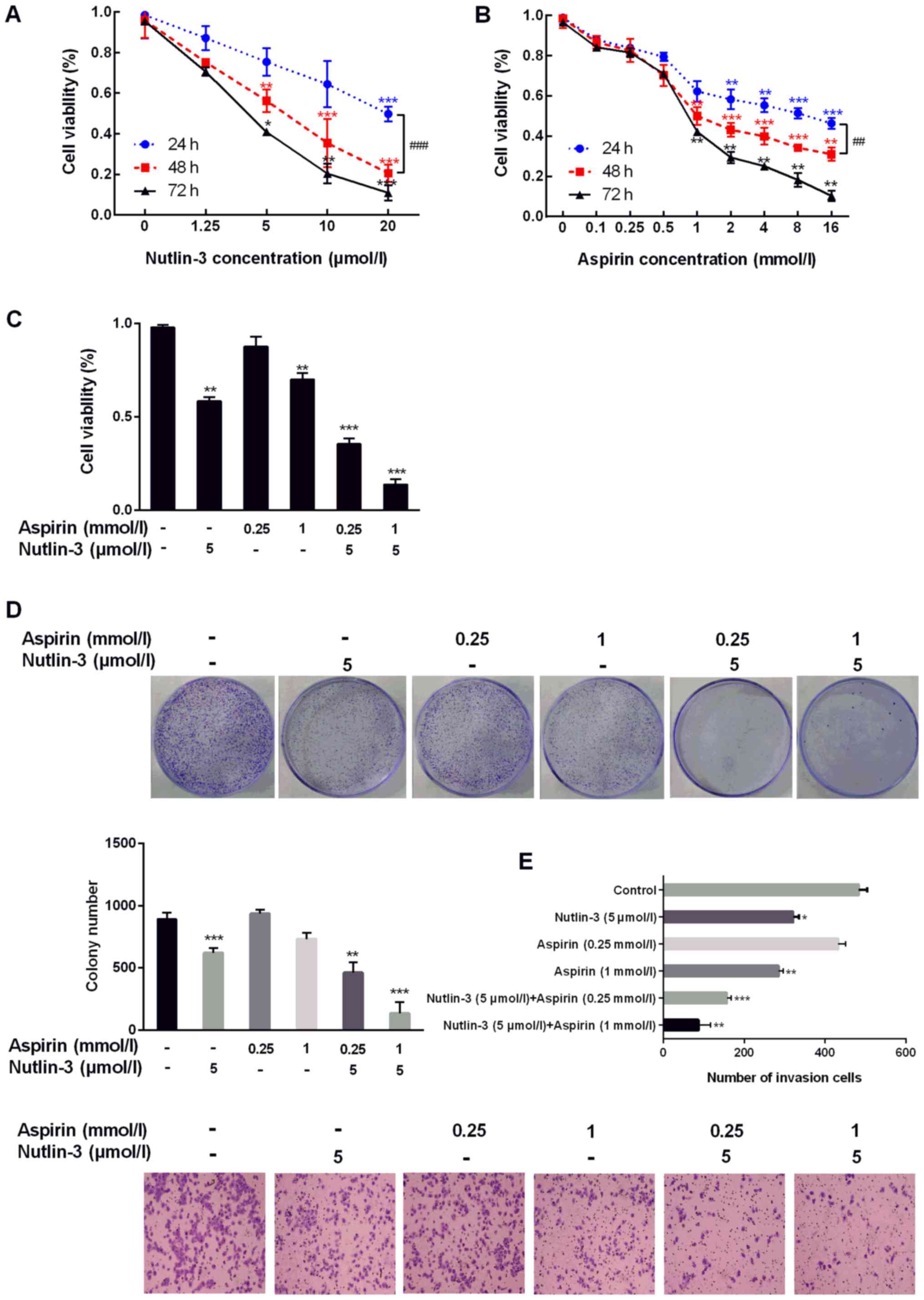
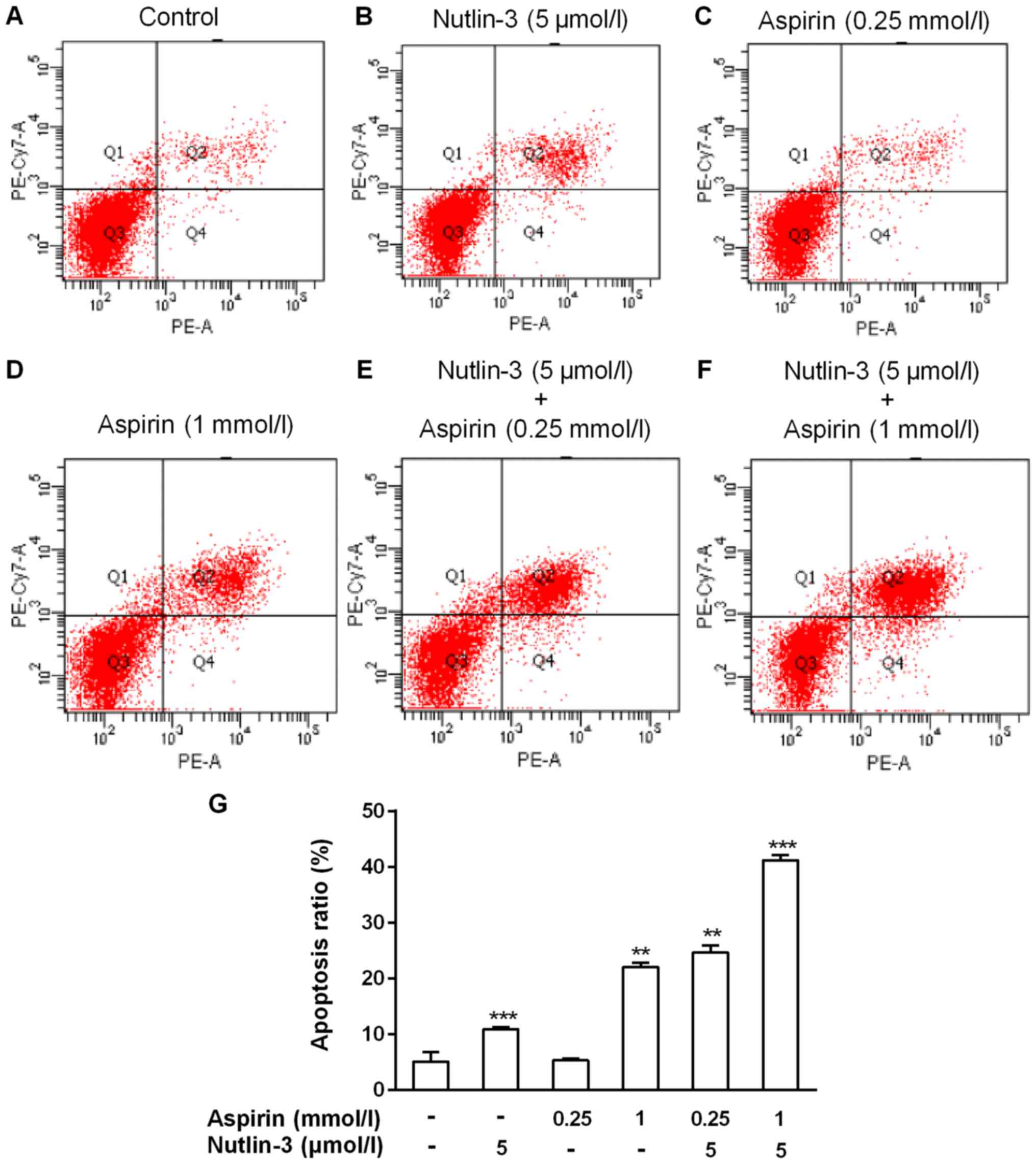
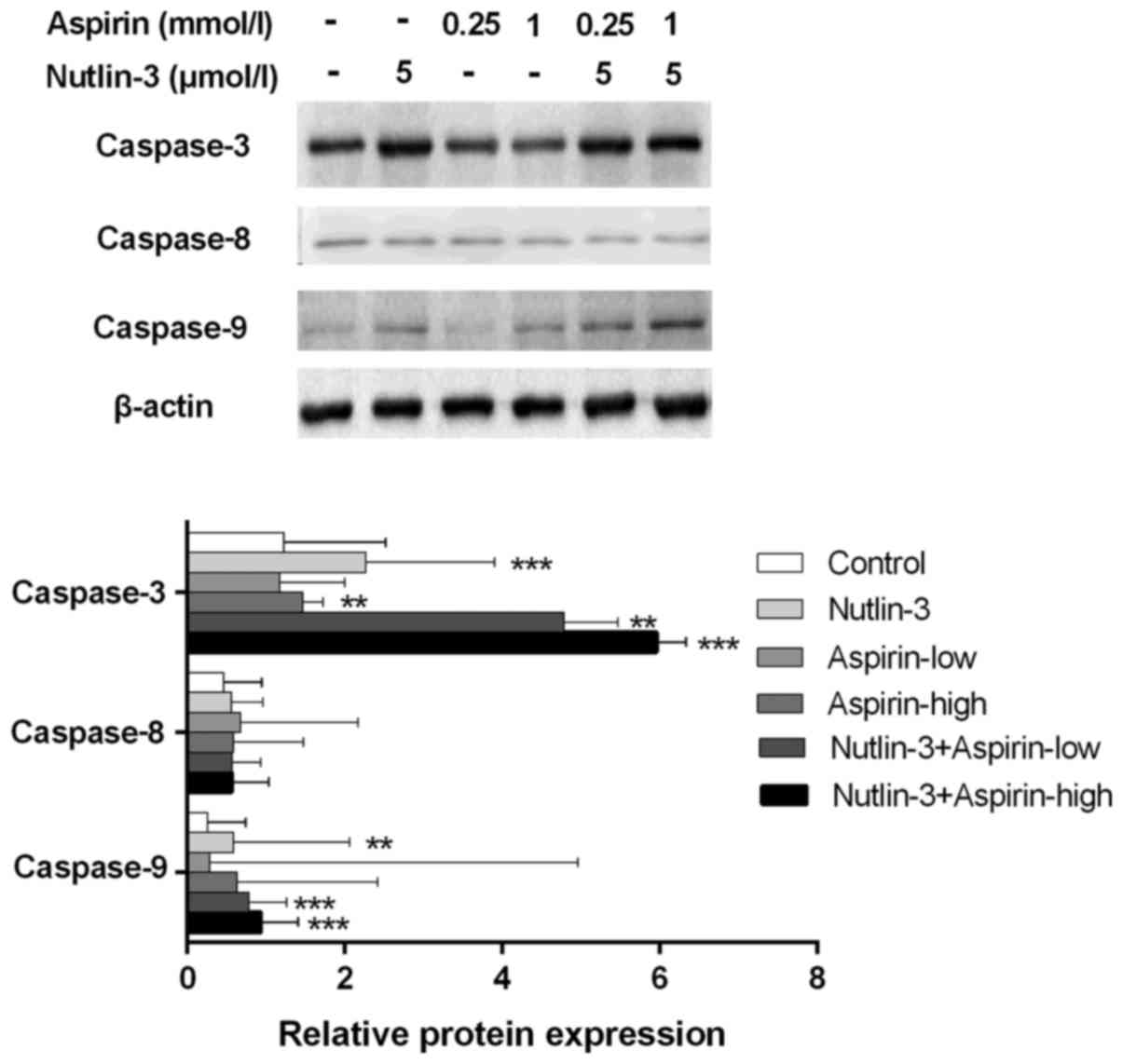
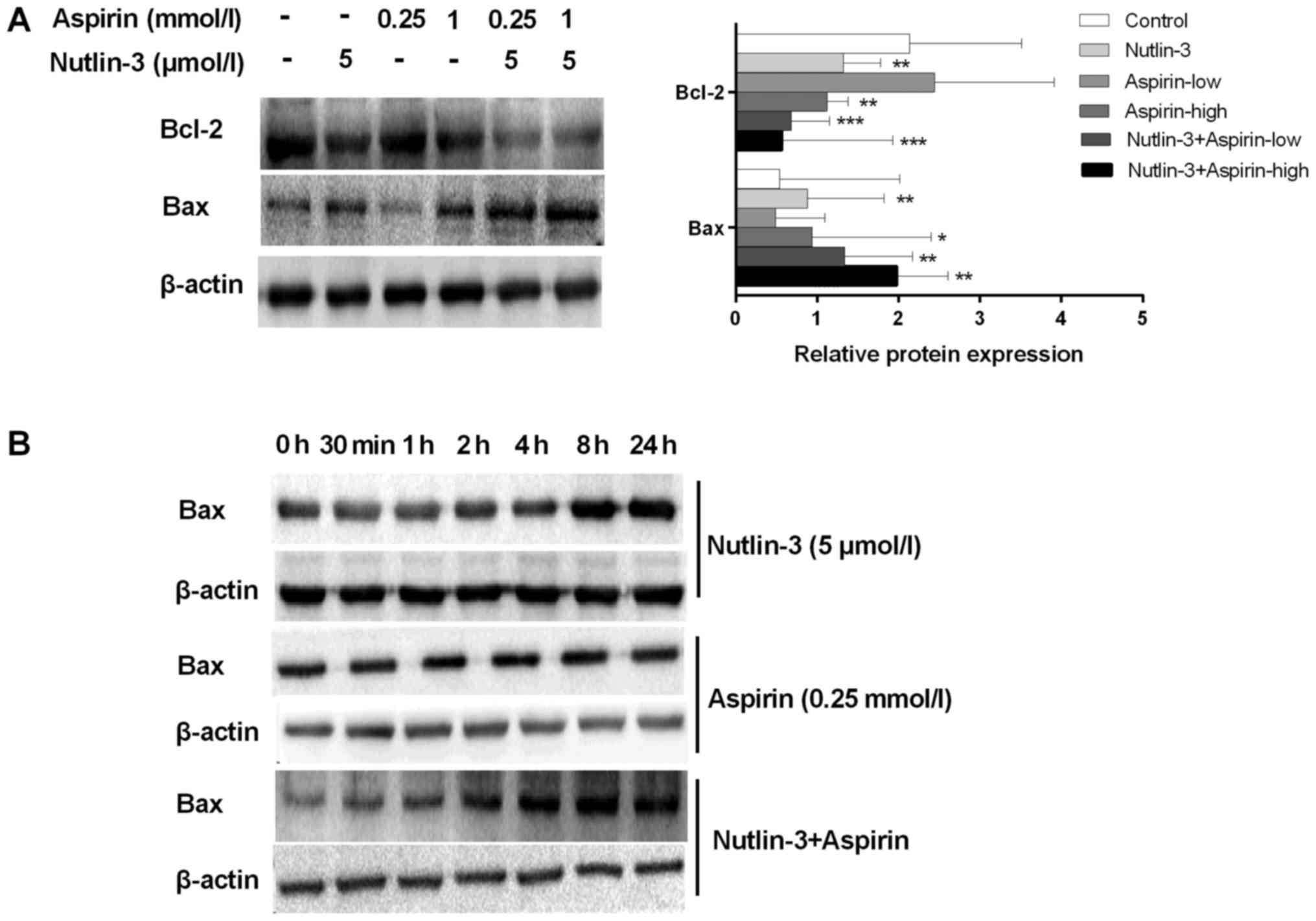
|
1
|
Gish RG: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Overcoming challenges in disease management. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 4:252–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsoulfas G, Agorastou P, Tooulias A and
Marakis GN: Current and future challenges in the surgical treatment
