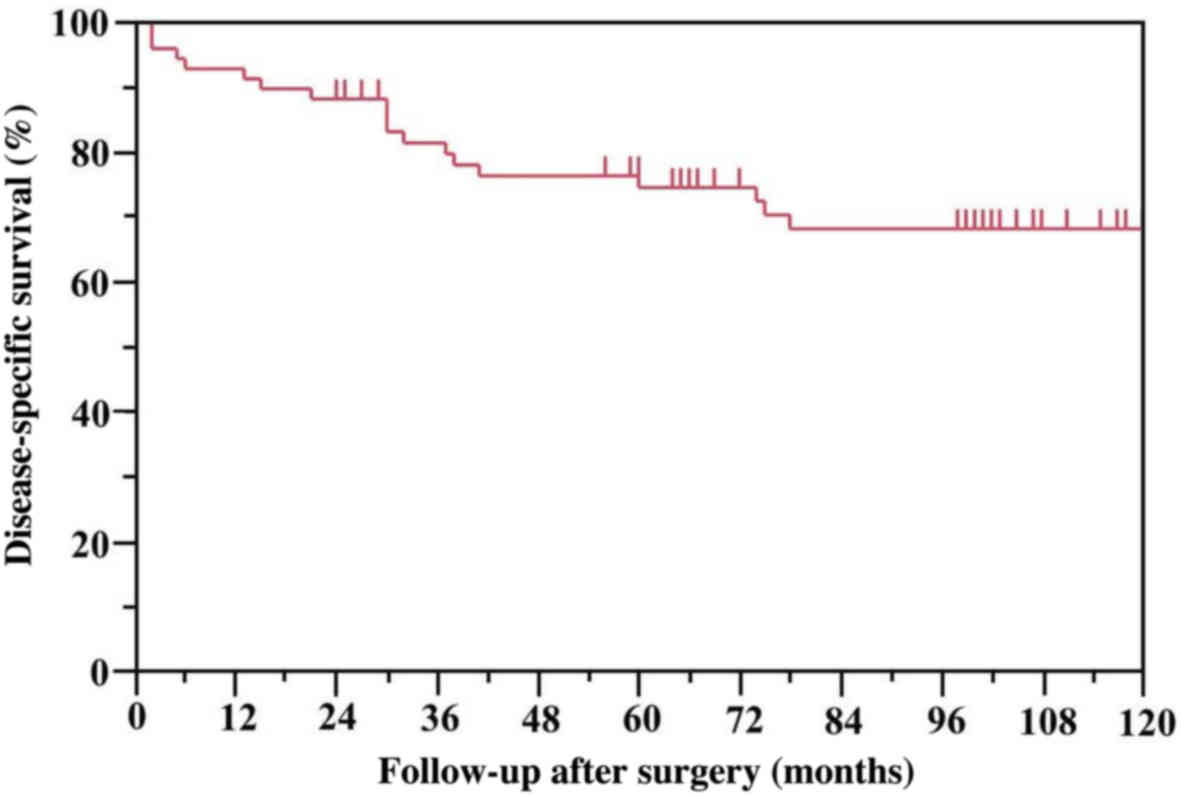
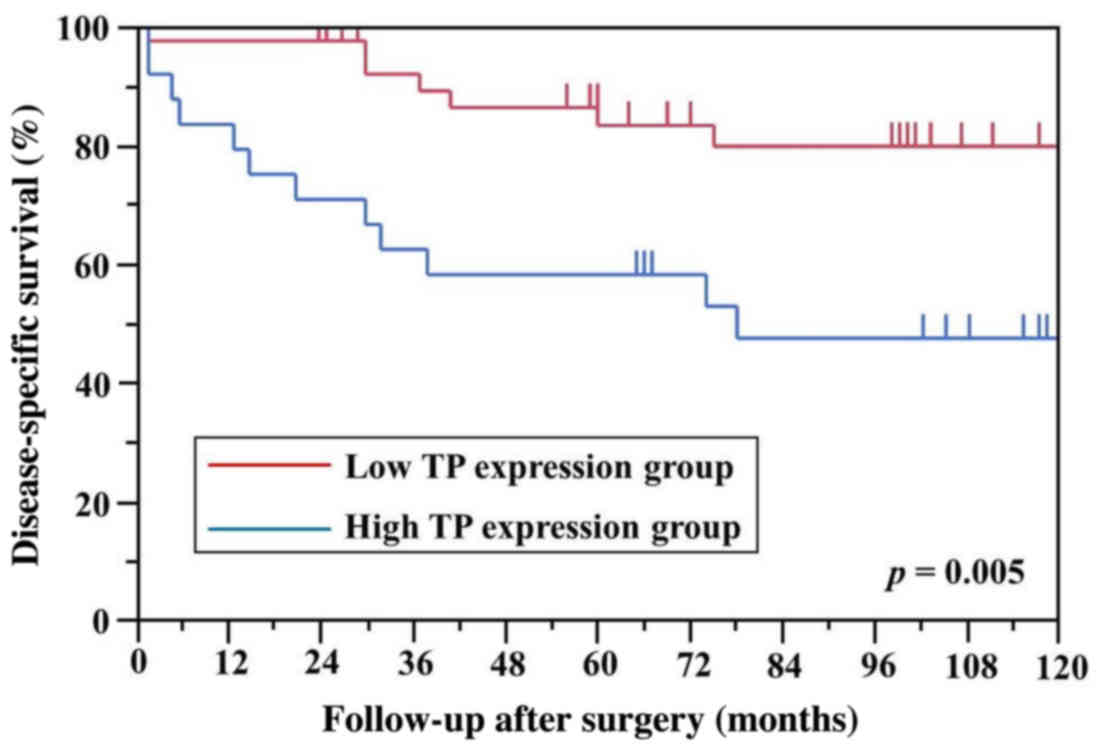
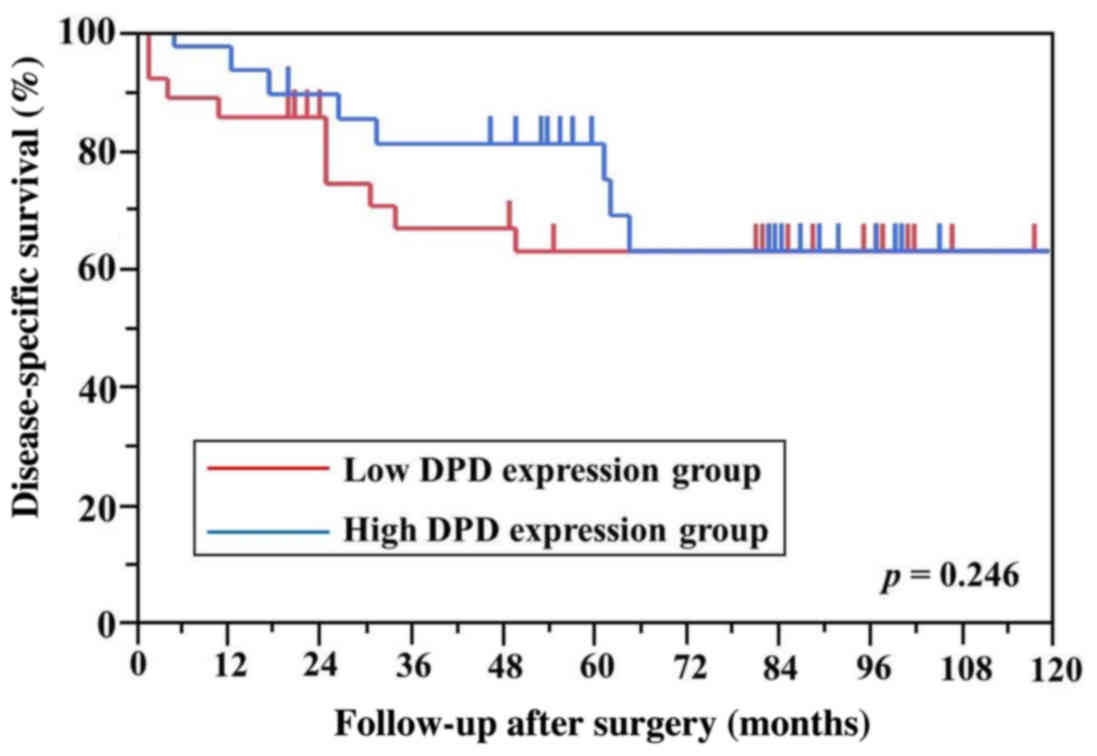
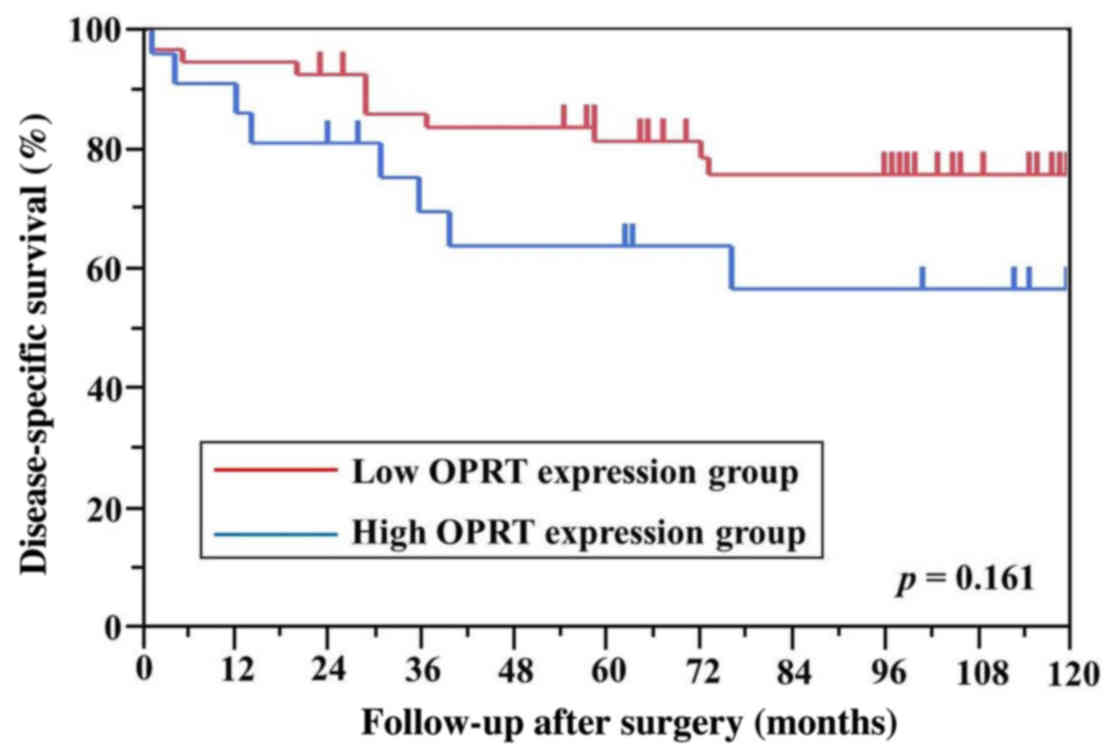
|
1
|
Committee for Scientific Affairs, The
Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery, . Masuda M, Kuwano H,
Okumura M, Arai H, Endo S, Doki Y, Kobayashi J, Motomura N, et al:
Thoracic and cardiovascular surgery in Japan during 2013: Annual
report by The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 63:670–701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sawabata N, Miyaoka E, Asamura H,
Nakanishi Y, Eguchi K, Mori M, Nomori H, Fujii Y, Okumura M and
Yokoi K; Japanese Joint Committee for Lung Cancer Registration, :
Japanese lung cancer registry study of 11,663 surgical cases in
2004: Demographic and prognosis changes over decade. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:1229–1235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brabender J, Park J, Metzger R, Schneider
PM, Lord RV, Hölscher AH, Danenberg KD and Danenberg PV: Prognostic
significance of cyclooxygenase 2 mRNA expression in non-small cell
lung cancer. Ann Surg. 235:440–443. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grimminger P, Ling FC, Neiss S, Vallböhmer
D, Lurje G, Schneider PM, Hölscher AH, Metzger R and Brabender J:
The role of the homeobox genes BFT and CDX2 in the pathogenesis of
non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 29:1281–1286.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Farrugia DC, Ford HE, Cunningham D,
