Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth and
seventh most common cancer in men and women, respectively (1) and the third leading cause of cancer
mortality worldwide (2). Although
radiofrequency ablation (RFA), percutaneous ethanol injection
(PEI), surgical resection and liver transplantation can be
curative, ~80% of patients with HCC are not candidates for these
strategies due to having advanced or metastatic disease at the time
of presentation (3). Multiple
advanced HCC has been treated using transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization (TACE), but only in patients without portal vein
tumor thrombus.
Sorafenib is a small molecular inhibitor of several
tyrosine proteins and Raf kinases and is widely used to treat
patients with advanced HCC with or without metastasis (4,5). Sorafenib
is now recommended as it confers survival benefits beyond the best
supportive care (6), but only
patients with Child-Pugh A grade are candidates (7) due to the adverse events such as liver
damage (8). Additionally, it is not
widely administered as it is extremely expensive (9).
Patients with advanced HCC are often treated with
transarterial infusion (TAI) chemotherapy according to indications.
However, TAI has not yet been established as a standard treatment
for advanced HCC without extrahepatic metastasis, as its effects
have not yet been supported by concrete evidence generated from
randomized controlled trials. Previous studies have identified
complete (CR) and partial (PR) response rates after TAI of 27 to
40%, respectively (10,11) and a clearly improved prognosis for
patients with stable (SD) or progressive disease (PD). However,
repeated TAI for patients with SD or PD imposes physical,
psychological and economic burdens. Therefore, patients with CR or
PR should be differentiated from those with SD or PD during the
earliest phase of the treatment.
α-Fetoprotein (AFP) and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin
(DCP) are established tumor markers for HCC and they are useful for
diagnosis (12,13). However, whether or not changes in
their levels can serve as markers of responses to treatment remains
controversial. Several recent studies have identified that changes
in AFP levels following systemic chemotherapy, chemoembolization
and radioembolization, may predict the effects of treatment
(14–16). Numerous studies have proven that AFP
and DCP are useful not only as tumor markers, but also as
prognostic factors for HCC (17,18).
Changes in tumor markers following anticancer
therapies closely correlate with treatment effects in various types
of solid tumors. Predicting treatment effects early will aid
physicians in determining whether current therapy should be
continued or changed.
However, correlations between AFP and DCP responses
and survival outcomes in patients treated with TAI have not yet
been established.
Therefore, the present study aimed to determine
whether or not AFP and DCP responses during the early phase of
treatment can predict the prognosis of patients with advanced HCC.
Correlations were evaluated between AFP and DCP responses to
treatment effects and survival rates in patients with HCC treated
with TAI.
Materials and methods
Patients
A total of 74 patients with HCC confirmed by
transcatheter arterial angiography and who received TAI comprising
25 mg cisplatin, 500 mg 5-fluorouracil, 6 mg mitomycin C and 30 mg
epirubicin were enrolled at the Tottori University Hospital
(Tottori, Japan) between January 2004 and December 2012. None of
the patients were candidates for liver transplantation, surgical
resection, PEI, RFA or TACE as multiple tumors were involved with
one or both of the hepatic lobes with or without portal vein tumor
thrombosis. Patients were treated with TAI once each month after
initial infusion chemotherapy. Twenty-one patients received other
treatments with subsequent TAI, and sorafenib was administered to
two patients after repeated TAI. Fifteen patients succumbed within
6 months after initial TAI due to disease progression, and they
were divided into PD. The study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the Tottori University Faculty of Medicine (no.
1863).
Protocols
Serum AFP and DCP levels were measured before the
initial TAI at baseline and at 1 and 4 weeks after TAI. A rapid
response rate was defined as the ratio of AFP or DCP value at 1
week after initial TAI compared to the baseline values and the
early response rate was the ratio at 4 weeks. Serum AFP and DCP
levels were measured using the Access AFP micro-particle enzyme
immunoassay (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) and Lumipulse presto
PIVKA-II (Eidia Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), respectively. Patients
with normal baseline AFP (<10 ng/ml) and DCP (<40 mAU/ml)
levels were excluded from the response evaluation. The effects of
treatment and disease progression were assessed using
contrast-enhanced computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging
every 8–12 weeks.
Response evaluation criteria
Antitumor responses were evaluated according to the
standards of the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan (19) at 6 months after the initial treatment.
Briefly, a CR was defined as the total radiological absence of all
the known lesions. A PR was defined as a decrease of ≥50% in the
product of two perpendicular diameters of the largest tumor nodule
for >4 weeks without the appearance of new lesions, or
progression of existing lesions. A SD was defined as <50%
decrease or not >25% increase in the product of two
perpendicular diameters of the largest tumor nodule. A PD was
defined as an increase of >25% in the product of two
perpendicular diameters of the largest tumor nodule or one of the
measurable lesions, or the appearance of new lesions. Patients who
succumbed due to HCC progression before 6 months were categorized
as having PD.
Statistical analysis
Data were statistically analyzed using Stat Flex
version 6 (Artech, Osaka, Japan). A two-sided P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. The
amount of change in AFP and DCP between the CR and PR+SD+PD, and
between the CR+PR and SD+PD groups was compared using the
Mann-Whitney U test and categorical variables were compared using
the Kruskal-Wallis test. Overall survival was calculated using the
Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test.
Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive values (PPV) and
negative predictive values were determined from receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results
Antitumor responses at 6 months after
TAI
Table I shows the
characteristics of the patients. Among the enrolled patients, 5
(6.8%), 10 (13.5%), 17 (23.0%) and 42 (56.8%) achieved CR, PR, SD
and PD, respectively. The objective response rate of overall
(CR+PR) was 20.3%.
 | Table I.Patient characteristics. |
Table I.
Patient characteristics.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|
| Age, median years
(range) | 67.7 (38–89) |
| Gender, n
(male/female) | 62/12 |
| Etiology, n |
|
| HBV | 23 |
| HCV | 34 |
|
Alcohol | 10 |
|
Others | 7 |
| Underlying liver
disease, n |
|
| Chronic
hepatitis | 26 |
| Liver
cirrhosis | 48 |
| Child-Pugh grade, n
(A/B/C) | 31/15/2 |
| HCC clinical stage, n
(II/III/IVa/IVb) | 15/26/25/8 |
| Portal vein tumor
thrombus, n (%) | 20 (27.0) |
| Hepatic vein tumor
thrombus, n | 1 |
| Lymph node
metastasis, n | 6 |
| Distant metastasis,
n |
|
| Lung | 5 |
| Bone | 3 |
| Adrenal
gland | 1 |
| Serum markers at
baseline, median (range) |
|
| AFP,
ng/ml | 98 (11–162,579) |
| DCP,
mAU/ml | 542 (46–652,830) |
| Treatment following
initial TAI, n |
|
| TAI | 29 |
| TAI +
others | 21 |
|
Others | 11 |
| None | 13 |
| Treatment response, n
(%) |
|
| CR | 5 (6.8) |
| PR | 10 (13.5) |
| SD | 17 (23.0) |
| PD | 42 (56.8) |
| Survival outcome,
n |
|
|
Succumbed | 54 |
|
Alive | 13 |
|
Unknown | 7 |
Survival outcomes according to
treatment effects
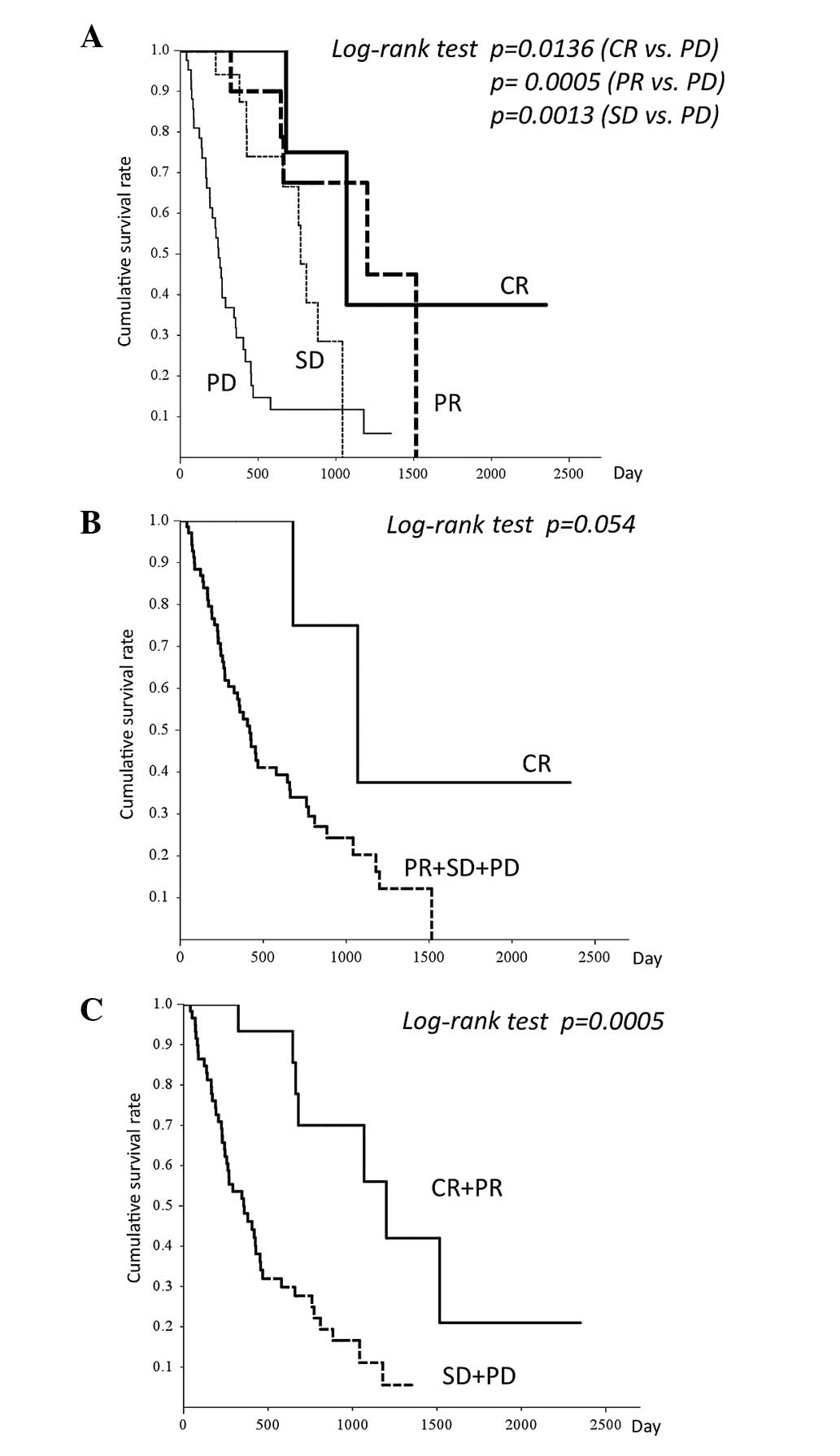
Fig. 1 shows that the
median overall survival of each group was 1,069, 1,201, 773 and 245
days for those who achieved CR, PR, SD and PD, respectively.
