Introduction
Synthetic angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)
inhibitory (ACEI) drugs, including captopril, lisinopril, enalapril
and ramipril, are effective to treat cardiovascular disease.
However, side effects accompany the application of these drugs,
including proteinuria, altered sense of taste, allergic skin
rashes, cough and drug fever (1).
Isolation of effective natural ACEI peptides from diets or crops is
an attractive prospect. A series of ACEI peptides derived from food
protein sources have been identified, including from fermented
milk, cheddar cheeses (2), hen egg
white (3), tuna (4), rice (5), soybean (6), peanut meal (7), skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin
gelatin (8), flaxseed (9) and pumpkin (10). These ACEI peptides were commonly
collected using proteolytic hydrolysis methods or during
fermentation processing. Although ACEI peptides from natural food
are considered to be safe, they exhibit low efficacy in comparison
with synthetic ACEI drugs. Sunflower protein is an important source
for ACEI peptides. The procedure for the purification of ACEI
peptides derived from sunflower protein, includes the gel
filtration chromatography, affinity chromatography and
reverse-phase chromatography (11,12).
However, it is important to improve the entrapment efficiency and
to reduce the release of ACEI peptides.
Liposomes have unique physicochemical properties
including the ability to incorporate lipophilic, amphiphilic and/or
hydrophilic compounds, and the ability to improve the stability and
reduce the toxicity of encapsulated drugs (13,14).
Different methodologies are reported to prepare multi-lamellar
vesicles, large unilamellar vesicles and small unilamellar vesicles
(15). Liposomes formed by
thin-film ultrasonic methods have also been widely reported in the
literatures (16–19). However, the production of these
phospholipids vesicles is poorly reproducible as that ACEI
peptides-liposomal experimental set-up is not described in
detail.
In this study, it was aimed to optimize the
encapsulation conditions for producing liposome ACEI peptides by
employing response surface methodology (RSM). In addition,
fractional factorial design (FFD) and the central composite design
were also used to identify the most important variables for
optimizing the encapsulation conditions during the experiments.
Materials and methods
Materials and chemical reagents
Defatted sunflower meal was supplied by China Oil
& Foodstuffs Corporation (Shihezi Branch, China). Alcalase
(ExPASy entry EC 3.4.21.62, Bacillus licheniformis; 2.4 L),
and flavourzyme (ExPASy entry EC 3.4.11.1; 1,000 mg) were purchased
from Novozymes (Bagsvard, Denmark). ACE (ExPASy entry EC 3.4.15.1,
rabbit lung; 0.25 U/ml) and N-[3-(2-furyl)
acryloyl]-L-phenyl-alanylglycylglycine (FAPGG) substrate were
purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
Bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein kit and bovine serum albumin were
purchased from Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
(Beijing, China). Cholesterol, L-α-dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine
(DPPC), phosphatidylcholine (PC), soybean phospholipids (SP),
sphingomyelin (SM),
1-myristoyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (MPPC),
and polyethylene glycol (PEG; molecular weight, 2,000) were
purchased from Rizhao Jia Qing Trading Co., Ltd. (Rizhao, China).
All other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade.
Preparation of sunflower protein
isolates
Defatted sunflower meal flour (20 g) was extracted
by stirring for 1 h in 200 ml 60% ethanol aqueous solution.
Following vacuum filtration, the residue was washed twice with
distilled water and extracted by stirring for 1 h in 200 ml NaOH
(0.05 M) at room temperature. Following centrifugation at 7,155.2 ×
g for 20 min, an additional extraction was performed with half the
volume of alkaline solution. The pH of the supernatant was adjusted
to the isoelectric point (pH 4.3) of sunflower proteins, and the
precipitate formed was recovered by a centrifugation as described
above, washed with distilled water and freeze-dried until further
use.
