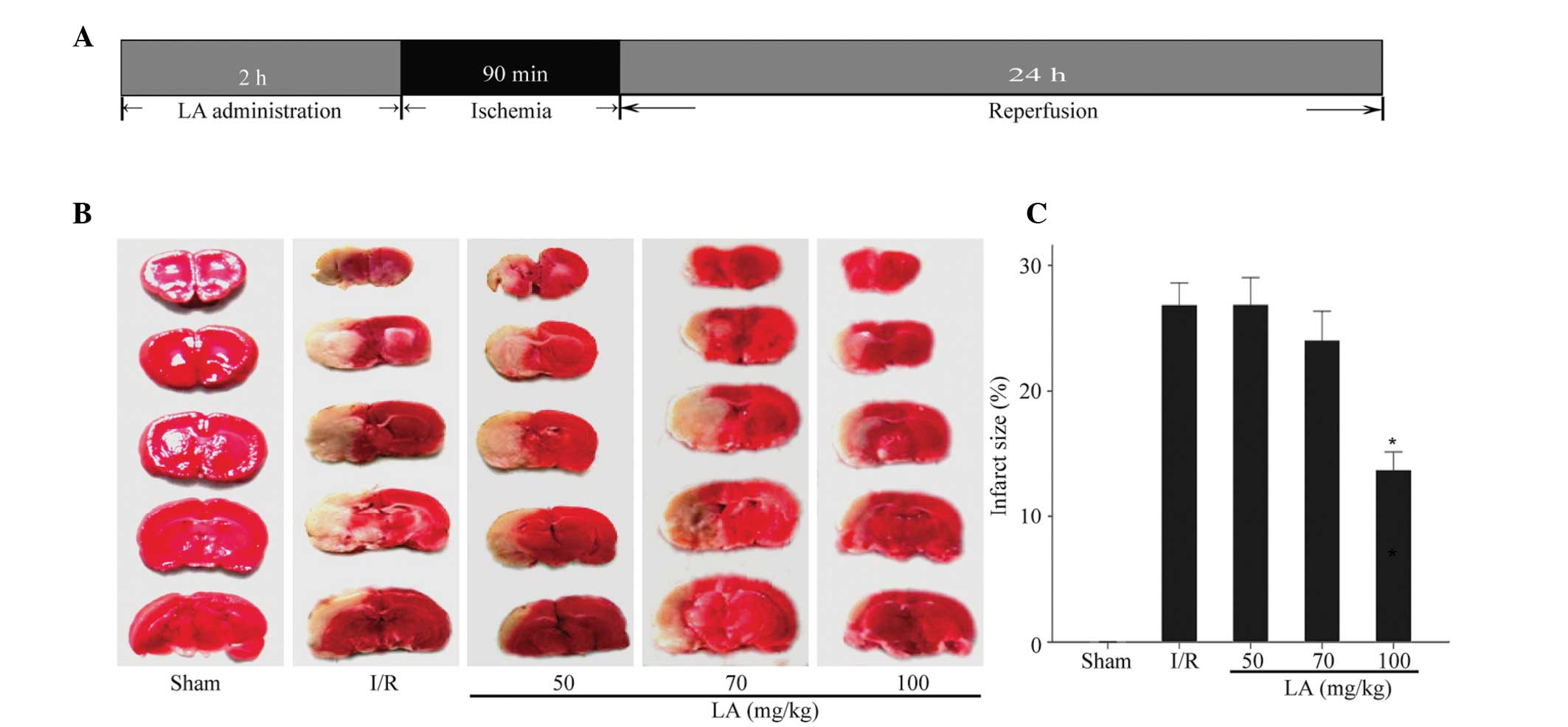
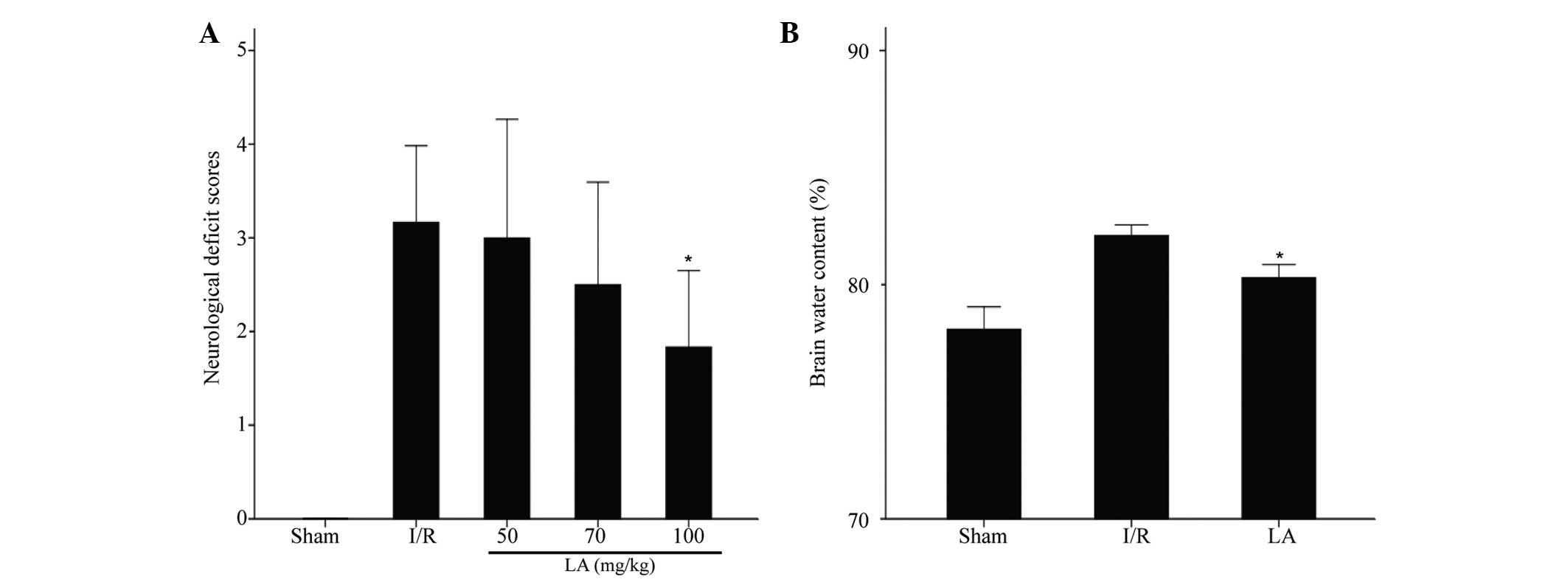
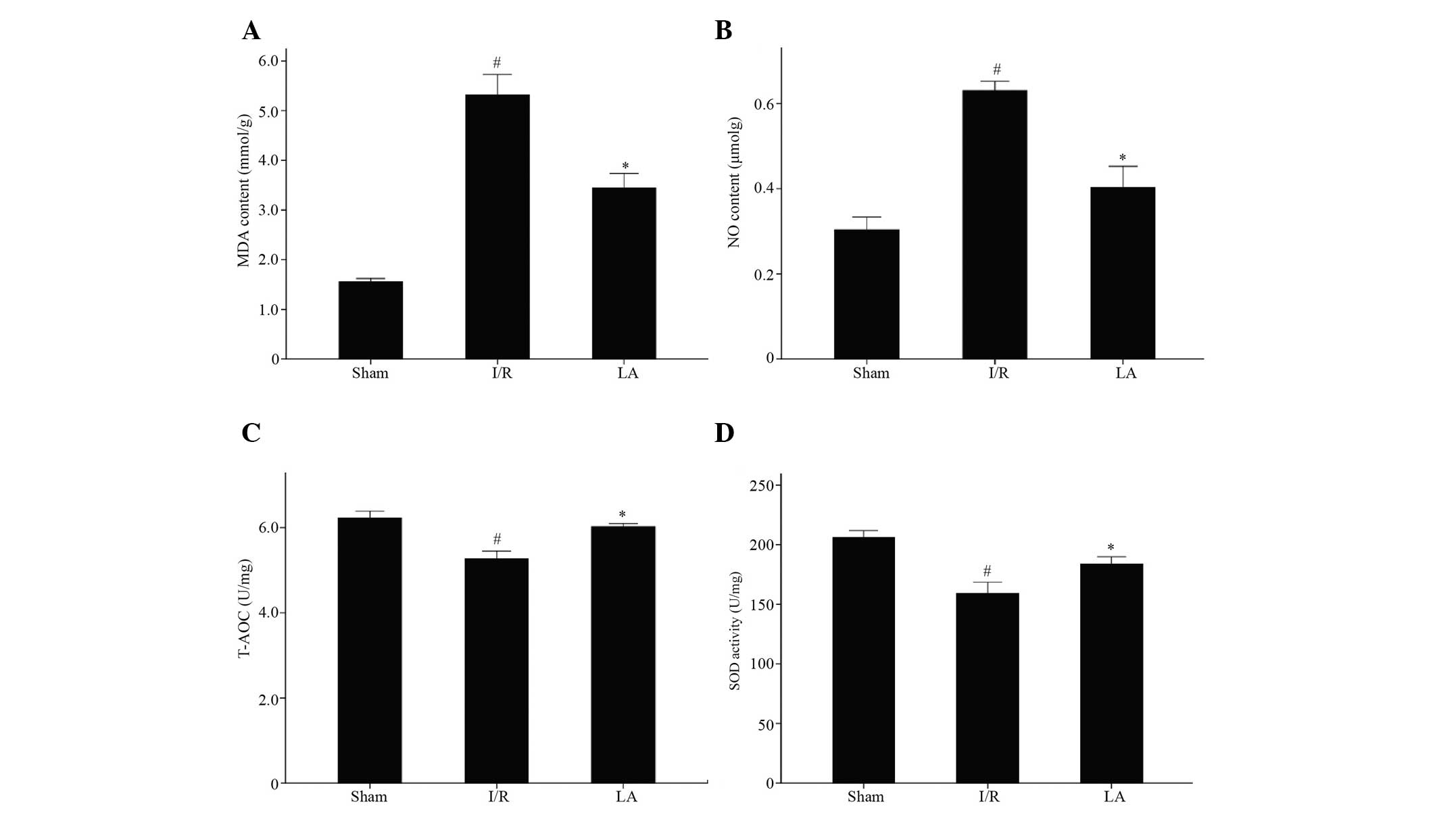
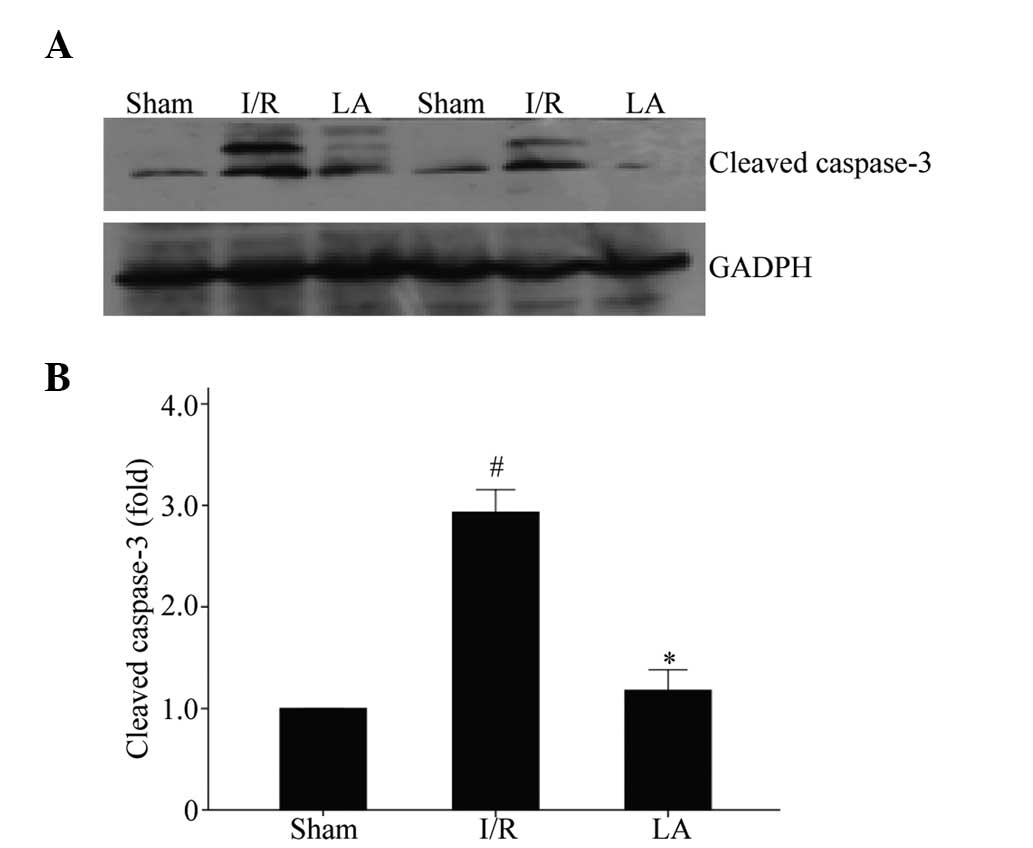
|
1
|
Tu Q, Wang R, Ding B, Zhong W and Cao H:
Protective and antioxidant effect of Danshen polysaccharides on
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Biol Macromol.
60:268–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sahota P and Savitz SI: Investigational
therapies for ischemic stroke: neuroprotection and neurorecovery.
Neurotherapeutics. 8:434–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mattson MP, Duan W, Pedersen WA and
Culmsee C: Neurodegenerative disorders and ischemic brain diseases.
Apoptosis. 6:69–81. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao ZQ: Oxidative stress-elicited