Danenberg KD, Danenberg PV, Brabender J, McVicar AD, Aherne GW,
Hardcastle A, McCarthy K and Jackman AL: Thymidylate synthase
expression in advanced colorectal cancer predicts for response to
raltitrexed. Clin Cancer Res. 9:792–801. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lenz HJ, Leichman CG, Danenberg KD,
Danenberg PV, Groshen S, Cohen H, Laine L, Crookes P, Silberman H,
Baranda J, et al: Thymidylate synthase mRNA level in adenocarcinoma
of the stomach: A predictor for primary tumor response and overall
survival. J Clin Oncol. 14:176–182. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyoshi Y, Uemura H, Ishiguro H, Kitamura
H, Nomura N, Danenberg PV and Kubota Y: Expression of thymidylate
synthase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, thymidine phosphorylase,
and orotate phosphoribosyl transferase in prostate cancer. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 8:260–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Uchida K, Danenberg PV, Danenberg KD and
Grem JL: Thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase,
ERCC1, and thymidine phosphorylase gene expression in primary and
metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma tissue in patients
treated on a phase I trial of oxaliplatin and capecitabine. BMC
Cancer. 8:3862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wada H, Hitomi S and Teramatsu T: Adjuvant
chemotherapy after complete resection in non-small-cell lung
cancer. West Japan Study Group for Lung Cancer Surgery. J Clin
