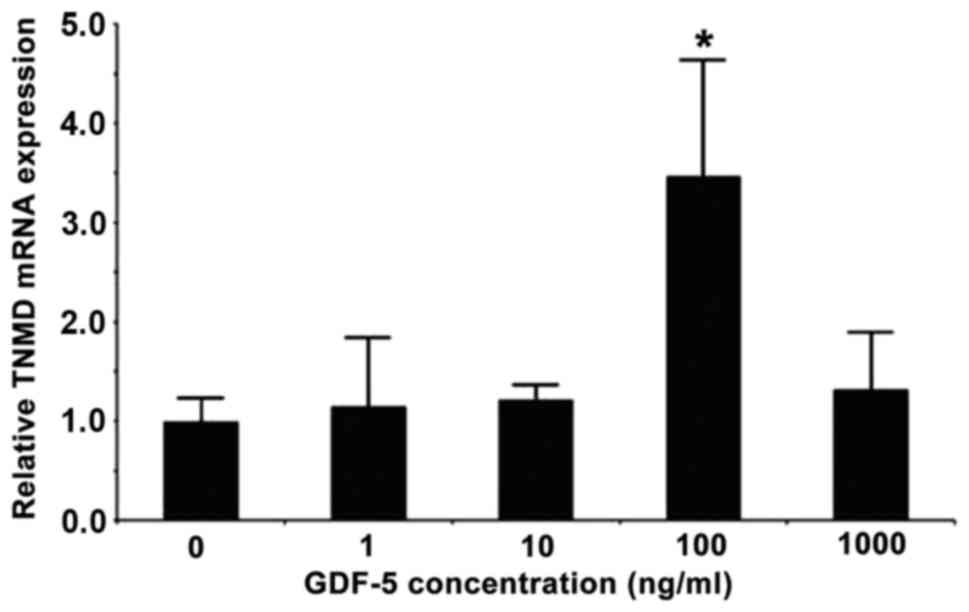
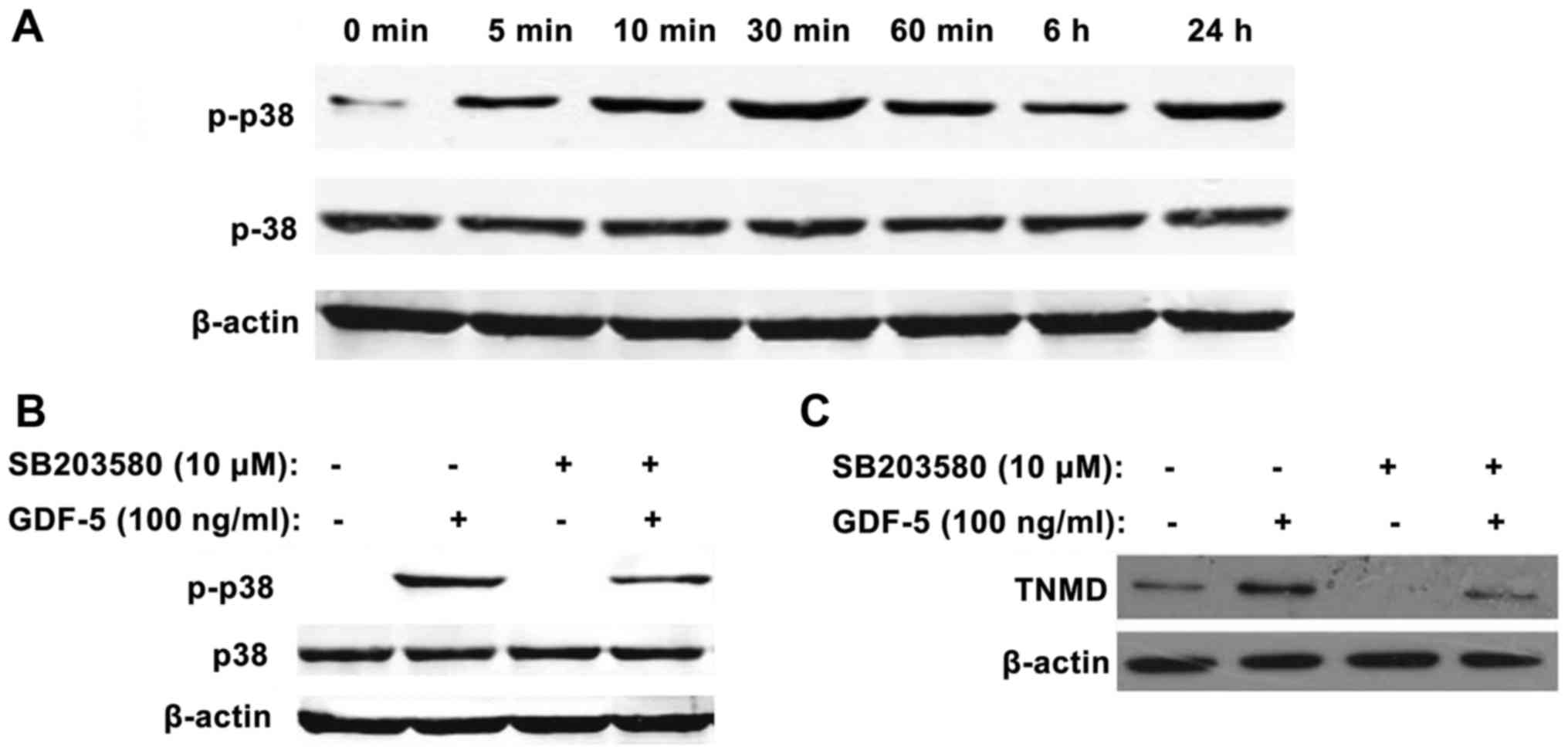
|
1
|
Sharma P and Maffulli N: Biology of tendon
injury: Healing, modeling, and remodeling. J Musculoskelet Neuronal
Interact. 6:181–190. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeFranco MJ, Derwin K and Iannotti JP: New
therapies in tendon reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.
12:298–304. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Park A, Hogan MV, Kesturu GS, James R,
Balian G and Chhabra AB: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
treated with growth differentiation factor-5 express
tendon-specific markers. Tissue Eng Part A. 16:2941–2951. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou S, Yates KE, Eid K and Glowacki J:
Demineralized bone promotes chondrocyte or osteoblast
differentiation of human marrow stromal cells cultured in collagen
sponges. Cell Tissue Bank. 6:33–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B and
Middleton J: Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells: Their
phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and
potential for homing. Stem Cells. 25:2739–2749. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howard D, Buttery LD, Shakesheff KM and
Roberts SJ: Tissue engineering: Strategies, stem cells and
scaffolds. J Anat. 213:66–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
da Silva Meirelles L, Chagastelles PC and
Nardi NB: Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal
organs and tissues. J Cell Sci. 119:2204–2213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu H, Guo ZK, Jiang XX, Li H, Wang XY,
Yao HY, Zhang Y and Mao N: A protocol for isolation and culture of
mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protoc.
5:550–560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oshin AO, Caporali E, Byron CR, Stewart AA
and Stewart MC: Phenotypic maintenance of articular chondrocytes in
vitro requires BMP activity. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 20:185–191.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aspenberg P: Stimulation of tendon repair:
Mechanical loading, GDFs and platelets. A mini-review. Int Orthop.
31:783–789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buxton P, Edwards C, Archer CW and
Francis-West P: Growth/differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) and
skeletal development. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A Suppl 1:S23–S30.
2001.
|
|
12
|
Daans M, Luyten FP and Lories RJ: GDF5
deficiency in mice is associated with instability-driven joint
damage, gait and subchondral bone changes. Ann Rheum Dis.
