
Patients
Between January, 2007 and December, 2009, an
orthotopic neobladder reconstruction was performed on 54 patients
(experimental group). In addition, non-orthotopic neobladder
surgery (cutaneous diversion), was performed in 28 patients
(control group). The experimental group included 50 patients with
transitional cell carcinoma (5 with T1, 31 with T2 and 14 with T3),
2 with squamous cell carcinoma, 1 with adenocarcinoma and 1 with
neuroendocrine carcinoma (mean age of the 54 patients, 66.0 years).
The control group included a total of 28 patients with a
non-orthotopic neobladder, 27 of which had transitional cell
carcinoma (14 had T2, 12 had T3 and 1 had T4) and 1 had
adenocarcinoma (T2) (mean age of the 28 patients, 65.6 years). The
82 patient samples were all confirmed by pathological examination
following surgery. This study complies with current ethical
considerations. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee
of Kunming Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from
all patients.
Methods
The functional results of the two groups were
compared at 6 months, 1 year and 2 years after surgery, using the
SF-36 survey method. Regarding the orthotopic reconstruction, most
of the surgical techniques were based on Studer’s method. At a time
point of >6 months after surgery, the SF-36 survey was conducted
by mail to determine the QOL of patients with an orthotopic and
that of patients with a non-orthotopic neobladder. The SF-36 survey
consisted of 36 questions and the 2nd question was a
self-evaluation of health status, which was not included in the
score calculation. We assessed 8 aspects of health-related QOL:
physical functioning, role-physical functioning, bodily pain,
general health, vitality, social functioning, role-emotional
functioning and mental health. The number of questions regarding
each health concept ranged from 2 for social functioning and bodily
pain to 10 for physical functioning and the number of response
options per question ranged from 2 (yes or no) to 6 (none, very
mild, mild, moderate, severe or very severe). The score per
question was estimated for each health concept, ranging from 0 to
100, with higher scores indicative of an improved outcome. For the
orthotopic neobladder patients, a detailed continence questionnaire
(not validated) including voiding questions was examined on the
same day as the SF-36 survey.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive data were reported as the means ± SD.
The differences in the mean values between the ileal neobladder and
the cutaneous diversion patients were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney
U test. Data regarding the percentage of patients with a
neobladder, the number of males, the number of patients with a
pathological stage T3 or higher and the current disease status were
analysed by the χ2 test. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Comparison of data from the SF-36 survey
between the experimental and control groups at the time point of 6
months
All 82 patients (100%) were available for assessment
at the time point of 6 months. A total of 51 out of the 54 patients
in the experimental group (94.4%) and 26 out of the 28 in the
control group (92.9%) were available for assessment at the time
point of 12 months. A total of 45 patients in the experimental
group (83.3%) and 23 in the control group (82.1%) were available
for assessment at the time point of 24 months. All questionnaires
were qualified. At the time point of 6 months, the response rate
was similar for the experimental group (54/54, 100%) and for the
control group (28/28, 100%). The majority of patients (76/82,
92.7%) indicated that their physical condition was worse compared
to 1 year before when were the questionnaires completed. Data from
the SF-36 survey are provided in Table
I and Fig. 1.
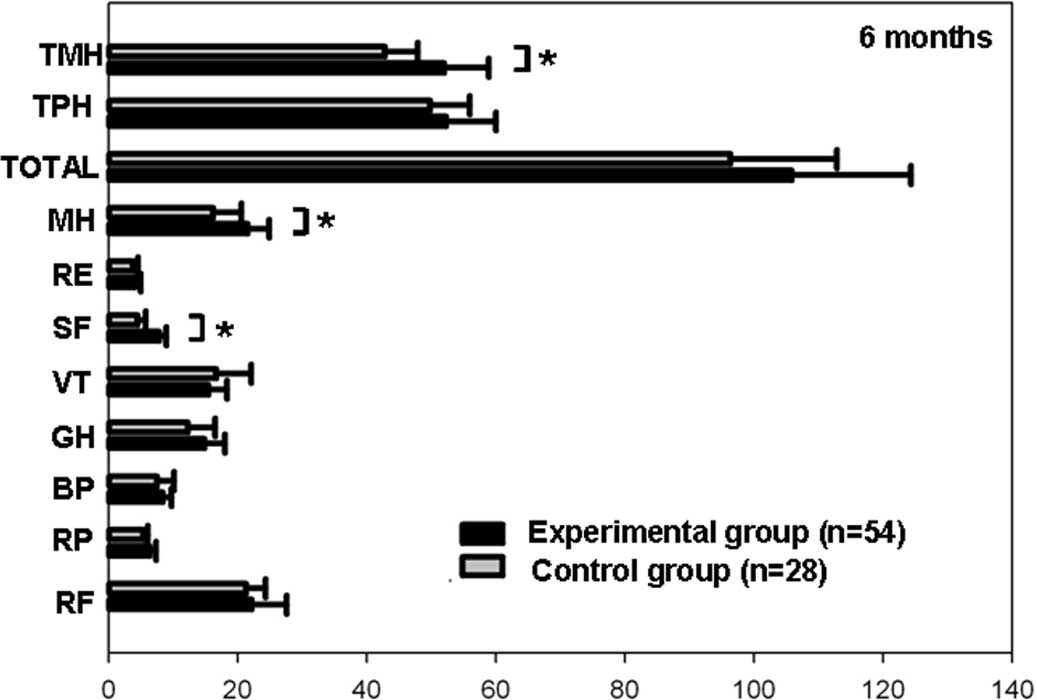 | Figure 1.Comparison of data from the Short-Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 6 months (*P<0.05). TMH, total mental health; TPH, total
physical health; MH, mental health; RE, role-emotional functioning;
SF, social functioning; VT, vitality; GH, general health; BP,
bodily pain; RP, role-physical functioning; RF, physical
functioning. |
 | Table I.Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 6 months. |
Table I.
Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 6 months.
| Items | Experimental group
(n=54) | Control group
(n=28) | P-value |
|---|
| Physical
functioning | 22.13±5.42 | 21.26±3.04 | 0.27 |
| Role-physical
functioning | 6.32±1.04 | 5.34±0.74 | 0.08 |
| Bodily pain | 8.36±1.41 | 7.52±2.63 | 0.29 |
| General health | 14.82±3.19 | 12.26±4.27 | 0.14 |
| Vitality | 15.49±2.88 | 16.62±5.43 | 0.31 |
| Social
functioning | 7.83±1.15 | 4.49±1.29 | 0.01 |
| Role-emotional
functioning | 3.96±1.03 | 3.73±0.82 | 0.77 |
| Mental health | 21.49±3.37 | 16.20±4.33 | 0.02 |
| Overall health | 105.80±18.49 | 96.36±16.42 | 0.11 |
| Total physical
health | 52.23±7.74 | 49.76±6.20 | 0.32 |
| Total mental
health | 51.93±6.91 | 42.77±5.12 | 0.01 |
Comparison of data from the SF-36 survey
between the experimental and control groups at the time point of 12
months
The social functioning and mental health scores in
the experimental group were significantly higher compared to those
in the control group (P<0.05) and the QOL score in the
experimental group was higher compared to the control group;
however, the difference was not statistically significant
(P>0.05). At the time point of 12 months, the response rates of
the experimental group and the control group were 51/54 (94.4%) and
26/28 (92.9%), respectively. In the experimental group, 1 patient
succumbed to multiple metastases of bladder cancer, 1 expired due
to non-cancerous causes and 1 was lost to follow-up. In the
experimental group, 22 patients (43.1%) indicated that their
physical condition was worse compared to 1 year before, 27 (52.9%)
indicated that their physical condition had improved compared to 1
year before and 2 (3.9%) observed no differences compared to 1 year
before when they completed the questionnaires. In the control
group, 16 patients (61.5%) indicated that their physical condition
was worse compared to 1 year before and 10 (38.5%) indicated that
their physical condition had improved compared to 1 year before
when they completed the questionnaires. Data from the SF-36 survey
are provided in Table II and
Fig. 2. The general health, social
functioning, role-emotional functioning and mental health scores in
the experimental group were significantly higher compared to those
in the control group (P<0.05). The QOL score in the experimental
group was higher compared to that in the control group; however,
the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05).
