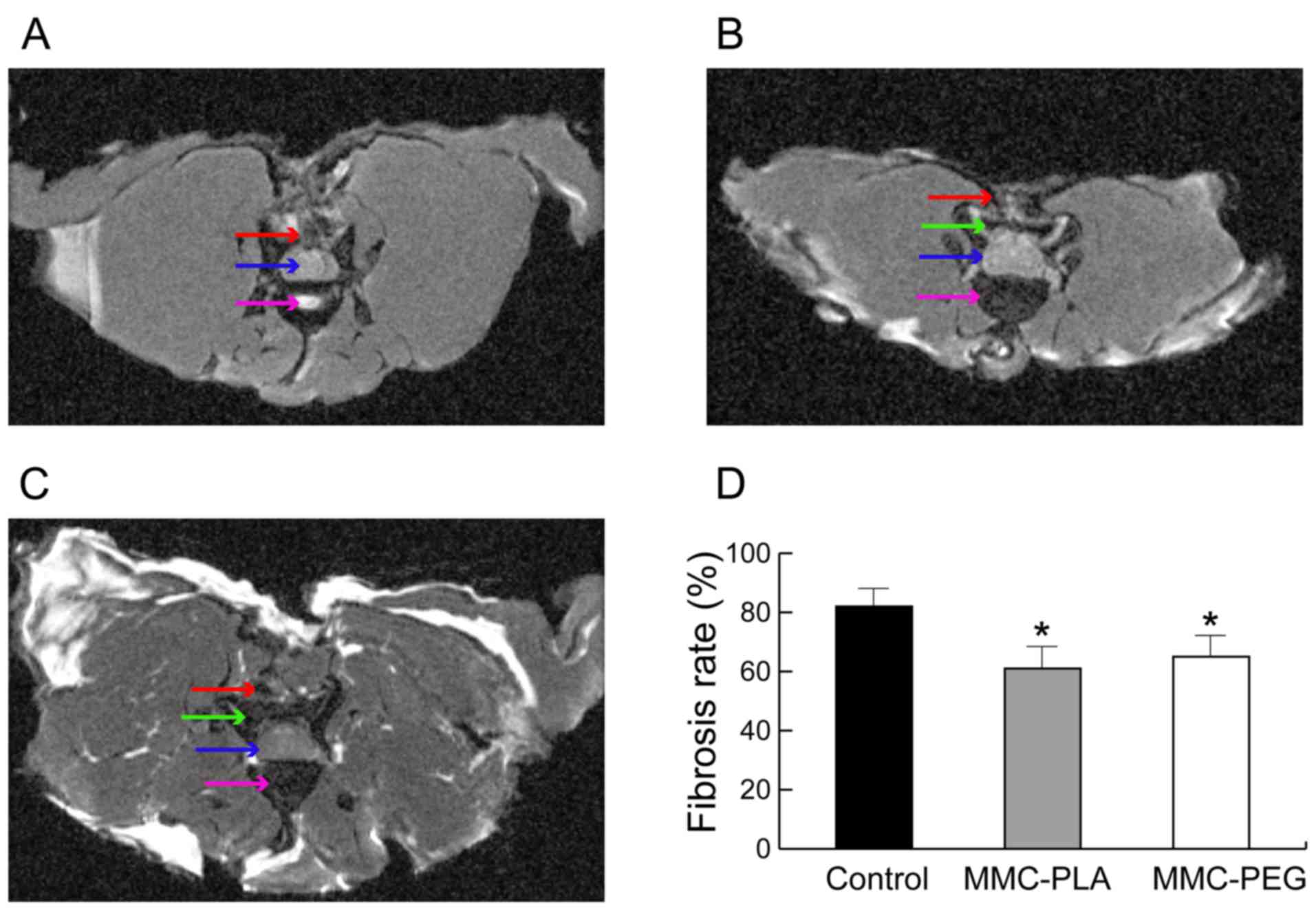
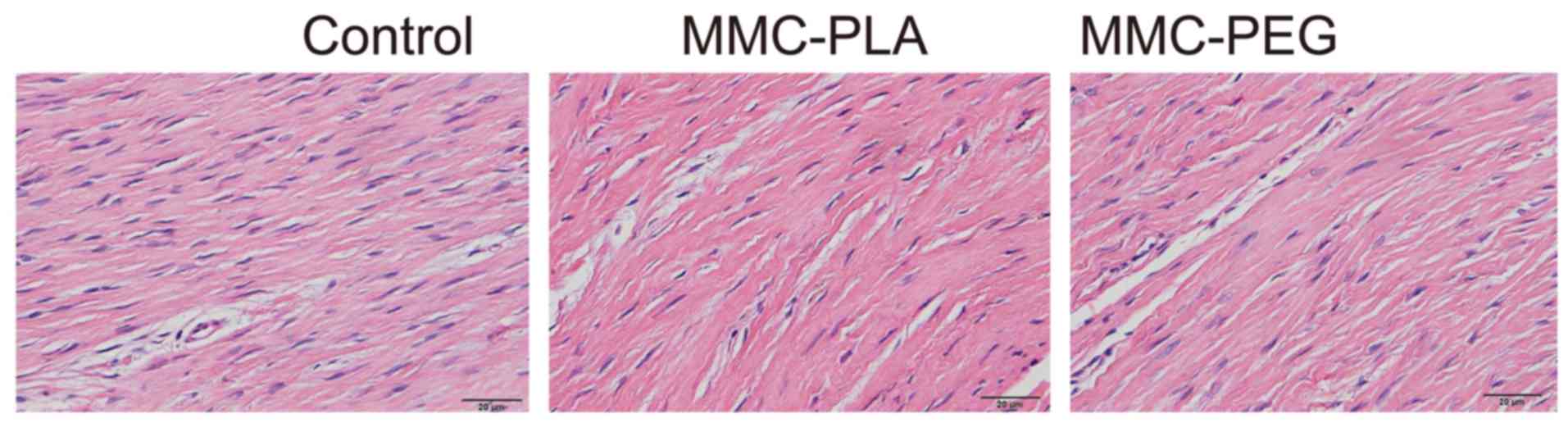
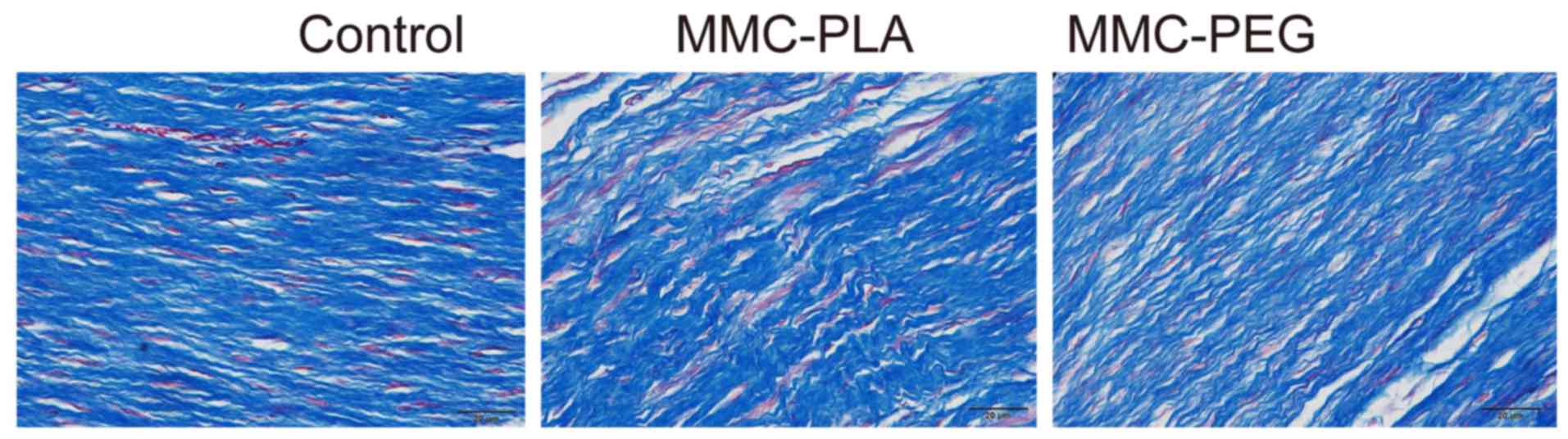
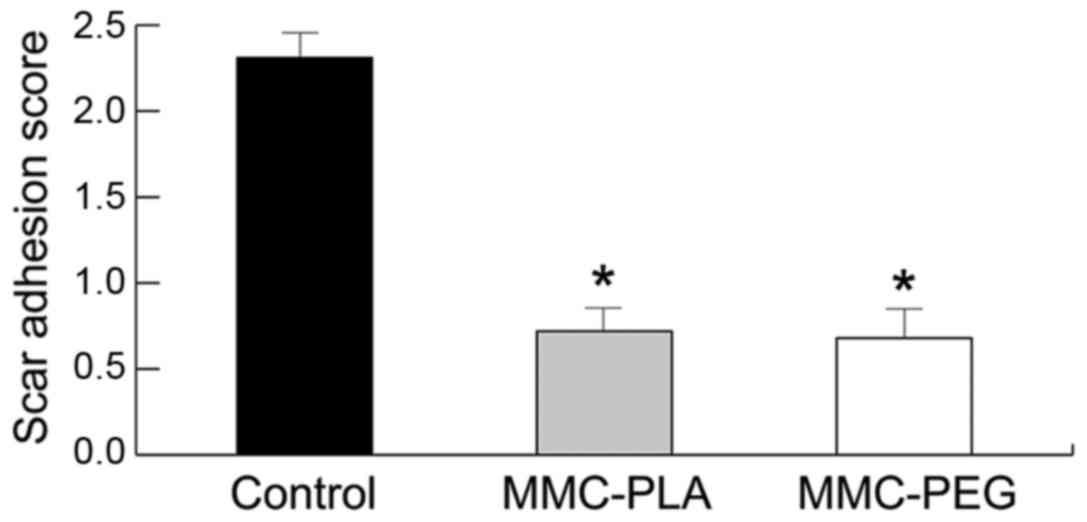
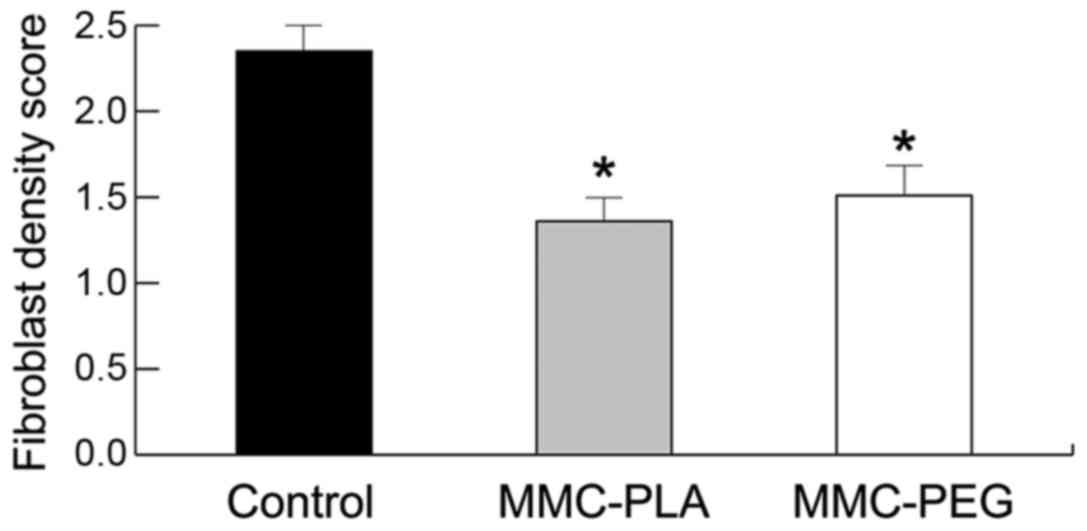
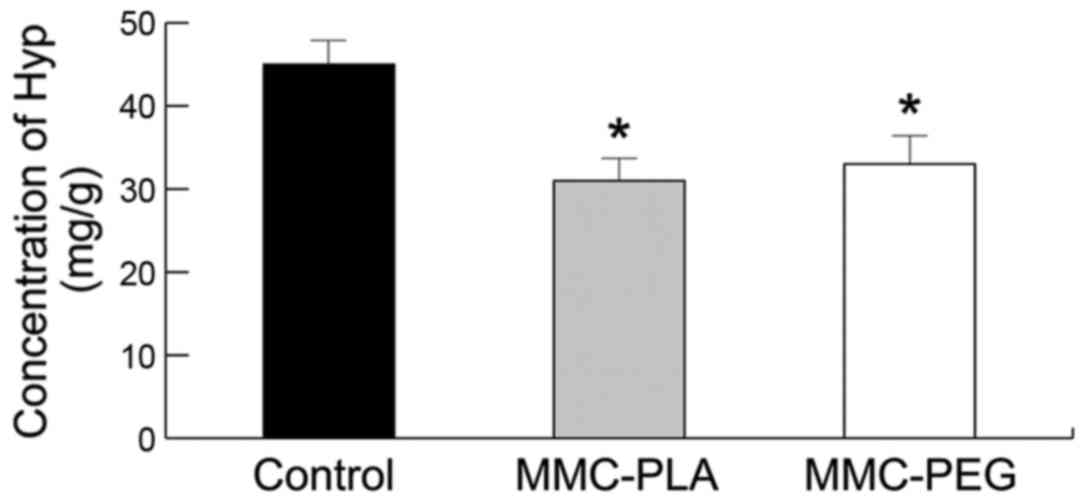
|
1
|
Key JA and Ford LT: Experimental
intervertebral-disc lesions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 30A:621–630.
1948. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang L, Tang J, Chen H, Ge D, Sui T, Que
J, Cao X and Ge Y: Taurine reduced epidural fibrosis in rat models
after laminectomy via downregulating EGR1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:2261–2271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bartynski WS and Petropoulou KA: The MR
imaging features and clinical correlates in low back pain-related
syndromes. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 15:137–154. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sizer PS Jr, Phelps V, Dedrick G and
Matthijs O: Differential diagnosis and management of spinal nerve
root-related pain. Pain Pract. 2:98–121. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lladó A, Guimerá J, Garcia F and Navarro
A: Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene membrane for the prevention of
peridural fibrosis after spinal surgery: An experimental study. Eur
Spine J. 8:138–143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Burton CV: Causes of failure of surgery on
the lumbar spine: Ten-year follow-up. Mt Sinai J Med. 58:183–187.
1991.
|
|
7
|
Ganzer D, Giese K, Völker L, Pietzner U,
Follak N and Merk H: Two-year results after lumbar microdiscectomy
with and without prophylaxis of a peridural fibrosis using Adcon-L.
