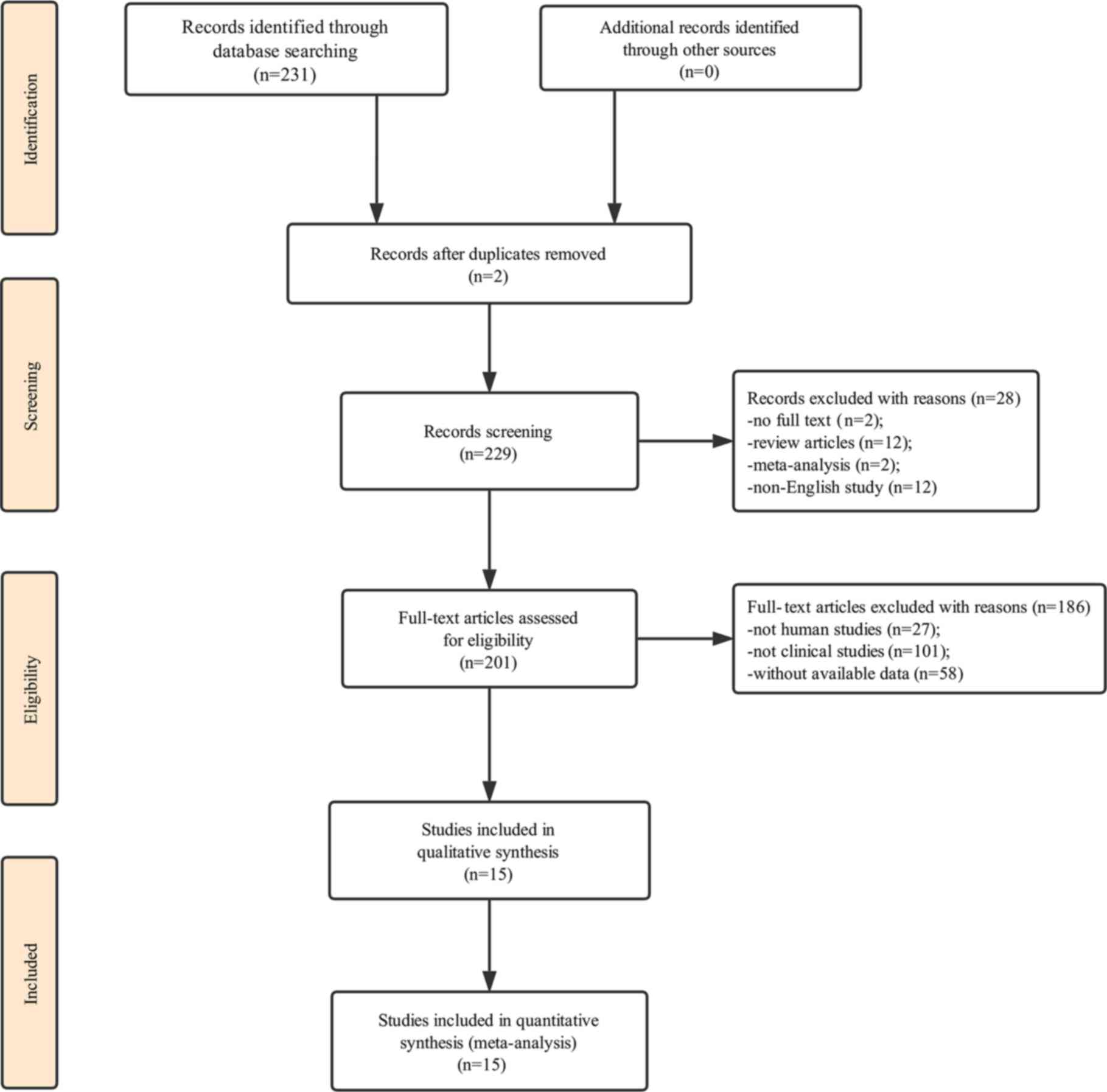
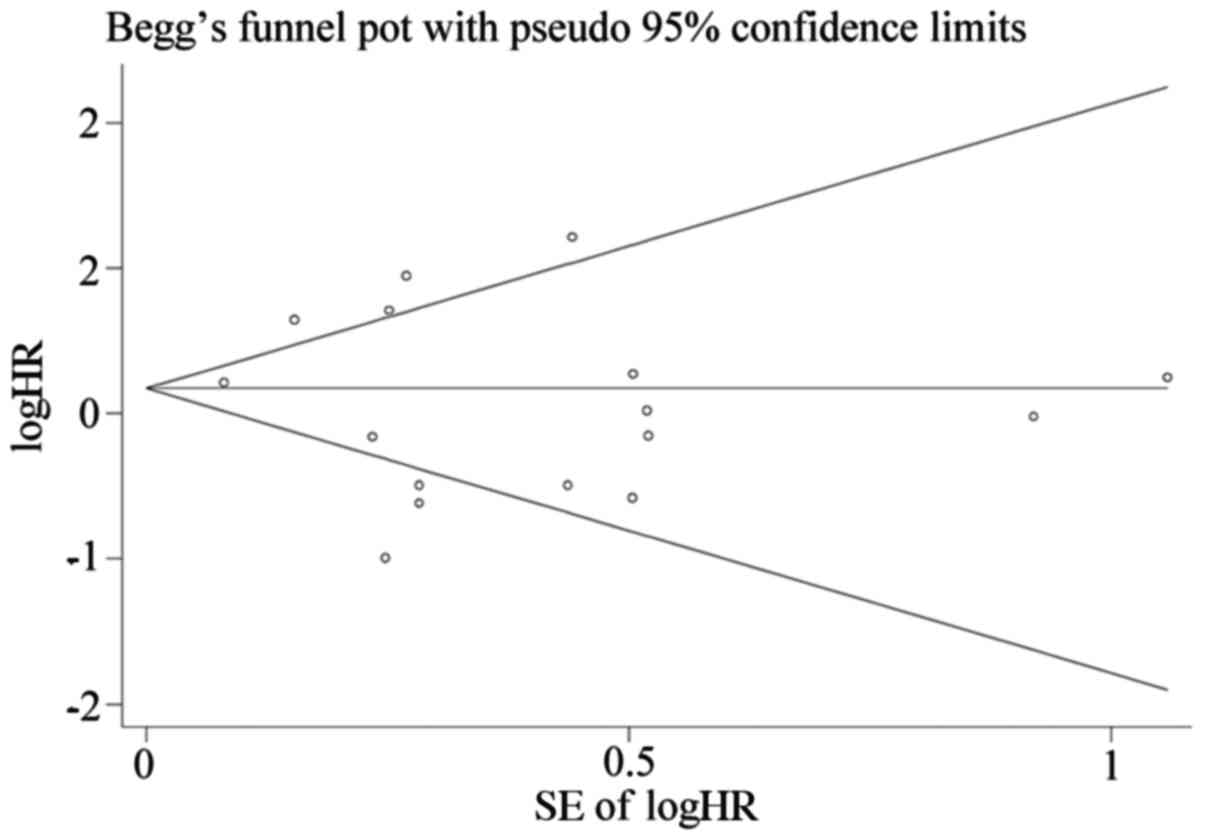
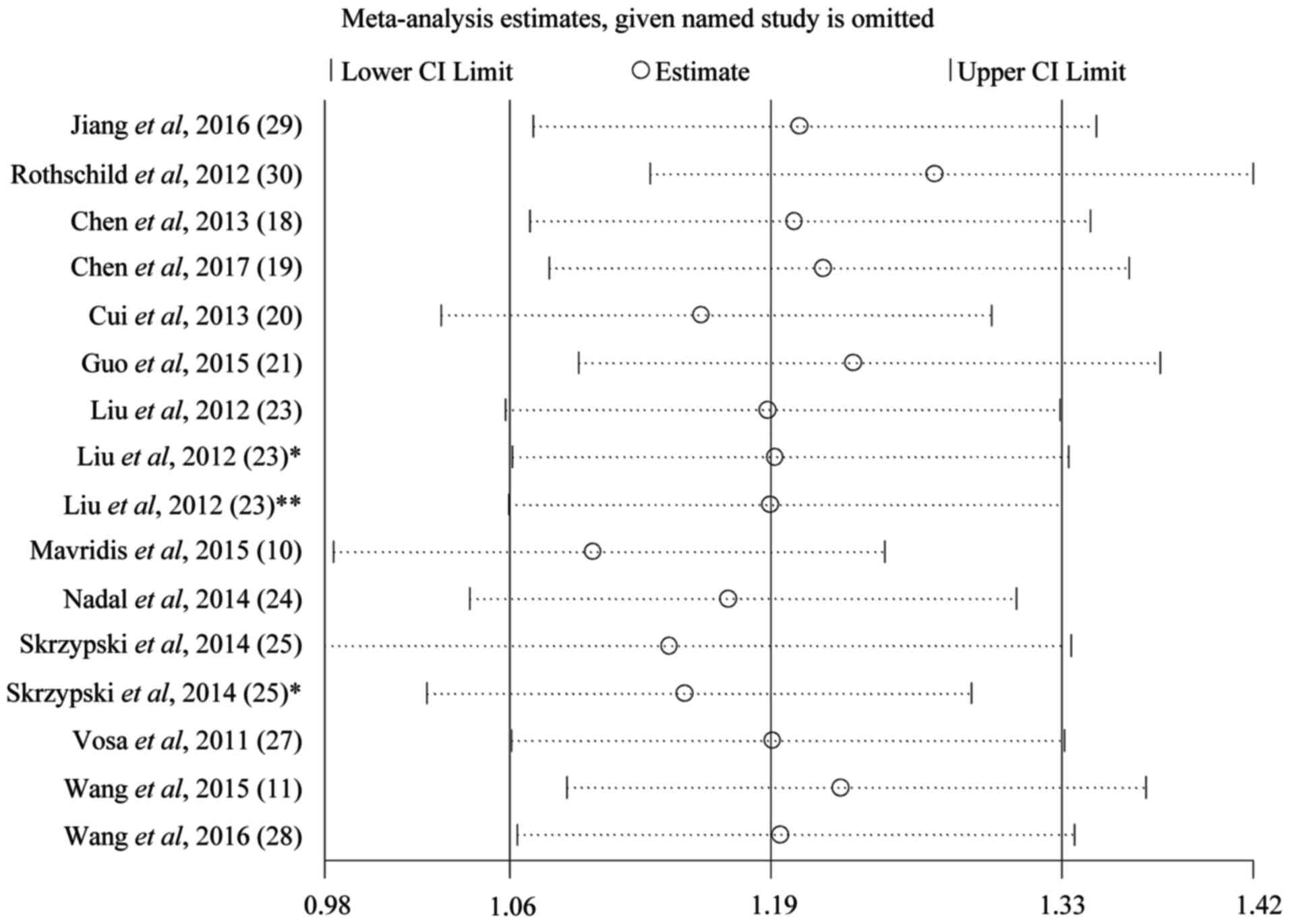
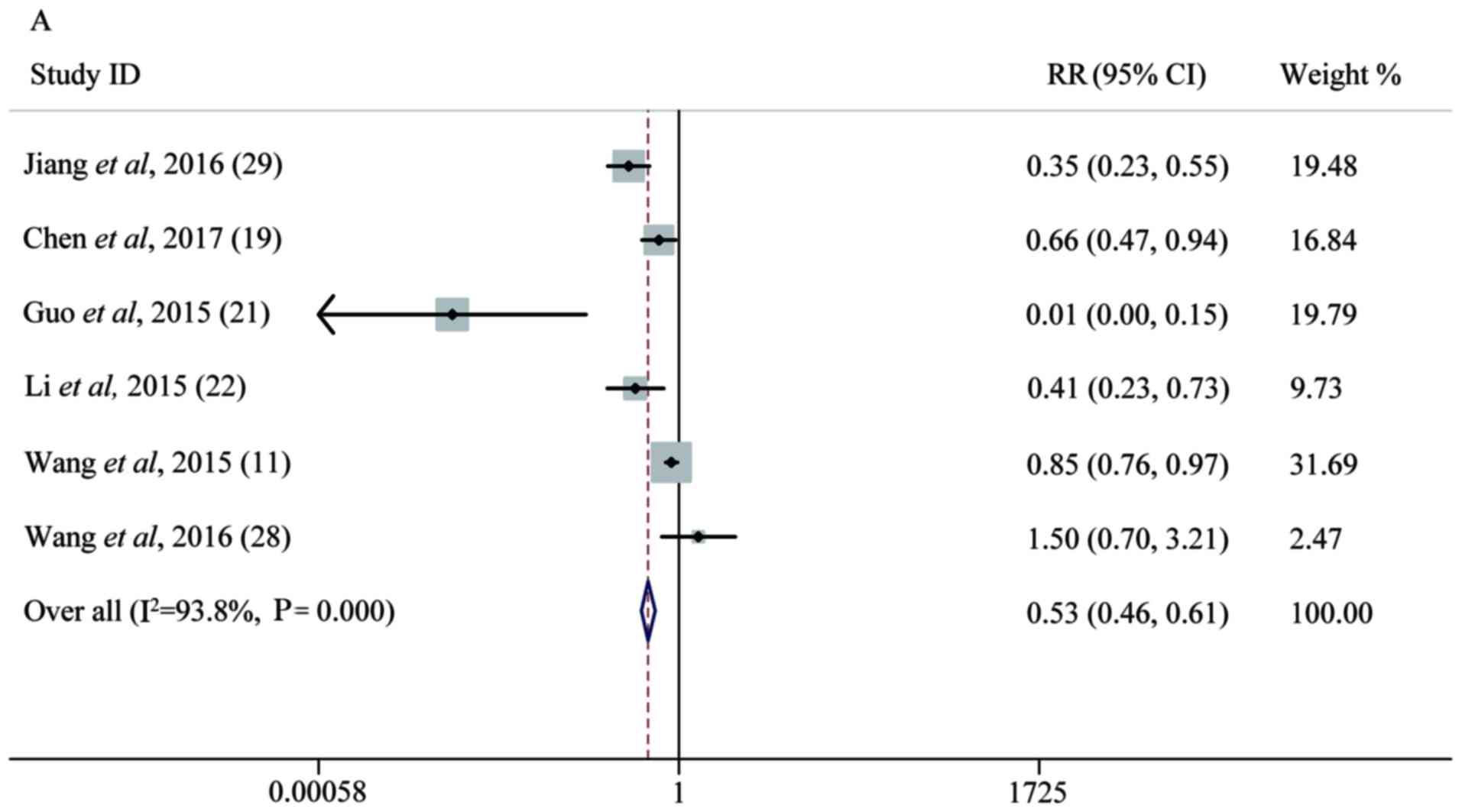
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li D, Song L, Wen Z, Li X, Jie J, Wang Y
and Peng L: Strong evidence for LncRNA ZNRD1-AS1, and its
functional Cis-eQTL locus contributing more to the susceptibility
of lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:35813–35817. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Castro D, Moreira M, Gouveia AM, Pozza DH
and De Mello RA: microRNAs in lung cancer. Oncotarget.
8:81679–81685. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aghanoori MR, Mirzaei B and Tavallaei M:
