Introduction
Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
mutations in lung cancer patients is vital in order to predict the
therapeutic response to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs)
(1). While patients harboring EGFR
mutations conferring sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs often exhibit a rapid
and marked response to these drugs, resistance frequently develops
after ~1 year. Mutations conferring resistance to EGFR-TKIs, such
as EGFR-T790M, represent the major mechanism underlying the
development of resistance to first-generation EGFR-TKIs.
Approximately half of EGFR-TKI-resistant cases are due to the
EGFR-T790M mutation. Recent advances in drug research have led to
the development of several novel EGFR-TKIs, including the pan-HER
inhibitor afatinib and the EGFR mutation-specific inhibitor
osimertinib (2). However, even with
the emergence of these novel drugs, tumor heterogeneity remains an
important issue when treating EGFR-TKI-resistant patients. Although
the tumor characteristics are similar between the primary site and
metastatic lesions (3), tumor
heterogeneity has been reported even within the original tumor, or
between primary and metastatic sites. Therefore, the same patient
may develop EGFR-TKI resistance through different mechanisms at
different sites (4).
EGFR-TKI-induced interstitial lung disease (ILD)
represents a major issue with this type of treatment, and its
incidence among Japanese patients is higher compared with that in
other ethnicities (5). There is
currently no established treatment for lung cancer patients with
EGFR-TKI-induced ILD and EGFR-TKI resistance.
The present study reports a case of a lung cancer
patient with an EGFR mutation conferring sensitivity to EGFR-TKIs,
who was treated with gefitinib followed by erlotinib, resulting in
EGFR-TKI-induced ILD. Treatment with afatinib and a glucocorticoid
effectively controlled the primary tumor, as well as the
EGFR-TKI-induced ILD. Therefore, afatinib in combination with a
glucocorticoid may be an effective treatment option for patients
with EGFR-TKI-induced ILD.
Case report
