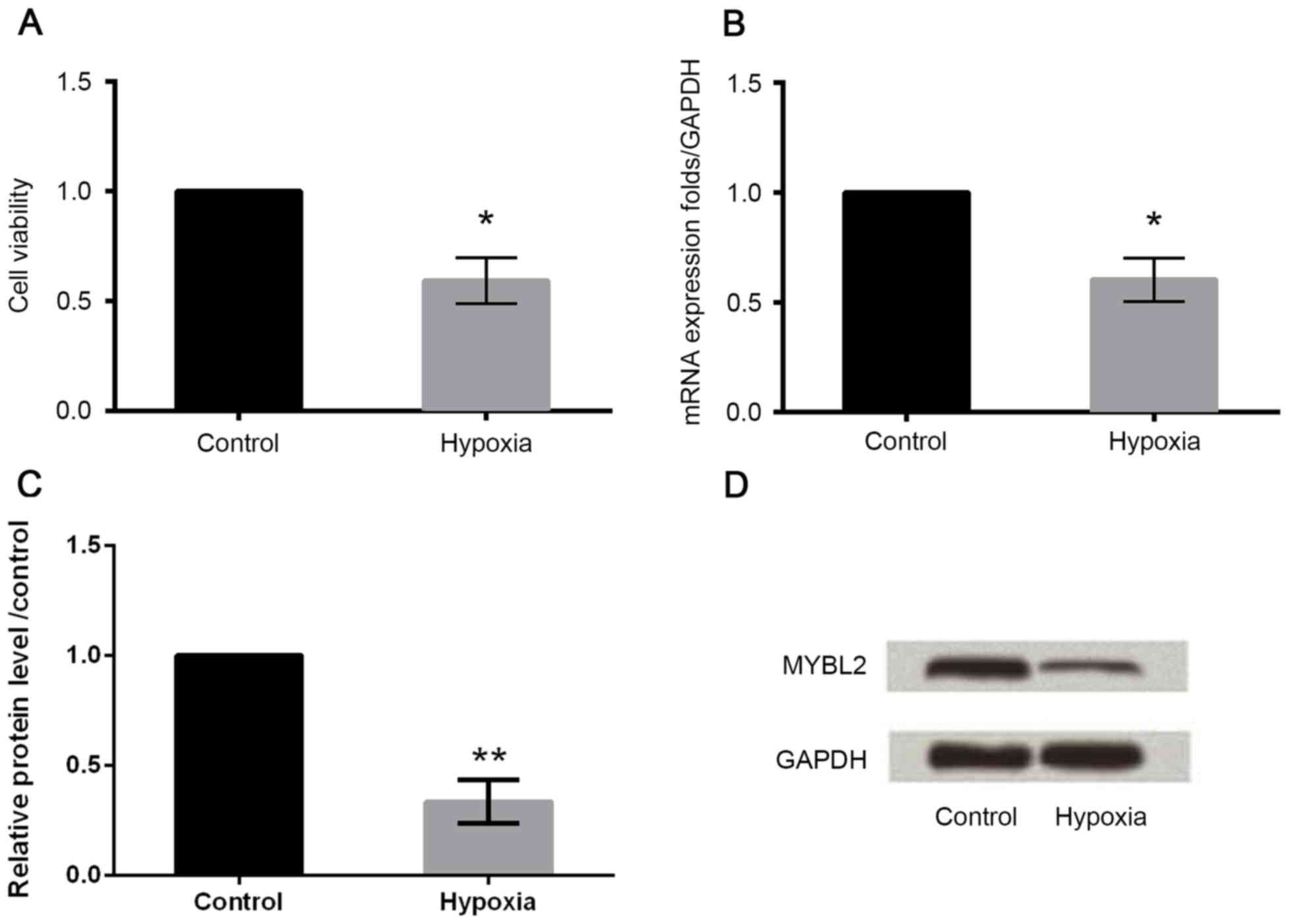
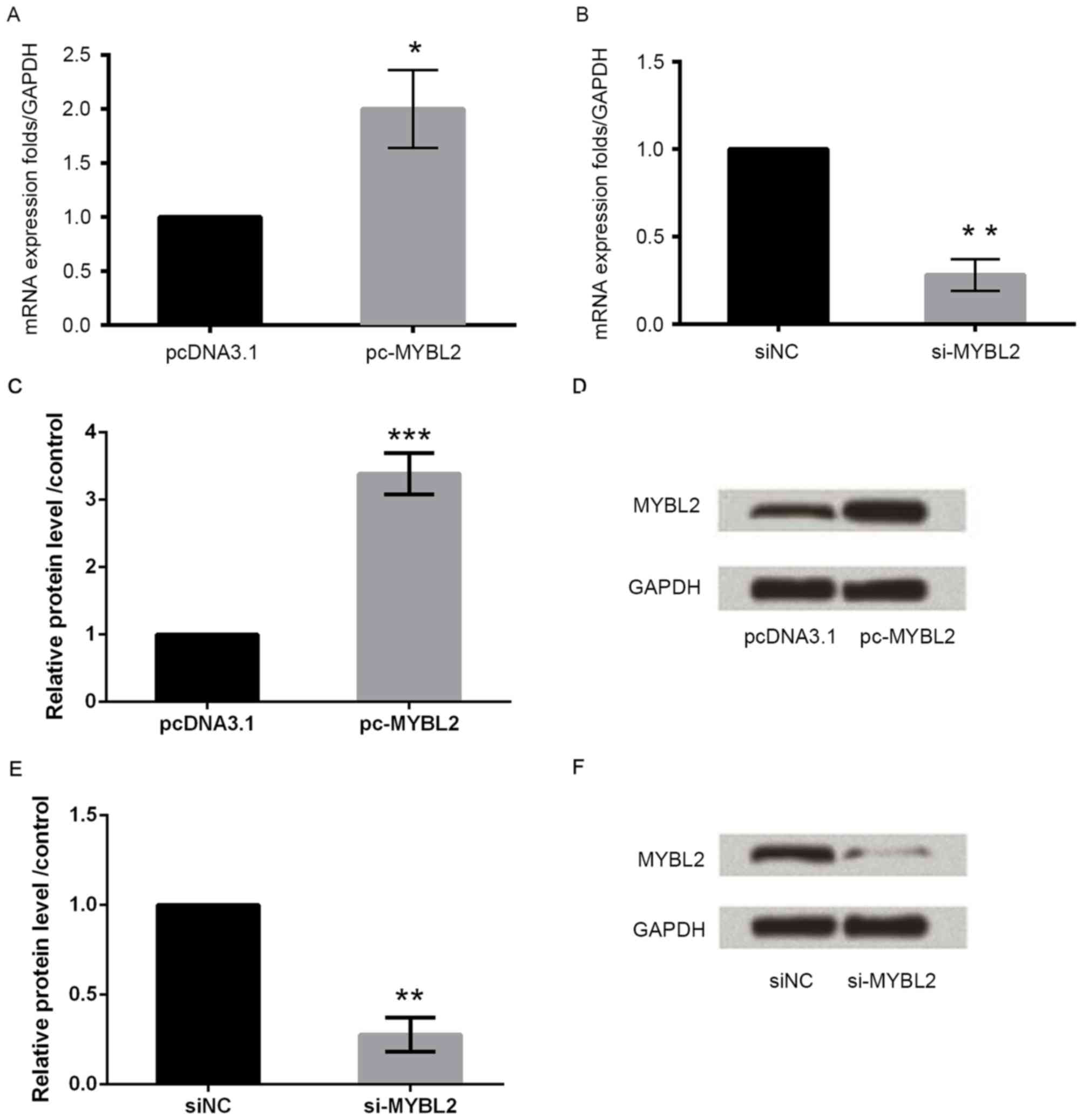
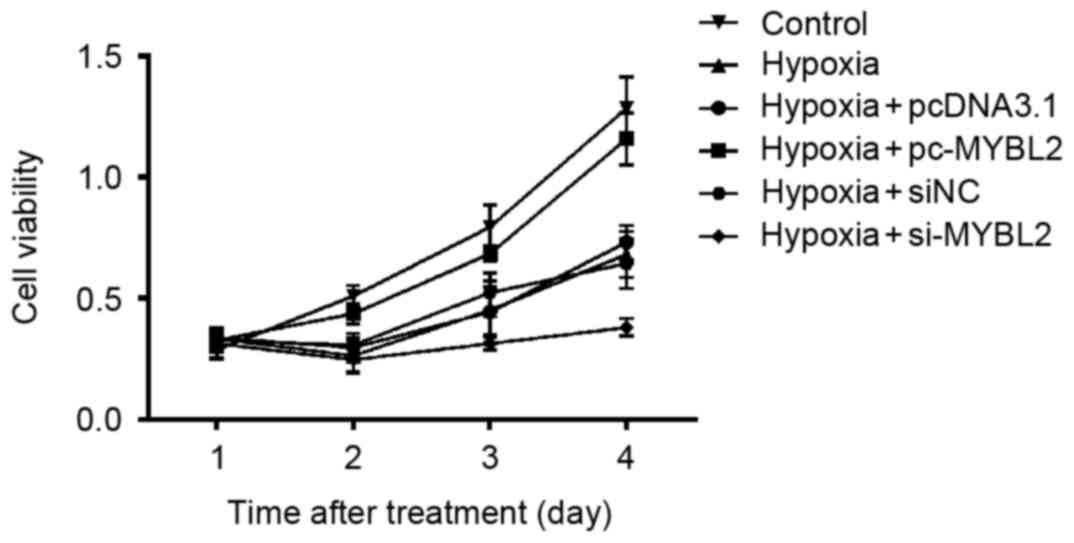
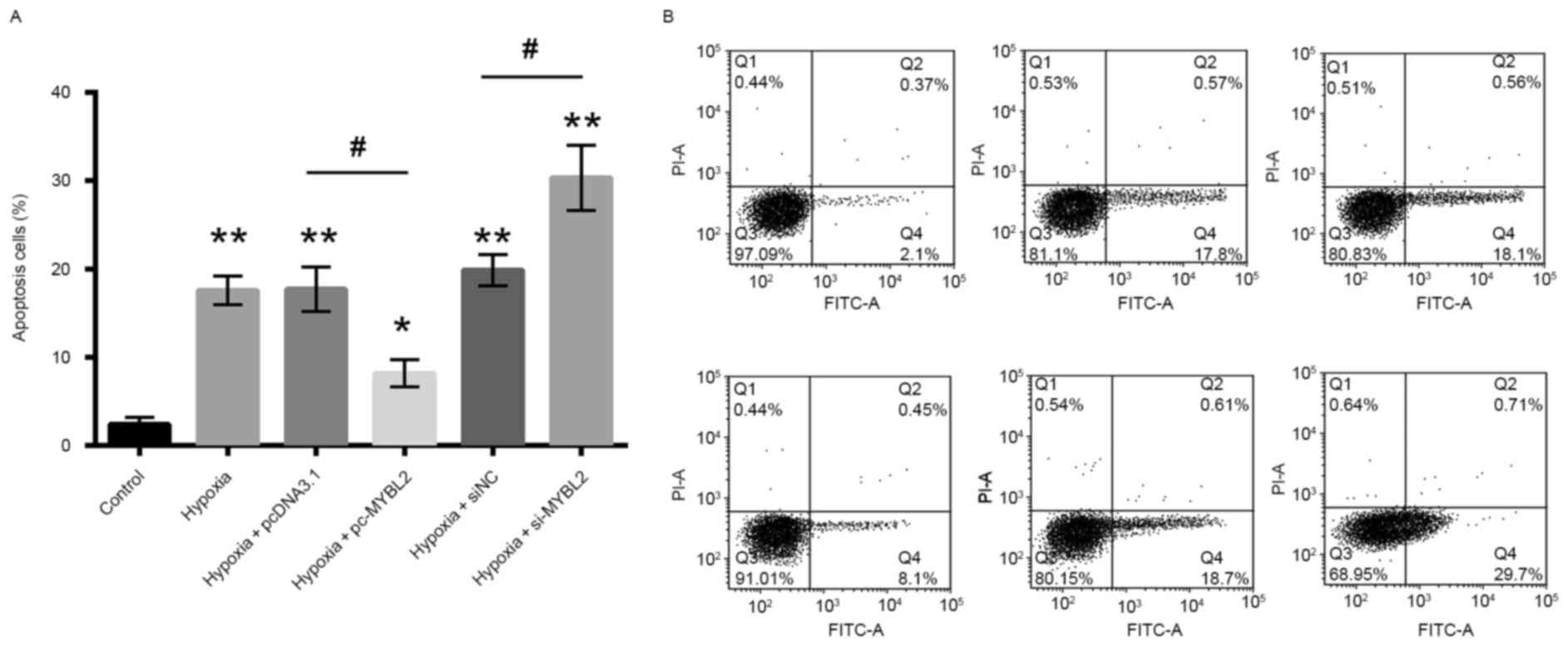
|
1
|
Writing Group Members, ; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, et al: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart
association. Circulation. 133:e38–360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Silva H, Freitas J, Moreira S, Santos A
and Almeida V: Alexithymia and psychopathology in patients with
acute myocardial infarction. Acta Cardiol. 71:213–220. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Taniyama Y, Katsuragi N, Sanada F, Azuma
J, Iekushi K, Koibuchi N, Okayama K, Ikeda-Iwabu Y, Muratsu J, Otsu
R, et al: Selective blockade of periostin exon 17 preserves cardiac
performance in acute myocardial infarction. Hypertension.