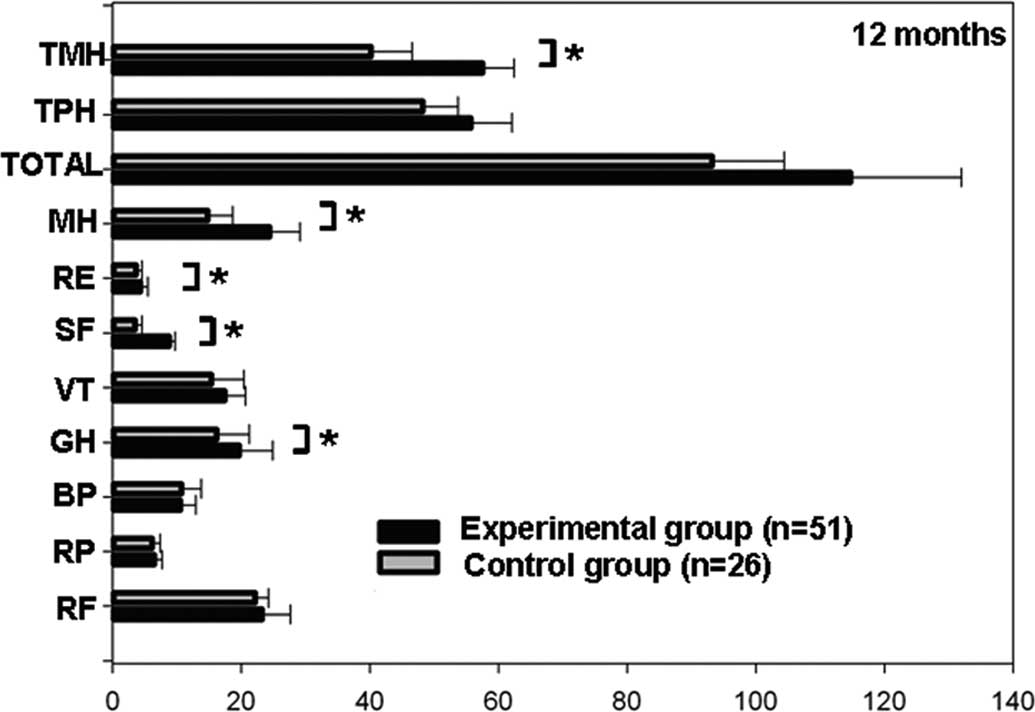 | Figure 2.Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental control groups at 12
months (*P<0.05). TMH, total mental health; TPH, total physical
health; MH, mental health; RE, role-emotional functioning; SF,
social functioning; VT, vitality; GH, general health; BP, bodily
pain; RP, role-physical functioning; RF, physical functioning. |
 | Table II.Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 12 months. |
Table II.
Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 12 months.
| Items | Experimental group
(n=51) | Control group
(n=26) | P-value |
|---|
| Physical
functioning | 23.22±4.37 | 22.14±2.03 | 0.17 |
| Role-physical
functioning | 6.46±1.18 | 6.07±1.24 | 0.26 |
| Bodily pain | 10.47±2.43 | 10.64±3.06 | 0.63 |
| General health | 19.64±5.23 | 16.18±5.01 | 0.03 |
| Vitality | 17.38±3.27 | 15.33±5.06 | 0.11 |
| Social
functioning | 8.72±0.96 | 3.47±1.04 | 0.01 |
| Role-emotional
functioning | 4.29±1.17 | 3.62±0.93 | 0.01 |
| Mental health | 24.36±4.74 | 14.71±3.89 | 0.01 |
| Overall health | 114.7±17.32 | 93.17±11.24 | 0.11 |
| Total physical
health | 55.69±6.34 | 48.17±5.47 | 0.08 |
| Total mental
health | 57.49±4.93 | 40.16±6.36 | 0.01 |
Comparison of data from the SF-36 survey
between the experimental and control groups at the time point of 24
months
At the time point of 24 months, the response rates
of the experimental and control groups were 45/54 (83.3%) and 23/28
(82.1%), respectively. In the experimental group, one patient
succumbed to multiple metastases of bladder cancer and 5 patients
died due to non-cancerous causes. In the control group, 2 patients
succumbed to non-cancerous causes and 1 was lost to follow-up. In
the experimental group, 8 patients (17.8%) indicated that their
physical condition was worse compared to 1 year before, 11 (24.4%)
indicated that their physical condition had improved compared to 1
year before and 26 (57.8%) observed no differences compared to 1
year before when they completed the questionnaires. In the control
group, 14 patients (60.9%) indicated that their physical condition
was worse compared to 1 year before, 7 (30.4%) indicated that their
physical condition had improved compared to 1 year before and 2
(8.7%) observed no differences compared to 1 year before when they
completed the questionnaires. Data from the SF-36 survey are
provided in Table III and Fig. 3. The general health, social
functioning, role-emotional functioning, mental health and QOL
scores in the experimental group were significantly higher compared
to those in the control group (P<0.05).
