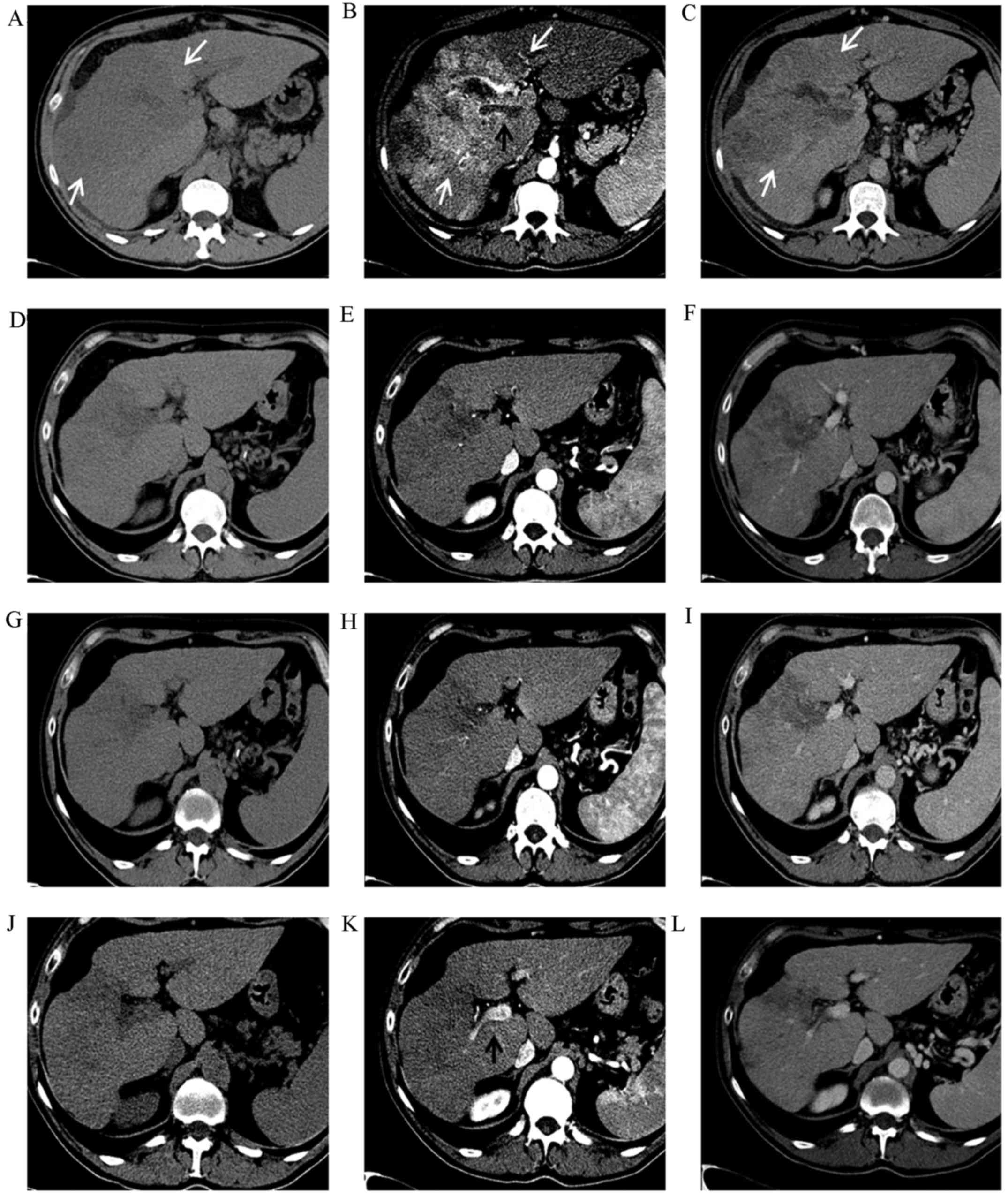
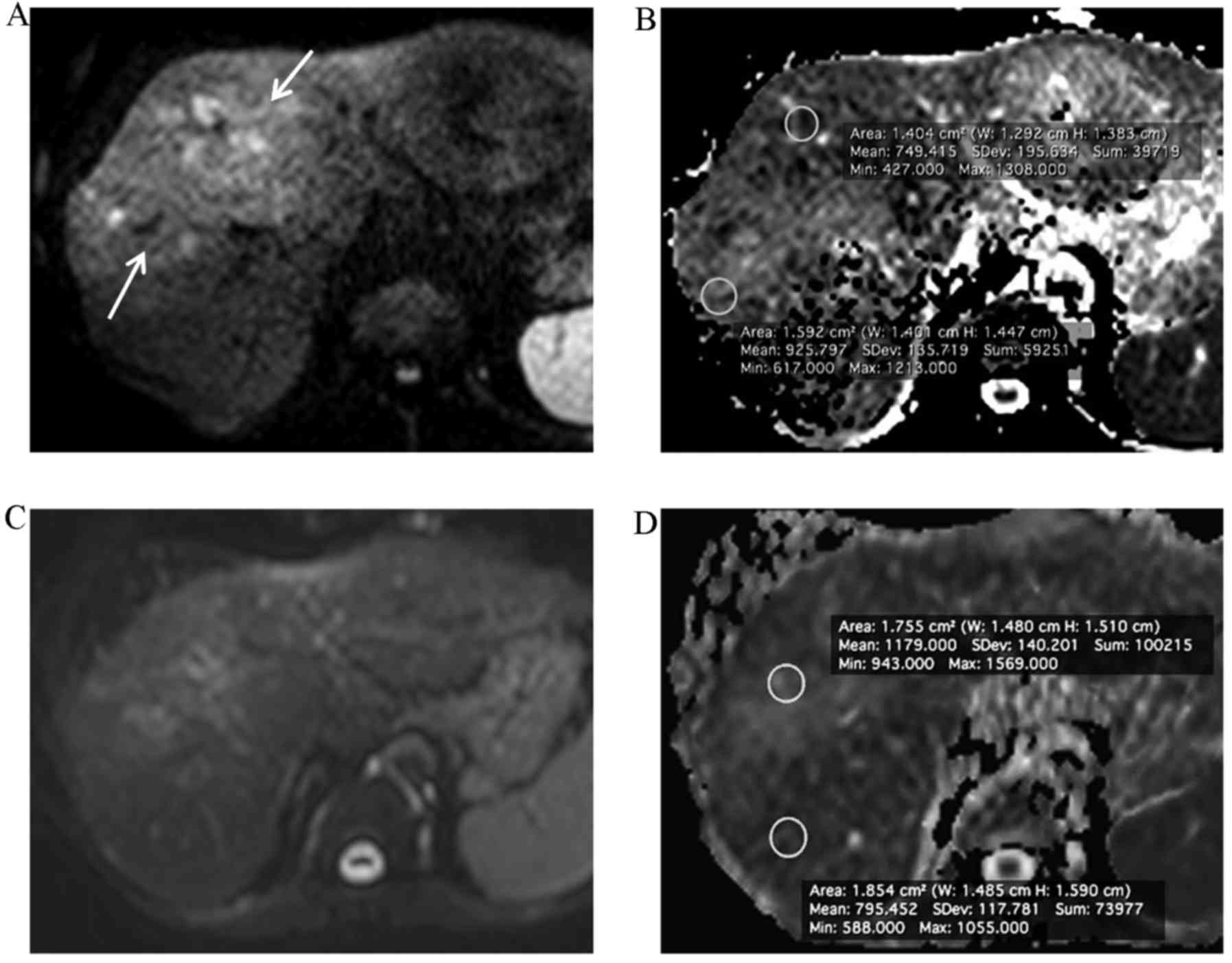
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL,
Pietroni MC and Williams R: Transection of the oesophagus for
bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 60:646–649. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raolul JL, Forner
A, et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Verstraete KL, Van der Woude HJ,
Hogendoorn PC, De-Deene Y, Kunnen M and Bloem JL: Dynamic
contrast-enhanced MR imaging of musculoskeletal tumors: Basic
principles and clinical applications. J Magn Reson Imaging.