Sunflower protein-derived ACEI peptides were
prepared according to Villanueva et al (20) and Dadzie et al (21) with modifications: Adjusted
hydrolysis pH for Alcalase from 8 to 8.5 and for Flavourzyme from 7
to 6.5. In the present study, the fraction of molecular mass <3
kDa was gained by ultrafiltration following hydrolysis and then
added to an open column (1.6×100 cm) packed with Sephadex G-25 gel
Beijing RuiDa HengHui Science and Technology Development Co.,
Ltd.,(Beijing, China), that had been pre-equilibrated with
distilled water.
The ACEI peptides were eluted by distilled water at
the speed of 60 ml/h and the elution peaks were monitored at 220
nm. Those fractions (IC50, 2.63±0.08 µg/ml) were vacuum
freeze-dried and stored at −20°C until use (22).
Preparation of liposome containing
ACEI peptides
Liposomal ACEI peptides were prepared by thin-film
ultrasonic method as described by Ferreira et al (23) and Cortesi et al (24) with certain modifications. The
obtained liposome preparation was incubated at room temperature
under continuous stirring (180 mot/min) for 16–18 h in order to
achieve higher entrapment efficiency (25). The preparation of liposome
containing ACEI peptides was confirmed by scanning electron
microscope (SEM) (JSM-6490LV; JEOL, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
Determination of entrapment
efficiency
Entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides was
determined using Centrifree® (EMD Millipore, Billerica,
MA, USA) according to previously reported method (26) with certain modifications: The
supernatant was analyzed via a BCA Protein Quantitation kit
(aforementioned) at 562 nm to determine the amount of
unencapsulated ACEIPs. A standard curve was established with bovine
serum albumin.
Liposomal ACEI peptides release assay
in vitro
An ACEI peptides release experiment was performed
using the dialysis method according to Cortesi et al
(24) with slight modification:
The adjusted molecular weight of the dialysis tube was reduced from
10,000–12,000 to 8,000–10,000. Analysis of ACEIPs content from by
HPLC to BCA Protein Quantitation kit.
FFD
A reduced (26-2) factorial design at two
levels with resolution IV was selected. The variables were coded
according to the following equation:
xi=(Xi-X0)/ΔXi; where
xi was the coded value of an independent variable,
Xi was the real value of an independent variable,
X0 was the real value of an independent variable at the
central point, and ΔXi was the step change value.
Central composite design (CCD)
In order to describe the nature of the response
surface in the optimum region, a central composite design RSM was
performed to examine the effect of the three independent variables
X1 (phospholipids to cholesterol ratio), X5
(ultrasound time), and X6 (phospholipids to ACEI
peptides ratio) at five levels for each variable on the entrapment
efficiency.
Statistical analysis
Design expert 8.0.5 software (Stat-Ease, Inc.,
Minneapolis, MN, USA) was used for analysis of variance (ANOVA) of
the mean responses fitted to a second order polynomial to obtain
regression equations. Entrapment efficiencies were compared using
one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni multiple comparisons test. P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
The adequacy of the model to navigate the design space of the
responses was determined using the coefficient of determination
(R2) and a lack of fit test. Two-dimensional (2D)
contour plots and three-dimensional (3D) response surface plots for
the responses were generated for two independent variables while
fixing the remaining variable at coded 0 levels. The release
profile of liposome containing ACEI peptides and the fitted curve
for the percentage ACEI peptides released and release time were
constructed by Origin 8.0 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA,
USA).