A 41-year-old female patient visited Keio University
Hospital due to a chronic cough. A chest radiograph and computed
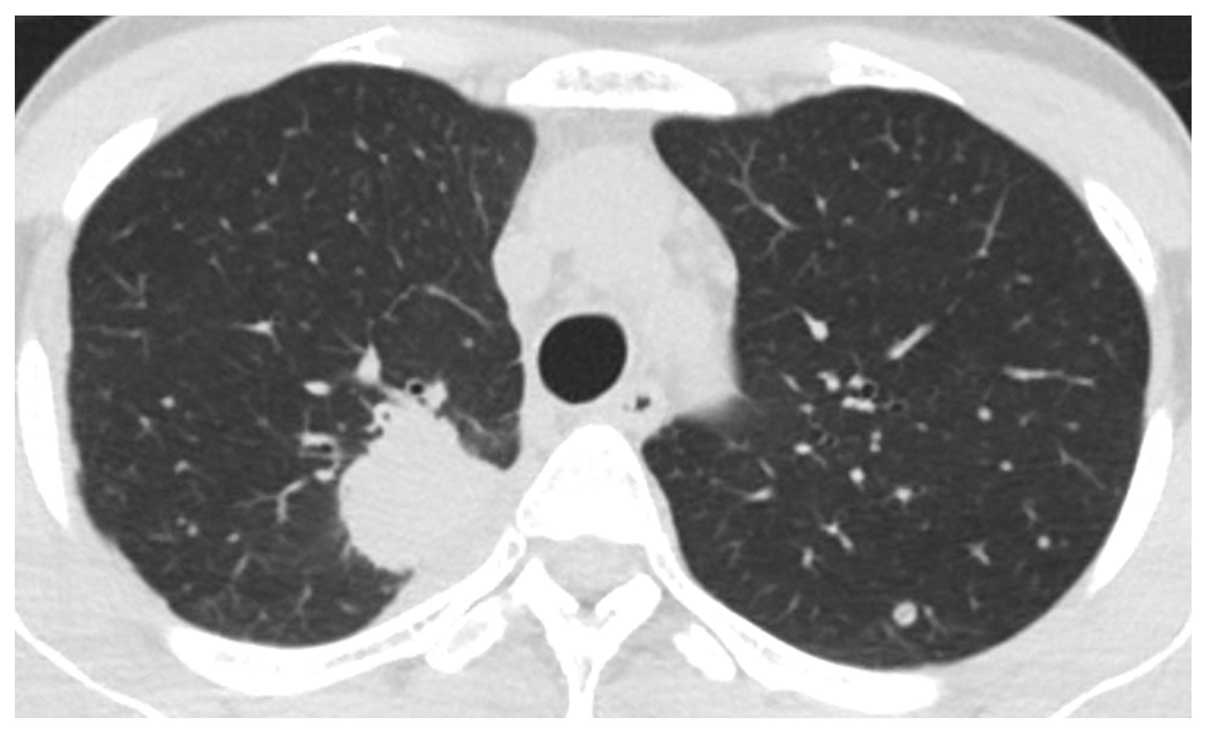
tomography (CT) scan revealed a mass in the right lung and multiple
lung metastatic lesions (Fig. 1). The
patient was diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma by transbronchial
lung biopsy, and an activating EGFR mutation (exon 19 deletion) was
detected. A 5-month treatment course with gefitinib achieved a
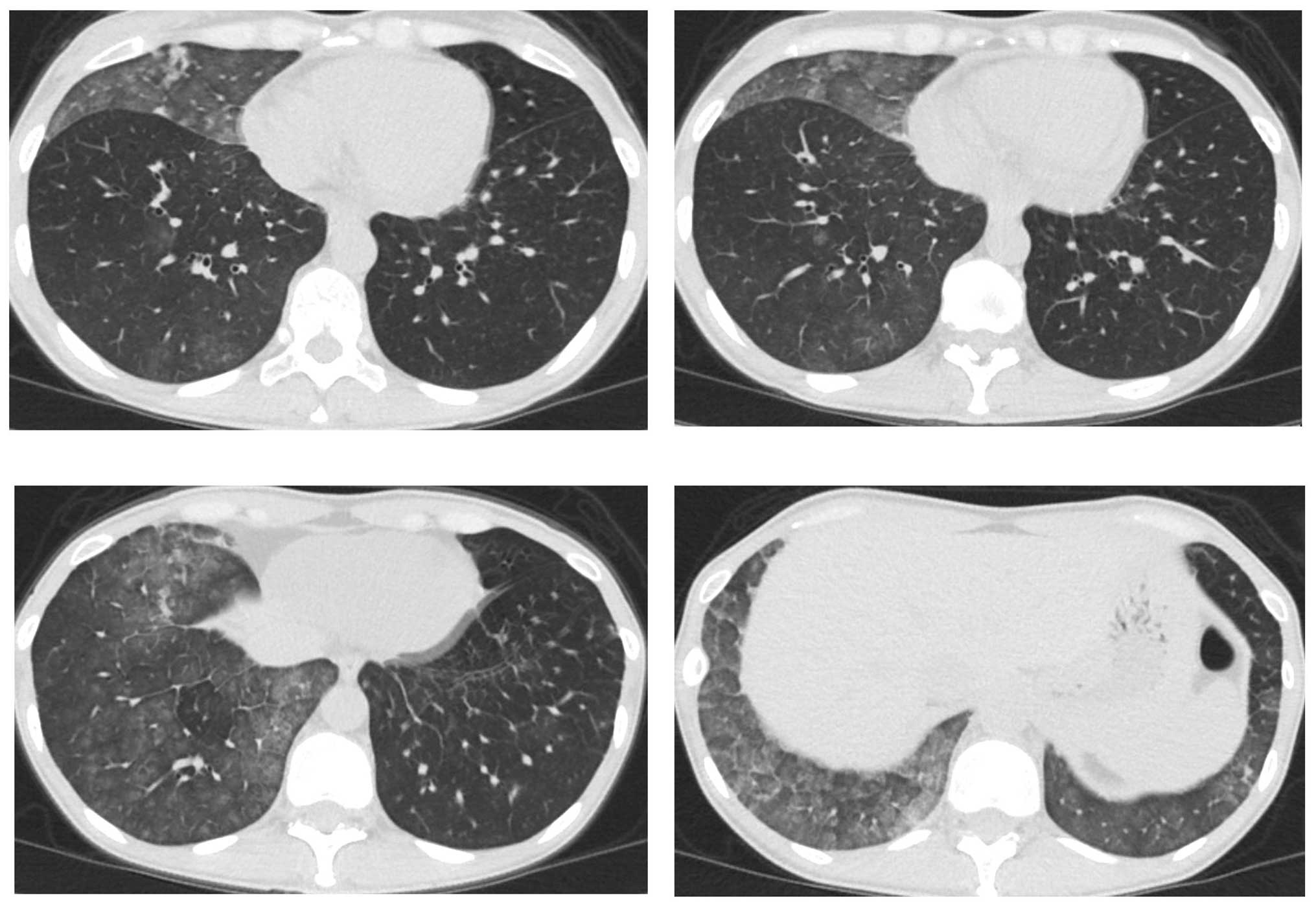
partial response. However, a CT scan revealed bilateral
ground-glass opacities (GGO) (Fig.
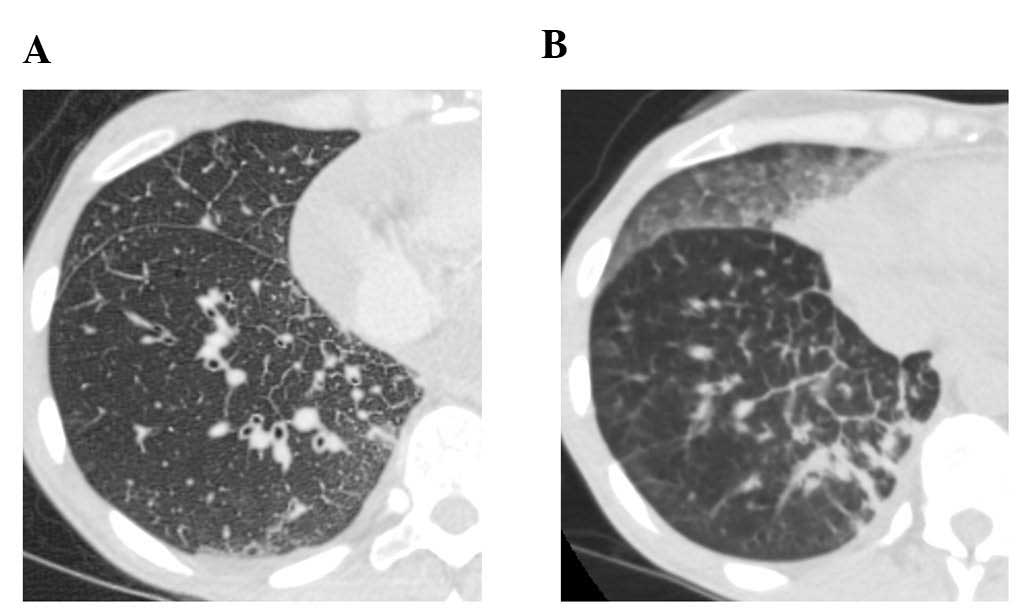
2), which improved following cessation of gefitinib treatment
(Fig. 3A). The patient was diagnosed
with gefitinib-induced ILD. One month after cessation of gefitinib,
lung cancer progression was detected. The patient was then treated
with carboplatin and pemetrexed for two cycles, but the treatment
was not successful. Due to the increased risk of ILD, the patient
was subsequently switched to erlotinib (25 mg/day) with informed