67:356–361. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun G, Ye N, Dai D, Chen Y, Li C and Sun
Y: The protective role of the TOPK/PBK pathway in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion and H2O2-induced injury
in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 17:2672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hearse DJ and Bolli R: Reperfusion induced
injury: Manifestations, mechanisms, and clinical relevance.
Cardiovasc Res. 26:101–108. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sandberg ML, Sutton SE, Pletcher MT,
Wiltshire T, Tarantino LM, Hogenesch JB and Cooke MP: c-Myb and
p300 regulate hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and
differentiation. Dev Cell. 8:153–166. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malaterre J, Carpinelli M, Ernst M,
Alexander W, Cooke M, Sutton S, Dworkin S, Heath JK, Frampton J,
McArthur G, et al: c-Myb is required for progenitor cell
homeostasis in colonic crypts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp.
3829–3834. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malaterre J, Mantamadiotis T, Dworkin S,
Lightowler S, Yang Q, Ransome MI, Turnley AM, Nichols NR, Emambokus
NR, Frampton J and Ramsay RG: c-Myb is required for neural
progenitor cell proliferation and maintenance of the neural stem
cell niche in adult brain. Stem Cells. 26:173–181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanaka Y, Patestos NP, Maekawa T and Ishii
S: B-myb is required for inner cell mass formation at an early
stage of development. J Biol Chem. 274:28067–28070. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhan M, Riordon DR, Yan B, Tarasova YS,
Bruweleit S, Tarasov KV, Li RA, Wersto RP and Boheler KR: The B-MYB
transcriptional network guides cell cycle progression and fate
decisions to sustain self-renewal and the identity of pluripotent
stem cells. PloS One. 7:e423502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Papetti M and Augenlicht LH: MYBL2, a link
between proliferation and differentiation in maturing colon
epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 226:785–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hibi K, Liu Q, Beaudry GA, Madden SL,
Westra WH, Wehage SL, Yang SC, Heitmiller RF, Bertelsen AH,
Sidransky D and Jen J: Serial analysis of gene expression in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 58:5690–5694.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calvisi DF, Simile MM, Ladu S, Frau M,
Evert M, Tomasi ML, Demartis MI, Daino L, Seddaiu MA, Brozzetti S,
et al: Activation of v-Myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene
homolog-like2 (MYBL2)-LIN9 complex contributes to human
hepatocarcinogenesis and identifies a subset of hepatocellular
carcinoma with mutant p53. Hepatology. 53:1226–1236. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Forozan F, Mahlamäki EH, Monni O, Chen Y,
Veldman R, Jiang Y, Gooden GC, Ethier SP, Kallioniemi A and
Kallioniemi OP: Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of 38
breast cancer cell lines: A basis for interpreting complementary
DNA microarray data. Cancer Res. 60:4519–4525. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ekhterae D, Lin Z, Lundberg MS, Crow MT,
Brosius FC III and Nunez G: ARC inhibits cytochrome c release from
mitochondria and protects against hypoxia-induced apoptosis in
heart-derived H9c2 cells. Circ Res. 85:e70–e77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirst M: Gene targeting: A practical
approach. J Med Genet. 31:8211994. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakajima T, Yasui K, Zen K, Inagaki Y,
Fujii H, Minami M, Tanaka S, Taniwaki M, Itoh Y, Arii S, et al:
Activation of B-Myb by E2F1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology
Res. 38:886–895. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Parikh N, Hilsenbeck S, Creighton CJ,
Dayaram T, Shuck R, Shinbrot E, Xi L, Gibbs RA, Wheeler DA and
Donehower LA: Effects of TP53 mutational status on gene expression
patterns across 10 human cancer types. J Pathol. 232:522–533. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fuster O, Llop M, Dolz S, García P, Such
E, Ibáñez M, Luna I, Gómez I, López M, Cervera J, et al: Adverse
prognostic value of MYBL2 overexpression and association with
microRNA-30 family in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leuk Res.
