Introduction
Fatigue is a common symptom in cancer patients. The
rate of metastatic cancer patients with cancer-related fatigue
(CRF) is >75%, and cancer survivors report that, even if their
condition improves after treatment, fatigue often persists for
months or even years. Cancer patients state that fatigue is one of
the most distressing symptoms associated with cancer, and the
general condition during cancer treatment is difficult to manage
with medications (1).
The pathophysiology of fatigue in cancer patients is
multifactorial. Suggested mechanisms include an imbalance in energy
metabolism due to tumor growth, infection, fever, or surgery,
malnutrition caused by anorexia, nausea, or vomiting, and an
increase in the abnormal production of substances that impair
metabolic homeostasis, such as cytokines and proteolysis-inducing
factors (2). Other researchers have
suggested mechanisms that link fatigue to the pathophysiology of
sleep disorders, major depression anemia, or hypoxia. However,
there is no conclusive evidence to support the application of
specific methods to reduce fatigue in cancer patients; thus,
further investigation is required (1).
Carnitine, a micronutrient derived from an amino
acid, is found in almost all cells of the body, and it plays an
important role in energy metabolism (3). Long-chain fatty acids are transported
by carnitine across the membranes of mitochondria in muscle cells,
and β-oxidation converts fatty acids into energy in the form of
adenosine triphosphate. Additionally, carnitine also transports
fatty acids out of the mitochondria (3). Carnitine reabsorption is regulated
through the proximal tubules of the kidney. Skeletal and cardiac
muscles use fatty acids as their primary source of energy; thus,
carnitine deficiency is associated with low energy levels and
muscle weakness (4).
Carnitine homeostasis is regulated by oral intake,
synthesis and renal reabsorption. In humans, carnitine is produced
in the liver and kidneys, stored in skeletal muscle and excreted in
the urine. Certain cytotoxic chemotherapies interfere with the
homeostasis and reabsorption of carnitine (5–7). Nausea,
vomiting and anorexia caused by cancer treatment may reduce the
oral intake of food, which may lead to low plasma levels of
carnitine (8).
Recent studies demonstrated that L-carnitine (LC)
supplementation in patients with cancer was effective in reducing
fatigue (4,5) and increasing the lean body mass and
appetite (9). However, the type of
patients who may benefit from LC supplementation has not been fully
elucidated. The aim of the present study was to monitor fatigue in
cancer patients who received chemotherapy, adjuvant chemotherapy or
treatment for metastatic disease, and to evaluate changes in
fatigue prior to and following LC supplementation.
Patients and methods
Patients
The present study was performed with the approval of
the Internal Review Board on ethical issues of Hokkaido Social Work
Association Obihiro Hospital. A total of 11 patients who underwent
chemotherapy in our hospital between September 2014 and December
2015 and experienced fatigue during chemotherapy were
retrospectively reviewed. The inclusion criteria were as follows:
i) Pathological diagnosis of cancer; ii) the patients must have
been informed of their cancer diagnosis; iii) administration of at
least one cycle of a chemotherapeutic regimen; iv) Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1; v) the
patients had to be able to understand and complete the
questionnaires; and vi) no severe mental or cognitive
disorders.
Fatigue measurements
The Brief Fatigue Inventory (BFI) was selected to
assess fatigue, as it is a multidimensional, independent, commonly
used scale for the clinical assessment of fatigue. The BFI consists
of 9 items, using a numerical scale of 0–10 on a single page. The
global score for the BFI is calculated as the mean value of these 9
items and categorized as follows: Scores of 1–3, mild; scores of
4–6, moderate; and scores of 7–10, severe (10,11).
Treatment plan with LC
Based on the current knowledge on carnitine use, its
metabolism, and treatment of deficiency, a daily oral dose of 1.5 g
LC divided into in three single doses of 0.5 g was administered for
8 weeks, preferably during or following meals.
Study design
The enrolled patients were evaluated for fatigue at
the baseline and after 2 weeks of LC supplementation. Following
baseline evaluation, the patients started treatment with 1.5 g of
oral LC three times daily for 8 weeks. During treatment, the
patients were monitored every 2 weeks with physical examination,
medical history and blood chemistry tests. The patients were
stratified into two categories according to chemotherapy, namely
the adjuvant chemotherapy (Adj.) and unresectable or recurrence
(Rec.) groups.