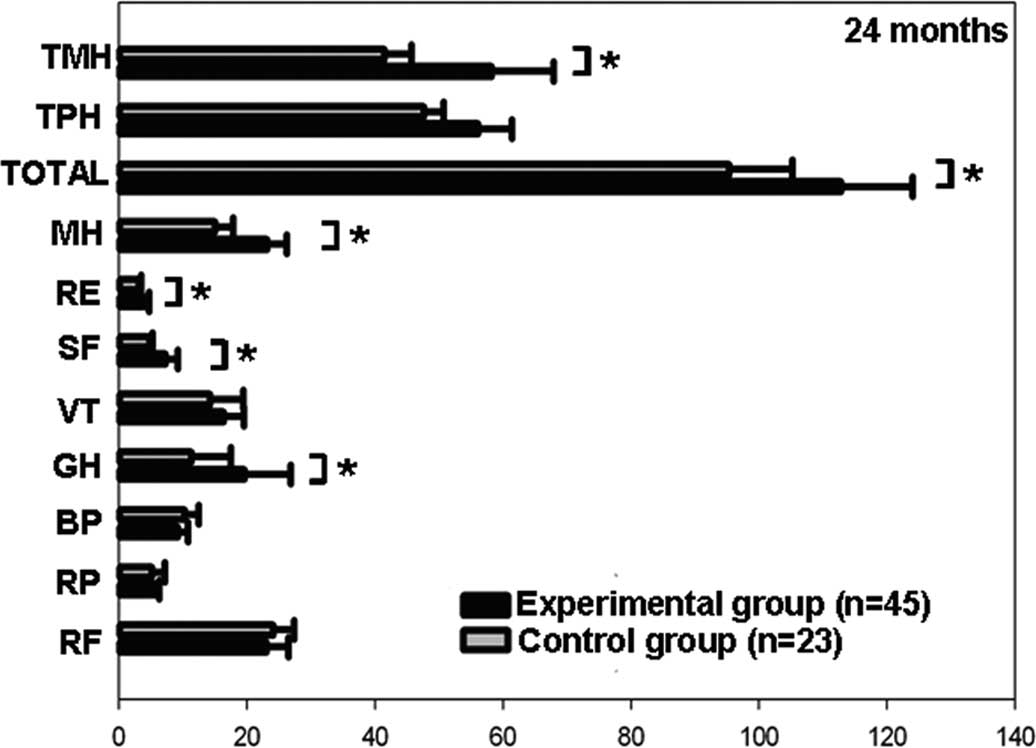 | Figure 3.Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental control groups at 24
months (*P<0.05). TMH, total mental health; TPH, total physical
health; MH, mental health; RE, role-emotional functioning; SF,
social functioning; VT, vitality; GH, general health; BP, bodily
pain; RP, role-physical functioning; RF, physical functioning. |
 | Table III.Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 24 months. |
Table III.
Comparison of data from the Short Form
Health Survey (SF-36) between the experimental and control groups
at 24 months.
| Items | Experimental group
(n=45) | Control group
(n=23) | P-value |
|---|
| Physical
functioning | 23.07±3.44 | 24.15±3.28 | 0.43 |
| Role-physical
functioning | 5.79±0.54 | 5.21±1.96 | 0.26 |
| Bodily pain | 9.27±1.54 | 10.33±2.17 | 0.56 |
| General health | 19.63±7.26 | 11.35±6.20 | 0.01 |
| Vitality | 16.37±3.19 | 14.28±5.17 | 0.06 |
| Social
functioning | 7.32±1.94 | 4.86±0.46 | 0.01 |
| Role-emotional
functioning | 3.92±0.81 | 3.12±0.42 | 0.01 |
| Mental health | 23.17±3.06 | 15.10±2.79 | 0.01 |
| Overall health | 112.8±11.23 | 95.41±9.86 | 0.01 |
| Total physical
health | 56.13±5.31 | 47.67±3.12 | 0.09 |
| Total mental
health | 58.22±9.71 | 41.47±4.29 | 0.01 |
Discussion
Urinary reconstruction is indispensable following
radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer (5,12).
In our institute (Yunnan Institute of Urology, China), orthotopic
neobladder reconstruction procedures were performed when the
patients had the appropriate indications for this type of surgery
from the viewpoint of cancer control, as well as when the patients
requested the surgery. However, we performed non-orthotopic
neobladder procedures when the patients did not have the
appropriate indications for the construction of an ileal
neobladder. Due to the increasing number of patients receiving an
orthotopic rather than a non-orthotopic neobladder following
radical cystectomy, it is significant to accurately demonstrate the
health-related QOL differences between the two procedures, in order
to select the patient-appropriate type of urinary diversion,
considering that they exhibit similar morbidity and mortality
rates. Although QOL is increasingly recognized as an important
outcome measure following treatment for urological malignancy, the
QOL findings after a cystectomy remain a controversial subject.