consent. The size of the multiple lung metastases was reduced with
erlotinib. However, a CT scan revealed new GGO regions, suggesting
erlotinib-induced ILD (Fig. 3B);
furthermore, a left pleural effusion was positive for EGFR exon 19
deletion and T790M. Following cessation of erlotinib, chest
drainage and pleurodesis with talc were performed. Within 2 weeks,
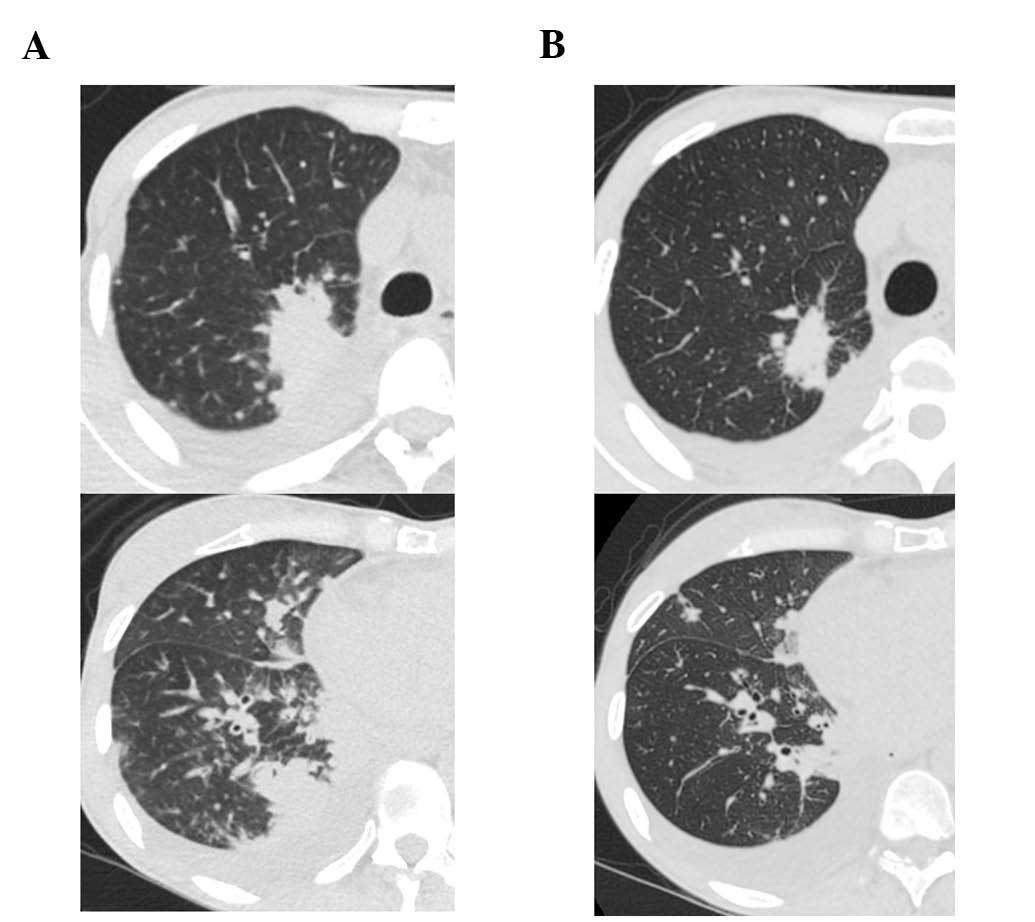
the right lung tumor and lymphangitis had markedly progressed
(Fig. 4A). The patient opted to
receive a molecular-targeted agent. Due to the previous positive
response to erlotinib, apart from the worsening of the pleural
effusion, the patient was treated with afatinib (20 mg/day) and
prednisolone (30 mg/day) with informed consent. During this
treatment, the primary tumor decreased in size and the
carcinomatous lymphangitis improved (Fig.
4B). The patient has been continuously receiving afatinib and
prednisolone for >3 months. The last follow-up took place 3
months later. Informed consent was obtained from the patient for
publication of the present case report.