Statistical analysis
The patient records were entered into our database
and completed with information obtained from a retrospective review
of hospital and physician records. Statistical analysis was
performed using the JMP 13.0.0 software package (SAS Institute,
Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
Results
Patient demographics and tumor
characteristics
The mean patient age was 67.5 years [standard
deviation (SD) ±7.3 years]. Of the 11 patients, 4 were men and 7
were women. The location of the cancer was colorectal in 8
patients, pancreatic in 2 patients, and in the biliary tract in 1
patient. A total of 6 cases received adjuvant chemotherapy and 5
cases received treatment for recurrent or metastatic cancer. The
chemotherapy regimens for colorectal cancer included FOLFIRI +
bevacizumab for 3 patients, FOLFOX for 2 patients, FOLFOX +
bevacizumab for 1 patient, FOLFIRI + panitumumab for 1 patient and
TAS-102 for 1 patient. The chemotherapy regimens used for
pancreatic cancer were S-1 and gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel. The
chemotherapy administered for biliary tract cancer was gemcitabine
+ cisplatin (Table I).
 | Table I.Characteristics of the patients
enrolled in the present study. |
Table I.
Characteristics of the patients
enrolled in the present study.
| Case no. | Age, years | Sex | Primary | Regimen | Adj. or Rec. |
|---|
| 1 | 73 | M | Bile duct | GEM + CDDP | Adj. |
| 2 | 68 | M | Rectum | FOLFOX | Adj. |
| 3 | 69 | F | Pancreas | TS-1 | Adj. |
| 4 | 52 | F | Colon | FOLFOX | Adj. |
| 5 | 65 | F | Colon | FOLFIRI + Bmab | Adj. |
| 6 | 74 | F | Rectum | FOLFIRI + Bmab | Adj. |
| 7 | 68 | F | Pancreas | GEM +
nab-paclitaxel | Rec. (bone) |
| 8 | 74 | F | Colon | FOLFOX + Bmab | Rec. (liver) |
| 9 | 64 | M | Colon | FOLFIRI + Pmab | Rec.
(peritoneal) |
| 10 | 77 | F | Colon | FOLFIRI + Bmab | Rec. (lung,
peritoneal) |
| 11 | 59 | M | Rectum | TAS-102 | Rec. (liver,
peritoneal) |
Assessment of fatigue
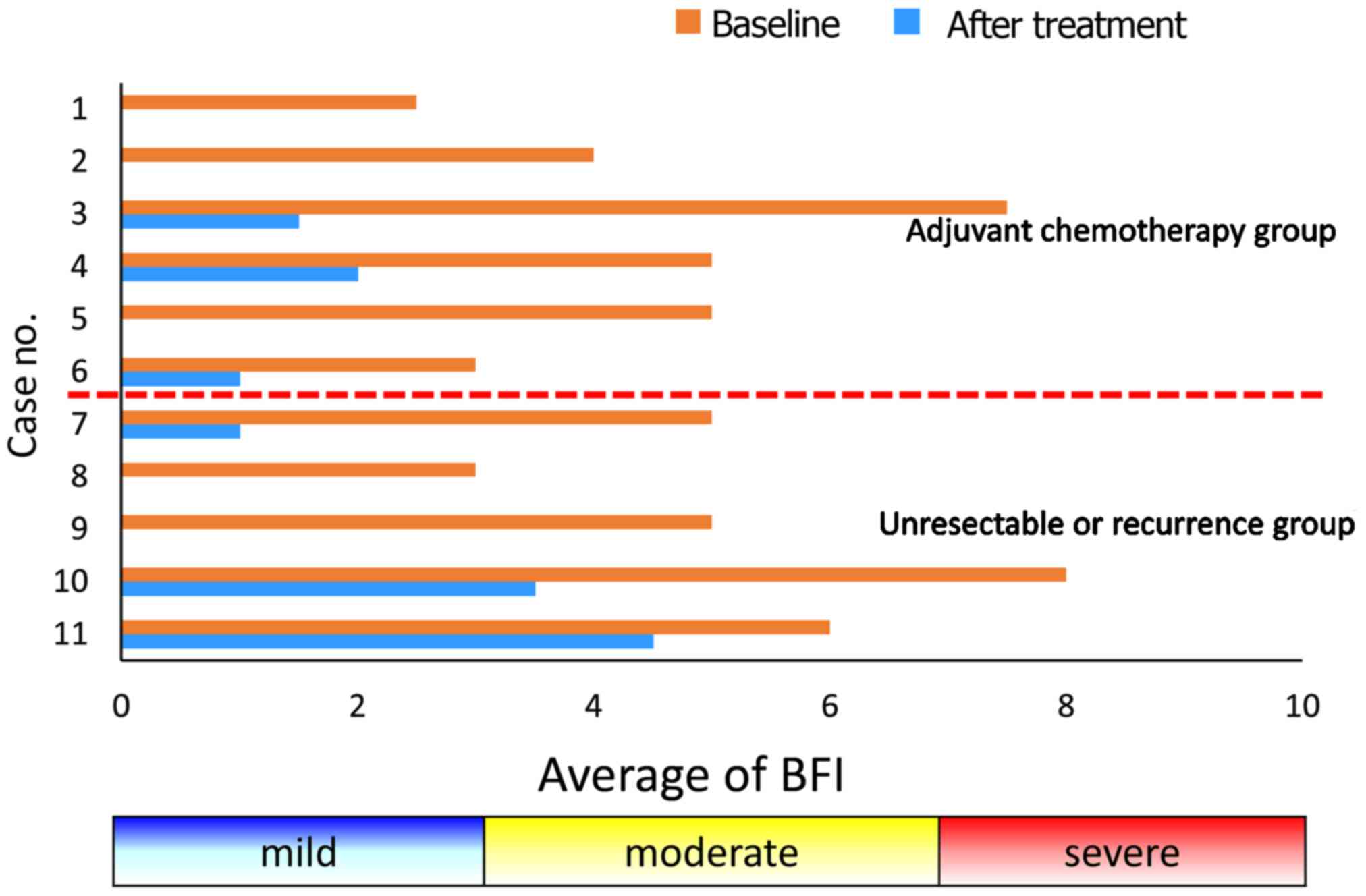
The BFI scores for all patients in the present study
are presented in Fig. 1. In all the
patients, the pre-treatment scores were significantly higher
compared with the post-treatment scores (mean pre-BFI: 4.9±1.8 vs.
post-BFI: 1.2±1.6; P<0.0001). The mean ± SD changes in the BFI
scores were −3.8±0.81 and −3.6±1.2 in the Adj. and Rec. groups,
respectively. The difference in the mean change in the scores
between the groups was −0.2 (not statistically significant). The
mean ± SD BFI scores after treatment were 0.75±0.88 in the Adj. and
1.8±2.1 in the Rec. group.