Results and Discussion
Effects of phospholipids on
preparation of liposome containing ACEI peptides
In order to identify the most appropriate
phospholipids for ACEI peptide entrapment, five phospholipids (SP,
PC, DPPC, MPPC and SM) were used to prepare the liposome containing
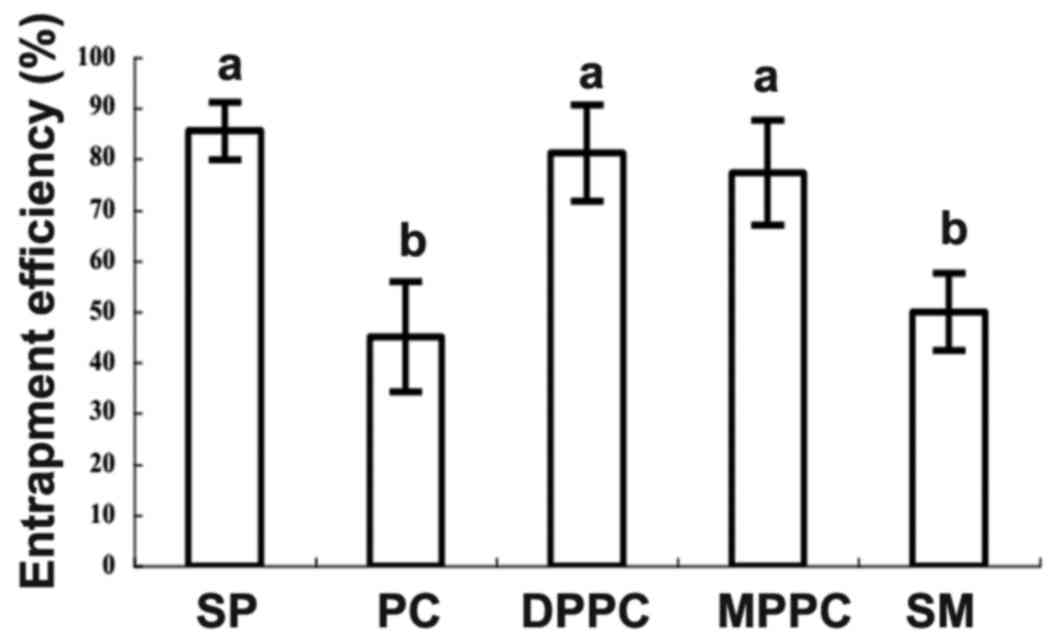
ACEI peptides (Fig. 1). The SP
formulation had the highest entrapment efficiency (85.57±5.68%),
followed by DPPC formulation (81.24±9.41%) and MPPC (77.31±10.32%),
and there was no significant difference among them. By contrast, PC
and SM formulation exhibited much lower entrapment efficiency (PC,
45.07±0.78%; SM, 50.03±7.55%), which were significantly lower than
those of the SP, MPPC and DPPC formulations. These results were
consistent with a previous report, in which there were markedly
different interactions among peptides and various types of charged
liposome (27). Therefore, the SP
formulation was chosen to further optimize the entrapment
conditions for producing liposomal ACEI peptides because of its
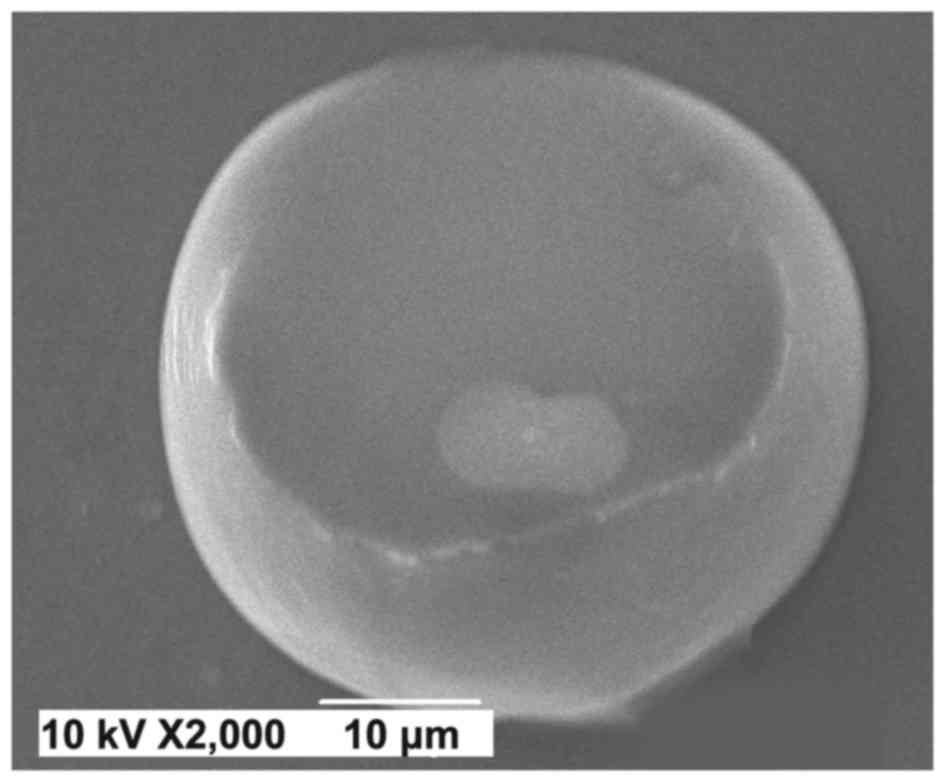
higher efficiency and lower cost. Liposomal ACEI peptides were
imaged using SEM (Fig. 2).
