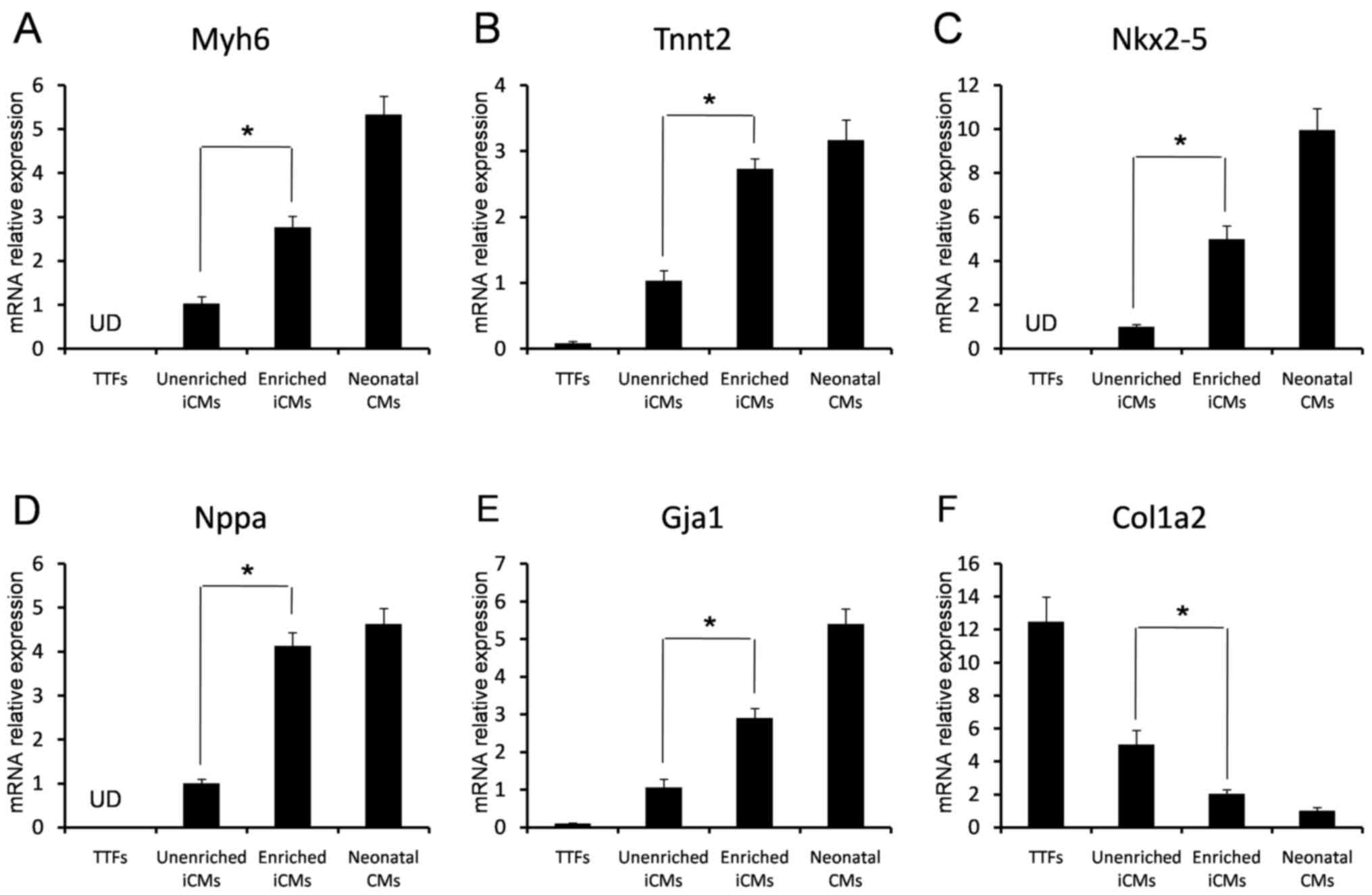
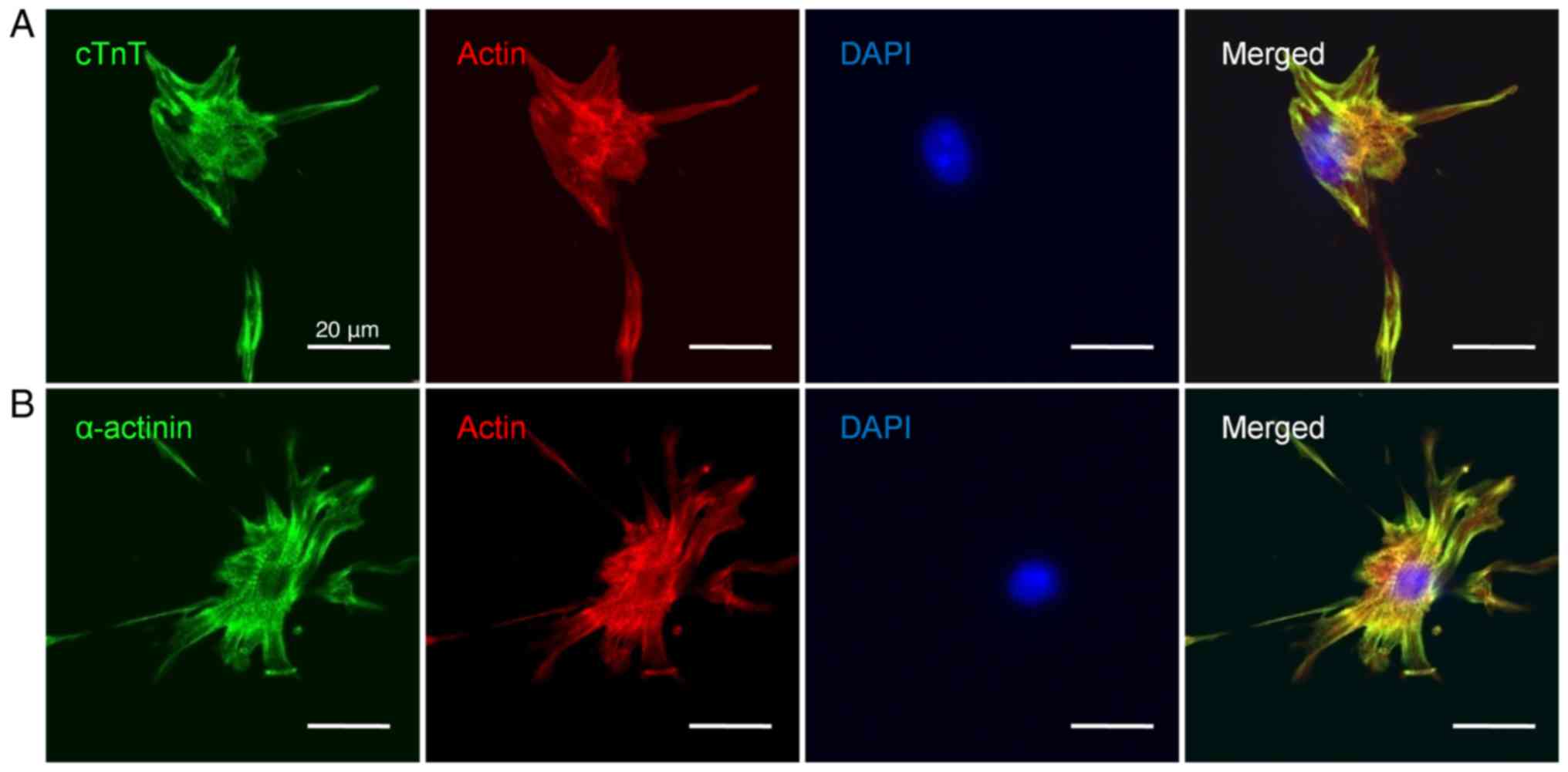
|
1
|
Malliaras K and Marbán E: Cardiac cell
therapy: Where we've been, where we are, and where we should be
headed. Br Med Bull. 98:161–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimmermann WH: Remuscularizing failing
hearts with tissue engineered myocardium. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:2011–2023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laflamme MA and Murry CE: Regenerating the
heart. Nat Biotechnol. 23:845–856. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zimmermann WH and Eschenhagen T: Embryonic
stem cells for cardiac muscle engineering. Trends Cardiovasc Med.
17:134–140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He W, Ye L, Li S, Liu H, Wu B, Wang Q, Fu
X, Han W and Chen Z: Construction of vascularized cardiac tissue
from genetically modified mouse embryonic stem cells. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 31:204–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J
and Melton DA: In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine
cells to beta-cells. Nature. 455:627–632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ieda M, Fu JD, Delgado-Olguin P, Vedantham
V, Hayashi Y, Bruneau BG and Srivastava D: Direct reprogramming of
fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors.
Cell. 142:375–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP,
Kokubu Y, Südhof TC and Wernig M: Direct conversion of fibroblasts
to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 463:1035–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sekiya S and Suzuki A: Direct conversion
of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors.
Nature. 475:390–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Szabo E, Rampalli S, Risueño RM, Schnerch
A, Mitchell R, Fiebig-Comyn A, Levadoux-Martin M and Bhatia M:
Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to multilineage blood
progenitors. Nature. 468:521–526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takeuchi JK and Bruneau BG: Directed
transdifferentiation of mouse mesoderm to heart tissue by defined
factors. Nature. 459:708–711. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jayawardena TM, Egemnazarov B, Finch EA,
Zhang L, Payne JA, Pandya K, Zhang Z, Rosenberg P, Mirotsou M and
Dzau VJ: MicroRNA-mediated in vitro and in vivo direct
reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts to cardiomyocytes. Circ Res.