of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Int Surg. 99:779–786. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chattopadhyay M, Kodela R, Nath N,
Barsegian A, Boring D and Kashfi K: Hydrogen sulfide-releasing
aspirin suppresses NF-κB signaling in estrogen receptor negative
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:723–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yiannakopoulou ECh: Aspirin and NSAIDs for
breast cancer chemoprevention. Eur J Cancer Prev. 24:416–421. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Diao Y, Liu Y, Gao N, Gao D, Wan
Y, Zhong J and Jin G: Synergistic apoptosis-inducing effect of
aspirin and isosorbide mononitrate on human colon cancer cells. Mol
Med Rep. 12:4750–4758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xiang S, Sun Z, He Q, Yan F, Wang Y and
Zhang J: Aspirin inhibits ErbB2 to induce apoptosis in cervical
cancer cells. Med Oncol. 27:379–387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen X, Han L, Ma Z, Chen C, Duan W, Yu S,
Li P, Zhang L, Li W, Xu Q and Ma Q: Aspirin: A potential
therapeutic approach in pancreatic cancer. Curr Med Chem.
20:4153–4162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu JF, Jamieson GG, Wu TC, Zhu GJ and
Drew PA: A preliminary study on the postoperative survival of
patients given aspirin after resection for squamous cell carcinoma
of the esophagus or adenocarcinoma of the cardia. Ann Surg Oncol.