miRNA molecular profiles in human medical conditions: Connecting
lung cancer and lung development phenomena. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:9557–9565. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miR
base: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing
data. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong Y, Chen Z, Guo S, Liao X, Xie H,
Zheng Y, Cai B, Huang P, Liu Y, Zhou Q, et al: TUG1, SPRY4-IT1, and
HULC as valuable prognostic biomarkers of survival in cancer: A
PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e85832017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kang M, Shi J, Peng N and He S:
MicroRNA-211 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation and
invasion by targeting MxA. OncoTargets Ther. 10:5667–5675. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mavridis K, Gueugnon F, Petit-Courty A,
Courty Y, Barascu A, Guyetant S and Scorilas A: The oncomiR miR-197
is a novel prognostic indicator for non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Br J Cancer. 112:1527–1535. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang F, Lou JF, Cao Y, Shi XH, Wang P, Xu
J, Xie EF, Xu T, Sun RH, Rao JY, et al: miR-638 is a new biomarker
for outcome prediction of non-small cell lung cancer patients
receiving chemotherapy. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Võsa U, Vooder T, Kolde R, Vilo J,
Metspalu A and Annilo T: Meta-analysis of microRNA expression in
lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:2884–2893. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guan P, Yin Z, Li X, Wu W and Zhou B:
Meta-analysis of human lung cancer microRNA expression profiling
studies comparing cancer tissues with normal tissues. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 31:542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang Y: An expression meta-analysis of
predicted microRNA targets identifies a diagnostic signature for
lung cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 1:612008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin Y, Ge Y, Wang Y, Ma G, Wang X, Liu H,
Wang M, Zhang Z and Chu H: The association of rs710886 in lncRNA
PCAT1 with bladder cancer risk in a Chinese population. Gene.