Discussion
The present case demonstrated that combined
treatment with afatinib and a glucocorticoid was effective in the
management of a lung cancer patient who developed gefitinib-and
erlotinib-induced ILD. The frequency of EGFR-TKI-induced ILD was
reported to be ~2.8–3.5% in the Japanese population (5–7). In a
study by Endo et al (8), the
average mortality rate of EGFR-TKI-induced ILD was reported to be
44.3%, whereas that of ILD with a diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)
pattern was 75%. Due to the risk of life-threatening adverse
events, EGFR-TKI rechallenge should not be considered for such
patients, particularly when they present with the DAD pattern of
ILD. Rechallenge with erlotinib in combination with a
glucocorticoid was reported to be successful in a patient with
EGFR-TKI-induced ‘non-DAD pattern’ ILD (9). In the present case, ILD induced by
gefitinib and erlotinib exhibited a non-DAD pattern without
respiratory symptoms. Treatment with afatinib and prednisolone
induced a partial response of the tumor, without worsening of the
ILD. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case
of a patient treated with afatinib for non-small-cell lung cancer
after developing EGFR-TKI-induced ILD.
The present case provides an example regarding
treatment selection for EGFR-TKI-resistant lung cancer from the
perspective of tumor heterogeneity. The second-generation EGFR-TKI
afatinib was effective in treating the primary tumor and the
carcinomatous lymphangitis, notwithstanding the T790M mutation
detected from cytological examination of the pleural effusion. The
pleural effusion was manageable following pleurodesis, but the
amount of the fluid increased despite shrinkage of the primary
right lung tumor. Tumor heterogeneity is a recently reported
phenomenon (4). In the present case,
we hypothesized that the majority of the cells in the primary right
lung tumor did not harbor a T790M mutation due to the repeated
response to EGFR-TKIs and the non-parallel response of the left
pleural effusion, where the T790M mutation was detected.
In conclusion, treatment with afatinib and a
glucocorticoid may be an effective treatment option for lung cancer
patients following development of EGFR-TKI-induced ILD.
References
|
1
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hirano T, Yasuda H, Tani T, Hamamoto J,
Oashi A, Ishioka K, Arai D, Nukaga S, Miyawaki M, Kawada I, et al:
In vitro modeling to determine mutation specificity of EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitors against clinically relevant EGFR mutants
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 6:38789–38803.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Naoki K, Soejima K, Okamoto H, Hamamoto J,
Hida N, Nakachi I, Yasuda H, Nakayama S, Yoda S, Satomi R, et al:
The PCR-invader method (structure-specific 5′ nuclease-based
method), a sensitive method for detecting EGFR gene mutations in
lung cancer specimens; comparison with direct sequencing. Int J
Clin Oncol. 16:335–344. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, Kaji R,
Masago K, Fujita S, Imai Y, Nishiyama A, Ishida T and Nishimura Y:
Spatiotemporal T790M heterogeneity in individual patients with
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer after acquired resistance to
EGFR-TKI. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1553–1559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kudoh S, Kato H, Nishiwaki Y, Fukuoka M,
Nakata K, Ichinose Y, Tsuboi M, Yokota S, Nakagawa K, Suga M, et
al: Interstitial lung disease in Japanese patients with lung
cancer. A cohort and nested case-control study. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 177:1348–1357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi L, Tang J, Tong L and Liu Z: Risk of
interstitial lung disease with gefitinib and erlotinib in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of clinical trials. Lung Cancer. 83:231–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ando M, Okamoto I, Yamamoto N, Takeda K,
Tamura K, Seto T, Ariyoshi Y and Fukuoka M: Predictive factors for
interstitial lung disease, antitumor response, and survival in
non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2549–2556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Endo M, Johkoh T, Kimura K and Yamamoto N:
Imaging of gefitinib-related interstitial lung disease:
Multi-institutional analysis by the West Japan Thoracic Oncology
Group. Lung Cancer. 52:135–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arakawa N, Tsujita A, Saito N, Ishikawa S
and Ohno S: Successful erlotinib rechallenge after both gefitinib-
and erlotinib-induced interstitial lung diseases. Respirol Case
Rep. 1:17–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|