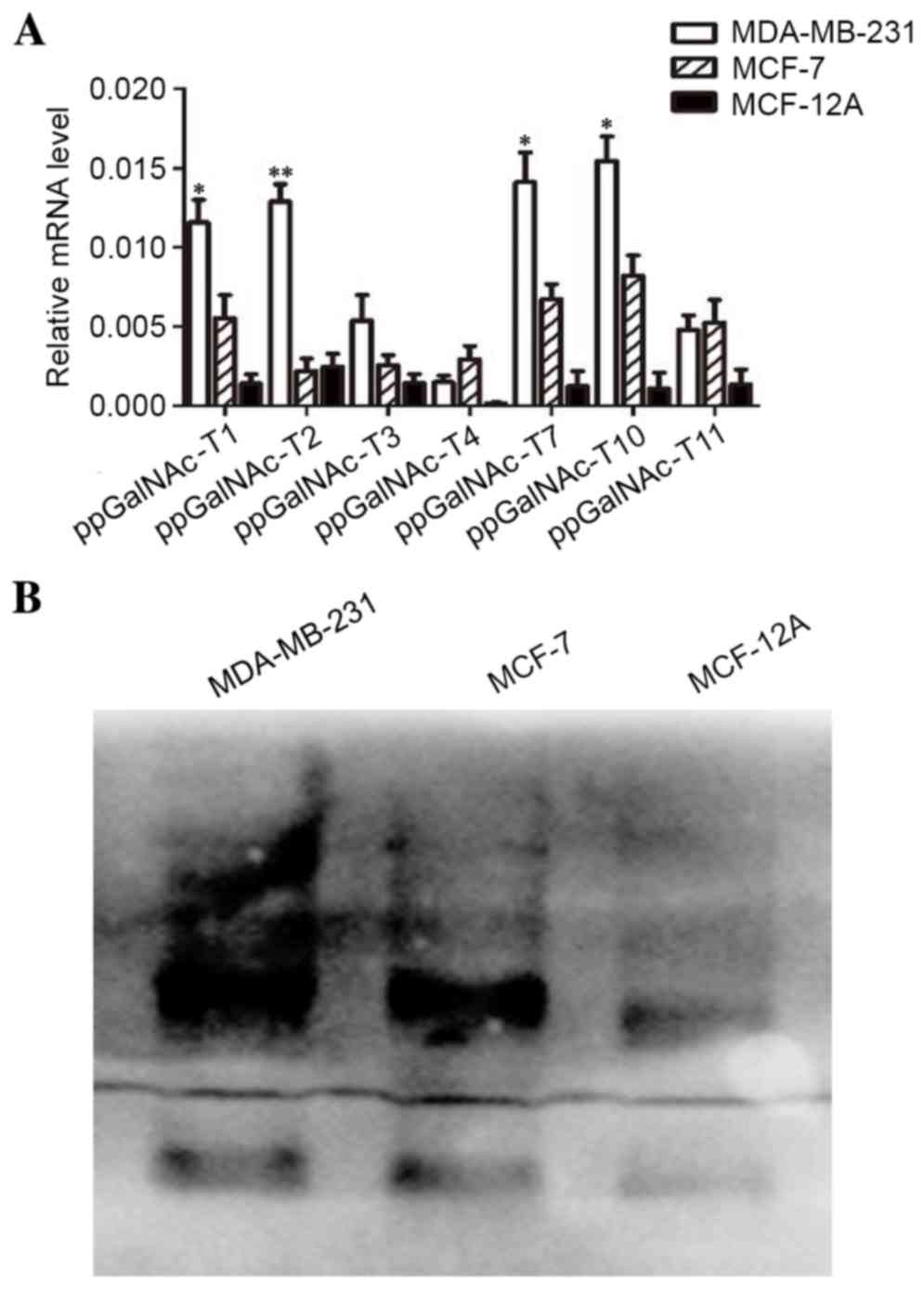
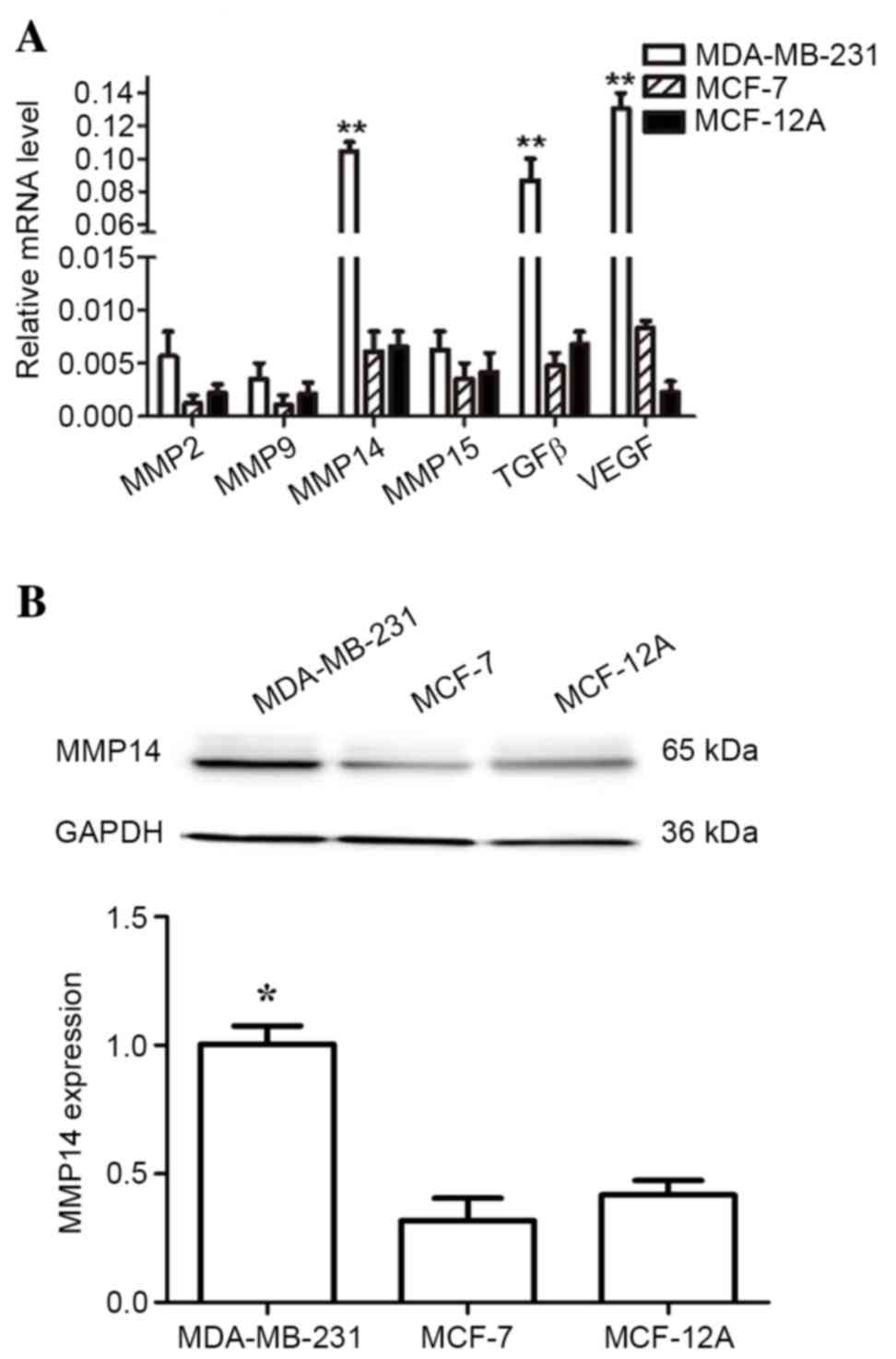
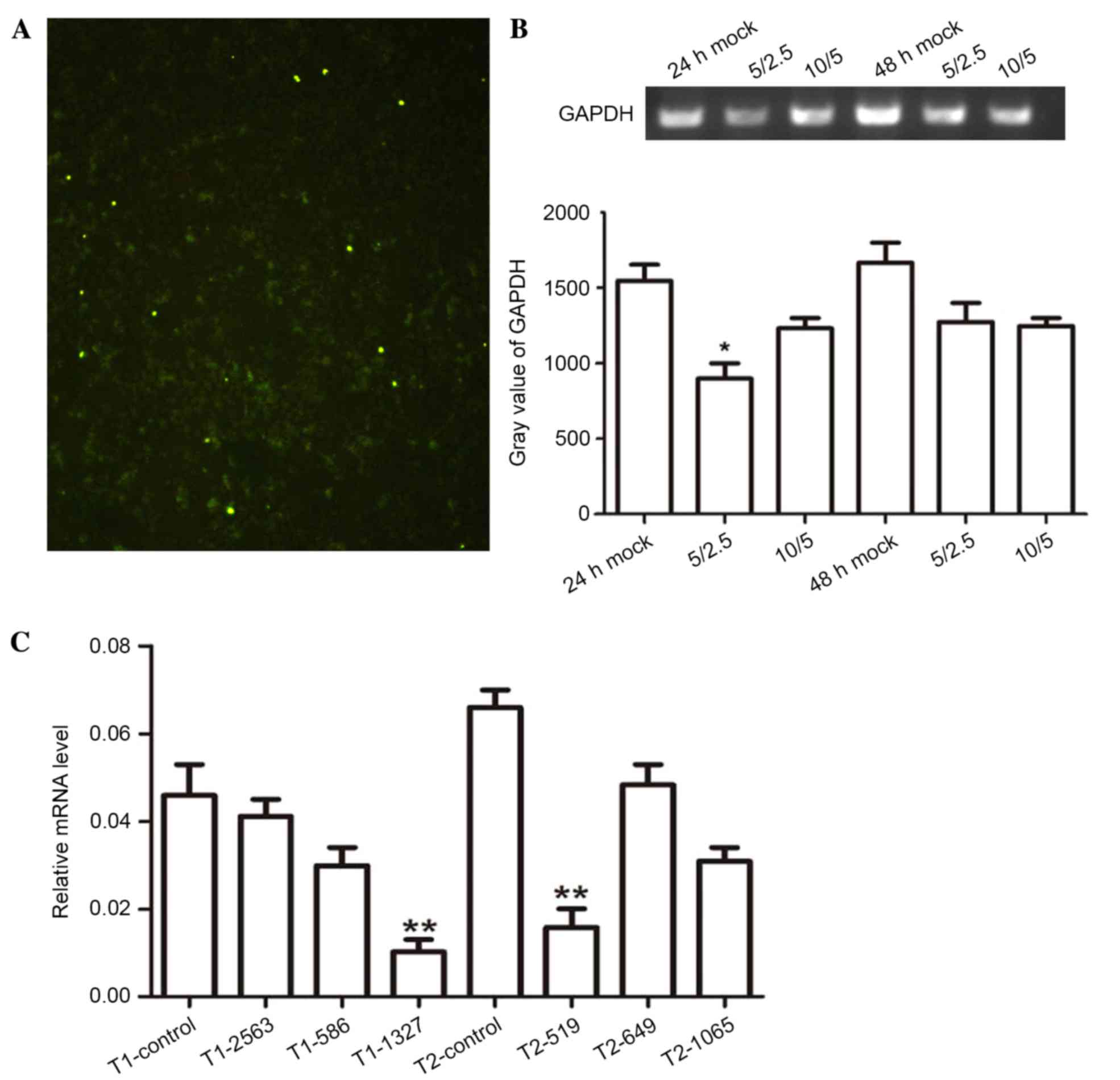
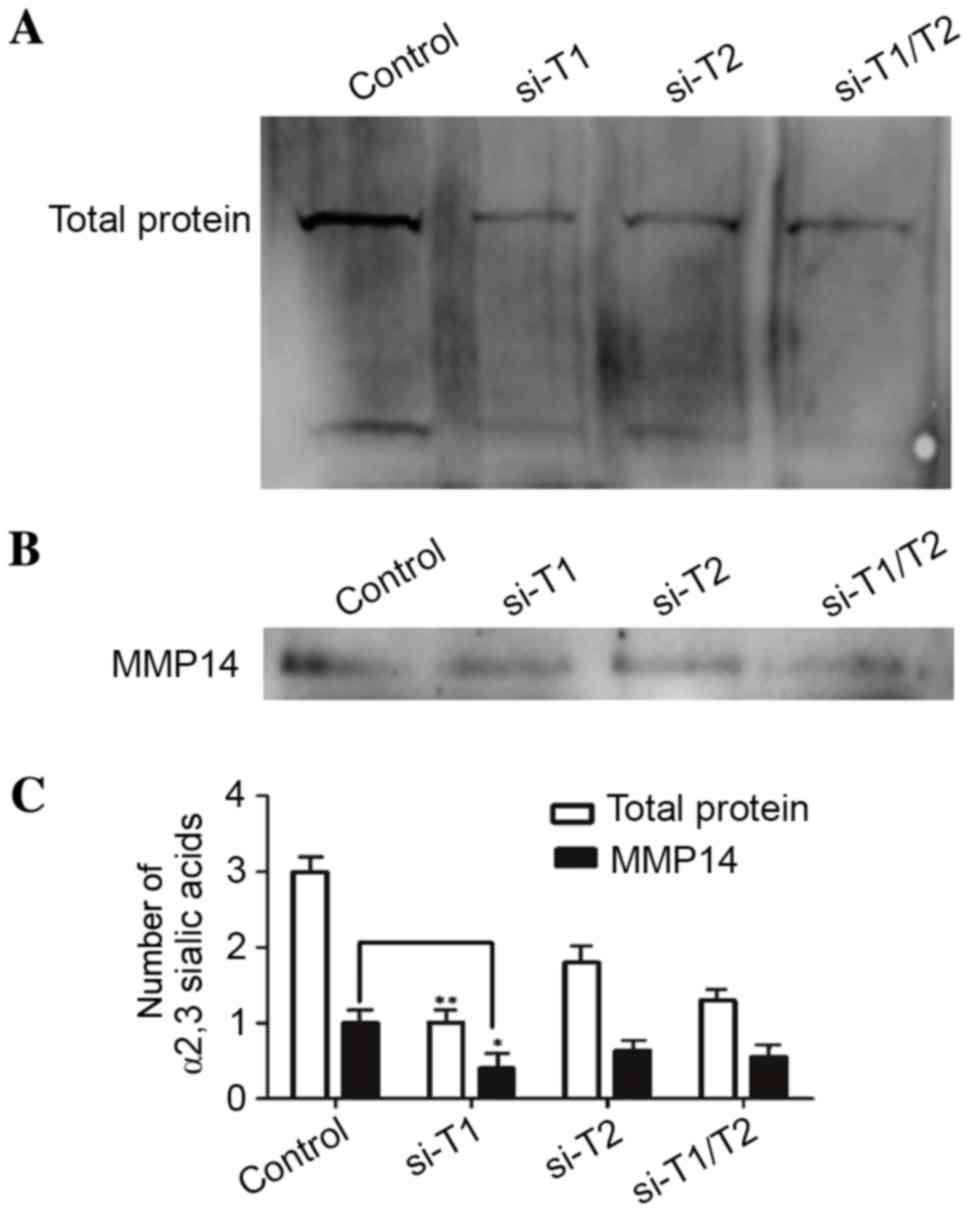
|
1
|
Davies EL: Breast cancer. Medicine.
44:42–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR,
Arnaout A and Winer EP: Sites of distant recurrence and clinical
outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer:
High incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer.
113:2638–2645. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim J, Villadsen R, Sørlie T, Fogh L,
Grønlund SZ, Fridriksdottir AJ, Kuhn I, Rank F, Wielenga VT,
Solvang H, et al: Tumor initiating but differentiated luminal-like
breast cancer cells are highly invasive in the absence of
basal-like activity. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109. pp.
6124–6129. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haddon L and Hugh J: MUC1-mediated
motility in breast cancer: A review highlighting the role of the
MUC1/ICAM-1/Src signaling triad. Clin Exp Metastasis. 32:393–403.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saitoh O, Wang WC, Lotan R and Fukuda M:
Differential glycosylation and cell surface expression of lysosomal
membrane glycoproteins in sublines of a human colon cancer
exhibiting distinct metastatic potentials. J Biol Chem.