The health-related QOL, as well as the micturition
status and continence following a cystectomy, are important
considerations in selecting the optimal treatment modality
(13,14). Therefore, we investigated whether
there were differences in QOL between the experimental and the
control groups. Numerous questionnaires have been developed in
order to evaluate the health-related QOL. The health-related QOL in
patients with urinary reconstructions has been evaluated thus far
using various types of questionnaires (15). The SF-36 score is extensively used
worldwide and is considered to be accurate (16). Furthermore, it is a standard
questionnaire that may be applied to patients as well as to healthy
subjects. In addition, the questions may be easily answered within
a short time and they are limited to the evaluation of basic issues
regarding overall health.
Our data demonstrated that more patients perceived
themselves as healthy following an orthotopic urinary diversion and
their total health scores were higher compared to those of patients
undergoing a non-orthotopic urinary diversion; however, there were
no differences in the scores of physical functioning between the
two groups. There were no statistical differences in the
health-related QOL between the orthotopic and the non-orthotopic
neobladder group; however, the functional results of orthotopic
neobladder patients were satisfactory and consistent with those
reported by other studies. In conclusion, the orthotopic neobladder
reconstructive surgery may be performed on patients with the
appropriate indications from the viewpoint of cancer control,
particularly on patients concerned over a negative body image due
to the presence of a urinary stoma. Our data may assist patients in
the selection of the most appropriate treatment option. However,
studies including larger patient samples may help elucidate the
relative psychological benefits associated with various types of
urinary tract reconstruction.
References
|
1.
|
Hautmann RE, de Petriconi RC, Pfeiffer C
and Volkmer BG: Radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the
bladder without neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy: long-term results
in 1100 patients. Eur Urol. 61:1039–1047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kübler H and Gschwend JE: Ileal neobladder
in women with bladder cancer: cancer control and functional
aspects. Curr Opin Urol. 21:478–482. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Erber B, Schrader M, Miller K, et al:
Morbidity and quality of life in bladder cancer patients following
cystectomy and urinary diversion: a single-institution comparison
of ileal conduit versus orthotopic neobladder. ISRN Urol. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Hashine K, Miura N, Numata K, Shirato A,
Sumiyoshi Y and Kataoka M: Health-related quality of life after
bladder preservation therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Int J Urol. 15:403–406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Jeong IG, You D, Kim J, et al: Factors
associated with nonorthotopic urinary diversion after radical
cystectomy. World J Urol. 30:815–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Philip J, Manikandan R, Venugopal S,
Desouza J and Javle PM: Orthotopic neobladder versus ileal conduit
urinary diversion after cystectomy - a quality-of-life based
comparison. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 91:565–569. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Takenaka A, Hara I, Soga H, et al:
Assessment of long-term quality of life in patients with orthotopic
neobladder followed for more than 5 years. Int Urol Nephrol.
43:749–754. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Cesarino CB, Beccaria LM, Aroni MM,
Rodrigues LC and Pacheco Sda S: Quality of life of patients with
implantable cardioverser-defibrillator: the usage of SF-36
questionnaire. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 26:238–243. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Maurino J, Cordero L and Ballesteros J:
The subjective well-being under neuroleptic scale - short version
(SWN-K) and the SF-36 health survey as quality of life measures in
patients with schizophrenia. Patient Prefer Adherence. 6:83–85.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
McPherson A and Martin CR: A review of the
measurement properties of the 36-item short-form health survey
(SF-36) to determine its suitability for use in an
alcohol-dependent population. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. Mar
27–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
11.
|
Wan C, Tu X, Messing S, et al: Development
and validation of the general module of the system of quality of
life instruments for chronic diseases and its comparison with
SF-36. J Pain Symptom Manage. 42:93–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kang SG, Ko YH, Jang HA, et al: Initial
experience of robot-assisted radical cystectomy with total
intracorporeal-urinary diversion: comparison with extracorporeal
method. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 22:456–462. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Goossens-Laan CA, Kil PJ, Ruud Bosch JL
and De Vries J: Pre-diagnosis quality of life (QoL) in patients
with hematuria: comparison of bladder cancer with other causes.
Qual Life Res. Mar 30–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
14.
|
Miyanaga N, Akaza H, Shinohara N, et al:
Assessment of QOL and survival for patients undergoing radical
cystectomy or bladder preservation for invasive bladder cancer.
Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 90:445–453. 1999.(In Japanese).
|
|
15.
|
Ridolo E, Baiardini I, Meschi T, et al:
Erratum to: HRQoL questionnaire evaluation in lactose intolerant
patients with adverse reactions to foods. Intern Emerg Med. Feb
24–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
16.
|
Velanovich V, Younga J, Bhandarkar V, et
al: A single, global patient-centered measure from the SF-36
instrument to assess surgical outcomes and quality of life: a pilot
study. World J Surg. 36:2045–2050. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|

