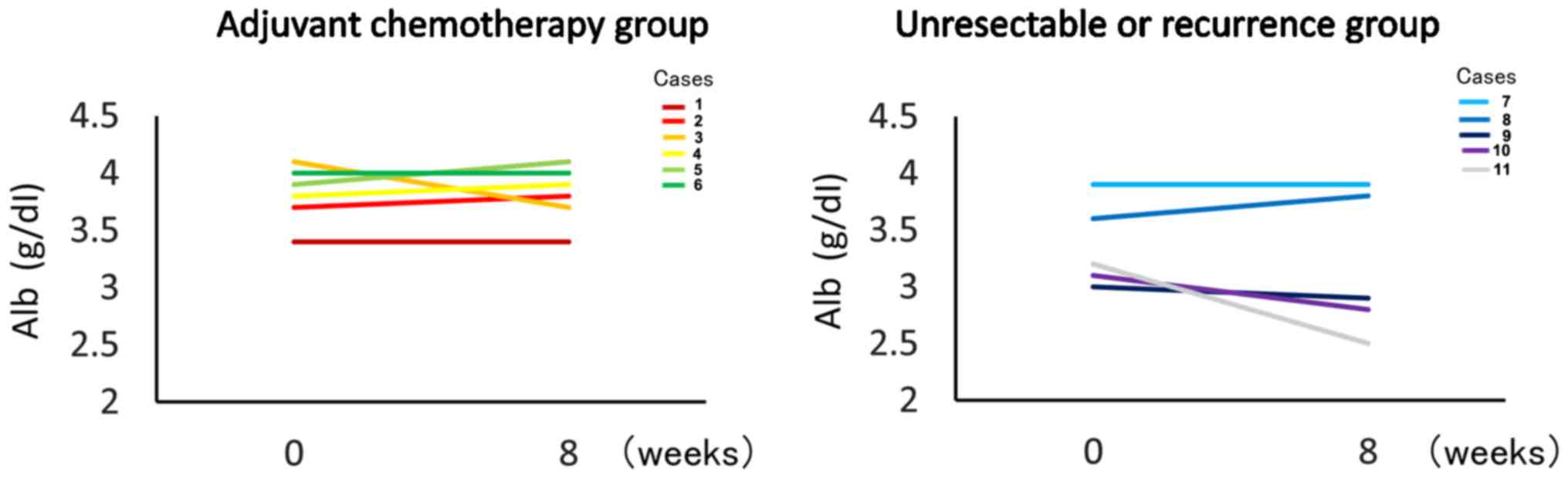
Nutritional assessment
The mean ± SD changes in the levels of albumin were
0.017±0.14 mg/dl in the Adj. group and −0.20±0.14 mg/dl in the Rec.
group. The difference was not statistically significant in either
group (Fig. 2).
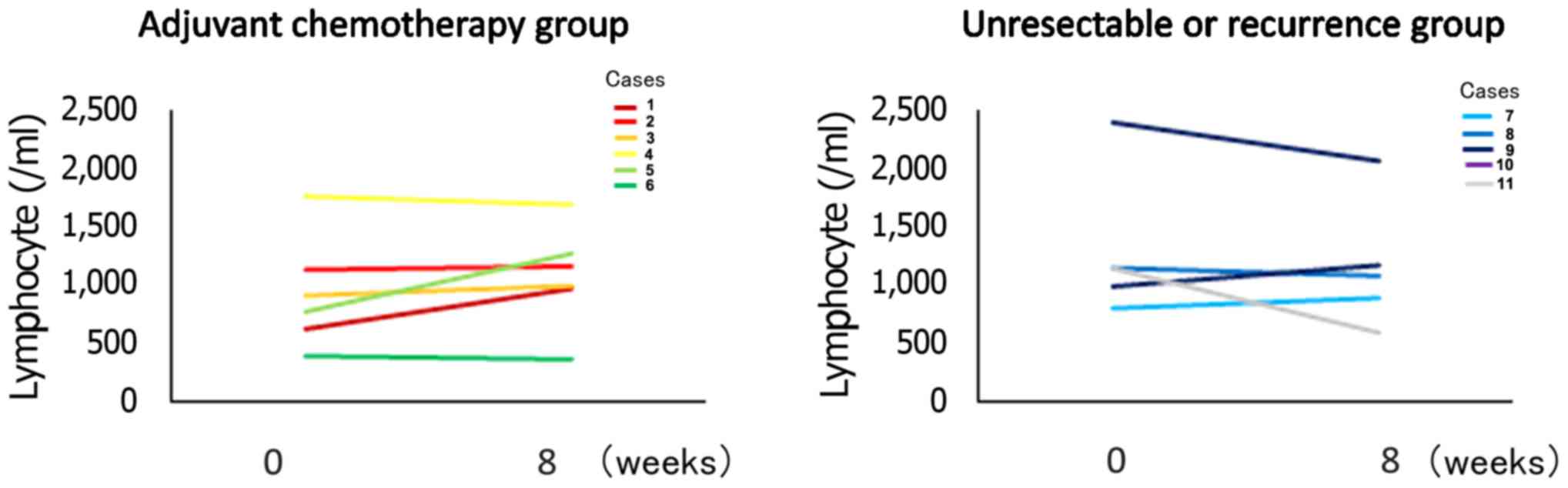
The mean ± SD lymphocyte counts in the Adj. group
were 939.7±478.5/µl pre-treatment and 1,085.5±478.5/µl
post-treatment. A total of 4 patients exhibited increased
lymphocyte counts after treatment. The mean ± SD lymphocyte counts
in the Rec. group were 1,291.6±637.7/µl pre-treatment and
1,169.2±554.0/µl post-treatment. The difference was not
statistically significant in either group (Fig. 3).
