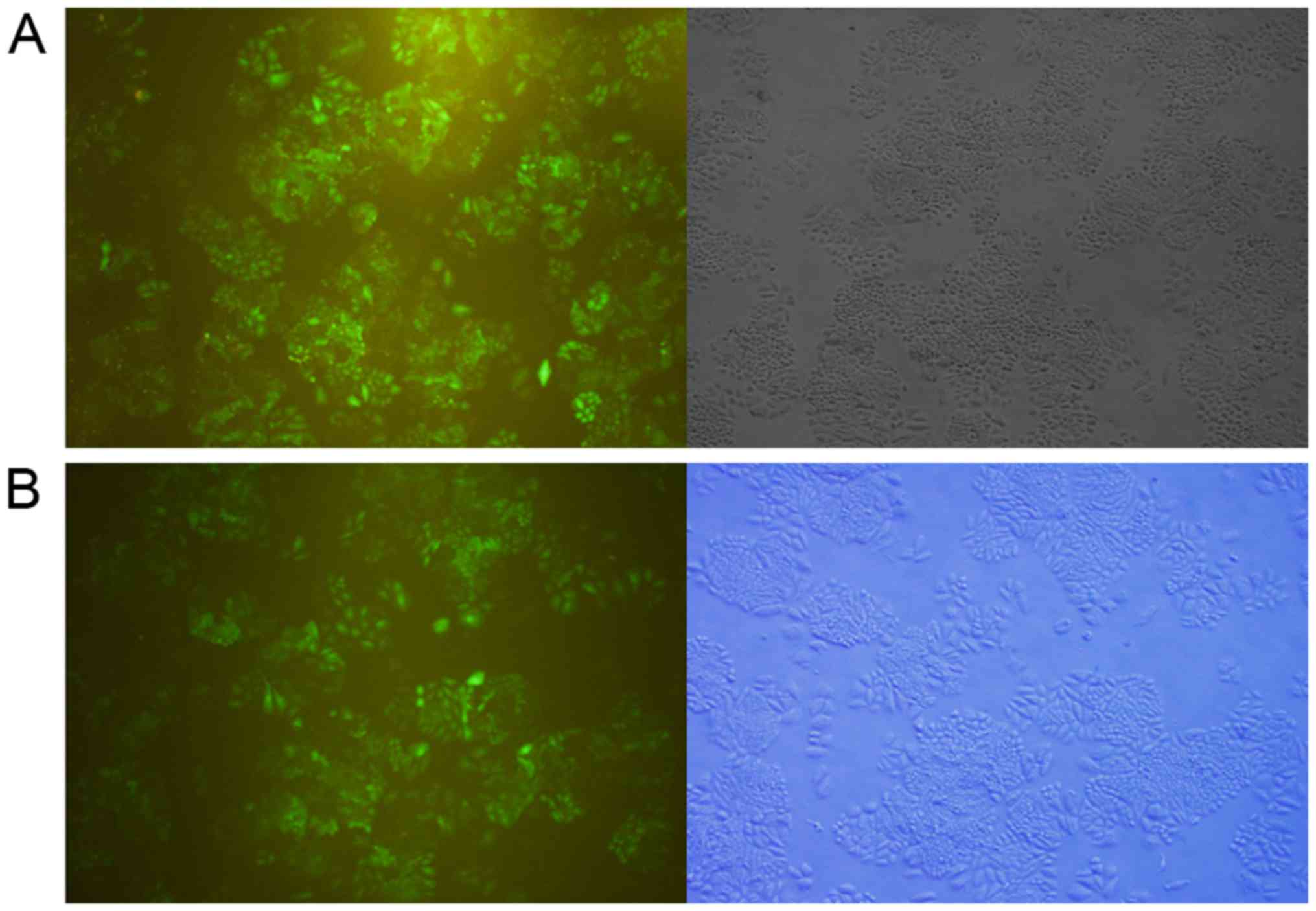
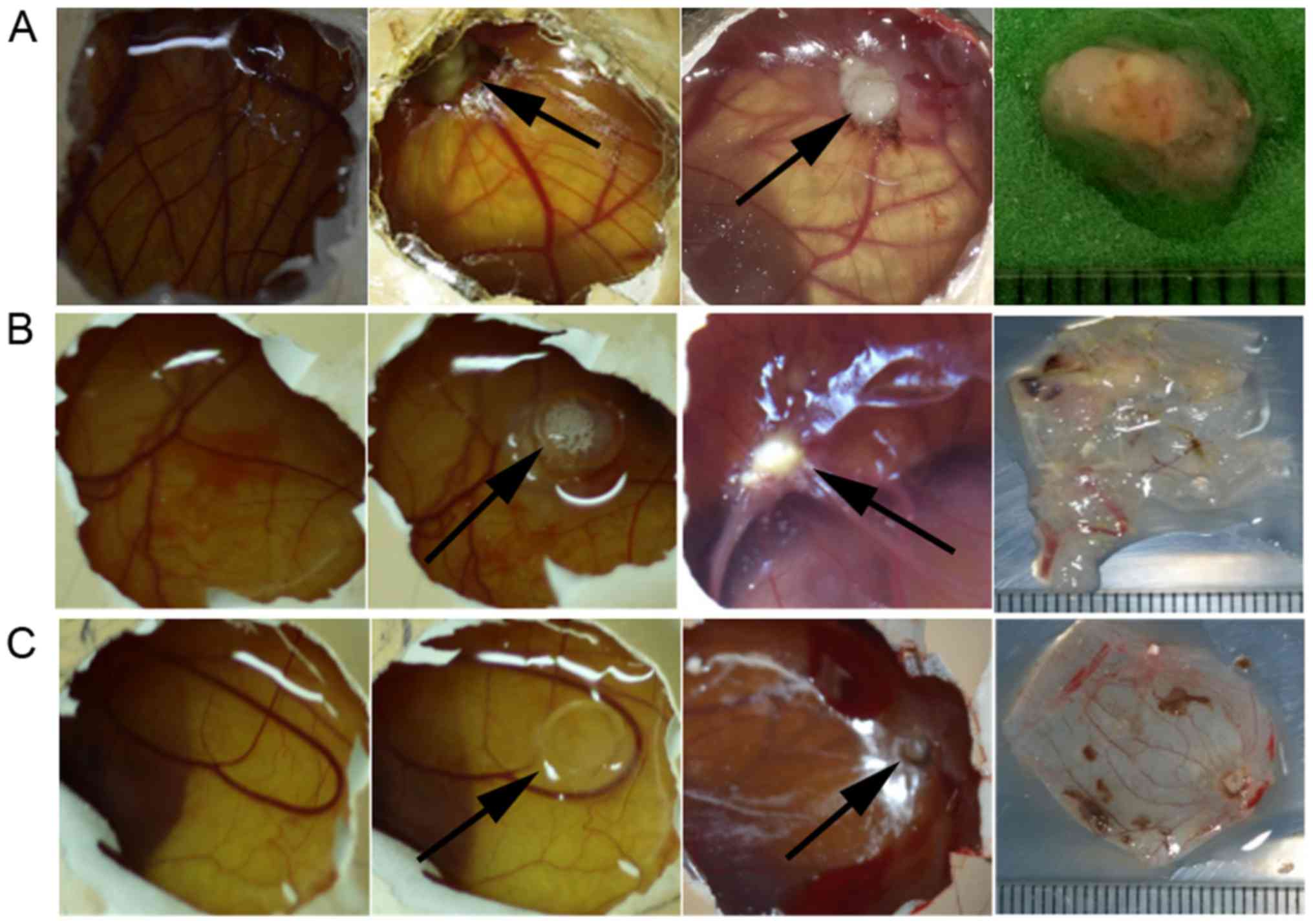
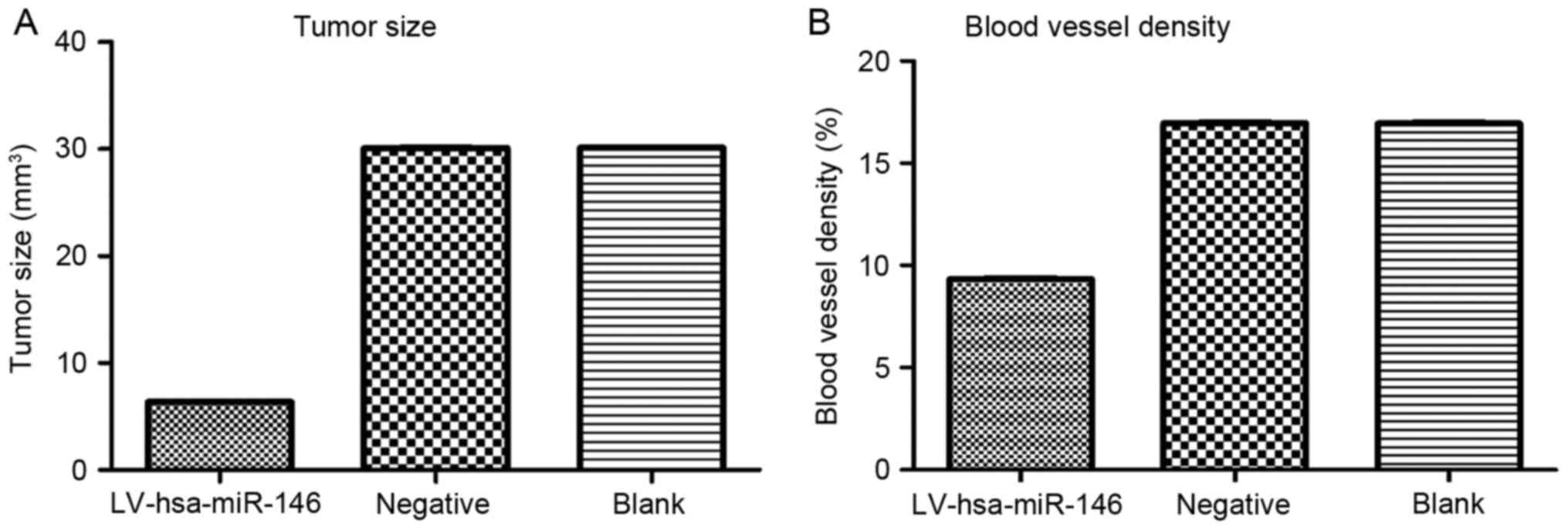