110:1465–1473. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qian L, Huang Y, Spencer CI, Foley A,
Vedantham V, Liu L, Conway SJ, Fu JD and Srivastava D: In vivo
reprogramming of murine cardiac fibroblasts into induced
cardiomyocytes. Nature. 485:593–598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song K, Nam YJ, Luo X, Qi X, Tan W, Huang
GN, Acharya A, Smith CL, Tallquist MD, Neilson EG, et al: Heart
repair by reprogramming non-myocytes with cardiac transcription
factors. Nature. 485:599–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen JX, Krane M, Deutsch MA, Wang L,
Rav-Acha M, Gregoire S, Engels MC, Rajarajan K, Karra R, Abel ED,
et al: Inefficient reprogramming of fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes
using Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. Circ Res. 111:50–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chien KR, Yi BA, Xu H and Mummery CL:
Cardiomyocyte reprogramming and the new age of cellular alchemy. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 53:311–313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Braam SR, Passier R and Mummery CL:
Cardiomyocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in regenerative
medicine and drug discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:536–545.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He W, Ye L, Li S, Liu H, Wang Q, Fu X, Han
W and Chen Z: Stirred suspension culture improves embryoid body
formation and cardiogenic differentiation of genetically modified
embryonic stem cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:308–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Doppler SA, Deutsch MA, Lange R and Krane
M: Direct reprogramming-the future of cardiac regeneration? Int J
Mol Sci. 16:17368–17393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nam YJ, Song K, Luo X, Daniel E, Lambeth
K, West K, Hill JA, DiMaio JM, Baker LA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson
EN: Reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a cardiac fate. Proc
Natl AcadSci USA. 110:pp. 5588–5593. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Olson EN: Gene regulatory networks in the
evolution and development of the heart. Science. 313:1922–1927.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Srivastava D: Making or breaking the
heart: From lineage determination to morphogenesis. Cell.
126:1037–1048. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cirillo LA, Lin FR, Cuesta I, Friedman D,
Jarnik M and Zaret KS: Opening of compacted chromatin by early
developmental transcription factors HNF3 (FoxA) and GATA-4. Mol
Cell. 9:279–289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Srivastava D, Thomas T, Lin Q, Kirby ML,
Brown D and Olson EN: Regulation of cardiac mesodermal and neural
crest development by the bHLH transcription factor, dHAND. Nat
Genet. 16:154–160. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsuchihashi T, Maeda J, Shin CH, Ivey KN,
Black BL, Olson EN, Yamagishi H and Srivastava D: Hand2 function in
second heart field progenitors is essential for cardiogenesis. Dev
Biol. 351:62–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yelon D, Ticho B, Halpern ME, Ruvinsky I,
Ho RK, Silver LM and Stainier DY: The bHLH transcription factor
hand2 plays parallel roles in zebrafish heart and pectoral fin
development. Development. 127:2573–2582. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schoenebeck JJ, Keegan BR and Yelon D:
Vessel and blood specification override cardiac potential in
anterior mesoderm. Dev Cell. 13:254–267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schindler YL, Garske KM, Wang J, Firulli
BA, Firulli AB, Poss KD and Yelon D: Hand2 elevates cardiomyocyte
production during zebrafish heart development and regeneration.
Development. 141:3112–3122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Efe JA, Hilcove S, Kim J, Zhou H, Ouyang
K, Wang G, Chen J and Ding S: Conversion of mouse fibroblasts into
cardiomyocytes using a direct reprogramming strategy. Nat Cell
Biol. 13:215–222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meshorer E, Yellajoshula D, George E,
Scambler PJ, Brown DT and Misteli T: Hyperdynamic plasticity of
chromatin proteins in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Dev Cell.
10:105–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hochedlinger K and Plath K: Epigenetic
reprogramming and induced pluripotency. Development. 136:509–523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Artyomov MN, Meissner A and Chakraborty
AK: A model for genetic and epigenetic regulatory networks
identifies rare pathways for transcription factor induced
pluripotency. PLoS Comput Biol. 6:e10007852010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cohen ED, Tian Y and Morrisey EE: Wnt
signaling: An essential regulator of cardiovascular
differentiation, morphogenesis and progenitor self-renewal.
Development. 135:789–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Developmental
signaling in myocardial progenitor cells: A comprehensive view of
Bmp- and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PediatrCardiol. 30:609–616.
2009.
|
|
38
|
Xu C, Police S, Rao N and Carpenter MK:
Characterization and enrichment of cardiomyocytes derived from
human embryonic stem cells. Circ Res. 91:501–508. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
E LL, Zhao YS, Guo XM, Wang CY, Jiang H,
Li J, Duan CM and Song Y: Enrichment of cardiomyocytes derived from
mouse embryonic stem cells. J Heart Lung Transplant. 25:664–674.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|