627:226–232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Altman DG, McShane LM, Sauerbrei W and
Taube SE: Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic
studies (REMARK): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med.
9:e10012162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bouwmeester W, Zuithoff NP, Mallett S,
Geerlings MI, Vergouwe Y, Steyerberg EW, Altman DG and Moons KG:
Reporting and methods in clinical prediction research: A systematic
review. PLoS Med. 9:1–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Grève J:
miR-146α inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Min L, Ren C, Xu X, Yang J, Sun X,
Wang T, Wang F, Sun C and Zhang X: miRNA-148α serves as a
prognostic factor and suppresses migration and invasion through
Wnt1 in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 12:e01717512017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui EH, Li HJ, Hua F, Wang B, Mao W, Feng
XR, Li JY and Wang X: Serum microRNA 125b as a diagnostic or
prognostic biomarker for advanced NSCLC patients receiving
cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:309–313. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo W, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Xi J, Fan
H and Xu S: Decreased expression of miR-204 in plasma is associated
with a poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Mol Med. 36:1720–1726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Yu T, Cao J, Liu L, Liu Y, Kong HW,
Zhu MX, Lin HC, Chu DD, Yao M, et al: MicroRNA-148α suppresses
invasion and metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:1847–1856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ,
Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH and Zhang YK: High expression of serum
miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in
patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 29:618–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nadal E, Zhong J, Lin J, Reddy RM, Ramnath
N, Orringer MB, Chang AC, Beer DG and Chen G: A microRNA cluster at
14q32 drives aggressive lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:3107–3117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Skrzypski M, Czapiewski P, Goryca K,
Jassem E, Wyrwicz L, Pawłowski R, Rzyman W, Biernat W and Jassem J:
Prognostic value of microRNA expression in operable non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 110:991–1000. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun Y, Su B, Zhang P, Xie H, Zheng H, Xu
Y, Du Q, Zeng H, Zhou X, Chen C, et al: Expression of miR-150 and
miR-3940-5p is reduced in non-small cell lung carcinoma and
correlates with clinicopathological features. Oncol Rep.
29:704–712. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Võsa U, Vooder T, Kolde R, Fischer K, Välk
K, Tõnisson N, Roosipuu R, Vilo J, Metspalu A and Annilo T:
Identification of miR-374α as a prognostic marker for survival in
patients with early-stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 50:812–822. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang R, Ye F, Zhen Q, Song T, Tan G, Chu
W, Zhang Y, Lv B, Zhao X and Liu J: MicroRNA-148b is a potential
prognostic biomarker and predictor of response to radiotherapy in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Physiol Biochem. 72:337–343. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang LP, Zhu ZT and He CY: Expression of
miRNA-26b in the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 12:1105–1115. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rothschild SI, Tschan MP, Jaggi R, Fey MF,
Gugger M and Gautschi O: microRNA-381 represses ID1 and is
deregulated in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1069–1077.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Al Khalaf MM, Thalib L and Doi SA:
Combining heterogenous studies using the random-effects model is a
mistake and leads to inconclusive meta-analyses. J Clin Epidemiol.
64:119–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sittka A and Schmeck B: MicroRNAs in the
lung. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:121–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Nelson RA, Bogardus A and Grannis
FW Jr: Five-year lung cancer survival: Which advanced stage
nonsmall cell lung cancer patients attain long-term survival?