Oncol. 14:1048–1054. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kato H, Ichinose Y, Ohta M, Hata E,
Tsubota N, Tada H, Watanabe Y, Wada H, Tsuboi M, Hamajima N, et al:
A randomized trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with uracil-tegafur for
adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 350:1713–1721. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
Ch: International Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumours. 7th. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
12
|
Horikoshi T, Danenberg K, Volkenandt M,
Stadlbauer T and Danenberg PV: Quantitative measurement of relative
gene expression in human tumors. Methods Mol Biol. 15:177–188.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lord RV, Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Peters
JH, DeMeester TR, Park JM, Johansson J, Skinner KA, Chandrasoma P,
DeMeester SR, et al: Telomerase reverse transcriptase expression is
increased early in the Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, carcinoma
sequence. Gastrointest Surg. 4:135–142. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Matsubara J, Nishina T, Yamada Y, Moriwaki
T, Shimoda T, Kajiwara T, Nakajima TE, Kato K, Hamaguchi T, Shimada
Y, et al: Impacts of excision repair cross-complementing gene 1
(ERCC1), dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, and epidermal growth
factor receptor on the outcomes of patients with advanced gastric
cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:832–839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eguchi K, Oyama T, Tajima A, Abiko T,
Sawafuji M, Horio H, Hashizume T, Matsutani N, Kato R, Nakayama M,
et al: Intratumoral gene expression of 5-fluorouracil
pharmacokinetics-related enzymes in stage I and II non-small cell
lung cancer patients treated with uracil-tegafur after surgery: A
prospective multi-institutional study in Japan. Lung Cancer.
87:53–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mochinaga K, Tsuchiya T, Nagasaki T, Arai
J, Tominaga T, Yamasaki N, Matsumoto K, Miyazaki T, Nanashima A,
Hayashi T, et al: High expression of dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with mutations
in epidermal growth factor receptor: Implications for the treatment
of NSCLC using 5-fluorouracil. Clin Lung Cancer. 15:136–140.e4.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tominaga T, Tsuchiya T, Mochinaga K, Arai
J, Yamasaki N, Matsumoto K, Miyazaki T, Nagasaki T, Nanashima A,
Tsukamoto K and Nagayasu T: Epidermal growth factor signals
regulate dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression in EGFR-mutated
non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:3542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizutani Y, Wada H, Fukushima M, Yoshida
O, Nakanishi H, Li YN and Miki T: Prognostic significance of
orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity in bladder carcinoma.
Cancer. 100:723–731. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mackintosh JA, Marshall HM, Yang IA,
Bowman RV and Fong KM: A retrospective study of volume doubling
time in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.