Overall survival was longer for the CR compared to the PR+SD+PD
group (P=0.054) and significantly longer for the CR+PR, compared to
the SD+PD group (P=0.0005).
Comparison of clinical characteristics
according to treatment effects
Table II shows the
clinical characteristics of the patients in each group. Age, gender
and rate of liver cirrhosis prior to the initial TAI did not
significantly differ among the four groups at baseline. Median
baseline levels of AFP and DCP did not significantly differ among
these groups (P=0.07 and 0.86, respectively). In total, 8, 7, 7, 5,
3, 2 and 2 patients each were treated with PEI, low-dose FP,
radiation therapy, TACE, TS-1 (tegafur-gimeracil-oteracil
potassium), sorafenib and RFA, respectively. Twenty-one patients
were treated using these approaches following repeated TAI and 11
were treated only with these approaches.
 | Table II.Patient characteristics according to
treatment efficacy. |
Table II.
Patient characteristics according to
treatment efficacy.
|
Characteristics | CR (n=5) | PR (n=10) | SD (n=17) | PD (n=42) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years | 66.8±11.5 | 66.8±11.4 | 70.0±9.1 | 67.1±12.2 | 0.86 |
| Gender, n
(male/female) | 5/0 | 9/1 | 15/2 | 33/9 | 0.51 |
| Etiology of liver
disease, n alcohol/B/C/others | 0/3/2/0 | 1/5/3/1 | 5/3/7/2 | 4/12/22/4 |
|
| Liver cirrhosis, n
(no/yes) | 1/4 | 4/6 | 7/10 | 14/28 | 0.82 |
| Clinical stage, n
(II/III/IVa/IVb) | 1/2/2/0 | 3/3/4/0 | 5/7/4/1 | 6/14/15/7 |
|
| Baseline tumor
markers, median (range) |
|
|
|
|
|
| AFP,
ng/ml | 395
(46–70,254) | 49 (13–35,730) | 20 (11–53,110) | 270
(11–162,579) | 0.07 |
| DCP,
mAU/ml | 360
(102–18,753) | 2,010
(46–9,342) | 425
(53–32,652) | 598
(46–652,830) | 0.86 |
| Following
treatment, n |
|
|
|
|
|
| TAI/TAI
+ others/others/none | 2/3/0/0 | 4/4/2/0 | 11/5/1/0 | 12/9/8/13 |
|
Rapid and early response indices
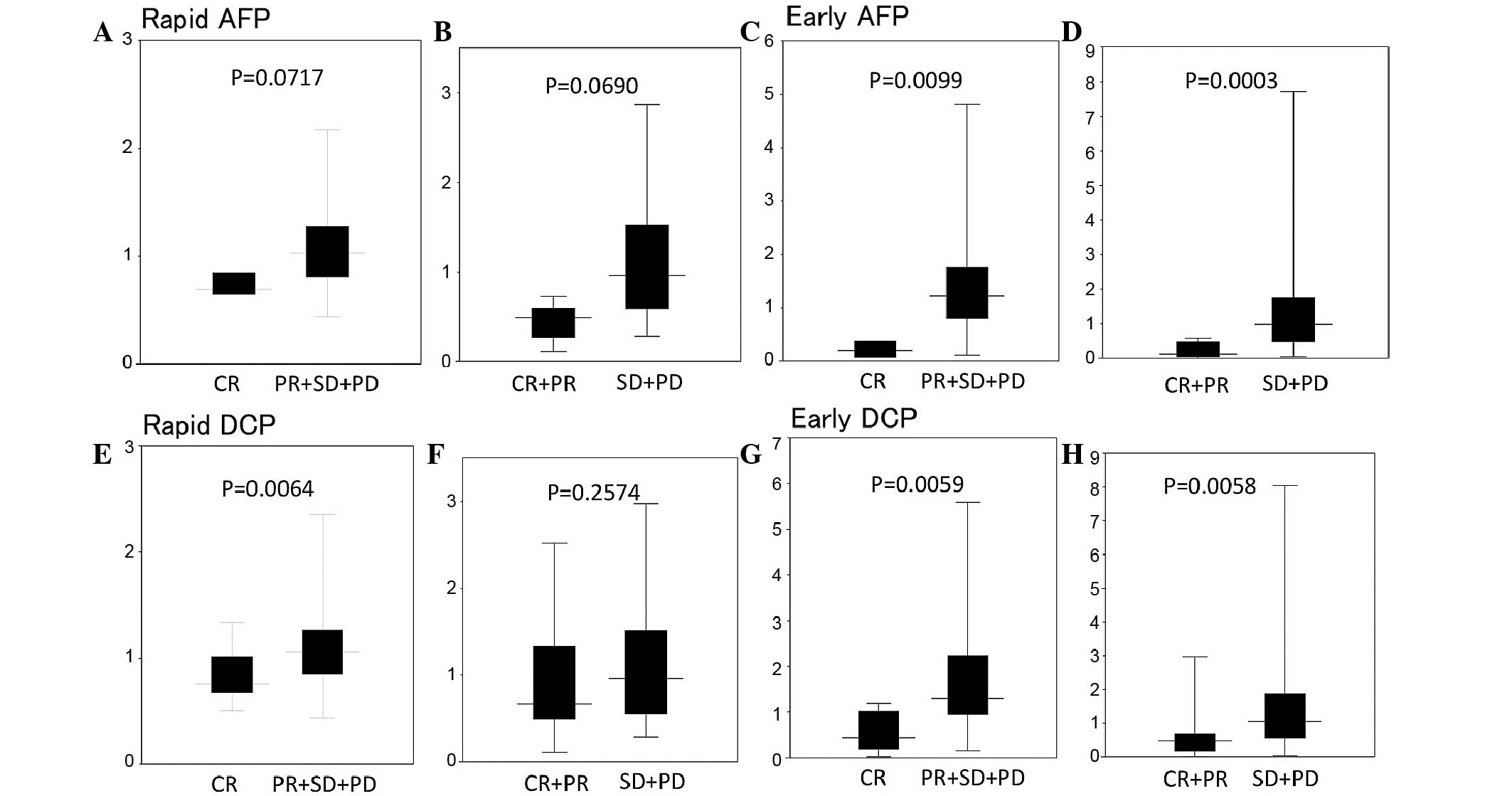
Fig. 2 shows the rapid
and early response indices of AFP and DCP following initial TAI.
The rapid AFP indices of median were 0.69, 0.83, 1.01 and 1.15 in
CR, PR, SD and PD, respectively, and the early AFP response indices
were 0.20, 0.51, 0.88 and 1.43 in CR, PR, SD and PD, respectively.
The rapid AFP response index was lower in the CR compared to the
PR+SD+PD group (P=0.0717) and in the CR+PR compared to the SD+PD
