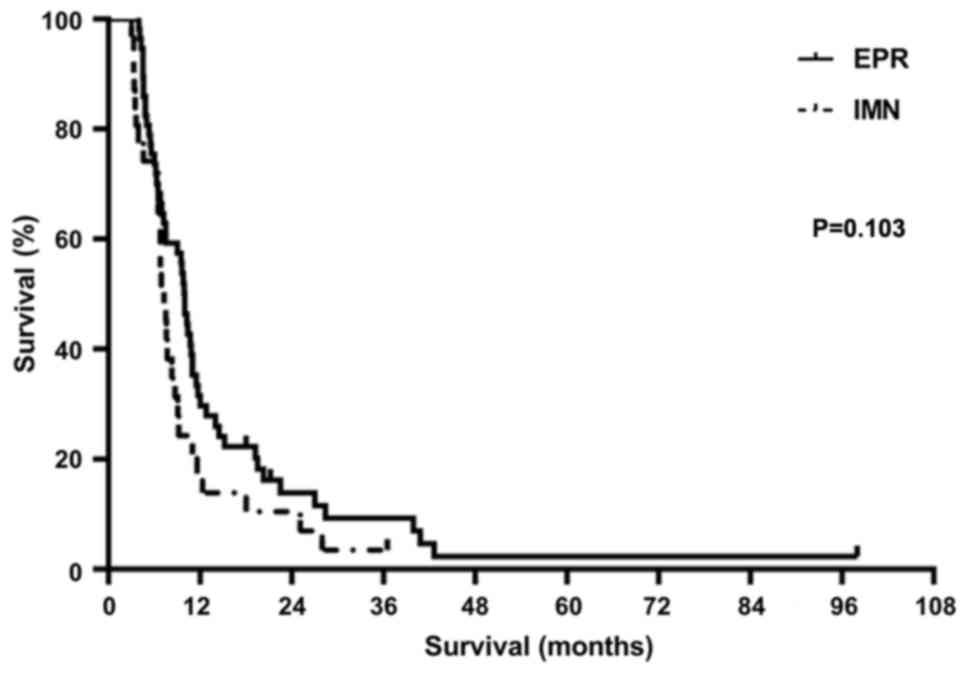
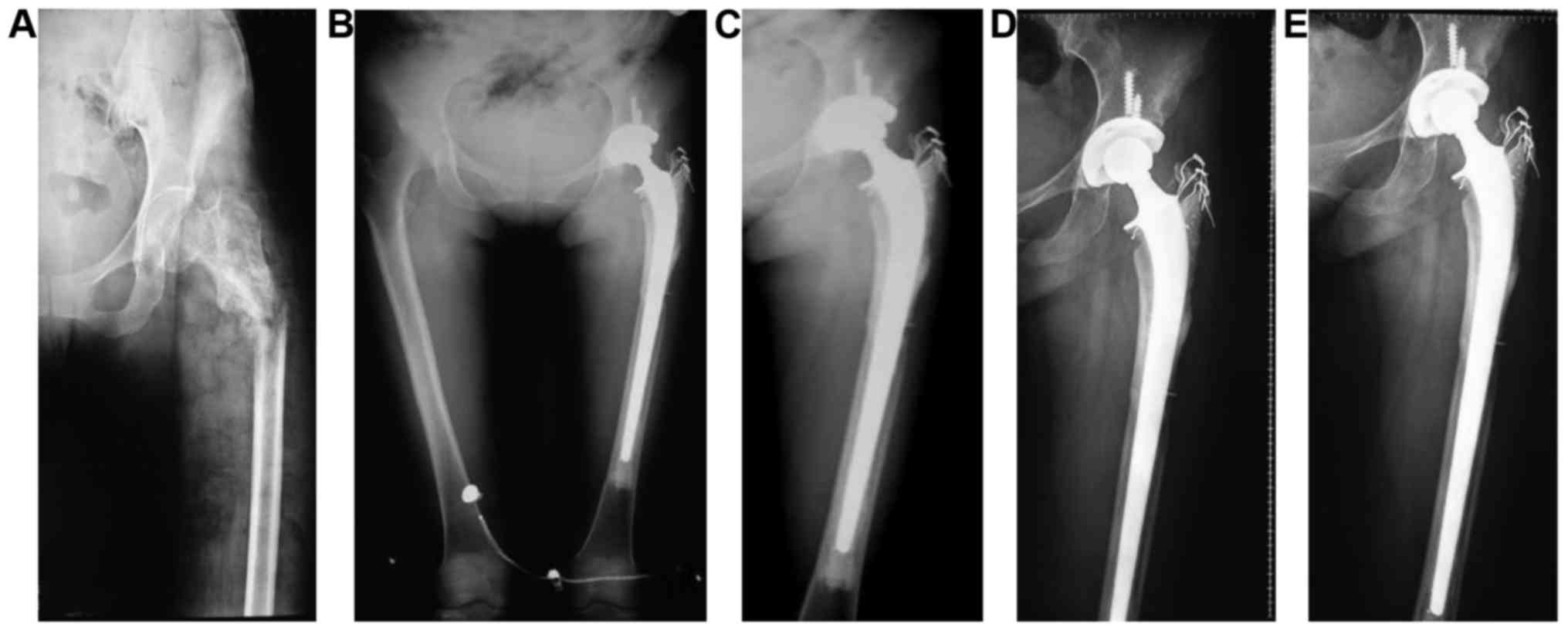
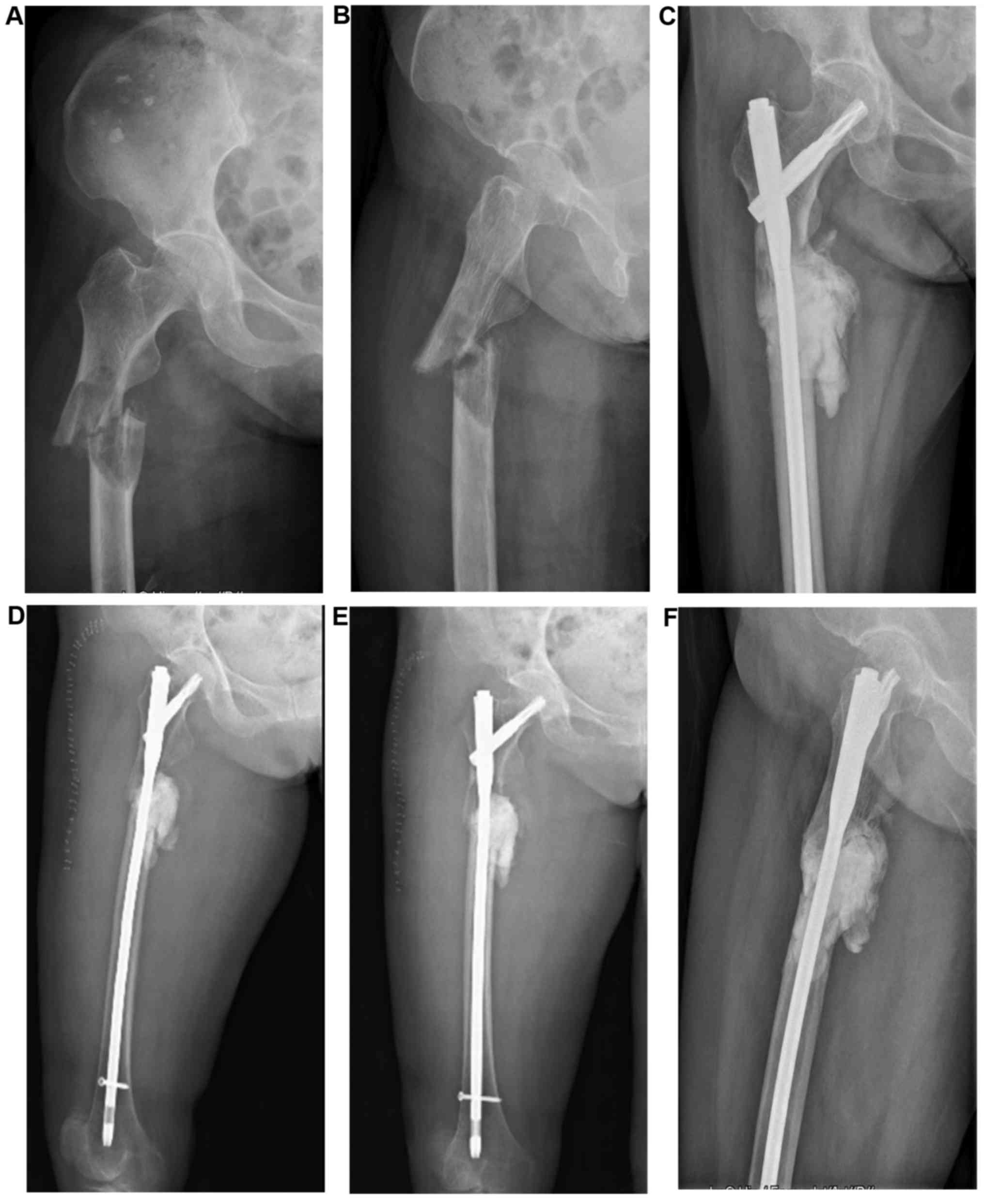
|
1
|
Camnasio F, Scotti C, Peretti GM, Fontana
F and Fraschini G: Prosthetic joint replacement for long bone
metastases: Analysis of 154 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.