6:311–321. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choi H, Charnsangavej C, de Castro Faria
S, Tamm EP, Benjamin RS, Johnosn MM, Macapiniac HA and Podoloff DA:
CT evaluation of the response of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
after imatinibmesylate treatment: A quantitative analysis
correlated with FDG PET findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
183:1619–1628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Namkung S, Zech CJ, Helmberger T, Reiser
MF and Schoenberg SO: Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-enhanced
liver MRI with ferucarbotran: Efficacy for characterization of
focal liver lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 25:755–765. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Santoro L, Grazioli L, Filippone A,
Grassedonio E, Belli G and Colagrande S: Resovist enhanced MR
imaging of the liver: Does quantitative assessment help in focal
lesion classification and characterization? J Magn Reson Imaging.
30:1012–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lencioni R and Llovet JM: Modified RECIST
(mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
30:52–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
So BJ, Bekaii-Saab T, Bloomston MA and
Patel T: Complete clinical response of metastatic hepatocellular
carcinoma to sorafenib in a patient with hemochromatosis: A case
report. J Hematol Oncol. 1:182008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Curtit E, Thiery-Vuillemin A, Nguyen T,
Heyd B, Pivot X, Di Martino V and Borg C: Complete histologic
response induced by sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:
A case report. J Clin Oncol. 29:e330–e332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Irtan S, Chopin-Laly X, Ronot M, Faivre S,
Paradis V and Belghiti J: Complete regression of locally advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma induced by sorafenib allowing curative
resection. Liver int. 31:740–743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang SX, Byrnes A, Verma S, Pancoast JR
and Rixe O: Complete remission of unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma treated with reduced dose of sorafenib: A case report.
Target Oncol. 5:59–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sacco R, Bargellini I, Gianluigi G,
Bertini M, Bozzi E, Altomare E, Battaglia V, Romano A, Bertoni M,
Capria A, et al: Complete response for advanced liver cancer during
sorafenib therapy: Case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:42011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abbadessa G, Rimassa L, Pressiani T,
Carrillo-Infante C, Cucchi E and Santoro A: Optimized management of
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Four long-lasting responses to
sorafenib. World J Gastroenterol. 17:2450–2453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shiba S, Okusaka T, Ikeda M, Saito H and
Ichida T: Characteristics of 18 patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma who obtained a complete response after treatment with
sorafenib. Hepatol Res. 44:1268–1276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Du J, Qian X and Liu B: Long-term
progression-free survival in a case of hepatocellular carcinoma
with vertebral metastasis treated with a reduced dose of sorafenib:
Case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 5:381–385.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ozenne V, Paradis V, Pernot S, Casteinau
C, Vullierme MP, Bouattour M, Valla D, Farges O and Degos F:
Tolerance and outcome of patients with unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
22:1106–1110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Llovet JM, Peña CE, Lathia CD, Shan M,
Meinhardt G and Bruix J: SHARP Investigators Study Group: Plasma
biomarkers as predictors of outcome in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 18:2290–2300. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Villanueva A and Llovet JM: Targeted
therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
140:1410–1426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Villanueva A and Llovet JM: Impact of
intra-individual molecular heterogeneity in personalized treatment
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:2416–2419. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee YS, Kim BH, Kim BC, Shin A, Kim JS,
Hong SH, Hwang JA, Lee JA, Nam S, Lee SH, et al: SLC15A2 genomic
variation is associated with the extraordinary response of
sorafenib treatment: Whole-genome analysis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:16449–16460. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shao YY, Lin ZZ, Hsu C, Shen YC, Hsu CH
and Cheng AL: Early alpha-fetoprotein response predicts treatment
efficacy of antiangiogenic systemic therapy in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 116:4590–4596. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huan HB, Lau WY, Xia F, Ma KS and Bie P:
Complete response to sorafenib in a patient with recurrent
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 20:14505–14509.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Xu B, Fu L and Hao XS: Correlation
of four vascular specific growth factors with carcinogenesis and
portal vein tumor thrombus formation in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 25:403–409. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Novi M, Lauritano EC, Piscaglia AC,