70:208–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bolt P, Clerk AN, Luu HH, Kang Q, Kummer
JL, Deng ZL, Olson K, Primus F, Montag AG, He TC, et al: BMP-14
gene therapy increases tendon tensile strength in a rat model of
Achilles tendon injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 89:1315–1320. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Docheva D, Hunziker EB, Fässler R and
Brandau O: Tenomodulin is necessary for tenocyte proliferation and
tendon maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 25:699–705. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aslan H, Kimelman-Bleich N, Pelled G and
Gazit D: Molecular targets for tendon neoformation. J Clin Invest.
118:439–444. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shukunami C, Takimoto A, Miura S,
Nishizaki Y and Hiraki Y: Chondromodulin-I and tenomodulin are
differentially expressed in the avascular mesenchyme during mouse
and chick development. Cell Tissue Res. 332:111–122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shukunami C, Takimoto A, Oro M and Hiraki
Y: Scleraxis positively regulates the expression of tenomodulin, a
differentiation marker of tenocytes. Dev Biol. 298:234–247. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pisani DF, Pierson PM, Massoudi A, Leclerc
L, Chopard A, Marini JF and Dechesne CA: Myodulin is a novel
potential angiogenic factor in skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res.
292:40–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shukunami C and Hiraki Y: Chondromodulin-I
and tenomodulin: The negative control of angiogenesis in connective
tissue. Curr Pharm Des. 13:2101–2112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mendias CL, Bakhurin KI and Faulkner JA:
Tendons of myostatin-deficient mice are small, brittle, and
hypocellular. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp. 388–393. 2008;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Popov C, Burggraf M, Kreja L, Ignatius A,
Schieker M and Docheva D: Mechanical stimulation of human tendon
stem/progenitor cells results in upregulation of matrix proteins,
integrins and MMPs and activation of p38 and ERK1/2 kinases. BMC
Mol Biol. 16:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwartz AJ, Sarver DC, Sugg KB,
Dzierzawski JT, Gumucio JP and Mendias CL: p38 MAPK signaling in
postnatal tendon growth and remodeling. PLoS One. 10:e01200442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pereira RF, Halford KW, O' Hara MD, Leeper
DB, Sokolov BP, Pollard MD, Bagasra O and Prockop DJ: Cultured
adherent cells from marrow can serve as long-lasting precursor
cells for bone, cartilage, and lung in irradiated mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:pp. 4857–4861. 1995; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for non hematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Varma MJ, Breuls RG, Schouten TE, Jurgens
WJ, Bontkes HJ, Schuurhuis GJ, van Ham SM and van Milligen FJ:
Phenotypical and functional characterization of freshly isolated
adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 16:91–104. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Phinney DG, Kopen G, Isaacson RL and
Prockop DJ: Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of
commonly used strains of inbred mice: Variations in yield, growth,
and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 72:570–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yin Z, Chen X, Chen JL and Ouyang HW: Stem
cells for tendon tissue engineering and regeneration. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 10:689–700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Farng E, Urdaneta AR, Barba D, Esmende S
and McAllister DR: The effects of GDF-5 and uniaxial strain on
mesenchymal stem cells in 3-D culture. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
466:1930–1937. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakamura K, Shirai T, Morishita S, Uchida
S, Saeki-Miura K and Makishima F: p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase functionally contributes to chondrogenesis induced by
growth/differentiation factor-5 in ATDC5 cells. Exp Cell Res.
250:351–363. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coleman CM and Tuan RS: Functional role of
growth/differentiation factor 5 in chondrogenesis of limb
mesenchymal cells. Mech Dev. 120:823–836. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Watanabe H, de Caestecker MP and Yamada Y:
Transcriptional cross-talk between Smad, ERK1/2 and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways regulates transforming
growth factor-beta-induced aggrecan gene expression in chondrogenic
ATDC5 cells. J Biol Chem. 276:14466–14473. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zaidi SH, Huang Q, Momen A, Riazi A and
Husain M: Growth differentiation factor 5 regulates cardiac repair
after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 55:135–143. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|