Screening of preparation conditions
for liposomal ACEI peptides using FFD
A 26-2 FFD was applied to evaluate the
impact of six factors. The entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI
peptides markedly varied in a range from 40.28–90.91%. The
factorial analysis of variances indicated that the ratio of
phospholipids to cholesterol (X1), ultrasound time
(X5) and the ratio of phospholipids to ACEI peptides
(X6) were significant factors (P<0.001), which
affected entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides, while
PEG-2000 dosage, NaCl concentration in PBS and hydration
temperature were non-significant factors (Table I). In this case, there was
significant interaction between X1 and X6,
between X1 and X4 (P<0.01). Using multiple
regression analysis, the response variables and the test variables
were related by the second-order polynomial equation as follows:
Y1=76.32–4.56X1-9.84X5+7.71X6+3.27X1X4-2.66X1X5+3.52X1X6.
The values of R2 and adjusted R2 were 88.76
and 83.58%, respectively, indicating that the model fitted well
with the experimental data. The comparable values revealed that
non-significant factors were not included in the model. The P-value
of lack-of-fit in ANOVA was insignificant for the model at a
confidence level of 95% (P=0.0605), suggesting that the model
represented the data satisfactorily.
 | Table I.Analysis of variances results of
fractional factorial designs for entrapment efficiency
(Y1) of liposomal angiotensin-I-converting enzyme
inhibitory peptides. |
Table I.
Analysis of variances results of
fractional factorial designs for entrapment efficiency
(Y1) of liposomal angiotensin-I-converting enzyme
inhibitory peptides.
| Source | Sum of squares | Degrees of
freedom | Mean square | F-value | P-value
(Prob>F) |
|---|
| Model | 3,314.86 | 6 | 552.48 | 43.82 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 332.70 | 1 | 332.70 | 26.39 |
0.0002 |
| X5 | 1,550.39 | 1 | 1,550.39 | 122.97 | <0.0001 |
| X6 | 950.18 | 1 | 950.18 | 75.36 | <0.0001 |
|
X1X4 | 170.69 | 1 | 170.69 | 13.54 |
0.0032 |
|
X1X5 | 113.21 | 1 | 113.21 | 8.98 |
0.0111 |
|
X1X6 | 197.68 | 1 | 197.68 | 15.68 |
0.0019 |
| Curvature | 268.28 | 1 | 268.28 | 21.28 |
0.0006 |
| Residual | 151.29 | 12 | 12.61 |
|
|
| Lack of fit | 144.99 | 9 | 16.11 | 7.66 |
0.0605 |
| Pure error | 6.31 | 3 | 2.10 |
|
|
| Corrected
total | 3,734.43 | 19 |
|
|
|
CCD and response surface analysis for
liposomal ACEI peptides preparation
RSM is a popular and effective method to solve
multivariate problems and optimize several responses in many types
of experimentation (28,29). Based on the results of FFD
analysis, the factors (X1, X5 and
X6) were selected for a further optimization of the
entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides using a Box-Wilson
CCD with six replicates at center point for each factor. PEG-2000
dosage (X2), NaCl concentration in PBS (X3),
hydration temperature (X4) were set as 4%, 50 mM/l and
45°C, respectively. The second-order polynomial equation is as
follows: Y2=78.34+1.89 X1-7.46
X5-9.89 X6-0.13 X1
X5-2.57 X1 X6+2.79 X5
X6-4.06
X12-13.29X52-0.61
X62; where Y2 is the predicted
entrapment efficiency in real value, and X1,
X5 and X6 are the coded values of independent
variable the ratio of phospholipids to cholesterol, ultrasound time
and the ratio of phospholipids to ACEI peptides, respectively.