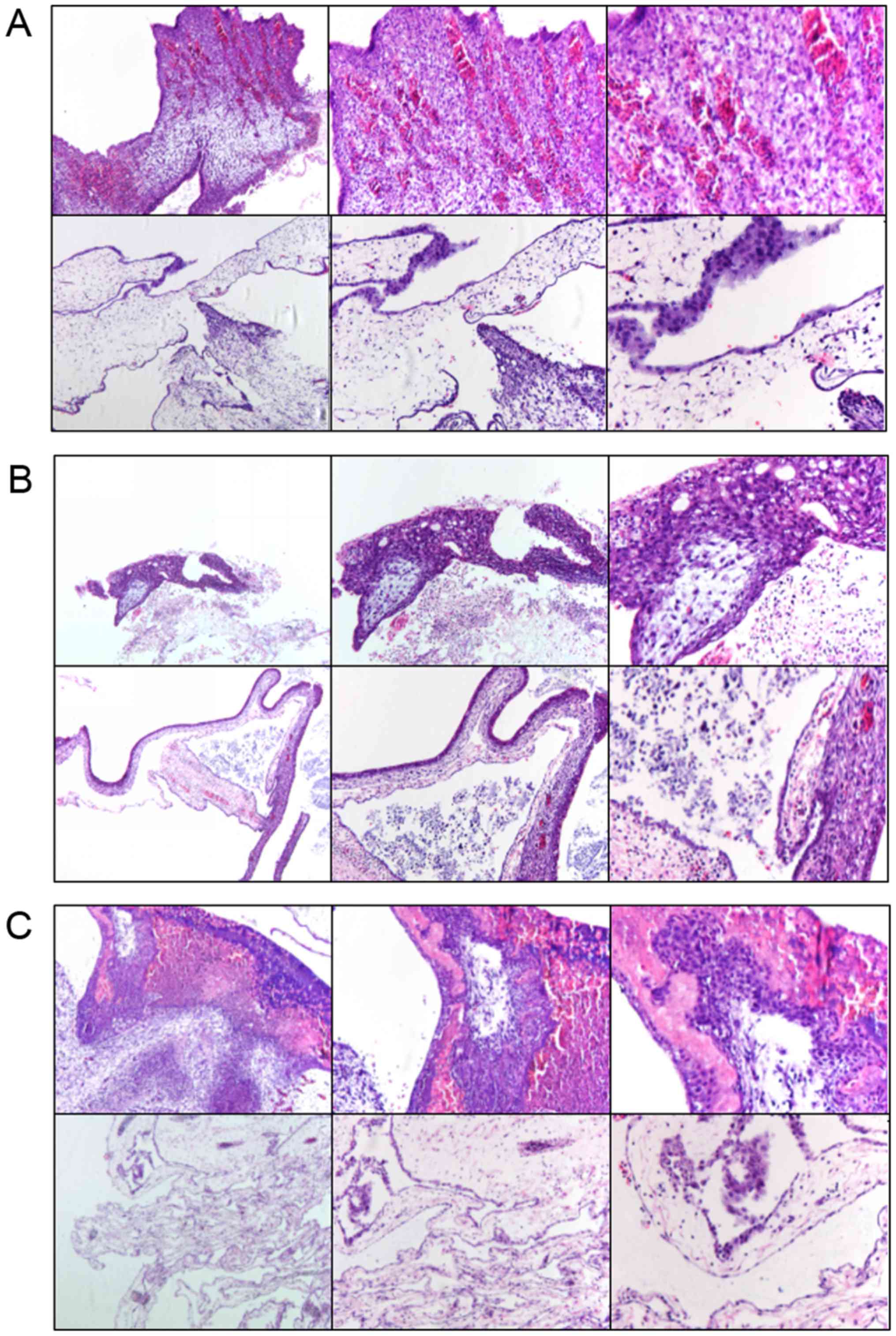
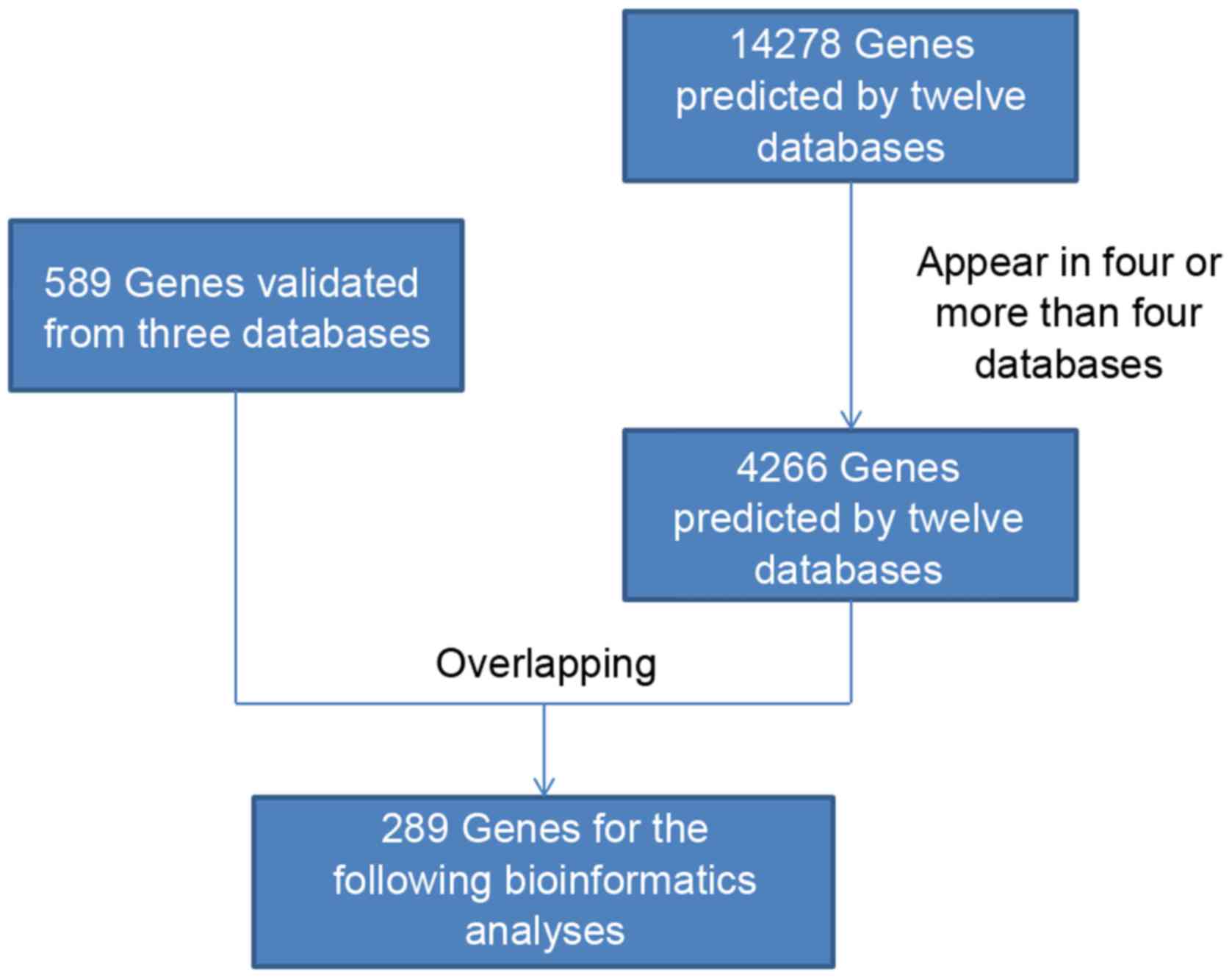
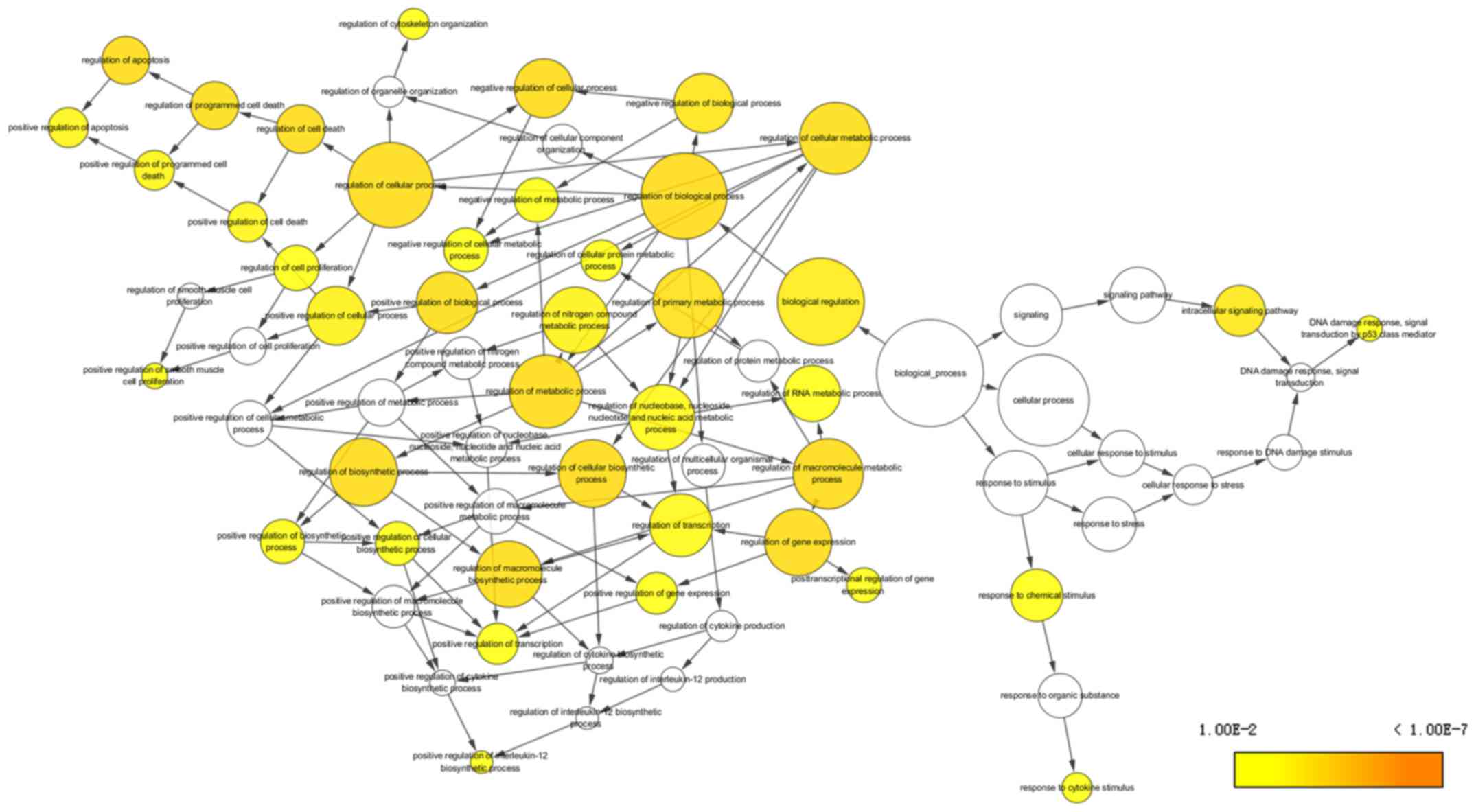