Safety
According to the National Cancer Network-Common
Terminology Criteria, no adverse events potentially associated with
LC were reported for any patient during this study. Chemotherapy
was well-tolerated by all patients during this study.
Discussion
In the present study, hat LC supplementation reduced
fatigue in all cancer patients. There was no significant difference
in the mean change of BFI scores between the Adj. and Rec. groups.
Based on these data, it may be suggested that chemotherapy-induced
damage of the carnitine system and secondary deficiency of this
molecule may cause fatigue due to impaired energy metabolism
(12,13). Thus, restoration of the carnitine
pool may alleviate the fatigue of cancer patients (14). In the Rec. group, fatigue was still
marked compared with the Adj. group after LC supplementation, as
cytokine production from cancer cells and pro-inflammatory
cytokines from cancer patients may also contribute to the fatigue
(15). To the best of our knowledge,
this is the first study to investigate therapeutic intervention
with carnitine in the Adj. and Rec. patient groups. The results
were encouraging, as LC supplementation reduced
chemotherapy-induced fatigue in all patients who received this
treatment.
Second, it was demonstrated that LC supplementation
improved the nutritional status of the patients. In addition, all
Adj. group patients continued chemotherapy sequentially, and did
not require a reduction in the dose of the chemotherapy regimen. LC
supplementation also leads to an improved nitrogen balance, either
due to increased protein synthesis or abrogation of the
inflammatory processes under pathological conditions, prevents
oxidative stress, and improves mitochondrial function (16).
The beneficial effect of LC supplementation on
mechanisms involved in skeletal muscle loss under pathological
conditions may explain its anti-catabolic effects and/or the
improvement of fatigue-related parameters following LC
supplementation in patients with chronic kidney disease (17), cancer (5,9,18,19), and
hepatitis C and hepatic encephalopathy (20).
LC supplementation improved general fatigue in all
cancer patients during chemotherapy. LC may improve the ability of
cancer patients to cope with chemotherapy by reducing general
fatigue and improving the nutritional status. The limitations of
the present study included its design (single-institution,
non-randomized study), the limited number of included patients, and
the fact that carnitine levels in the plasma were not measured.
Despite these limitations, our findings may provide evidence to
support the efficacy of LC supplementation in controlling CRF.
However, further research is required to confirm our findings. A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial is currently
being planned to demonstrate the efficacy of LC supplementation,
based on previously published LC supplementation articles (18,21).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank assistant secretary
Ms. Sachiko Saito for her support.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Mock V, Atkinson A, Barsevick AM, Berger
AM, Cimprich B, Eisenberger MA, Hinds P, Kaldor P, Otis-Green SA
and Piper BF: Cancer-related fatigue. Clinical practice guidelines
in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 5:1054–1078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Glaspy J: Anemia and fatigue in cancer
patients. Cancer. 92 Suppl 6:S1719–S1724. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Foster DW: The role of the carnitine
system in human metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1033:1–16. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cruciani RA, Dvorkin E, Homel P, Culliney
B, Malamud S, Shaiova L, Fleishman S, Lapin J, Klein E, Lesage P,
et al: L-carnitine supplementation for the treatment of fatigue and
depressed mood in cancer patients with carnitine deficiency: A
preliminary analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1033:168–176. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Graziano F, Bisonni R, Catalano V, Silva
R, Rovidati S, Mencarini E, Ferraro B, Canestrari F, Baldelli AM,
De Gaetano A, et al: Potential role of levocarnitine
supplementation for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced fatigue
in non-anaemic cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 86:1854–1857. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Waldner R, Laschan C, Lohninger A, Gessner
M, Tüchler H, Huemer M, Spiegel W and Karlic H: Effects of
doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy and a combination with
L-carnitine on oxidative metabolism in patients with non-Hodgkin
lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 132:121–128. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bianchi G, Vitali G, Caraceni A, Ravaglia
S, Capri G, Cundari S, Zanna C and Gianni L: Symptomatic and
neurophysiological responses of paclitaxel- or cisplatin-induced
neuropathy to oral acetyl-L-carnitine. Eur J Cancer. 41:1746–1750.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hockenberry MJ, Hooke MC, Gregurich M and
McCarthy K: Carnitine plasma levels and fatigue in
children/adolescents receiving cisplatin, ifosfamide, or
doxorubicin. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 31:664–669. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gramignano G, Lusso MR, Madeddu C, Massa
E, Serpe R, Deiana L, Lamonica G, Dessì M, Spiga C, Astara G, et
al: Efficacy of l-carnitine administration on fatigue, nutritional
status, oxidative stress and related quality of life in 12 advanced
cancer patients undergoing anticancer therapy. Nutrition.
