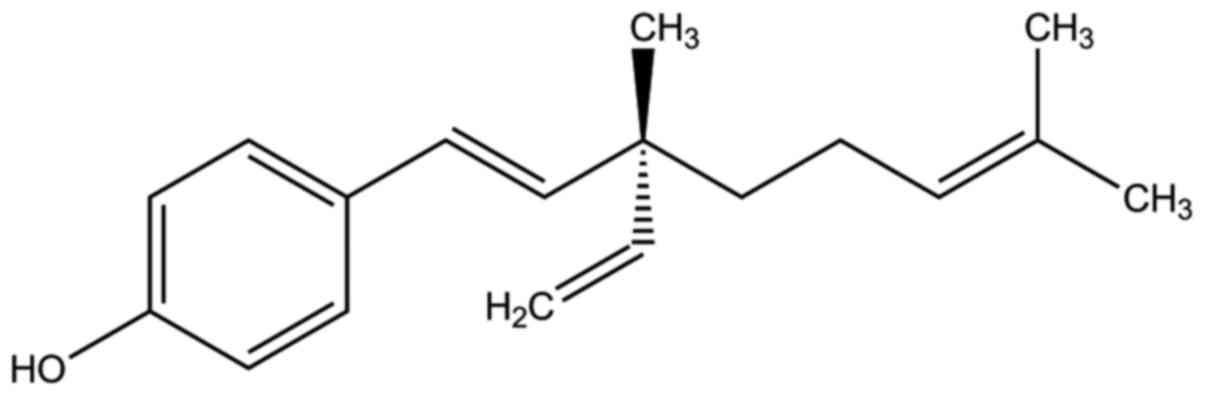
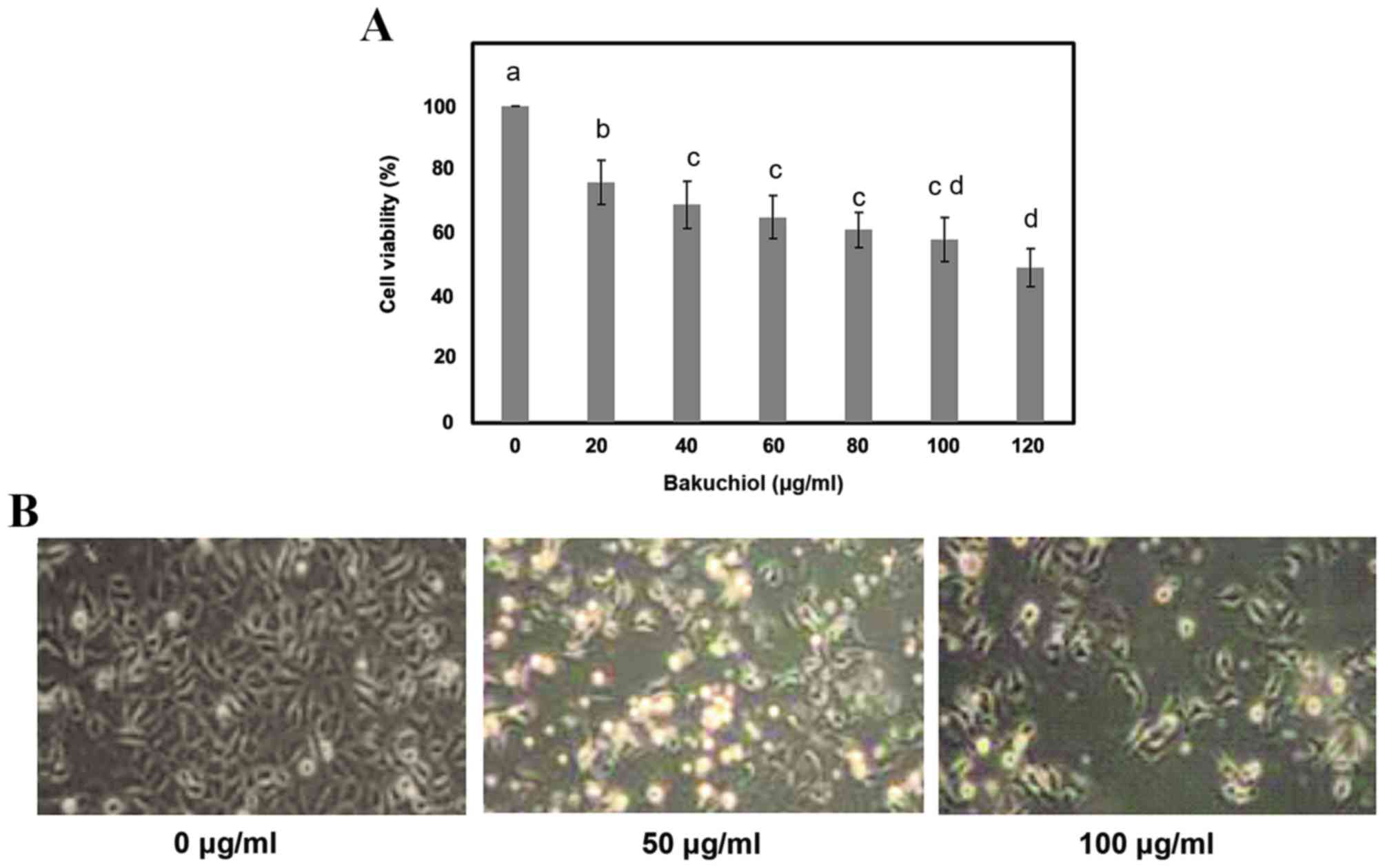
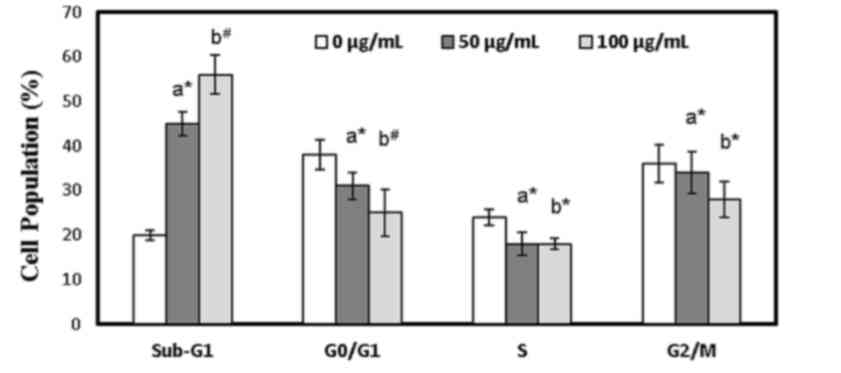
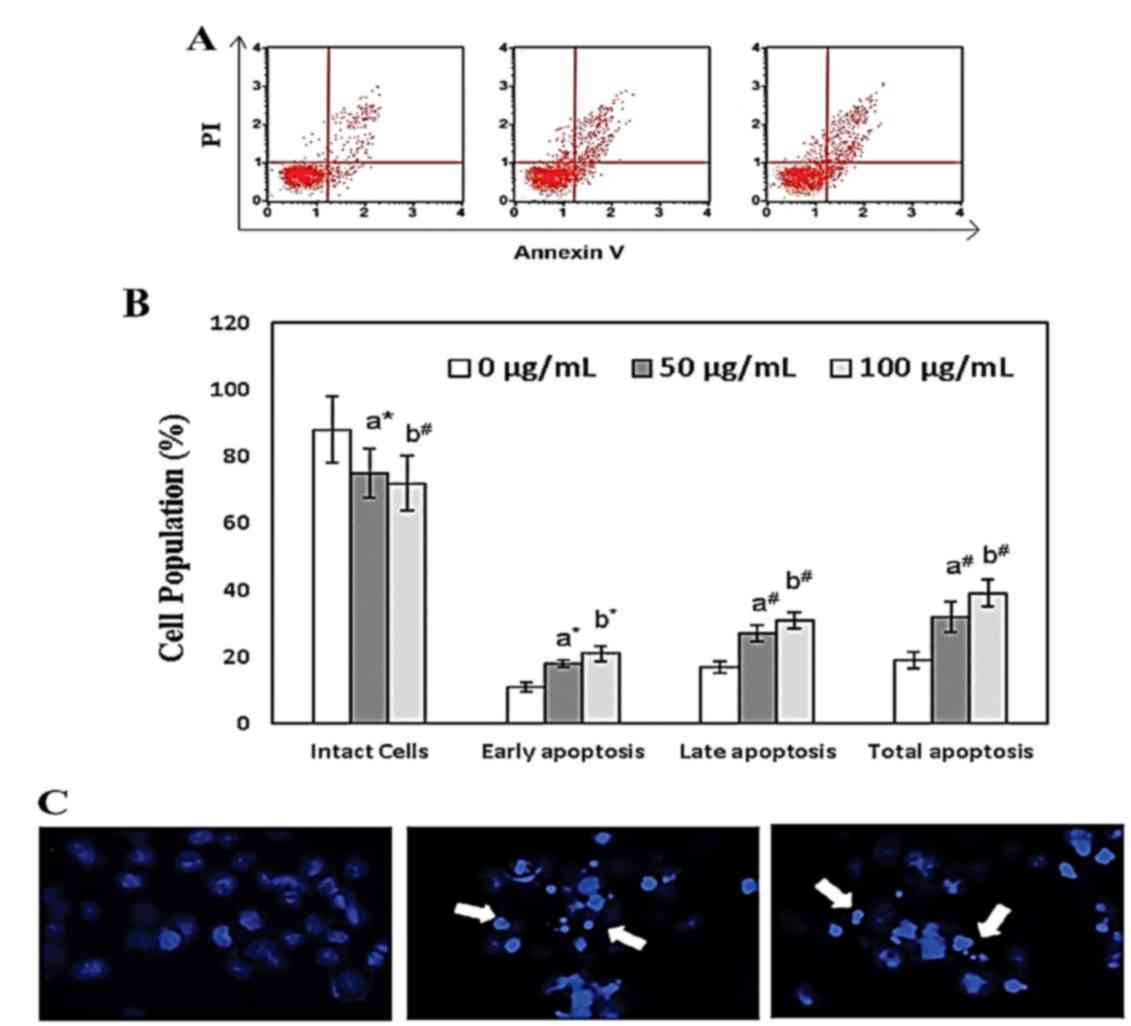
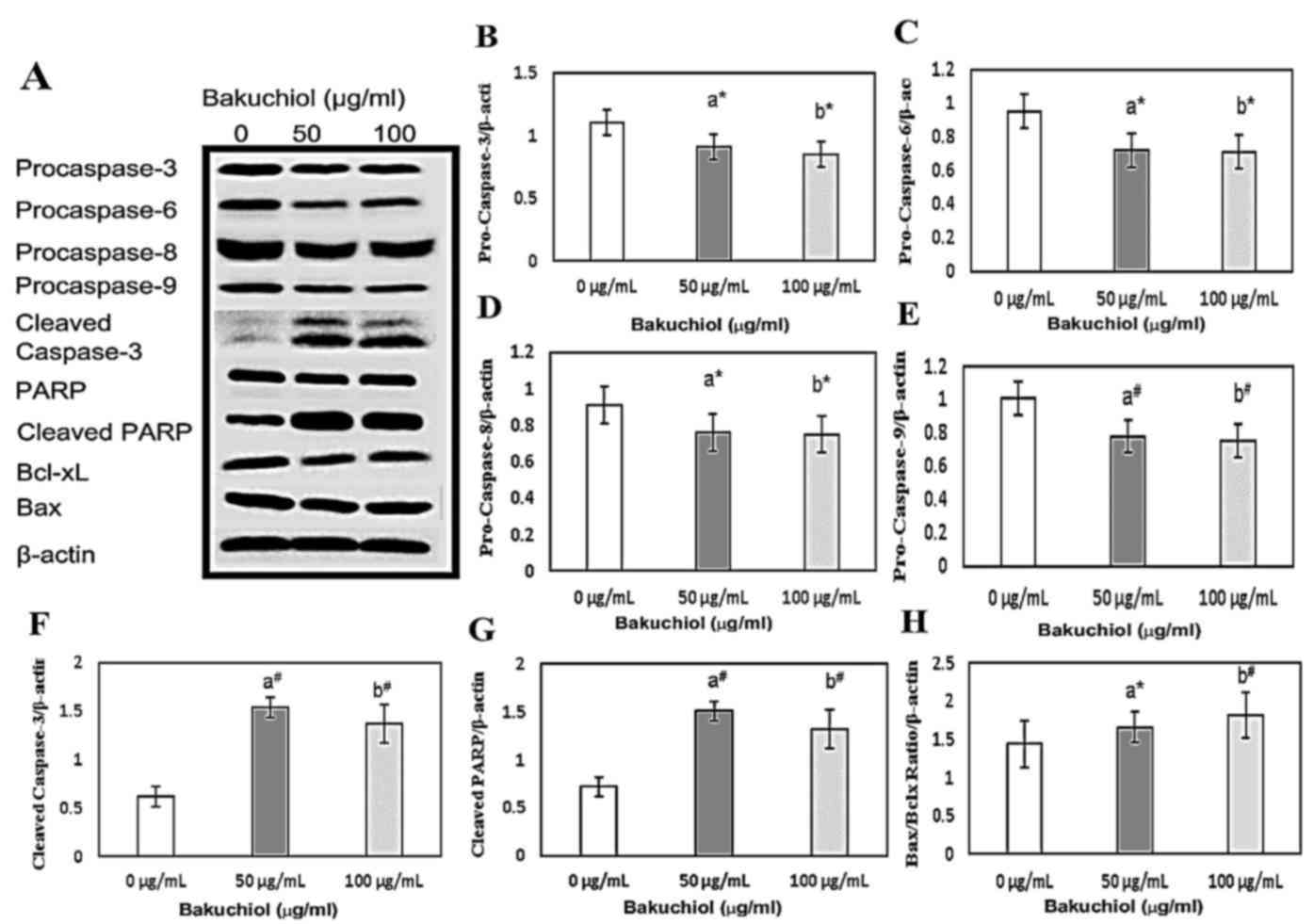
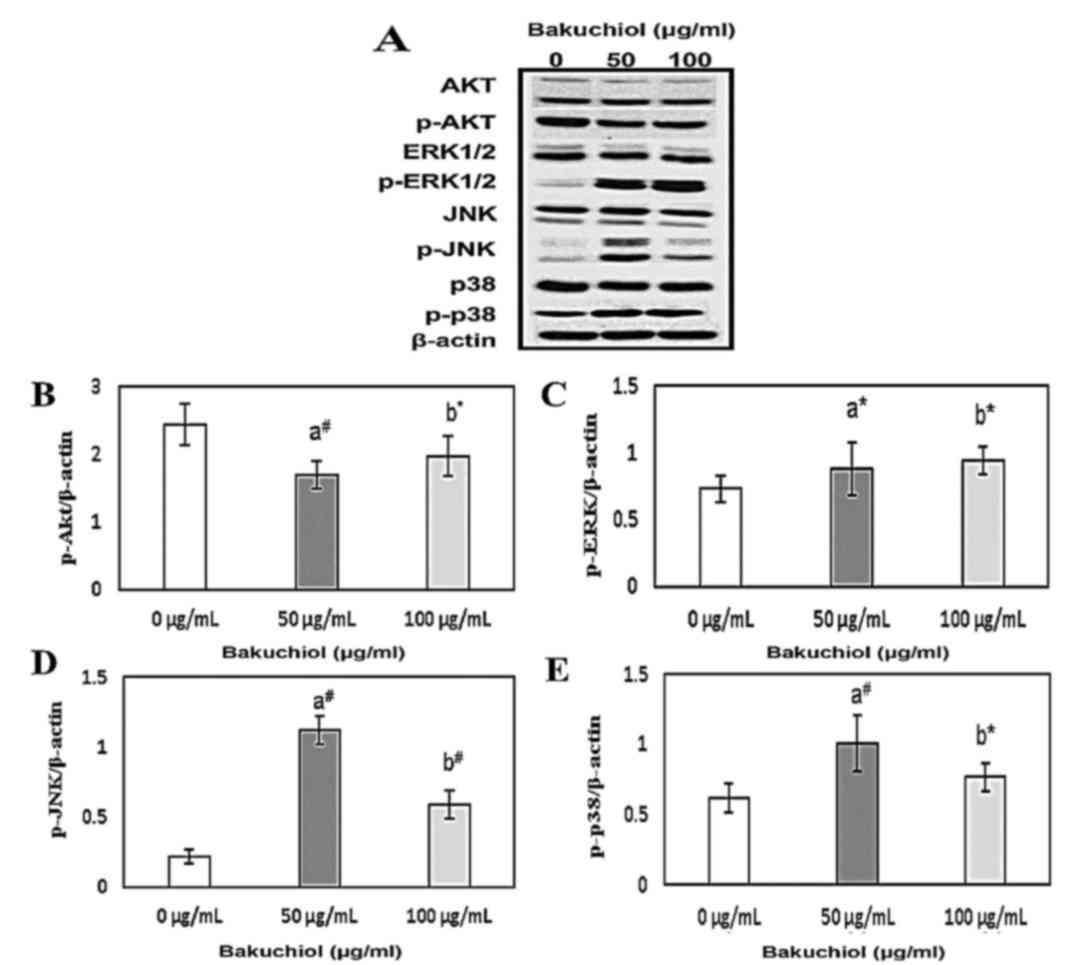
|
1
|
Guggenheim DE and Shah MA: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Surg Oncol. 107:230–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herszényi L and Tulassay Z: Epidemiology
of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
14:249–258. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ren J, Huang HJ, Gong Y, Yue S, Tang LM
and Cheng SY: MicroRNA-206 suppresses gastric cancer cell growth
and metastasis. Cell Biosci. 4:262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaing JB, Thesson DP, Dusak BA, Dexter DL,
Kang GJ and Hamel E: Synthesis and biological evaluation of
2-styrylquinazolin-4(3H)-ones, a new class of antimitotic
anticancer agents which inhibit tubulin polymerization. J Med Chem.
