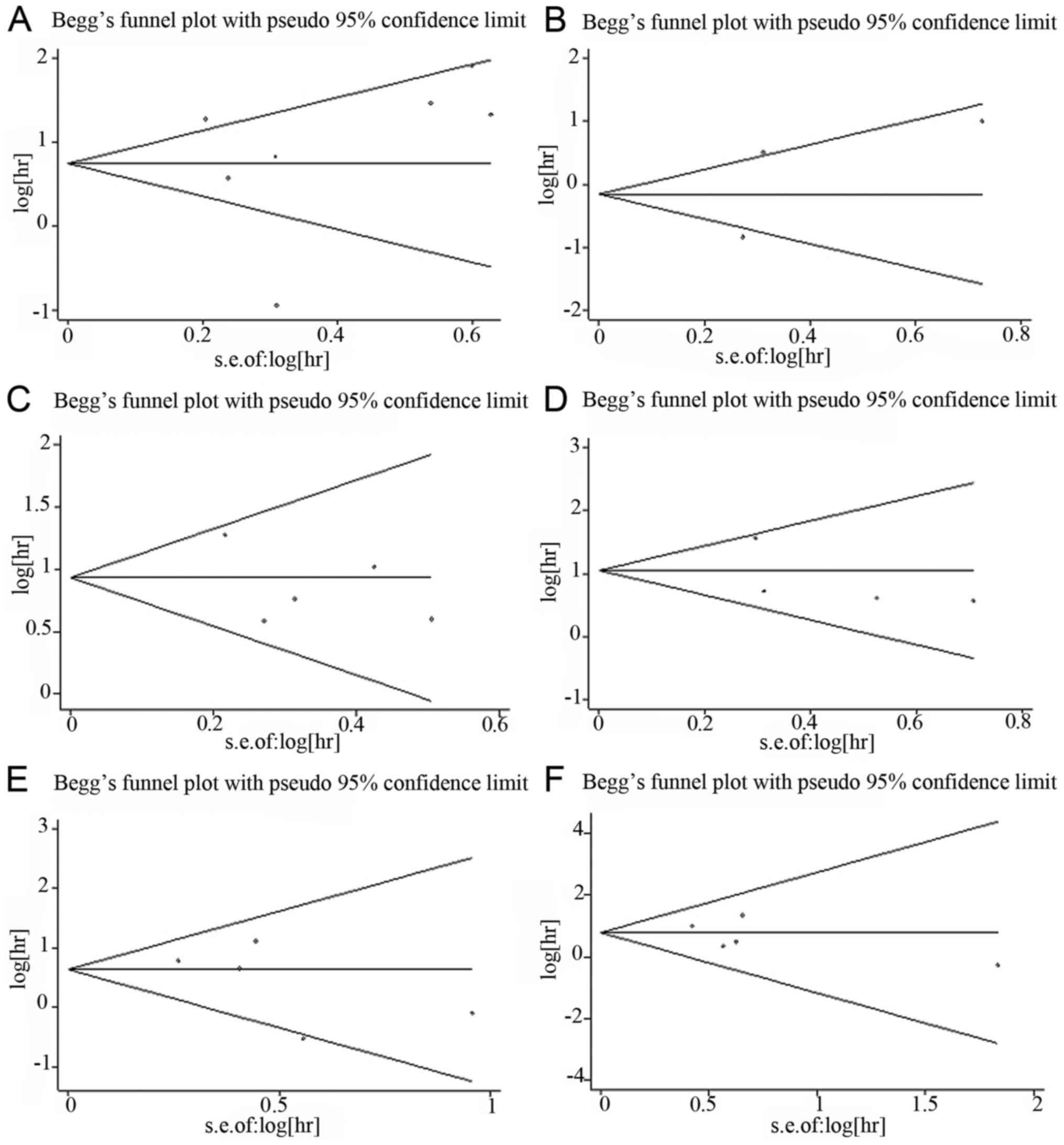
|
1
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Horvitz HR and Sulston JE: Isolation and
genetic characterization of cell-lineage mutants of the nematode
Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 96:435–454. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hua K, Jin J, Zhang H, Zhao B, Wu C, Xu H
and Fang L: MicroRNA-7 inhibits proliferation, migration and
invasion of thyroid papillary cancer cells via targeting CKS2. Int
J Oncol. 49:1531–1540. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nip H, Dar AA, Saini S, Colden M, Varahram
S, Chowdhary H, Yamamura S, Mitsui Y, Tanaka Y, Kato T, et al:
Oncogenic microRNA-4534 regulates PTEN pathway in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:68371–68384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin L, Li Y, Liu J, Yang S, Gui Y, Mao X,
Nie G and Lai Y: Tumor suppressor miR-149-5p is associated with
cellular migration, proliferation and apoptosis in renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:5386–5392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek
SH and Kim VN: MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang S, He X, Ding J, Huang S, He X, Ding
J, Liang L, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Yao X, Pan Z, Zhang P, Li J, et al:
Upregulation of miR-23a approximately 27a approximately 24
decreases transforming growth factor-beta-induced tumor-suppressive
activities in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer.