group (P=0.0690). The early AFP response index was lower in the CR
compared to the PR+SD+PD group (P=0.0099) and in the CR+PR compared
to the SD+PD group (P=0.0003).
The rapid DCP response indices of median were 0.49,
1.22, 0.89 and 0.96 in CR, PR, SD and PD, respectively. The early
DCP response indices were 0.12, 0.51, 0.63 and 1.14 in CR, PR, SD
and PD, respectively. The rapid DCP response index was
significantly lower in the CR compared to the PR+SD+PD group
(P=0.0064). The early DCP response index was significantly lower in
the CR, compared to the PR+SD+PD group and in the CR+PR, compared
to the SD+PD group (P< 0.01).
Predicting performance based on the
rapid and early response indices of AFP and DCP
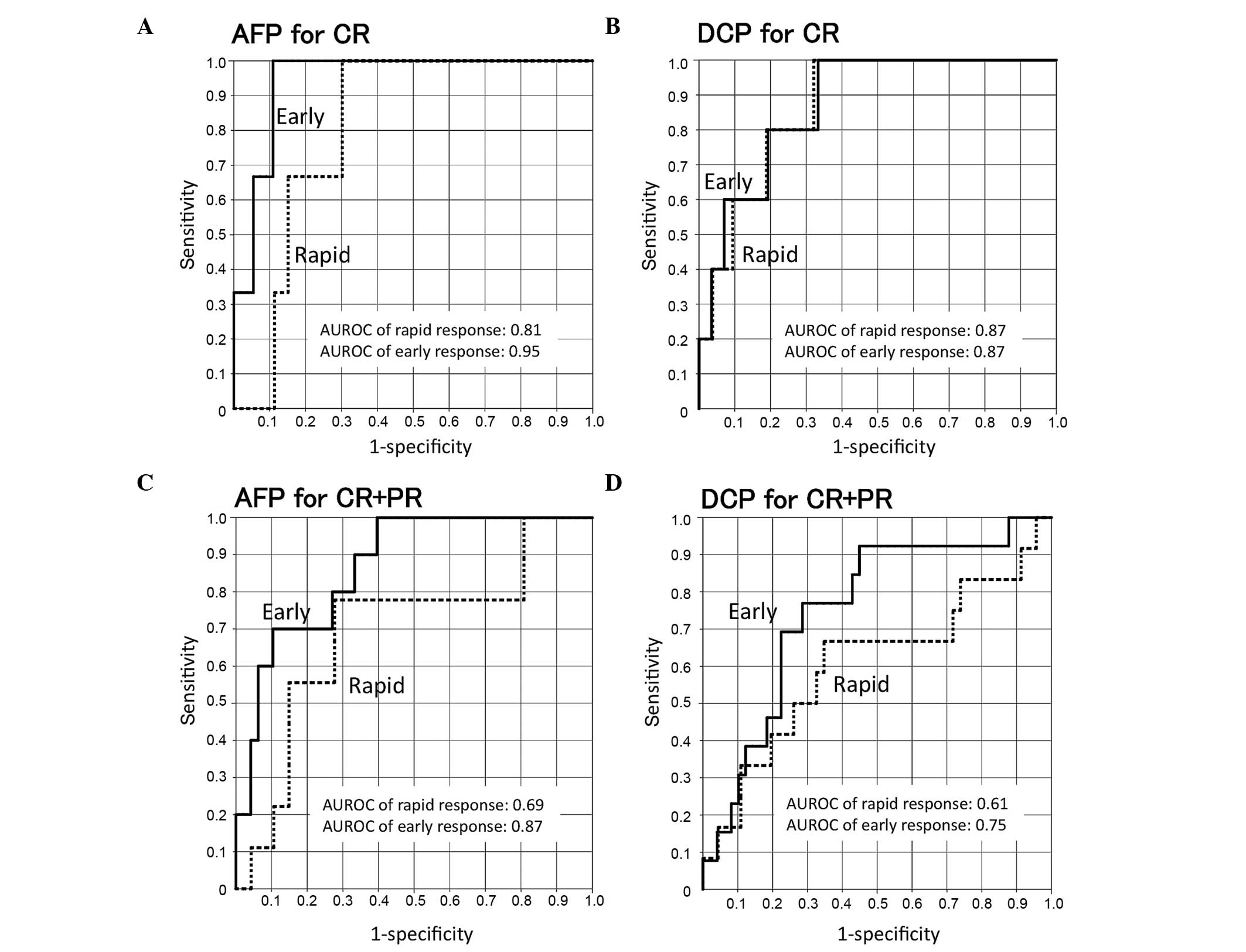
Fig. 3 shows the ROC
curves for treatment responses (CR vs. PR+SD+PD and CR+PR vs.
SD+PD). The areas under the ROC curves of early AFP or DCP
responses were larger for the CR than for the CR+PR group. The
sensitivity and specificity for the CR group were 0.67 and 0.85 for
a rapid AFP response (cut-off, 0.72), 1.00 and 0.89 for an early
AFP response (cut-off, 0.46), 0.80 and 0.81 for a rapid DCP
response (cut-off, 0.55) and 0.80 and 0.81 for an early DCP
response (cut-off, 0.45), respectively. The sensitivity and
specificity for the CR+PR groups were 0.78 and 0.72 for a rapid AFP
response (cut-off, 0.92), 0.80 and 0.73 for an early AFP response
(cut-off, 1.02), 0.67 and 0.65 for a rapid DCP response (cut-off,
0.77) and 0.77 and 0.71 for an early DCP response (cut-off, 0.61),
respectively (Table III).
 | Table III.Predicting performance by AFP or
DCP. |
Table III.
Predicting performance by AFP or
DCP.
|
Characteristics | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Hazard ratio | AUROC |
|---|
| AFP |
|
Rapid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CR | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.20 | 0.98 | 11.3 | 0.81 |
|
CR+PR | 0.92 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 0.94 | 9.2 | 0.69 |
|
Early |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CR | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 1.00 | NA | 0.95 |
|
CR+PR | 1.02 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.38 | 0.95 | 10.8 | 0.87 |