267:5700–5711. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Devi KS, Behera B, Mishra D and Maiti TK:
Immune augmentation and Dalton's Lymphoma tumor inhibition by
glucans/glycans isolated from the mycelia and fruit body of
Pleurotus ostreatus. Int Immunopharmacol. 25:207–217. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kalra AV and Campbell RB: Mucin
overexpression limits the effectiveness of 5-FU by reducing
intracellular drug uptake and antineoplastic drug effects in
pancreatic tumours. Eur J Cancer. 45:164–173. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ecker M, Mrsa V, Hagen I, Deutzmann R,
Strahl S and Tanner W: O-mannosylation precedes and potentially
controls the N-glycosylation of a yeast cell wall glycoprotein.
EMBO Rep. 4:628–632. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brockhausen I: Mucin-type O-glycans in
human colon and breast cancer: Glycodynamics and functions. EMBO
Rep. 7:599–604. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Varki A, Kannagi R and Toole BP:
Glycosylation Changes in CancerEssentials of Glycobiology. 2nd.
Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Freeze HH, Stanley P, Bertozzi CR,
Hart GW and Etzler ME: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold
Spring Harbor, NY: 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nakada H: Map 2: Biosynthetic Pathways of
O-Glycans. handbook of glycosyltransferases and related genes.
1667–1671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Büll C, Stoel MA, den Brok MH and Adema
GJ: Sialic acids sweeten a tumor's life. Cancer Res. 74:3199–3204.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schultz MJ, Swindall AF and Bellis SL:
Regulation of the metastatic cell phenotype by sialylated glycans.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:501–518. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin S, Kemmner W, Grigull S and Schlag PM:
Cell surface alpha 2,6 sialylation affects adhesion of breast
carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 276:101–110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sproviero D, Julien S, Burford B,
Taylor-Papadimitriou J and Burchell JM: Cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme
induces the expression of the α-2,3-sialyltransferase-3 (ST3Gal-I)
in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 287:44490–44497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Picco G, Julien S, Brockhausen I, Beatson
R, Antonopoulos A, Haslam S, Mandel U, Dell A, Pinder S,
Taylor-Papadimitriou J and Burchell J: Over-expression of ST3Gal-I
promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Glycobiology. 20:1241–1250. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tagashira M and Toma K: Effect of Peptide
Glycosylation on the Conformation of the Peptide Backbone.
Cheminform. 37:362006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu YI, Munshi HG, Sen R, Snipas SJ,
Salvesen GS, Fridman R and Stack MS: Glycosylation broadens the
substrate profile of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. J
Biol Chem. 279:8278–8289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Remacle AG, Chekanov AV, Golubkov VS,
Savinov AY, Rozanov DV and Strongin AY: O-glycosylation regulates
autolysis of cellular membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase
(MT1-MMP). J Biol Chem. 281:16897–16905. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gómez H, Rojas R, Patel D, Tabak LA, Lluch
JM and Masgrau L: A computational and experimental study of
O-glycosylation. Catalysis by human UDP-GalNAc polypeptide: GalNAc
transferase-T2. Org Biomol Chem. 12:2645–2655. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shaverdashvili K, Wong P, Ma J, Zhang K,
Osman I and Bedogni B: MT1-MMP modulates melanoma cell
dissemination and metastasis through activation of MMP2 and RAC1.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27:287–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Loomans HA and Andl CD: Intertwining of
Activin A and TGFβ Signaling: Dual roles in cancer progression and
cancer cell invasion. Cancers (Basel). 7:70–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hui P, Xu X, Xu L, Hui G, Wu S and Lan Q:
Expression of MMP14 in invasive pituitary adenomas: Relationship to
invasion and angiogenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3556–3567.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M,
Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler
L, et al: Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guiu S, Michiels S, André F, Cortes J,
Denkert C, Di Leo A, Hennessy BT, Sorlie T, Sotiriou C, Turner N,
et al: Molecular subclasses of breast cancer: How do we define
them? The IMPAKT 2012 Working Group Statement. Ann Oncol.