Cancer. 116:1518–1525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mizuno K, Mataki H, Seki N, Kumamoto T,
Kamikawaji K and Inoue H: MicroRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer
and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Hum Genet. 62:57–65. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gyoba J, Shan S, Roa W and Bédard EL:
Diagnosing lung cancers through examination of micro-RNA biomarkers
in blood, plasma, serum and sputum: A review and summary of current
literature. Int J Mol Sci. 17:4942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Zhang J, Yin L, Pu
Y and Liang G: MicroRNA-125b may function as an oncogene in lung
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:3880–3887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Markou A, Zavridou M and Lianidou ES:
miRNA-21 as a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer. Lung Cancer
(Auckl). 7:19–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mei Z, He Y, Feng J, Shi J, Du Y, Qian L,
Huang Q and Jie Z: MicroRNA-141 promotes the proliferation of
non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating expression of PHLPP1
and PHLPP2. FEBS Lett. 588:3055–3061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li J, Tan Q, Yan M, Liu L, Lin H, Zhao F,
Bao G, Kong H, Ge C, Zhang F, et al: miRNA-200c inhibits invasion
and metastasis of human non-small cell lung cancer by directly
targeting ubiquitin specific peptidase 25. Mol Cancer. 13:1662014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fiori ME, Barbini C, Haas TL, Marroncelli
N, Patrizii M, Biffoni M and De Maria R: Antitumor effect of
miR-197 targeting in p53 wild-type lung cancer. Cell Death Differ.
21:774–782. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Du L, Schageman JJ, Subauste MC, Saber B,
Hammond SM, Prudkin L, Wistuba II, Ji L, Roth JA, Minna JD, et al:
miR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor
gene FUS1. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1234–1243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Remon J, Alvarez-Berdugo D, Majem M, Moran
T, Reguart N and Lianes P: miRNA-197 and miRNA-184 are associated
with brain metastasis in EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Trans
Oncol. 18:153–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen T, Gao F, Feng S, Yang T and Chen M:
MicroRNA-370 inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer
by downregulating oncogene TRAF4. Oncol Rep. 34:461–468. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Cong W, Wu G, Ju X, Li Z, Duan X,
Wang X and Gao H: miR-376α suppresses the proliferation and
invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting c-Myc. Cell
Biol Int. 42:25–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao J, He Y, Liu HQ, Wang SB, Zhao BC and
Cheng YS: MicroRNA 192 regulates chemo-resistance of lung
adenocarcinoma for gemcitabine and cisplatin combined therapy by
targeting Bcl-2. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:12397–12403. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tu C, Wang F and Wan J: MicroRNA-381
inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in endometrial carcinoma
by targeting the IGF-1R. Mol Med Rep. 17:4090–4098. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shi L, Xu Z, Wu G, Chen X, Huang Y, Wang
Y, Jiang W and Ke B: Up-regulation of miR-146α increases the
sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to DDP by downregulating
cyclin J. BMC Cancer. 17:1382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhai G, Li G, Xu B, Jia T, Sun Y, Zheng J
and Li J: miRNA-148b regulates radioresistance in non-small lung
cancer cells via regulation of MutL homologue 1. Biosci Rep.
36:e003542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang S, Gao L, Thakur A, Shi P, Liu F,
Feng J, Wang T, Liang Y, Liu JJ, Chen M, et al: miRNA-204
suppresses human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ATF2.
Tumour Biol. 37:11177–11186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cheng J, Chen Y, Zhao P, Liu X, Dong J, Li
J, Huang C, Wu R and Lv Y: Downregulation of miRNA-638 promotes
angiogenesis and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting
VEGF. Oncotarget. 7:30702–30711. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shi GL, Chen Y, Sun Y, Yin YJ and Song CX:
Significance of serum microRNAs in the auxiliary diagnosis of
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Lab. 63:133–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhan B, Lu D, Luo P and Wang B: Prognostic
value of expression of microRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 62:2203–2211. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu N, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Yang J and Zhang S:
A meta-analysis: microRNAs' prognostic function in patients with
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 6:2098–2105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jiang M, Li X, Quan X, Li Xi and Zhou B:
Clinically correlated microRNAs in the diagnosis of non-small cell
lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int.
2018:59309512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|