| DCP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rapid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CR | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.29 | 0.98 | 17.2 | 0.87 |
|
CR+PR | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.33 | 0.88 | 3.8 | 0.61 |
|
Early |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CR | 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 0.98 | 16.7 | 0.87 |
|
CR+PR | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.92 | 8.3 | 0.75 |
Predicting performance based on a
combination of AFP and DCP
Combining the AFP and DCP responses markedly
increased the ability to predict CR and CR+PR compared with each
marker alone (Table IV). The cut-off
values of AFP and DCP were the same as those used for the single
marker analysis. The sensitivity and specificity were 0.67 and 0.98
for a rapid response, 1.00 and 1.00 for an early response for the
CR group, 0.63 and 0.88 for a rapid response, and 0.75 and 0.88 for
an early response, respectively, for the CR+PR group. The PPVs of
rapid and early responses for CR were 0.67 and 1.00, and those for
CR+PR were 0.50 and 0.55, respectively.
 | Table IV.Predicting performance by combination
of AFP and DCP. |
Table IV.
Predicting performance by combination
of AFP and DCP.
|
Characteristics | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Hazard ratio |
|---|
| Rapid AFP+DCP |
|
|
|
|
|
| CR | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.98 | 88.0 |
|
CR+PR | 0.63 | 0.88 | 0.50 | 0.92 | 11.6 |
| Early AFP+DCP |
|
|
|
|
|
| CR | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | NA |
|
CR+PR | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 21.6 |
Antitumor responses and survival
outcomes according to subsequent treatments following initial
TAI
The objective response rate of repeated TAI,
repeated TAI + others and others as subsequent treatments were
20.7, 33.3 and 18.2%, respectively. The median overall survival of
each group was 659, 646, 418 and 140 days for those who received
repeated TAI, repeated TAI + others, others and no treatment
following initial TAI, respectively. All the patients without
subsequent treatment had PD. Survival outcome in patients without
subsequent treatment was significantly low compared to other
treatments (data not shown, P<0.01). There were no significant
differences between repeated TAI, repeated TAI + others and
others.