23:2997–3006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triplenegative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bilir B, Kucuk O and Moreno CS: Wnt
signaling blockage inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and
induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Transl
Med. 11:2802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brooks M: Breast cancer screening and
biomarkers. Methods Mol Biol. 472:307–321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paszek MJ, DuFort CC, Rossier O, Bainer R,
Mouw JK, Godula K, Hudak JE, Lakins JN, Wijekoon AC, Cassereau L,
et al: The cancer glycocalyx mechanically primes integrin-mediated
growth and survival. Nature. 511:319–325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Tian T, Kelly G and Hagen T:
UDP-N-Acetyl-Alpha-D Galactosamine: Polypeptide
N-Acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (ppGalNAc-Ts). Handbook of
Glycosyltransferases and Related Genes. 495–505. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ten Hagen KG, Fritz TA and Tabak LA: All
in the family: The UDP-GalNAc: Polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases. Glycobiology. 13:1R–16R. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tian E and Ten Hagen KG: Expression of the
UDP-GalNAc: Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase family is
spatially and temporally regulated during Drosophila development.
Glycobiology. 16:83–95. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Perrine CL, Ganguli A, Wu P, Bertozzi CR,
Fritz TA, Raman J, Tabak LA and Gerken TA: Glycopeptide-preferring
polypeptide GalNAc transferase 10 (ppGalNAc T10), involved in
mucin-type O-glycosylation, has a unique GalNAc-O-Ser/Thr-binding
site in its catalytic domain not found in ppGalNAc T1 or T2. J Biol
Chem. 284:20387–20397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bennett EP, Hassan H, Hollingsworth MA and
Clausen H: A novel human UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine: Polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, GalNAc-T7, with specificity for
partial GalNAc-glycosylated acceptor substrates. FEBS Lett.
460:226–230. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng L, Tachibana K, Zhang Y, Guo JM,
Kahori Tachibana K, Kameyama A, Wang H, Hiruma T, Iwasaki H,
Togayachi A, et al: Characterization of a novel human UDP-GalNAc
transferase, pp-GalNAc-T10. FEBS Lett. 531:115–121. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brooks SA, Carter TM, Bennett EP, Clausen
H and Mandel U: Immunolocalisation of members of the polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase (ppGalNAc-T) family is
consistent with biologically relevant altered cell surface
glycosylation in breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 109:273–284. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding MX, Wang HF, Wang JS, Zhan H, Zuo YG,
Yang DL, Liu JY, Wang W, Ke CX and Yan RP: ppGalNAc T1 as a
potential novel marker for human bladder cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 13:5653–5657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hua D, Shen L, Xu L, Jiang Z, Zhou Y, Yue
A, Zou S, Cheng Z and Wu S: Polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 regulates cellular
metastasis-associated behavior in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med.
30:1267–1274. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fukuda M:
Beta-1,3-Galactosyl-O-Glycosyl-Glycoprotein
Beta-1,6-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (GCNT1) (C2GnT-L) and
Beta-1,3-Galactosyl-O-Glycosyl-Glycoprotein
Beta-1,6-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase 3 (GCNT4) (C2GnT-T).
Handbook Of Glycosyltransferases and Related genes. 355–366.
2014.
|
|
42
|
Skrincosky D, Kain R, El-Battari A, Exner
M, Kerjaschki D and Fukuda M: Altered Golgi localization of core 2
beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase leads to decreased
synthesis of branched O-glycans. J Biol Chem. 272:22695–22702.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pearce OM and Läubli H: Sialic acids in
cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology. 26:111–128. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Woskowicz AM, Weaver SA, Shitomi Y, Ito N
and Itoh Y: MT-LOOP-dependent localization of membrane type I
matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) to the cell adhesion complexes
promotes cancer cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 288:35126–35137. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Têtu B, Brisson J, Wang CS, Lapointe H,
Beaudry G, Blanchette C and Trudel D: The influence of MMP-14,
TIMP-2 and MMP-2 expression on breast cancer prognosis. Breast
Cancer Res. 8:R282006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, Cao J,
Shinagawa A, Yamamoto E and Seiki M: A matrix metalloproteinase
expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature.
370:61–65. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Deng YP, Li W and Li YL, Xu H, Liang SS,
Zhang LH and Li YL: MT1-MMP up-regulates VEGF expression in human
breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells and induces tumor angiogenesis.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 31:727–731. 2009.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|