128:787–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hage WD, Aboulafia AJ and Aboulafia DM:
Incidence, location and diagnostic evaluation of metastatic bone
disease. Orthop Clin North Am. 31:515–528. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clarke HD, Damron TA and Sim FH: Head and
neck replacement endoprosthesis for pathologic proximal femoral
lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–217. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Steensma M, Boland PJ, Morris CD,
Athanasian E and Healey JH: Endoprosthetic treatment is more
durable for pathologic proximal femur fractures. Clin Orthop Relat
Res. 470:920–926. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harvey N, Ahlmann ER, Allison DC, Wang L
and Menendez LR: Endoprostheses last longer than intramedullary
devices in proximal femur metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
470:684–691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gainor BJ and Buchert P: Fracture healing
in metastatic bone disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–302. 1983.
|
|
7
|
Sarahrudi K, Greitbauer M, Platzer P,
Hausmann JT, Heinz T and Vecsei V: Surgical treatment of metastatic
fractures of the femur: A retrospective analysis of 142 patients. J
Trauma. 66:1158–1163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Selek H, Basarir K, Yildiz Y and Sağlik Y:
Cemented endoprosthetic replacement for metastatic bone disease in
the proximal femur. J Arthroplasty. 23:112–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao H, Liu Z, Wang B and Guo A: Clinical
and functional comparison of endoprosthetic replacement with
intramedullary nailing for treating proximal femur metastasis. Chin
J Cancer Res. 28:209–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wedin R and Bauer H: Surgical treatment of
skeletal metastatic lesions of the proximal femur: Endoprosthesis
or reconstruction nail? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 87:1653–1657. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lane JM, Sculco TP and Zolan S: Treatment
of pathological fractures of the hip by endoprosthetic replacement.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 62:954–959. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sarahrudi K, Hora K, Heinz T, Millington S
and Vécsei V: Treatment results of pathological fractures of the
long bones: A retrospective analysis of 88 patients. Int Orthop.
30:519–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xing Z, Moon BS, Satcher RL, Lin PP and
Lewis VO: A long femoral stem is not always required in hip
arthroplasty for patients with proximal femur metastases. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 471:1622–1627. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanaka T, Imanishi J, Charoenlap C and
Choong PF: Intramedullary nailing has sufficient durability for
metastatic femoral fractures. World J Surg Oncol. 14:802016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steensma M and Healey JH: Trends in the
surgical treatment of pathologic proximal femur fractures among
musculoskeletal tumor society members. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
471:2000–2006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mirels H: Metastatic disease in long
bones: A proposed scoring system for diagnosing impending
pathologic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–264. 1989.
|
|
17
|
Van Acker HH, Anguille S, Willemen Y,
Smits EL and Van Tendeloo VF: Bisphosphonates for cancer treatment:
Mechanisms of action and lessons from clinical trials. Pharmacol
Ther. 158:24–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Enneking WF, Dunham W, Gebhardt MC,
Malawar M and Pritchard DJ: A system for the functional evaluation
of reconstructive procedures after surgical treatment of tumors of
the musculoskeletal system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–246.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jacofsky DJ and Haidukewych GJ: Management
of pathologic fractures of the proximal femur: State of the art. J
Orthop Trauma. 18:459–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Algan SM and Horowitz SM: Surgical
treatment of pathologic hip lesions in patients with metastatic
disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–231. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Damron TA: Management of metastatic
carcinoma to the hip and proximal femurMenendez LR: Orthopaedic
Knowledge Update: Musculoskeletal Tumors. Rosemont, IL: American
Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; pp. 363–371. 2002
|
|
22
|
Talbot M, Turcotte RE, Isler M, Normandin
D, Iannuzzi D and Downer P: Function and health status in
surgically treated bone metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
438:215–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katagiri H, Takahashi M, Wakai K, Sugiura
H, Kataoka T and Nakanishi K: Prognostic factors and a scoring
system for patients with skeletal metastasis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
87:698–703. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsuya A, Kurata T, Tamura K and Fukuoka M:
Skeletal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective
study. Lung Cancer. 57:229–232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Body JJ: New developments for treatment
and prevention of bone metastases. Curr Opin Oncol. 23:338–342.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coluzzi F, Di Bussolo E, Mandatori I and
Mattia C: Bone metastatic disease: Taking aim at new therapeutic
targets. Curr Med Chem. 18:3093–3115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schneiderbauer MM, von Knoch M, Schleck
CD, Harmsen WS, Sim FH and Scully SP: Patient survival after hip
arthroplasty for metastatic disease of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 86-A:1–1689. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manoso MW, Frassica DA, Lietman ES and
Frassica FJ: Proximal femoral replacement for metastatic bone
disease. Orthopedics. 30:384–388. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yazawa Y, Frassica FJ, Chao EY, Pritchard
DJ, Sim FH and Shives TC: Metastatic bone disease. A study of the
surgical treatment of 166 pathologic humeral and femoral fractures.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1–219. 1990.
|
|
30
|
Dijstra S, Wiggers T, van Geel BN and
Boxma H: Impending and actual pathological fractures in patients
with bone metastases of the long bones. A retrospective study of
233 surgically treated fractures. Eur J Surg. 160:535–542.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Narazaki DK, de Alverga Neto CC, Baptista
AM, Caiero MT and de Camargo OP: Prognostic factors in pathologic
fractures secondary to metastatic tumors. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
61:313–320. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|