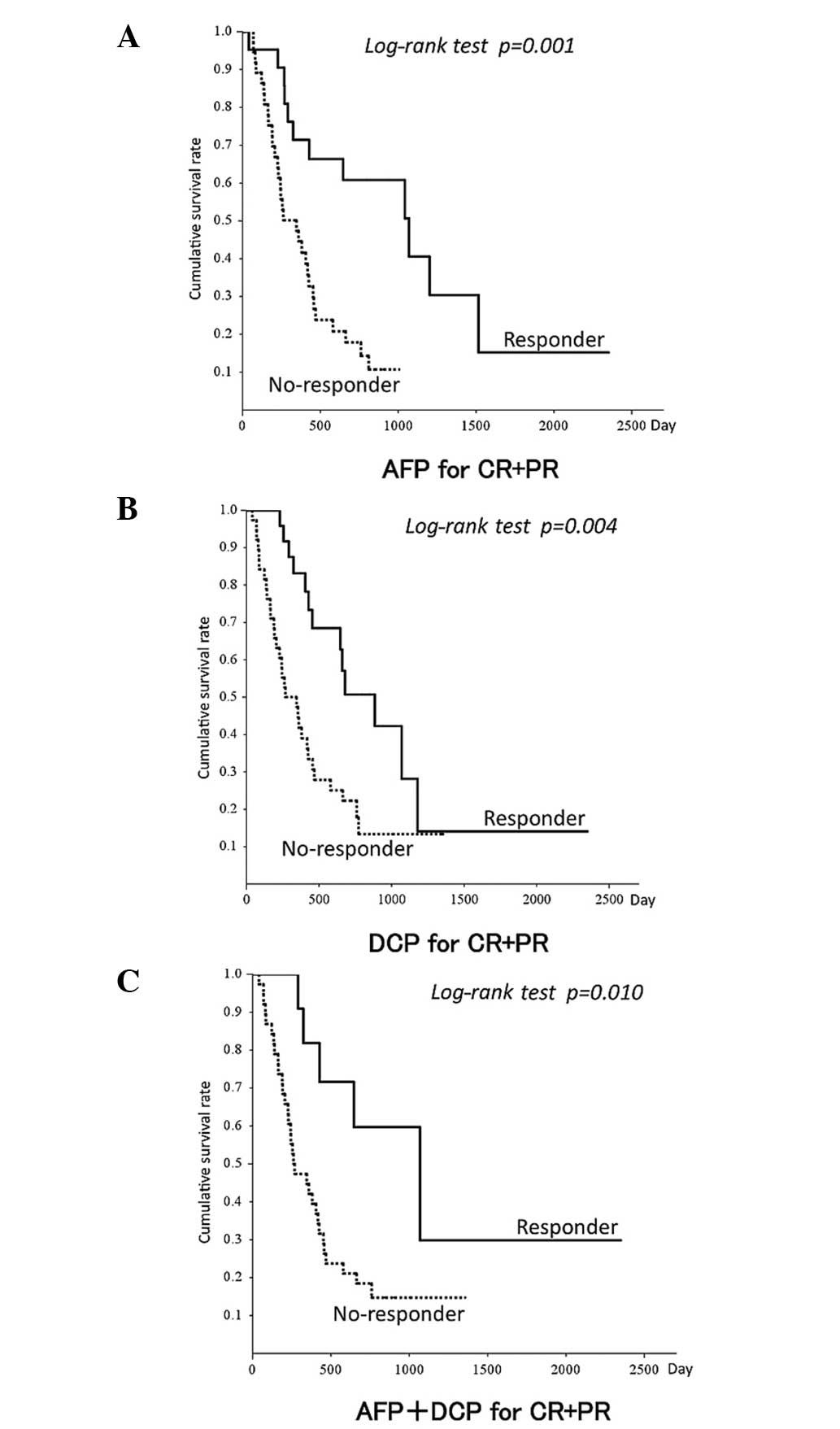
Survival outcomes according to AFP and
DCP responses
Based on the cut-off values of CR and CR+PR,
patients were divided into responder and non-responder groups to
evaluate the prediction of survival outcome (Fig. 4, Table
V). Early responders of AFP and AFP+DCP for predicting CR
survived significantly longer than non-responders (P<0.05).
Early responders of AFP, DCP and AFP+DCP in predicting CR+PR
survived significantly longer than non-responders (P<0.05).
Rapid responders of AFP, DCP and AFP+DCP were not significantly
different from non-responders with regards to survival.
 | Table V.Survival outcomes according to AFP
and DCP responses. |
Table V.
Survival outcomes according to AFP
and DCP responses.
|
Characteristics | Median survival
time, days | P-value |
|---|
| AFP |
|
|
|
Rapid |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 345/405 | 0.146 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 380/291 | 0.667 |
|
Early |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 359/1,069 | 0.015 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 345/1,069 | 0.001 |
| DCP |
|
|
|
Rapid |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 359/453 | 0.402 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 269/456 | 0.150 |
|
Early |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 380/884 | 0.056 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 269/884 | 0.004 |
| AFP+DCP |
|
|
|
Rapid |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 345/>2,000 | 0.113 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 324/646 | 0.134 |
|
Early |
|
|
|
CR responder/non
responder | 345/1,069 | 0.062 |
|
CR+PR
responder/non responder | 262/1,069 | 0.010 |
Discussion
Patients with advanced HCC who had early AFP and DCP
responses following initial TAI had significantly improved
treatment effects and longer overall survival than those without
AFP and DCP responses.