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 123:17–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vogelsang JP, Finkenstaedt M, Vogelsang M
and Markakis E: Recurrent pain after lumbar discectomy: The
diagnostic value of peridural scar on MRI. Eur Spine J. 8:475–479.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Ozgen S, Naderi S, Ozek MM and Pamir MN:
Findings and outcome of revision lumbar disc surgery. J Spinal
Disord. 12:287–292. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Abdou M Samy and Hardy RW Jr: Epidural
fibrosis and the failed back surgery syndrome: History and physical
findings. Neurol Res. 21 Suppl 1:S5–S8. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
BenDebba M, van Alphen H Augustus and Long
DM: Association between peridural scar and activity-related pain
after lumbar discectomy. Neurol Res. 21 Suppl 1:S37–S42. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chandler K and Cappello R: Laminectomy
membrane formation in dogs: Is the answer still elusive? Vet J.
172:1–2. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ming J, Wei T, Lin C, Min T, Sheng W and
Chih Y: Spinal somatosensory evoked potential to evaluate
neurophysiologic changes associated with postlaminotomy fibrosis:
An experimental study. Spine. 32:2111–2118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
da Costa RC, Pippi NL, Graça DL, Fialho
SA, Alves A, Groff AC and Rezler U: The effects of free fat graft
or cellulose membrane implants on laminectomy membrane formation in
dogs. Vet J. 171:491–499. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kato T, Haro H, Komori H and Shinomiya K:
Evaluation of hyaluronic acid sheet for the prevention of
postlaminectomy adhesions. Spine J. 5:479–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Temel SG, Ozturk C, Temiz A, Ersozlu S and
Aydinli U: A new material for prevention of epidural fibrosis after
laminectomy: Oxidized regenerated cellulose (interceed), an
absorbable barrier. J Spinal Disord Tech. 19:270–275. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Akeson WH, Massie JB, Huang B, Giurea A,
Sah R, Garfin SR and Kim CW: Topical high-molecular-weight
hyaluronan and a roofing barrier sheet equally inhibit
postlaminectomy fibrosis. Spine J. 5:180–190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pasut G, Guiotto A and Veronese FM:
Protein, peptide and non-peptide drug PEGylation for therapeutical
application (Review). Expert Opin Ther Patents. 14:859–894. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Schiavon O, Pasut G, Moro S, Orsolini P,
Guiotto A and Veronese FM: PEG-Ara-C conjugates for controlled
release. Eur J Med Chem. 39:123–133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tao H and Fan H: Implantation of amniotic
membrane to reduce postlaminectomy epidural adhesions. Eur Spine J.
18:1202–1212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Cao B, Yin J, Yan S, Cui L, Chen X and Xie
Y: Porous scaffolds based on cross-linking of poly(L-glutamic
acid). Macromol Biosci. 11:427–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dogulu F, Kurt G, Emmez H, Erdem O, Memis
L, Baykaner K and Ceviker N: Topical mitomycin C-induced inhibition
of postlaminectomy peridural fibrosis in rabbits. J Neurosurg. 99
Suppl 1:76–79. 2003.
|
|
23
|
Sun Y, Wang LX, Wang L, Sun SX, Cao XJ,
Wang P and Feng L: A comparison of the effectiveness of mitomycin C
and 5-fluorouracil in the prevention of peridural adhesion after
laminectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 7:423–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee JY, Stenzel W, Löhr M, Stützer H,
Ernestus RI and Klug N: The role of mitomycin C in reducing
recurrence of epidural fibrosis after repeated operation in a
laminectomy model in rats. J Neurosurg Spine. 4:329–333. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Ni B, Zhu L, Yang J, Cao X and Zhou
W: Mitomycin C- polyethylene glycol controlled-release film
inhibits collagen secretion and induces apoptosis of fibroblasts in
the early wound of a postlaminectomy rat model. Spine J.
10:441–447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sen O, Kizilkilic O, Aydin MV, Yalcin O,
Erdogan B, Cekinmez M, Caner H and Altinors N: The role of
closed-suction drainage in preventing epidural fibrosis and its
correlation with a new grading system of epidural fibrosis on the
basis of MRI. Eur Spine J. 14:409–414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Canis M, Botchorishvili R, Tamburro S,
Safi A, Wattiez A, Mage G, Pouly JL and Bruhat MA: Adhesion
prevention in the surgical treatment of pelvic endometriosis.