123:972–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner
MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ and Schmittgen
TD: Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in
pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:1046–1054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K,
Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R and Haqq C:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
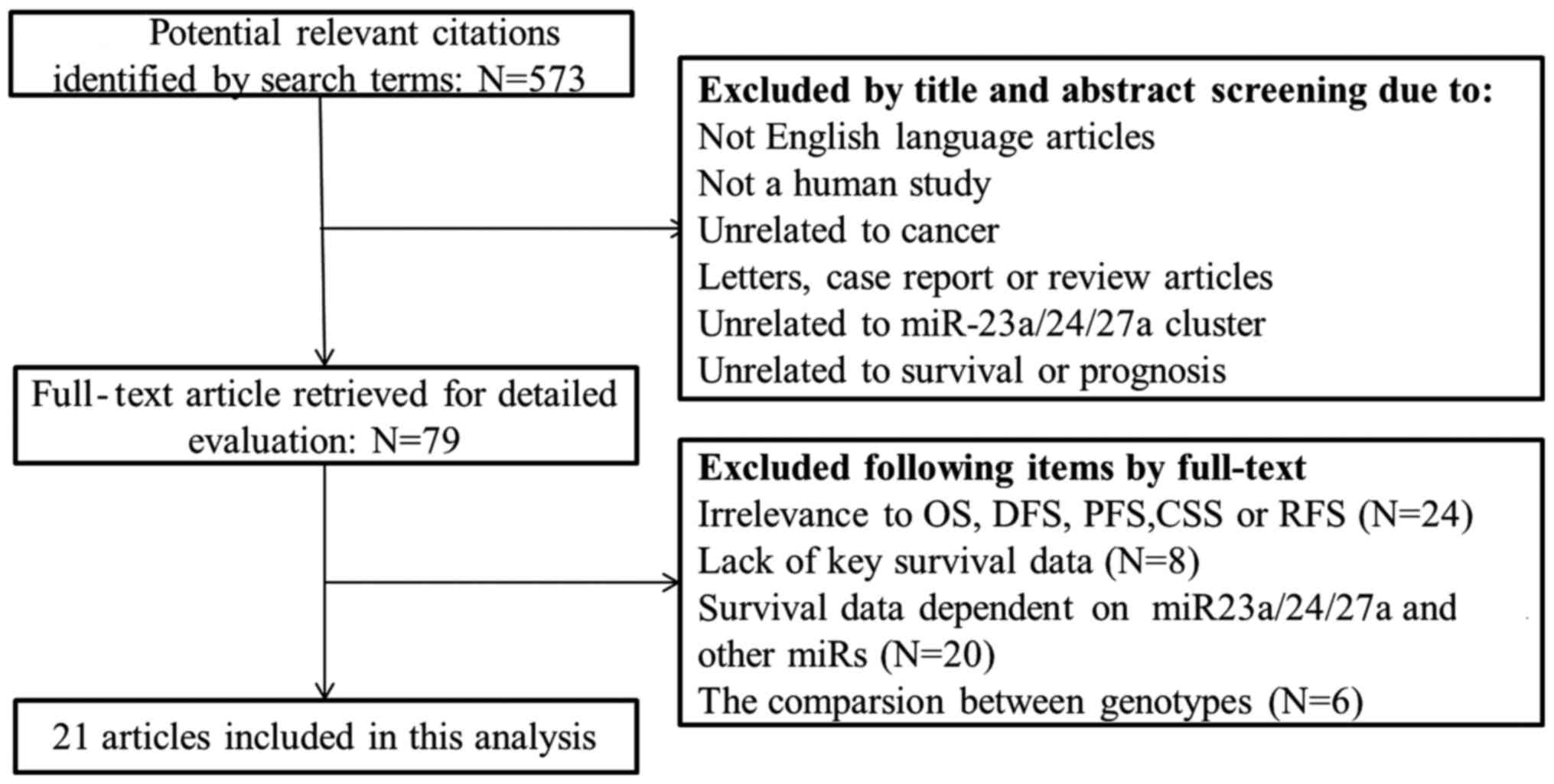
Bao L, Zhao J, Dai X, Wang Y, Ma R, Su Y,
Cui H, Niu J, Bai S, Xiao Z, et al: Correlation between miR-23a and
onset of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
38:318–330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai S, Chen R, Li X, Cai Y, Ye Z, Li S, Li
J, Huang H, Peng S, Wang J, et al: Downregulation of microRNA-23a
suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting the PAK6-LIMK1
signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 6:3904–3917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
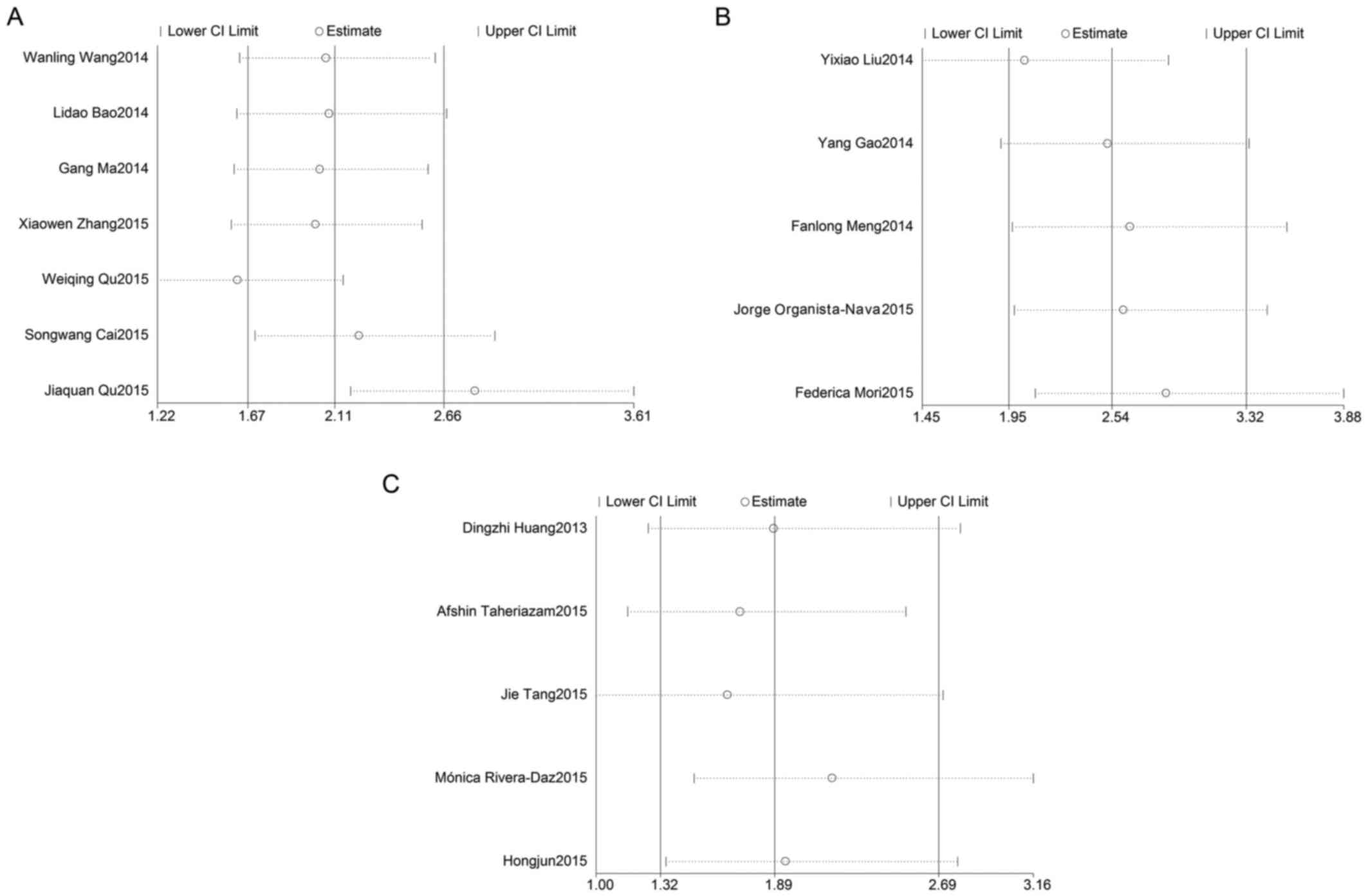
Eitan R, Kushnir M, Lithwick-Yanai G,
David MB, Hoshen M, Glezerman M, Hod M, Sabah G, Rosenwald S and
Levavi H: Tumor microRNA expression patterns associated with
resistance to platinum based chemotherapy and survival in ovarian
cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol. 114:253–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao Y, Liu Y, Du L, Li J, Qu A, Zhang X,
Wang L and Wang C: Down-regulation of miR-24-3p in colorectal
cancer is associated with malignant behavior. Med Oncol.