AFP is secreted in ~70% of patients with HCC and it
is frequently measured in clinical practice for diagnosis or
pretreatment prognosis, but the predictive or prognostic
significance of the AFP response during treatment has not been
evaluated frequently. DCP was also used as a tumor marker of HCC
and was more likely to be elevated in patients with advanced HCCs,
such as vascular invasion or distant metastasis (20). Investigators have proposed a role for
tumor marker dynamics during surgical treatment, more specifically,
that a change in AFP or DCP can predict prognosis or recurrence
following surgical resection (21–23).
However, the AFP and/or DCP responses have not been assessed in
patients treated with TAI.
Three recent studies of patients with advanced HCC
who received various types of systemic therapy, such as thalidomide
(24), doxorubicin-based combination
chemotherapy (15) and chemotherapy
with or without molecularly targeted therapies (14), concluded that a change in AFP during
treatment is a useful surrogate for predicting treatment effects
and the survival rate of patients. The criteria for an AFP response
have various definitions according to treatment modalities that
affect AFP responses in different ways. Riaz et al (16) and Vora et al (14) defined an AFP response as >50%
reduction from baseline for locoregional therapy and systemic
chemotherapy, whereas Chan et al (15) defined it as >20% reduction in
systemic chemotherapy. The present study identified that the rapid
AFP and DCP responses in CR were 31 and 51% decreased from
baseline, respectively. Early AFP and DCP responses in the same
group were 80 and 88%, respectively. These data were appropriate
considering that the half-lives of AFP and DCP are 6 and 3.2 days,
respectively (25).
Serum AFP and DCP levels have been routinely
measured in the clinical setting for decades and they can be
immediately, easily and broadly monitored in outpatient clinics as
a potential surrogate for the effects of treatment in patients with
advanced HCC. The present study found that the early AFP response
was most sensitive for predicting CR and the sensitivity of rapid
DCP for this group was 80%. Early responders of AFP, DCP and a
combination of these markers were shown to have improved survival
outcomes than non-responders. To the best of our knowledge, this is
the earliest time point used in similar studies and it was
apparently the most relevant to the clinical treatment of advanced
HCC. Treatment effects may be more accurately predicted at 1 month
after the initial TAI as the areas under the ROC curves for AFP or
DCP were larger for early, compared to the rapid responses.
The combination of AFP and DCP responses markedly
increased the ability to predict CR and CR+PR compared to each
marker alone. One explanation may be that 2 of the 5 patients who
achieved CR and 5 of 10 who achieved PR had high baseline values of
either AFP or DCP.
A biomarker that can be detected during the early
phase of treatment is valuable, as it may help to identify a
subgroup of patients with a poor prognosis who would thus be
candidates for other treatment strategies. Subsequent treatment
methods following initial TAI except for no treatment did not
affect treatment outcomes in terms of overall survival rate in the
present study. Indeed, the predicting performance for all the
treatments was similar to that for subsequent repeated TAI. At the
advanced stage of HCC, multidisciplinary and personalized therapy
was required. From this view point, predicting treatment outcomes
in the early period following initial TAI is extremely important.
The present results may aid physicians to accurately determine
disease courses and establish further treatment plans following
completion of the initial TAI. Thus, adding other types of systemic
therapy, such as sorafenib, should be considered if possible at an
earlier stage of treatment for patients with little or no AFP and
DCP responses.
Several studies have examined the predictive roles
of AFP and DCP responses (26–28), but
the present findings are important for several reasons. First, to
the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have simultaneously
evaluated the clinical value of AFP and DCP responses through
correlations with clinical outcomes in patients who were treated
with homogeneous TAI protocols. Second, tumor markers were
evaluated at an earlier time point than similar studies.
The potential limitations of the present study
included a relatively small and less homogeneous patient
population. AFP and DCP levels were measured only at baseline and
at 1 and 4 weeks following TAI. Validation study in larger patient
cohorts and/or with more stringent criteria for early AFP and DCP
responses may help to verify the usefulness of such an
approach.
In conclusion, early AFP and DCP responses appear to
be significant predictors of the effects of TAI and the survival of
patients with advanced HCC. Levels of AFP and DCP, particularly
during the early phase of treatment, should be further explored in
larger clinical studies.
References
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Blum HE: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapy
and prevention. World J Gastroenterol. 11:7391–7400.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Furuse J: Sorafenib for the treatment of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Biologics. 2:779–788.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wörns MA, Weinmann A, Pfingst K,
Schulte-Sasse C, Messow CM, Schulze-Bergkamen H, Teufel A,
Schuchmann M, Kanzler S, Düber C, et al: Safety and efficacy of
sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in
consideration of concomitant stage of liver cirrhosis. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 43:489–495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keating GM and Santoro A: Sorafenib: A
review of its use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Drugs.