Gynaecol Endosc. 10:99–106. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Z, Tarone G and Turner DC:
Expression of integrin α1 β1 is regulated by nerve growth factor
and dexamethasone in PC12 cells. Functional consequences for
adhesion and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 268:5557–5565.
1993.
|
|
29
|
Dumont RJ, Verma S, Okonkwo DO, Hurlbert
RJ, Boulos PT, Ellegala DB and Dumont AS: Acute spinal cord injury,
part II: Contemporary pharmacotherapy. Clin Neuropharmacol.
24:265–279. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gerszten PC, Moossy JJ, Flickinger JC,
Gerszten K, Kalend A and Martínez AJ: Inhibition of peridural
fibrosis after laminectomy using low-dose external beam radiation
in a dog model. Neurosurgery. 46:1478–1485. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gerszten PC, Moossy JJ, Bahri S, Kalend A
and Martínez AJ: Inhibition of peridural fibrosis after laminectomy
using low-dose external beam radiation in a rat model.
Neurosurgery. 44:597–602; discussion 602–603. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gibbs IC, Patil C, Gerszten PC, Adler JR
Jr and Burton SA: Delayed radiation-induced myelopathy after spinal
radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 64(suppl_2): A67–A72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pospiech J, Pajonk F and Stolke D:
Epidural scar tissue formation after spinal surgery: An
experimental study. Eur Spine J. 4:213–219. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Silva SS, Motta A, Rodrigues MT, Pinheiro
AF, Gomes ME, Mano JF, Reis RL and Migliaresi C: Novel
genipin-cross-linked chitosan/silk fibroin sponges for cartilage
engineering strategies. Biomacromolecules. 9:2764–2774. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Klopp LS, Welch WC, Tai JW, Toth JM,
Cornwall GB and Turner AS: Use of polylactide resorbable film as a
barrier to postoperative peridural adhesion in an ovine dorsal
laminectomy model. Neurosurg Focus. 16:E22004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bakaltcheva I, Ganong JP, Holtz BL, Peat
RA and Reid T: Effects of high-molecular-weight cryoprotectants on
platelets and the coagulation system. Cryobiology. 40:283–293.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fujii H, Fujii S, Togashi H, Yoshioka M,
Nakai K, Satoh H, Sakuma I, Kenmotsu O and Kitabatake A:
Attenuation of hypothermia-induced platelet activation and platelet
adhesion to artificial surfaces in vitro by modification of
hemoglobin to carry S-nitric oxide and polyethylene glycol. Thromb
Res. 100:519–528. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Welch WC, Cornwall GB, Toth JM, Turner AS,
Thomas KA, Gerszten PC and Nemoto EM: Use of polylactide resorbable
film as an adhesion barrier. Orthopedics. 25(10 Suppl):
s1121–s1130. 2002.
|
|
39
|
Songer MN, Rauschning W, Carson EW and
Pandit SM: Analysis of peridural scar formation and its prevention
after lumbar laminotomy and discectomy in dogs. Spine. 20:571–580,
discussion 579–580. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee JY, Stenzel W, Ebel H, Wedekind C,
Ernestus RI and Klug N: Mitomycin C in preventing spinal epidural
fibrosis in a laminectomy model in rats. J Neurosurg. 100(1 Suppl
Spine): 52–55. 2004.
|
|
41
|
Fielding JW, Crocker J, Stockley RA and
Brookes VS: Interstitial fibrosis in a patient treated with
5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C. BMJ. 2:551–552. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Kuhn J, Hofmann B, Knitelius HO, Coenen HH
and Bewermeyer H: Bilateral subdural haematomata and lumbar
pseudomeningocele due to a chronic leakage of liquor
cerebrospinalis after a lumbar discectomy with the application of
ADCON-L gel. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 76:1031–1033. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|