myocardial apoptosis during reperfusion. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
4:159–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perham RN: Swinging arms and swinging
domains in multifunctional enzymes: catalytic machines for
multistep reactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:961–1004. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, Suh JH
and Hagen TM: Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic
diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem.
11:1135–1146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Yu Y, Ji L, Liang X, Zhang T and
Hai CX: Alpha-lipoic acid protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via multiple target effects. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:2750–2757. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mitsui Y, Schmelzer JD, Zollman PJ, Mitsui
M, Tritschler HJ and Low PA: Alpha-lipoic acid provides
neuroprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury of peripheral
nerve. J Neurol Sci. 163:11–16. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ozbal S, Ergur BU, Erbil G, Tekmen I,
Bagrıyanık A and Cavdar Z: The effects of α-lipoic acid against
testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:4892482012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chidlow G, Schmidt KG, Wood JP, Melena J
and Osborne NN: Alpha-lipoic acid protects the retina against
ischemia-reperfusion. Neuropharmacology. 43:1015–1025. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng C, Sun Z, Tong G, et al: α-Lipoic
acid reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in rat
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. PLoS One. 8:e583712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Oh SK, Yun KH, Yoo NJ, et al:
Cardioprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on myocardial
reperfusion injury: suppression of reactive oxygen species
generation and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Korean Circ J. 39:359–366. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie R, Li X, Ling Y, et al: Alpha-lipoic
acid pre- and post-treatments provide protection against in vitro
ischemia-reperfusion injury in cerebral endothelial cells via
Akt/mTOR signaling. Brain Res. 1482:81–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cameron NE, Cotter MA, Horrobin DH and
Tritschler HJ: Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on neurovascular
function in diabetic rats: interaction with essential fatty acids.