Respirology. 19:755–762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SW, Chen TJ, Lin LC, Li CF, Chen LT,
Hsing CH, Hsu HP, Tsai CJ, Huang HY and Shiue YL: Overexpression of
thymidylate synthetase confers an independent prognostic indicator
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 95:83–90. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shintani Y, Ohta M, Hirabayashi H, Tanaka
H, Iuchi K, Nakagawa K, Maeda H, Kido T, Miyoshi S and Matsuda H:
Thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase mRNA
levels in tumor tissues and the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 45:189–196.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakano J, Huang C, Liu D, Masuya D,
Nakashima T, Yokomise H, Ueno M, Wada H and Fukushima M:
Evaluations of biomarkers associated with 5-FU sensitivity for
non-small-cell lung cancer patients postoperatively treated with
UFT. Br J Cancer. 95:607–615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Basaki Y, Chikahisa L, Aoyagi K, Miyadera
K, Yonekura K, Hashimoto A, Okabe S, Wierzba K and Yamada Y:
Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and 5-fluorouracil, metabolites of UFT,
inhibit the angiogenesis induced by vascular endothelial growth
factor. Angiogenesis. 4:163–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishihama H, Chida M, Araki O, Karube Y,
Seki N, Tamura M, Umezu H, Honma K, Masawa N and Miyoshi S:
Comparison of 5-fluorouracil-related gene expression levels between
adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas of the lung. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 39:33–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Che J, Pan L, Yang X, Liu Z, Huang L, Wen
C, Lin A and Liu H: Thymidine phosphorylase expression and
prognosis in colorectal cancer treated with 5-fluorouracil-based
chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. 7:943–952.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elamin YY, Rafee S, Osman N, Byrne O KJ
and Gately K: Thymidine phosphorylase in cancer; enemy or friend?
Cancer Microenviron. 1:33–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Metzger R, Danenberg K, Leichman CG,
Salonga D, Schwartz EL, Wadler S, Lenz HJ, Groshen S, Leichman L
and Danenberg PV: High basal level gene expression of thymidine
phosphorylase (platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor) in
colorectal tumors is associated with nonresponse to 5-fluorouracil.
Clin Cancer Res. 4:2371–2376. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Toi M, Hoshina S, Taniguchi T, Yamamoto Y,
Ishitsuka H and Tominaga T: Expression of platelet-derived
endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human
breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 64:79–82. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amaya H, Tanigawa N, Lu C, Matsumura M,
Shimomatsuya T, Horiuchi T and Muraoka R: Association of vascular
endothelial growth factor expression with tumor angiogenesis,
survival and thymidine phosphorylase/platelet-derived endothelial
cell growth factor expression in human colorectal cancer. Cancer
Lett. 119:227–235. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maeda K, Kang SM, Ogawa M, Onoda N, Sawada
T, Nakata B, Kato Y, Chung YS and Sowa M: Combined analysis of
vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived endothelial
cell growth factor expression in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
74:545–550. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, O'Byrne
KJ, Comley M, Whitehouse RM, Talbot DC, Gatter KC and Harris AL:
Platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor expression
correlates with tumour angiogenesis and prognosis in non-small-cell
lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 75:477–481. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haybittle JL, Blamey RW, Elston CW,
Johnson J, Doyle PJ, Campbell FC, Nicholson RI and Griffiths K: A
prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 45:361–366.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsuji T, Sawai T, Yamashita H, Takeshita
H, Nakagoe T, Shindou H, Fukuoka H, Yoshinaga M, Hidaka S, Yasutake
T, et al: Platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor
expression is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer
patients after curative surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 30:296–302.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsunoda Y, Suzuki K, Tsunoda A, Takimoto M
and Kusano M: Evaluation of 5-fluorouracil related genes in breast
cancer to predict the effect of adjuvant therapy with oral
fluorouracil derivatives. Oncol Rep. 23:771–777. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nishina T, Hyodo I, Miyaike J, Inaba T,
Suzuki S and Shiratori Y: The ratio of thymidine phosphorylase to
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in tumour tissues of patients with
metastatic gastric cancer is predictive of the clinical response to
5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine. Eur J Cancer. 40:1556–1571. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ahlin C, Aaltonen K, Amini RM, Nevanlinna
H, Fjällskog ML and Blomqvist C: Ki67 and cyclin A as prognostic
factors in early breast cancer. What are the optimal cut-off
values? Histopathology. 51:491–498. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kojima H, Shijubo N and Abe S: Thymidine
phosphorylase and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients
with Stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 94:1083–1093. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|