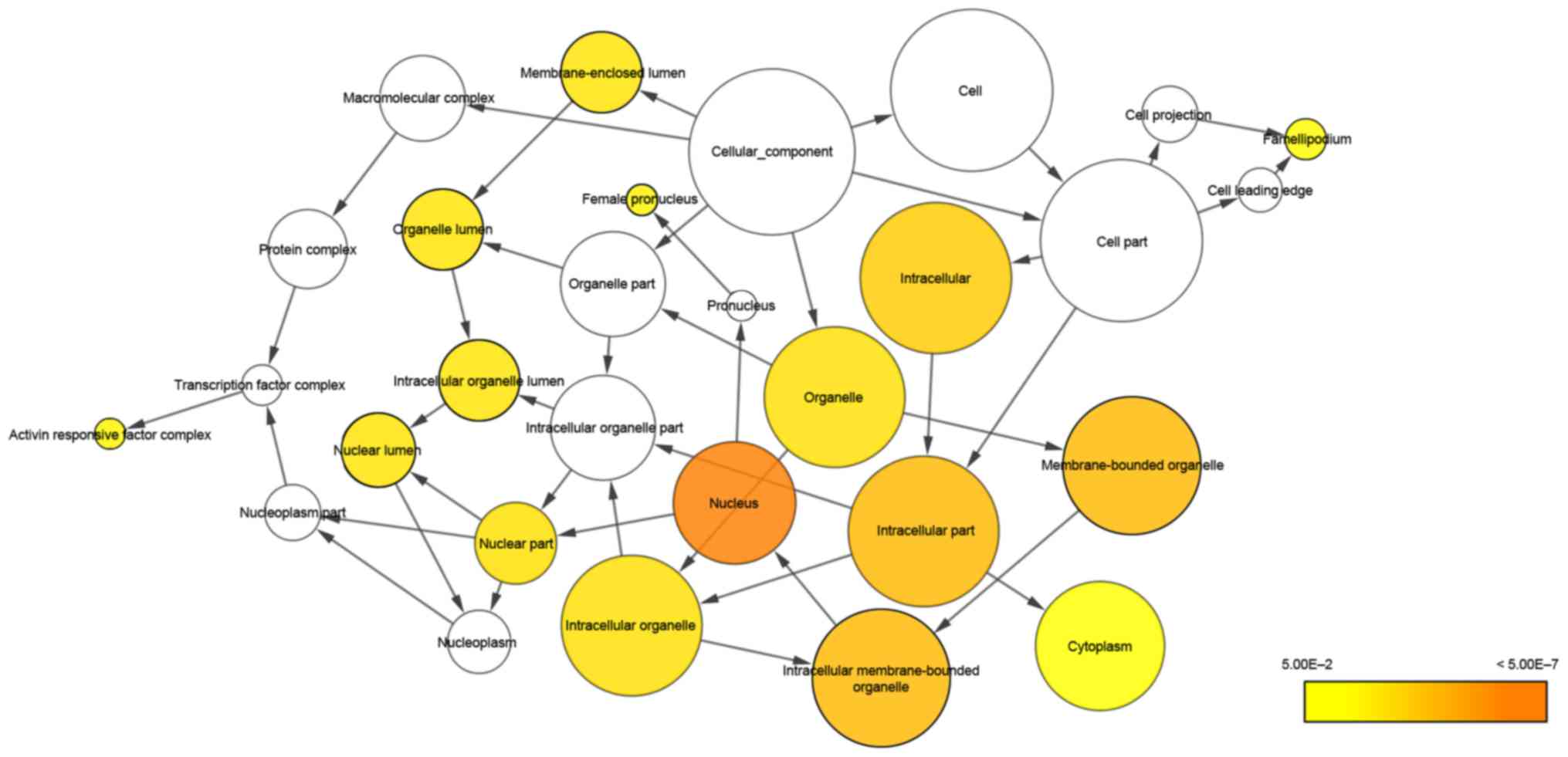
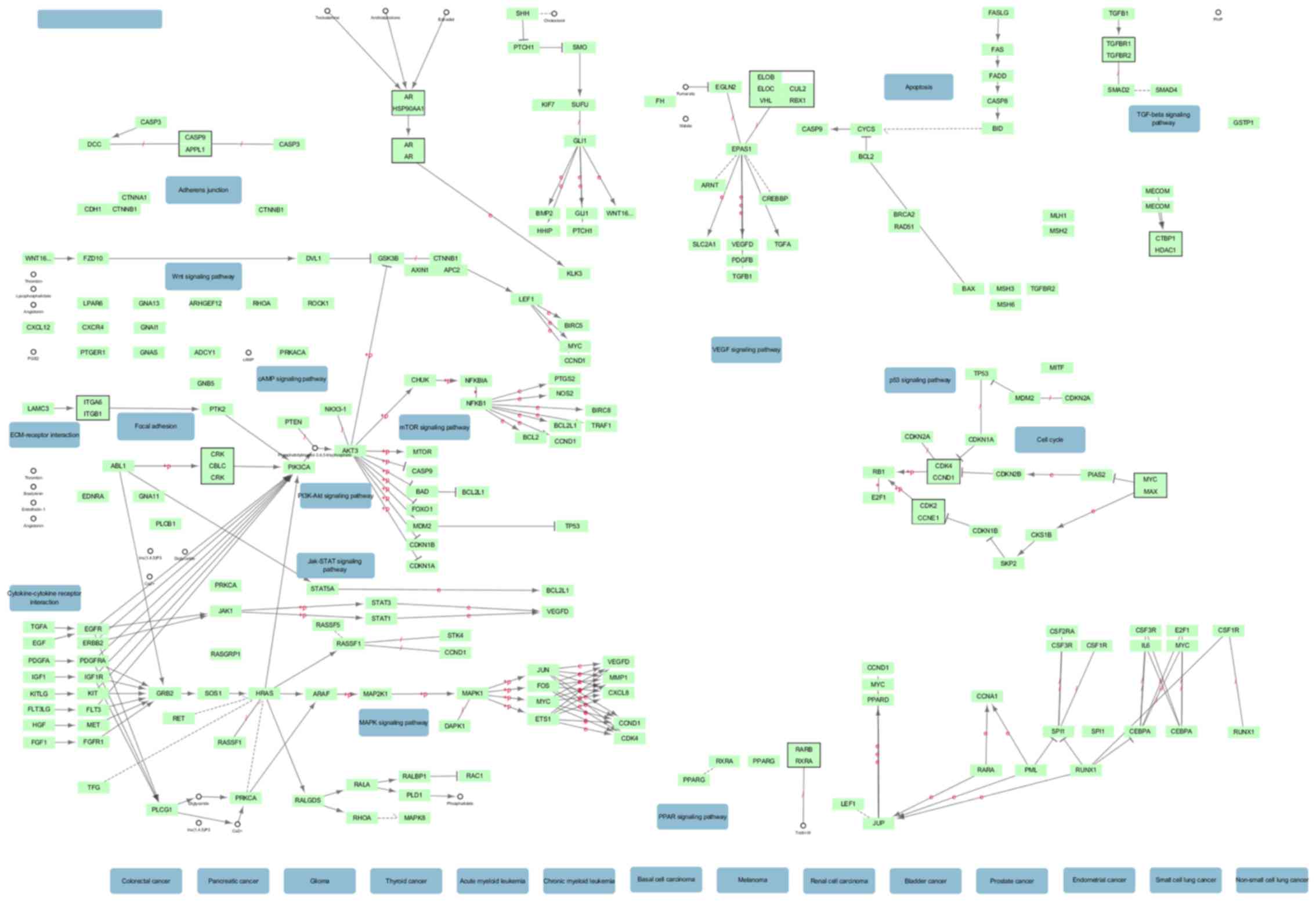
|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, et
al: The global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dietel M, Bubendorf L, Dingemans AM, Dooms
C, Elmberger G, García RC, Kerr KM, Lim E, López-Ríos F, Thunnissen
E, et al: Diagnostic procedures for non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Recommendations of the European Expert Group. Thorax.