Barbaro B, Zocco MA, Pompili M and Gasbarrini A: Portal vein tumor
thrombosis revascularization during sorafenib treatment for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:1852–1854. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu AX, Holalkere NS, Muzikansky A, Horgan
K and Sahani DV: Early antiangiogenic activity of bevacizumab
evaluated by computed tomography perfusion scan in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 13:120–125. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang T, Zhu AX and Sahani DV: Established
and novel imaging biomarkers for assessing response to therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 58:169–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mungai F, Pasquinelli F, Mazzoni LN,
Virgili G, Ragozzino A, Quaia E, Morana G, Giovagnoni A, Grazioli L
and Colagrande S: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in
prediction and assessment of chemotherapy outcome in liver
metastases. Radiol Med. 119:625–633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pantaleo MA, Mandrioli A, Saponara M,
Nannini M, Erente G, Lolli C and Biasco G: Development of coronary
artery stenosis in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
treated with sorafenib. BMC Cancer. 12:2312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hagihara A, Teranishi Y, Kawamura E, Fujii
H, Iwai S, Morikawa H, Enomoto M, Tamori A and Kawada N: A complete
response induced by 21-day sorafenib therapy in a patient with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Intern Med. 52:1589–1592. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shiozawa K, Watanabe M, Ikcara T,
Matsukiyo Y, Kogame M, Kanayama M, Matsui T, Kikuchi Y, Ishii K,
Igarashi Y and Sumino Y: Sustained complete response of
hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus following
discontinuation of sorafenib: A case report. Oncol Lett. 7:50–52.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sivendran S, Liu Z, Portas LJ Jr, Yu M,
Hahn N, Sonpavde G, Oh WK and Galsky MD: Treatment-related
mortality with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced solid tumors: A
meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:919–925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Staehler M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Desai AA, Rolland
F, et al: Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Final
efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches
in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol.
27:3312–3318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Madabushi R, Booth B,
Chattopadhyay S, Sridhara R, Justice R and Pazdur R: Sorafenib for
the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist.
14:95–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tolcher AW, Appleman LJ, Shapiro GI, Mita
AC, Cihon F, Mazzu A and Sundaresan PR: Aphase I open-label study
evaluating the cardiovascular safety of sorafenib in patients with
advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:751–764. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schmidinger M, Zielinski CC, Vogl UM,
Bojic A, Bojic M, Schukro C, Ruhsam M, Hejna M and Schmidinger H:
Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib and sorafenib in patients with
metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 26:5204–5212. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arima Y, Oshima S, Noda K, Fukushima H,
Taniguchi I, Nakamura S, Shono M and Ogawa H: Sorafenib-induced
acute myocardial infarction due to coronary artery spasm. J
Cardiol. 54:512–515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Porto I, Leo A, Miele L, Pompili M,
Landolfi R and Crea F: A case of variant angina in a patient under
chronic treatment with sorafenib. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:476–480.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Naib T, Steingart RM and Chen CL:
Sorafenib-associated multivessel coronary artery vasospasm. Herz.
36:348–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hoshijima M and Chien KR: Mixed signals in
heart failure: Cancer rules. J Clin Invest. 109:849–855. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ederhy S, Izzedine H, Massard C, Dufaitre
G, Spanp JP, Milano G, Meuleman C, Besse B, Boccara F, Kahyat D, et
al: Cardiac side effects of molecular targeted therapies: Towards a
better dialogue between oncologists and cardiologists. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 80:369–379. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Force T, Krause DS and Van Etten RA:
Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase
inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:332–344. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hasinoff BB and Patel D: Mechanisms of
myocyte cytotoxicity induced by the multikinase inhibitor
sorafenib. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 10:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kamba T and McDonald DM: Mechanisms of
adverse effects of anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Br J Cancer.
96:1788–1795. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kawabata M, Umemoto N, Shimada Y,
Nishimura Y, Zhang B, Kuroyanagi J, Miyabe M and Tanaka T:
Downregulation of stanniocalcin 1 is responsible for
sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 143:374–384. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|