32:3622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han BW, Feng DD, Li ZG, Luo XQ, Zhang H,
Li XJ, Zhang XJ, Zheng LL, Zeng CW, Lin KY, et al: A set of miRNAs
that involve in the pathways of drug resistance and leukemic
stem-cell differentiation is associated with the risk of relapse
and glucocorticoid response in childhood ALL. Hum Mol Genet.
20:4903–4915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang D, Wang H, Liu R, Li H, Ge S, Bai M,
Deng T, Yao G and Ba Y: miRNA27a is a biomarker for predicting
chemosensitivity and prognosis in metastatic or recurrent gastric
cancer. J Cell Biochem. 115:549–556. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu YX, Long XD, Xi ZF, Ma Y, Huang XY,
Yao JG, Wang C, Xing TY and Xia Q: MicroRNA-24 modulates aflatoxin
B1-related hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis and tumorigenesis.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:4829262014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma G, Dai W, Sang A, Yang X and Gao C:
Upregulation of microRNA-23a/b promotes tumor progression and
confers poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:8833–8840. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng FL, Wang W and Jia WD: Diagnostic and
prognostic significance of serum miR-24-3p in HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:1772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mori F, Ferraiuolo M, Santoro R, Sacconi
A, Goeman F, Pallocca M, Pulito C, Korita E, Fanciulli M, Muti P,
et al: Multitargeting activity of miR-24 inhibits long-term