71:177–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: World Health Classification of Tumours. Pathology
and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC
Press/Oxford University Press/Oxford University Press.
(distributor). Lyon: 2004
|
|
4
|
Ul Hussain M: Micro-RNAs (miRNAs): Genomic
organisation, biogenesis and mode of action. Cell Tissue Res.
349:405–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baehrecke EH: miRNAs: Micro managers of
programmed cell death. Curr Biol. 13:R473–R475. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Michael MZ, O' Connor SM, van Holst
Pellekaan NG, Young GP and James RJ: Reduced accumulation of
specific mircoRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res.
1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY,
Huang KH, Lee MJ, Galas DJ and Wang K: The microRNA spectrum in 12
body fluids. Clin Chem. 56:1733–1741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bishop JA, Benjamin H, Cholakh H, Chajut
A, Clark DP and Westra WH: Accurate classification of non-small
cell lung carcinoma using a novel microRNA-based approach. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:610–619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu SL, Chen HY, Chang GC, Chen CY, Chen
HW, Singh S, Cheng CL, Yu CJ, Lee YC, Chen HS, et al: MicroRNA
signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer
Cell. 13:48–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raponi M, Dossey L, Jatkoe T, Wu X, Chen
G, Fan H and Beer DG: MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis
of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5776–5783. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S and
Yendamuri S: Evaluation of microRNA expression profiles that may
predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer
after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 70:36–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jazdzewski K, Boguslawska J, Jendrzejewski
J, Liyanarachchi S, Pachucki J, Wardyn KA, Nauman A and de la
Chapelle A: Thyroid hormone receptor beta (THRB) is a major target
gene for microRNAs deregulated in papillary thyroid carcinoma
(PTC). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E546–E553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun M, Fang S, Li W, Li C, Wang L, Wang F
and Wang Y: Associations of miR-146a and miR-146b expression and
clinical characteristics in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 15:33–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng T, Chou J, Zhang F, Liu Y, Ni H, Li
X, Zheng L, Tang T, Jin L and Xi T: CXCR4 3′UTR functions as a
ceRNA in promoting metastasis, proliferation and survival of MCF-7
cells by regulating miR-146a activity. Eur J Cell Biol. 94:458–469.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu B, Wang N, Wang X, Tong N, Shao N, Tao
J, Li P, Niu X, Feng N, Zhang L, et al: miR-146a suppresses tumor
growth and progression by targeting EGFR pathway and in a
p-ERK-dependent manner in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Prostate. 72:1171–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun Q, Zhao X, Liu X, Wang Y, Huang J,
Jiang B, Chen Q and Yu J: miR-146a functions as a tumor suppressor
in prostate cancer by targeting Rac1. Prostate. 74:1613–1621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu B, Huang Y, Niu X, Tao T, Jiang L, Tong
N, Chen S, Liu N, Zhu W and Chen M: hsa-miR-146a-5p modulates
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells apoptosis by targeting
ROCK1. Prostate. 75:1896–1903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Vandenboom TG II, Wang Z, Kong D,
Ali S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH: miR-146a suppresses invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:1486–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yao Q, Cao Z, Tu C, Zhao Y, Liu H and
Zhang S: MicroRNA-146a acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric
cancer by targeting WASF2. Cancer Lett. 335:219–224. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:4277–484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hou Z, Yin H, Chen C, Dai X, Li X, Liu B
and Fang X: microRNA-146a targets the L1 cell adhesion molecule and
suppresses the metastatic potential of gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep.