16:1397–1402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mc Menamin ÚC, Cardwell CR, Hughes CM and
Murray LJ: Low-dose aspirin use and survival in breast cancer
patients: A nationwide cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. 47:20–27.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Frouws MA, Bastiaannet E, Langley RE, Chia
WK, van Herk-Sukel MP, Lemmens VE, Putter H, Hartgrink HH, Bonsing
BA, Van de Velde CJ, et al: Effect of low-dose aspirin use on
survival of patients with gastrointestinal malignancies; an
observational study. Br J Cancer. 116:405–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kastrati I, Litosh VA, Zhao S, Alvarez M,
Thatcher GR and Frasor J: A novel aspirin prodrug inhibits NFκB
activity and breast cancer stem cell properties. BMC Cancer.
15:8452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rao CV, Reddy BS, Steele VE, Wang CX, Liu
X, Ouyang N, Patlolla JM, Simi B, Kopelovich L and Rigas B: Nitric
oxide-releasing aspirin and indomethacin are potent inhibitors
against colon cancer in azoxymethane-treated rats: Effects on
molecular targets. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1530–1538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bhat IA, Rasool R, Qasim I, Masoodi KZ,
Paul SA, Bhat BA, Ganaie FA, Aziz SA and Shah ZA: COX-2
overexpression and −8473 T/C polymorphism in 3′UTR in non-small
cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:11209–11218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buskens CJ, Ristimäki A, Offerhaus GJ,
Richel DJ and van Lanschot JJ: Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the
development and treatment of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Scand J
Gastroenterol Suppl. 1–93. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh Ranger G: The role of aspirin in
colorectal cancer chemoprevention. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
104:87–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sciulli MG, Filabozzi P, Tacconelli S,
Padovano R, Ricciotti E, Capone ML, Grana M, Carnevale V and
Patrignani P: Platelet activation in patients with colorectal
cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 72:79–83. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Polanski R, Noon AP, Blaydes J, Phillips
A, Rubbi CP, Parsons K, Vlatković N and Boyd MT: Senescence
induction in renal carcinoma cells by Nutlin-3: A potential
therapeutic strategy based on MDM2 antagonism. Cancer Lett.
353:211–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shangary S and Wang S: Small-molecule
inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction to
reactivate p53 function: A novel approach for cancer therapy. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 49:223–241. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang P, Chen W, Li X, Eilers G, He Q, Liu
L, Wu Y, Wu Y, Yu W, Fletcher JA and Ou WB: Downregulation of
cyclin D1 sensitizes cancer cells to MDM2 antagonist Nutlin-3.
Oncotarget. 7:32652–32663. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pechackova S, Burdova K, Benada J,
Kleiblova P, Jenikova G and Macurek L: Inhibition of WIP1
phosphatase sensitizes breast cancer cells to genotoxic stress and
to MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3. Oncotarget. 7:14458–14475. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghassemifar S and Mendrysa SM: MDM2
antagonism by nutlin-3 induces death in human medulloblastoma
cells. Neurosci Lett. 513:106–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Secchiero P, Bosco R, Celeghini C and
Zauli G: Recent advances in the therapeutic perspectives of
Nutlin-3. Curr Pharm Des. 17:569–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Endo S, Yamato K, Hirai S, Moriwaki T,
Fukuda K, Suzuki H, Abei M, Nakagawa I and Hyodo I: Potent in vitro
and in vivo antitumor effects of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 in gastric
cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 102:605–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zanjirband M, Edmondson RJ and Lunec J:
Pre-clinical efficacy and synergistic potential of the MDM2-p53
antagonists, Nutlin-3 and RG7388, as single agents and in combined
treatment with cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
7:40115–40134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng T, Yin D, Lu Z, Wang J, Li Y, Chen
X, Liang Y, Song X, Qi S, Sun B, et al: Nutlin-3 overcomes arsenic
trioxide resistance and tumor metastasis mediated by mutant p53 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shao QS, Ye ZY, Ling ZQ and Ke JJ: Cell
cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death in cultured human gastric
carcinoma cells mediated by arsenic trioxide. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:3451–3456. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi X, Liu J, Ren L, Mao N, Tan F, Ding N,
Yang J and Li M: Nutlin-3 downregulates p53 phosphorylation on
serine392 and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
BMB Rep. 47:221–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Zheng T, Chen X, Song X, Meng X,
Bhatta N, Pan S, Jiang H and Liu L: MDM2 antagonist can inhibit
tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma with different types of
p53 in vitro. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:371–377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aden DP, Fogel A, Plotkin S, Damjanov I
and Knowles BB: Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated
human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 282:615–616. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Human
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tougeron D, Sha D, Manthravadi S and
Sinicrope FA: Aspirin and colorectal cancer: Back to the future.