melatonin anticancer effects. Oncotarget. 7:20532–20548. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakata W, Uemura M, Sato M, Fujita K,
Jingushi K, Ueda Y, Kitae K, Tsujikawa K and Nonomura N: Expression
of miR-27a-3p is an independent predictive factor for recurrence in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:21645–21654. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Organista-Nava J, Gómez-Gómez Y,
Illades-Aguiar B, Del Carmen Alarcón-Romero L, Saavedra-Herrera MV,
Rivera-Ramírez AB, Garzón-Barrientos VH and Leyva-Vázquez MA: High
miR-24 expression is associated with risk of relapse and poor
survival in acute leukemia. Oncol Rep. 33:1639–1649. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng H, Wang X, Zhang P, Sun T, Ren X and
Xia Z: miR-27a promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2259–2266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qu JQ, Yi HM, Ye X, Li LN, Zhu JF, Xiao T,
Yuan L, Li JY, Wang YY, Feng J, et al: MiR-23a sensitizes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting IL-8/Stat3
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28341–28356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qu WQ, Liu L and Yu Z: Clinical value of
microRNA-23a upregulation in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:13598–13603. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rivera-Diaz M, Miranda-Roman MA, Soto D,
Quintero-Aguilo M, Ortiz-Zuazaga H, Marcos-Martinez MJ and
Vivas-Mejía PE: MicroRNA-27a distinguishes glioblastoma multiforme
from diffuse and anaplastic astrocytomas and has prognostic value.