6:501–506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sha M, Ye J, Zhang LX, Luan ZY and Chen
YB: Celastrol induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by miR-146a
inhibition of NF-κB activity. Cancer Cell Int. 13:502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou L, Zhao X, Han Y, Lu Y, Shang Y, Liu
C, Li T, Jin Z, Fan D and Wu K: Regulation of UHRF1 by miR-146a/b
modulates gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. FASEB J.
27:4929–4939. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang RJ, Zheng YH, Wang P and Zhang JZ:
Serum miR-125a-5p, miR-145 and miR-146a as diagnostic biomarkers in
non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:765–771.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Grève J:
miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li YL, Wang J, Zhang CY, Shen YQ, Wang HM,
Ding L, Gu YC, Lou JT, Zhao XT, Ma ZL and Jin YX: MiR-146a-5p
inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in NSCLC
cell lines by targeting CCND1 and CCND2. Oncotarget. 7:59287–59298.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mira E, Lacalle RA, Gómez-Moutón C,
Leonardo E and Mañes S: Quantitative determination of tumor cell
intravasation in a real-time polymerase chain reaction-based assay.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 19:313–318. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Busch C, Krochmann J and Drews U: The
chick embryo as an experimental system for melanoma cell invasion.
PLoS One. 8:e539702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kunzi-Rapp K, Genze F, Küfer R, Reich E,
Hautmann RE and Gschwend JE: Chorioallantoic membrane assay:
Vascularized 3-dimensional cell culture system for human prostate
cancer cells as an animal substitute model. J Urol. 166:1502–1507.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu M, Scanlon CS, Banerjee R, Russo N,
Inglehart RC, Willis AL, Weiss SJ and D'Silva NJ: The histone
methyltransferase EZH2 mediates tumor progression on the chick
chorioallantoic membrane assay, a novel model of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol. 6:273–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ribatti D, Vacca A, Roncali L and Dammacco
F: The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for in vivo
research on angiogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 40:1189–1197.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lokman NA, Elder AS, Ricciardelli C and
Oehler MK: Chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay as an in vivo
model to study the effect of newly identified molecules on ovarian
cancer invasion and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 13:9959–9970. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lester RD, Jo M, Montel V, Takimoto S and
Gonias SL: uPAR induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hypoxic breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 178:425–436. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen PY and Long QC: Effects of
cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors on biological traits of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:943–949. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
da W Huang, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McGuire S: World Cancer Report 2014.
Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International
Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr.
7:418–419. 2016.doi: 10.3945/an.116.012211.
|
|
42
|
Beasley MB, Dembitzer FR and Flores RM:
Surgical pathology of early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Ann Transl Med. 4:2382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Di Leva G and Croce CM: Roles of small
RNAs in tumor formation. Trends Mol Med. 16:257–267. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weidhaas JB, Babar I, Nallur SM, Trang P,
Roush S, Boehm M, Gillespie E and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs as potential
agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy. Cancer
Res. 67:11111–11116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Webster RJ, Giles KM, Price KJ, Zhang PM,
Mattick JS and Leedman PJ: Regulation of epidermal growth factor
receptor signaling in human cancer cells by microRNA-7. J Biol
Chem. 284:5731–5741. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yamaguchi G, Takanashi M, Tanaka M, Fujita
K, Ohira T, Kuroda M and Ikeda N: Isolation of miRNAs that target
EGFR mRNA in human lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
420:411–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jost M, Kari C and Rodeck U: The EGF
receptor - an essential regulator of multiple epidermal functions.
Eur J Dermatol. 10:505–510. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, Dull
TJ, Gray A, Tam AW, Lee J, Yarden Y, Libermann TA, Schlessinger J,
et al: Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and
aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid
carcinoma cells. Nature. 309:418–425. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Quadros MR, Peruzzi F, Kari C and Rodeck
U: Complex regulation of signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 activation in normal and malignant keratinocytes.
Cancer Res. 64:3934–3939. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rajan P, Elliott DJ, Robson CN and Leung
HY: Alternative splicing and biological heterogeneity in prostate
cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 6:454–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nicholas MK, Lukas RV, Jafri NF, Faoro L
and Salgia R: Epidermal growth factor receptor - mediated signal
transduction in the development and therapy of gliomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:7261–7270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shigematsu H and Gazdar AF: Somatic
mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in
lung cancers. Int J Cancer. 118:257–262. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
van den Eynden GG, Van der Auwera I, Van
Laere SJ, Colpaert CG, van Dam P, Dirix LY, Vermeulen PB and Van
Marck EA: Distinguishing blood and lymph vessel invasion in breast
cancer: A prospective immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer.
94:1643–1649. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kambouchner M and Bernaudin JF:
Intralobular pulmonary lymphatic distribution in normal human lung
using D2-40 antipodoplanin immunostaining. J Histochem Cytochem.
57:643–648. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|