33:1721–1728. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zouhiri F, Danet M, Bénard C, Normad-Boyle
M, Mouscadet JF, Leh H, Thomas CM, Mbemba G, d'Angelo J and
Desmaële D: HIV-1 replication inhibitors of the styrylquinoline
class: Introduction of an additional carboxyl group at the C-5
position of the quinolone. Tetrahedron Lett. 46:2201–2205. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Eltahla AA, Lim KL, Eden JS, Kelly AG,
Mackenzie JM and White PA: Nonnucleoside inhibitors of norovirus
RNA Polymerase: Scaffolds for rational drug design. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 58:3115–3123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee IK, Han MS, Lee MS, Kim YS and Yun BS:
Styrylpyrones from the medicinal fungus Phellinus baumii and their
antioxidant properties. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 20:5459–5461. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bapat SA, Mali AM, Koppikar CB and Kurrey
NK: Stem and progenitor like cells contribute to the aggressive
behaviour of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
65:3025–3029. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vansteenkiste J: Improving patient
management in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
57 Suppl 2:S12–S17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chevalier A and Kindersley D: The
encyclopedia of medicinal plants. ISBN 9-780751-303148. London:
1996
|
|
12
|
Duke JA and Ayensu ES: Medicinal plants of
China Inc. ISBN 0-917256,. 20:41985.
|
|
13
|
Sun NJ, Woo SH, Cassady JM and Snapka RM:
DNA polymerase and topoisomerase II inhibitors from Psoralea
corylifolia. J Nat Prod. 61:362–366. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Katsura H, Tsukiyama RI, Suzuki A and
Kobayashi M: In vitro antimicrobial activities of bakuchiol against
oral microorganisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45:3009–3013.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reddy MV, Thota N, Sangwan PL, Malhotra P,
Ali F, Khan IA, Chimni SS and Koul S: Novel bisstyryl derivatives
of bakuchiol: Targeting oral cavity pathogens. Eur J Med Chem.
45:3125–3134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi Y: Caspase activation: Revisiting the
induced proximity model. Cell. 117:855–858. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SJ, Ahmad F, Philp A, Baar K,
Williams T, Luo H, Ke H, Rehmann H, Taussig R, Brown AL, et al:
Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by
inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases. Cell. 148:421–433. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee DH, Park KI, Park HS, Kang SR,
Nagappan A, Kim JA, Kim EH, Lee WS, Hah YS, Chung HJ, et al:
Flavonoids isolated from Korea Citrus aurantium L. Induce G2/M
phase arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer AGS cells. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5159012012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hussain AR, Al-Rasheed M, Manogaran PS,
Al-Hussein KA, Platanias LC, Al Kuraya K and Uddin S: Curcumin
induces apoptosis via inhibition of PI3′-kinase/AKT pathway in
acute T cell leukemias. Apoptosis. 11:245–254. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gururajan M, Dasu T, Shahidain S, Jennings
CD, Robertson DA, Rangnekar VM and Bondada S: Spleen tyrosine
kinase (Syk), a novel target of curcumin, is required for B
lymphoma growth. J Immunol. 178:111–121. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raman M, Chen W and Cobb MH: Differential
regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 26:3100–3112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van den Brink MR, Kapeller R, Pratt JC,
Chang JH and Burakoff SJ: The extracellular signal-regulated kinase
pathway is required for activation-induced cell death of T cells. J
Biol Chem. 274:11178–11185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Basu S, Bayoumy S, Zhang Y, Lozano J and
Kolesnick R: BAD enables ceramide to signal apoptosis via Ras and
Raf-1. J Biol Chem. 273:30419–30426. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Faris M, Kokot N, Latinis K, Kasibhatla S,
Green DR, Koretzky GA and Nel A: The c-Jun N-terminal kinase
cascade plays a role in stress-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells by
up-regulating Fas ligand expression. J Immunol. 160:134–144.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Reddy EP: JNK
signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:6245–6225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang YJ, Zhou ZX, Wang GW, Buridi A and
Klein JB: Suppression by metallothionein of doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 275:13690–13698. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|