22:136–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mendoza TR, Wang XS, Cleeland CS,
Morrissey M, Johnson BA, Wendt JK and Huber SL: The rapid
assessment of fatigue severity in cancer patients: Use of the brief
fatigue inventory. Cancer. 85:1186–1196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okuyama T, Wang XS, Akechi T, Mendoza TR,
Hosaka T, Cleeland CS and Uchitomi Y: Validation study of the
Japanese version of the brief fatigue inventory. J Pain Symptom
Manage. 25:106–117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dodson WL, Sachan DS, Krauss S and Hanna
W: Alterations of serum and urinary carnitine profiles in cancer
patients: Hypothesis of possible significance. J Am Coll Nutr.
8:133–142. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peluso G, Nicolai R, Reda E, Benatti P,
Barbarisi A and Calvani M: Cancer and anticancer therapy-induced
modifications on metabolism mediated by carnitine system. J Cell
Physiol. 182:339–350. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brass EP, Adler S, Sietsema KE, Hiatt WR,
Orlando AM and Amato A; CHIEF Investigators, : Intravenous
L-carnitine increases plasma carnitine, reduces fatigue and may
preserve exercise capacity in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney
Dis. 37:1018–1028. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McNeil C: Cancer fatigue: One drug fails
but more are in the pipeline. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:892–893. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ringseis R, Keller J and Eder K:
Mechanisms underlying the anti-wasting effect of L-carnitine
supplementation under pathologic conditions: Evidence from
experimental and clinical studies. Eur J Nutr. 52:1421–1442. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fatouros IG, Douroudos I, Panagoutsos S,
Pasadakis P, Nikolaidis MG, Chatzinikolaou A, Sovatzidis A,
Michailidis Y, Jamurtas AZ, Mandalidis D, et al: Effects of
L-carnitine on oxidative stress responses in patients with renal
disease. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 42:1809–1818. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cruciani RA, Dvorkin E, Homel P, Culliney
B, Malamud S, Lapin J, Portenoy RK and Esteban-Cruciani N:
L-carnitine supplementation in patients with advanced cancer and
carnitine deficiency: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J
Pain Symptom Manage. 37:622–631. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwase S, Kawaguchi T, Yotsumoto D, Doi T,
Miyara K, Odagiri H, Kitamura K, Ariyoshi K, Miyaji T, Ishiki H, et
al: Efficacy and safety of an amino acid jelly containing coenzyme
Q10 and L-carnitine in controlling fatigue in breast cancer
patients receiving chemotherapy: A multi-institutional, randomized,
exploratory trial (JORTC-CAM01). Support Care Cancer. 24:637–646.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Giordano M,
Pennisi G, Bella R, Rampello L, Malaguarnera M, Li Volti G and
Galvano F: Oral acetyl-L-carnitine therapy reduces fatigue in overt
hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:799–808. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cruciani RA, Zhang JJ, Manola J, Cella D,
Ansari B and Fisch MJ: L-carnitine supplementation for the
management of fatigue in patients with cancer: An eastern
cooperative oncology group phase III, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 30:3864–3869. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|