69:223–240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma YT and Palmer DH: Impact of restricting
access to high-cost medications for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 12:465–473. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Miyaki D, Aikata H, Honda Y, Naeshiro N,
Nakahara T, Tanaka M, Nagaoki Y, Kawaoka T, Takaki S, Waki K, et
al: Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma according to Child-Pugh classification. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:1850–1857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nouso K, Miyahara K, Uchida D, Kuwaki K,
Izumi N, Omata M, Ichida T, Kudo M, Ku Y, Kokudo N, et al: Liver
Cancer Study Group of Japan: Effect of hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma in the Nationwide Survey of Primary Liver
Cancer in Japan. Br J Cancer. 109:1904–1907. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bellet DH, Wands JR, Isselbacher KJ and
Bohuon C: Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in human disease:
Perspective from a highly specific monoclonal radioimmunoassay.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:3869–3873. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weitz IC and Liebman HA: Des-gamma-carboxy
(abnormal) prothrombin and hepatocellular carcinoma: A critical
review. Hepatology. 18:990–997. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vora SR, Zheng H, Stadler ZK, Fuchs CS and
Zhu AX: Serum alpha-fetoprotein response as a surrogate for
clinical outcome in patients receiving systemic therapy for
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 14:717–725. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan SL, Mo FK, Johnson PJ, Hui EP, Ma BB,
Ho WM, Lam KC, Chan AT, Mok TS and Yeo W: New utility of an old
marker: Serial alpha-fetoprotein measurement in predicting
radiologic response and survival of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma undergoing systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
27:446–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Riaz A, Ryu RK, Kulik LM, Mulcahy MF,
Lewandowski RJ, Minocha J, Ibrahim SM, Sato KT, Baker T, Miller FH,
et al: Alpha-fetoprotein response after locoregional therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Oncologic marker of radiologic response,
progression, and survival. J Clin Oncol. 27:5734–5742. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamasaki T, Kimura T, Kurokawa F, Aoyama
K, Ishikawa T, Tajima K, Yokoyama Y, Takami T, Omori K, Kawaguchi
K, et al: Prognostic factors in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy. J Gastroenterol. 40:70–78. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamamoto K, Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Kume
Y, Ikeda H, Norman GL, Shums Z, Aoki T, Hasegawa K, Beck Y, et al:
AFP, AFP-L3, DCP and GP73 as markers for monitoring treatment
response and recurrence and as surrogate markers of
clinicopathological variables of HCC. J Gastroenterol.
45:1272–1282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kudo M, Kubo S, Takayasu K, Sakamoto M,
Tanaka M, Ikai I, Furuse J, Nakamura K and Makuuchi M: Liver Cancer
Study Group of Japan (Committee for Response Evaluation Criteria in
Cancer of the Liver, Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan): Response
Evaluation Criteria in Cancer of the Liver (RECICL) proposed by the
Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan (2009 Revised Version). Hepatol
Res. 40:686–692. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Matsuyama Y, Mine
N, Kondo Y and Omata M: Diagnostic accuracy of tumor markers for
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol Int.
2:17–30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim Y, Paik YH, Ahn SH, Youn YJ, Choi JW,
Kim JK, Lee KS, Chon CY and Han KH: PIVKA-II is a useful tumor
marker for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical
resection. Oncology. 72:(Suppl 1). 52–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamamoto K, Imamura H, Matsuyama Y,
Hasegawa K, Beck Y, Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M and Kokudo N:
Significance of alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatectomy.
Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2795–2804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Toyoda H, Kumada T, Kaneoka Y, Osaki Y,
Kimura T, Arimoto A, Oka H, Yamazaki O, Manabe T, Urano F, et al:
Prognostic value of pretreatment levels of tumor markers for
hepatocellular carcinoma on survival after curative treatment of
patients with HCC. J Hepatol. 49:223–232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen LT, Liu TW, Chao Y, Shiah HS, Chang
JY, Juang SH, Chen SC, Chuang TR, Chin YH and Whang-Peng J:
Alpha-fetoprotein response predicts survival benefits of
thalidomide in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol
Ther. 22:217–226. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kishi K, Sonomura T, Mitsuzane K, Nishida
N, Kimura M, Satoh M, Yamada R, Kodama N, Kinoshita M, Tanaka H, et
al: Time courses of PIVKA-II and AFP levels after hepatic artery
embolization and hepatic artery infusion against hepatocellular
carcinoma: Relation between the time course and tumor necrosis.
Radiat Med. 10:189–195. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MH, Kim SU, Kim Y, Ahn SH, Choi EH,
Lee KH, Lee Y, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY, et al: Early on-treatment
predictions of clinical outcomes using alpha-fetoprotein and
des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin responses in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:313–322.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim BK, Ahn SH, Seong JS, Park JY, Kim Y,
Kim JK, Lee Y, Lee KH and Han KH: Early α-fetoprotein response as a
predictor for clinical outcome after localized concurrent
chemoradiotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int.
31:369–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao YY, Lin ZZ, Hsu C, Shen YC, Hsu CH
and Cheng AL: Early alpha-fetoprotein response predicts treatment
efficacy of antiangiogenic systemic therapy in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 116:4590–4596. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|