Am J Cancer Res. 5:201–218. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taheriazam A, Bahador R, Karbasy SH,
Jamshidi SM, Torkaman A, Yahaghi E and Shakeri M: Down-regulation
of microRNA-26a and up-regulation of microRNA-27a contributes to
aggressive progression of human osteosarcoma. Diagn Pathol.
10:1662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang J, Zhao H, Cai H and Wu H: Diagnostic
and prognostic potentials of microRNA-27a in osteosarcoma. Biomed
Pharmacother. 71:222–226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang WL, Yang C, Han XL, Wang R, Huang Y,
Zi YM and Li JD: MicroRNA-23a expression in paraffin-embedded
specimen correlates with overall survival of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. Med Oncol. 31:9192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang XW, Liu N, Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang ZX,
Sun YY, Qiu GB and Fu WN: High microRNA-23a expression in laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis.
Diagn Pathol. 10:222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao G, Liu L, Zhao T, Jin S, Jiang S, Cao
S, Han J, Xin Y, Dong Q, Liu X and Cui J: Upregulation of miR-24
promotes cell proliferation by targeting NAIF1 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:3693–3701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou Q, Gallagher R, Ufret-Vincenty R, Li
X, Olson EN and Wang S: Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal
neovascularization by members of microRNA-23~27~24 clusters. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:pp. 8287–8292. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li X, Liu X, Xu W, Zhou P, Gao P, Jiang S,
Lobie PE and Zhu T: c-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster
promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by
targeting Sprouty2. J Biol Chem. 288:18121–18133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goto Y, Kojima S, Nishikawa R, Enokida H,
Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T and Seki
N: The microRNA-23b/27b/24-1 cluster is a disease progression
marker and tumor suppressor in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
5:7748–7759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao M, Seike M, Soeno C, Mizutani H,
Kitamura K, Minegishi Y, Noro R, Yoshimura A, Cai L and Gemma A:
MiR-23a regulates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:869–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kong KY, Owens KS, Rogers JH, Mullenix J,
Velu CS, Grimes HL and Dahl R: MIR-23A microRNA cluster inhibits
B-cell development. Exp Hematol. 38:629–640 e1. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM and
Hogan BL: Transgenic over-expression of the microRNA miR-17-92
cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung
epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 310:442–453. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mehta A, Mann M, Zhao JL, Marinov GK,
Majumdar D, Garcia-Flores Y, Du X, Erikci E, Chowdhury K and
Baltimore D: The microRNA-212/132 cluster regulates B cell
development by targeting Sox4. J Exp Med. 212:1679–1692. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang CM, Chiba T, Brill B, Delis N, von
Manstein V, Vafaizadeh V, Oellerich T and Groner B: Expression of
the miR-302/367 cluster in glioblastoma cells suppresses
tumorigenic gene expression patterns and abolishes transformation
related phenotypes. Int J Cancer. 137:2296–2309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett
S and Sydes MR: Practical methods for incorporating summary
time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 8:162007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|