37:1690–1696. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thorner AR, Hoadley KA, Parker JS, Winkel
S, Millikan RC and Perou CM: In vitro and in vivo analysis of B-Myb
in basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene. 28:742–751. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gualdrini F, Corvetta D, Cantilena S,
Chayka O, Tanno B, Raschellà G and Sala A: Addiction of MYCN
amplified tumours to B-MYB underscores a reciprocal regulatory
loop. Oncotarget. 1:278–288. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frau M, Ladu S, Calvisi DF, Simile MM,
Bonelli P, Daino L, Tomasi ML, Seddaiu MA, Feo F and Pascale RM:
Mybl2 expression is under genetic control and contributes to
determine a hepatocellular carcinoma susceptible phenotype. J
Hepatol. 55:111–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi H, Bevier M, Johansson R,
Enquist-Olsson K, Henriksson R, Hemminki K, Lenner P and Försti A:
Prognostic impact of polymorphisms in the MYBL2 interacting genes
in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:1039–1047. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grassilli E, Salomoni P, Perrotti D,
Franceschi C and Calabretta B: Resistance to apoptosis in CTLL-2
cells overexpressing B-Myb is associated with B-Myb-dependent bcl-2
induction. Cancer Res. 59:2451–2456. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V and
Chariot A: Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins:
Implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:43–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Checker R, Patwardhan RS, Sharma D, Menon
J, Thoh M, Bhilwade HN, Konishi T and Sandur SK: Schisandrin B
exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through modulation of the
redox-sensitive transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB. Free Radic
Biol Med. 53:1421–1430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu J, Nakano H, Sakurai H and Colburn NH:
Insufficient p65 phosphorylation at S536 specifically contributes
to the lack of NF-kappaB activation and transformation in resistant
JB6 cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:1991–2003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, Park S,
Kanno T, Brown K and Siebenlist U: The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly
transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with
DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 72:729–739. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Massoumi R, Chmielarska K, Hennecke K,
Pfeifer A and Fässler R: Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by
blocking Bcl-3-Dependent NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 125:665–677.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rocha S, Martin AM, Meek DW and Perkins
ND: p53 represses cyclin D1 transcription through down regulation
of Bcl-3 and inducing increased association of the p52 NF-kappaB
subunit with histone deacetylase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 23:4713–4727.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Westerheide SD, Mayo MW, Anest V, Hanson
JL and Baldwin AS Jr: The putative oncoprotein Bcl-3 induces cyclin
D1 to stimulate G(1) transition. Mol Cell Biol. 21:8428–8436. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang HJ, Jung TW, Hong HC, Choi HY, Seo
JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH and Yoo HJ:
Progranulin protects vascular endothelium against atherosclerotic
inflammatory reaction via Akt/eNOS and nuclear factor-κB pathways.
PloS One. 8:e766792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guha M and Mackman N: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway limits lipopolysaccharide
activation of signaling pathways and expression of inflammatory
mediators in human monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 277:32124–32132.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Timmers L, Henriques JP, de Kleijn DP,
Devries JH, Kemperman H, Steendijk P, Verlaan CW, Kerver M, Piek
JJ, Doevendans PA, et al: Exenatide reduces infarct size and
improves cardiac function in a porcine model of ischemia and
reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 53:501–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|