Clin Cancer Res. 20:1087–1094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maity G, De A, Das A, Banerjee S, Sarkar S
and Banerjee SK: Aspirin blocks growth of breast tumor cells and
tumor-initiating cells and induces reprogramming factors of
mesenchymal to epithelial transition. Lab Invest. 95:702–717. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Shen C, Ge J and Duan H: Regular
aspirin use and stomach cancer risk in China. Eur J Surg Oncol.
41:801–804. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin HY, Delmas D, Vang O, Hsieh TC, Lin S,
Cheng GY, Chiang HL, Chen CE, Tang HY, Crawford DR, et al:
Mechanisms of ceramide-induced COX-2-dependent apoptosis in human
ovarian cancer OVCAR-3 cells partially overlapped with resveratrol.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1940–1954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu L, Stevens J, Hilton MB, Seaman S,
Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Logsdon D, Morris H, Swing DA, Patel NL,
et al: COX-2 inhibition potentiates antiangiogenic cancer therapy
and prevents metastasis in preclinical models. Sci Transl Med.
6:242ra842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cronin-Fenton DP, Heide-Jørgensen U, Ahern
TP, Lash TL, Christiansen P, Ejlertsen B and Sørensen HT: Low-dose
aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, selective COX-2
inhibitors and breast cancer recurrence. Epidemiology. 27:586–593.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Santilli F, Boccatonda A and Davi G:
Aspirin, platelets, and cancer: The point of view of the internist.
Eur J Intern Med. 34:11–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qin HX, Yang J, Cui HK, Li SP, Zhang W,
Ding XL and Xia YH: Synergistic antitumor activity of reversine
combined with aspirin in cervical carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.
Cytotechnology. 65:643–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shu Y, Liu Y, Li X, Cao L, Yuan X, Li W
and Cao Q: Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced
EndMT through increasing the expression of smad7 and is closely
related to oxidative stress. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 24:132–139. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li T, Dong ZR, Guo ZY, Wang CH, Tang ZY,
Qu SF, Chen ZT, Li XW and Zhi XT: Aspirin enhances IFN-α-induced
growth inhibition and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
JAK1/STAT1 pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 20:366–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ding JH, Yuan LY, Huang RB and Chen GA:
Aspirin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of multiple
myeloma cells through regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax and suppression
of VEGF. Eur J Haematol. 93:329–339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SY, Choi HC, Choe YJ, Shin SJ, Lee SH
and Kim HS: Nutlin-3 induces BCL2A1 expression by activating ELK1
through the mitochondrial p53-ROS-ERK1/2 pathway. Int J Oncol.
45:675–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SY, Choe YJ, Park JY, Lee SS, Kim YH,
Shin SJ, Chung YJ and Kim HS: Wilms' tumor gene 1 enhances
nutlin-3-induced apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 31:131–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Patrono C, Coller B, Dalen JE, Fuster V,
Gent M, Harker LA, Hirsh J and Roth G: Platelet-active drugs: The
relationships among dose, effectiveness, and side effects. Chest.
114 5 Suppl:470S–488S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jonsson F, Yin L, Lundholm C, Smedby KE,
Czene K and Pawitan Y: Low-dose aspirin use and cancer
characteristics: A population-based cohort study. Br J Cancer.
109:1921–1925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Flossmann E and Rothwell PM: British
Doctors Aspirin Trial and the UK-TIA Aspirin Trial: Effect of
aspirin on long-term risk of colorectal cancer: Consistent evidence
from randomised and observational studies. Lancet. 369:1603–1613.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lu L, Sun HC, Zhang W, Chai ZT, Zhu XD,
Kong LQ, Wang WQ, Zhang KZ, Zhang YY, Zhang QB, et al: Aspirin
minimized the pro-metastasis effect of sorafenib and improved
survival by up-regulating HTATIP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS
One. 8:e650232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|