Diabetologia. 41:390–399. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolz P and Krieglstein J: Neuroprotective
effects of alpha-lipoic acid and its enantiomers demonstrated in
rodent models of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuropharmacology.
35:369–375. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zuo XL, Wu P and Ji AM: Nylon filament
coated with paraffin for intraluminal permanent middle cerebral
artery occlusion in rats. Neurosci Lett. 519:42–46. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lan R, Xiang J, Wang GH, et al:
Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction protects against blood-brain barrier
disruption and neurological injury induced by cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6297822013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Namura S, Zhu J, Fink K, et al: Activation
and cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental
cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 18:3659–3668. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
D’Amelio M, Cavallucci V and Cecconi F:
Neuronal caspase-3 signaling: not only cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 17:1104–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Clark WM, Rinker LG, Lessov NS, Lowery SL
and Cipolla MJ: Efficacy of antioxidant therapies in transient
focal ischemia in mice. Stroke. 32:1000–1004. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Connell BJ, Saleh M, Khan BV and Saleh TM:
Lipoic acid protects against reperfusion injury in the early stages
of cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1375:128–136. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yabuki Y and Fukunaga K: Oral
administration of glutathione improves memory deficits following
transient brain ischemia by reducing brain oxidative stress.
Neuroscience. 250:394–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou XQ, Zeng XN, Kong H and Sun XL:
Neuroprotective effects of berberine on stroke models in vitro and
in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 447:31–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang PR, Wang JS, Zhang C, Song XF, Tian N
and Kong LY: Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decotion induced protective
autophagy against the injury of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via
MAPK-mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:270–280. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Packer L, Tritschler HJ and Wessel K:
Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid.
Free Radic Biol Med. 22:359–378. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang G, Chan PH, Chen J, et al: Human
copper-zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice are highly
resistant to reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia.
Stroke. 25:165–170. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haylor JL, Harris KP, Nicholson ML, Waller
HL, Huang Q and Yang B: Atorvastatin improving renal ischemia
reperfusion injury via direct inhibition of active caspase-3 in
rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 236:755–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Binder DK and Scharfman HE: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors. 22:123–131. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferrer I, Krupinski J, Goutan E, Marti E,
Ambrosio S and Arenas E: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces
cortical cell death by ischemia after middle cerebral artery
occlusion in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 101:229–238.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Muller HD, Hanumanthiah KM, Diederich K,
Schwab S, Schabitz WR and Sommer C: Brain-derived neurotrophic
factor but not forced arm use improves long-term outcome after
photothrombotic stroke and transiently upregulates binding
densities of excitatory glutamate receptors in the rat brain.
Stroke. 39:1012–1021. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ploughman M, Windle V, MacLellan CL, White
N, Doré JJ and Corbett D: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
contributes to recovery of skilled reaching after focal ischemia in
rats. Stroke. 40:1490–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patapoutian A and Reichardt LF: Trk
receptors: mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
11:272–280. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burgering BM and Coffer PJ: Protein kinase
B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction.
Nature. 376:599–602. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, et al: The
protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the
PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 81:727–736.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels,
decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance
myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 10:301–312.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou L and Miller CA: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling, oxygen sensors and hypoxic induction of
neurogenesis. Neurodegener Dis. 3:50–55. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA
and Sugimoto C: PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene.
22:8983–8998. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu H, Liu X, Wei X, et al: Losartan, an
angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, ameliorates cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt-mediated eNOS
phosphorylation. Brain Res Bull. 89:65–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dong J, Ramachandiran S, Tikoo K, Jia Z,
Lau SS and Monks TJ: EGFR-independent activation of p38 MAPK and
EGFR-dependent activation of ERK1/2 are required for ROS-induced
renal cell death. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 287:F1049–F1058.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|