Table II presents
results of the second-order response surface model in the form of
ANOVA. The Fisher's F-test with a very low probability value
[(Prob>F) <0.0001] indicated the model was highly
significant. The model fitted the data with an acceptable
determination coefficient (R2=0.9761) and no significant
lack-of-fit (P=0.1491), which indicated that the sample variation
of 97.61% could be attributed to the independent variables, and the
model did not explain only 2.39% of the total variations. The
adjusted determination coefficient (R2=0.9546) was also
satisfactory to confirm the significance of the model. Meanwhile,
the low value of coefficient of variation (CV=5.26%) implicated
accuracy and reliability of the experiments.
 | Table II.Analysis of variances for the
entrapment efficiency (Y2) in coded level variables. |
Table II.
Analysis of variances for the
entrapment efficiency (Y2) in coded level variables.
| Source | Sum of squares | Degrees of
freedom | Mean square | F-value | P-value
(Prob>F) |
|---|
| Model | 4,927.74 | 9 | 547.53 | 45.35 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 48.58 | 1 | 48.58 | 4.02 |
0.0727 |
| X5 | 759.19 | 1 | 759.19 | 62.88 | <0.0001 |
| X6 | 1,337.10 | 1 | 1,337.10 | 110.74 | <0.0001 |
|
X1X5 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 0.01 |
0.9192 |
|
X1X6 | 52.75 | 1 | 52.75 | 4.37 |
0.0631 |
|
X5X6 | 62.49 | 1 | 62.49 | 5.17 |
0.0462 |
|
X12 | 238.00 | 1 | 238.00 | 19.71 |
0.0013 |
|
X52 | 2,544.30 | 1 | 2,544.30 | 210.72 | <0.0001 |
|
X62 | 5.29 | 1 | 5.29 | 0.44 |
0.5231 |
| Residual | 120.74 | 10 | 12.07 |
|
|
| Lack of fit | 88.18 | 5 | 17.64 | 2.71 |
0.1491 |
| Pure error | 32.56 | 5 | 6.51 |
|
|
| Corrected
total | 5,048.48 | 19 |
|
|
|
The regression analysis showed that the ultrasound
time (X5) and the ratio of phospholipids to ACEI
peptides (X6) had a very significant linear effect on
entrapment efficiency. Meanwhile the ultrasound time
(X5) and the ratio of cholesterol to phospholipids
(X1) exhibited a significant quadratic effect
(P<0.01). In addition, an interaction between the ultrasound
time and the ratio of phospholipids to ACEI peptides for the
entrapment efficiency (P<0.05) was also observed. The linear
effects of X1, quadratic effect of
X62 and interaction effects of
X1X5 and X1X6 were
demonstrated to be non-significant on the entrapment efficiency of
liposomal ACEI peptides.
To illustrate the interaction of the ratio of
phospholipids to cholesterol, ultrasound time and ratio of
phospholipids to ACEI peptides and to efficiently optimize the
variables, 3D response surface plots and the 2D contour plots were
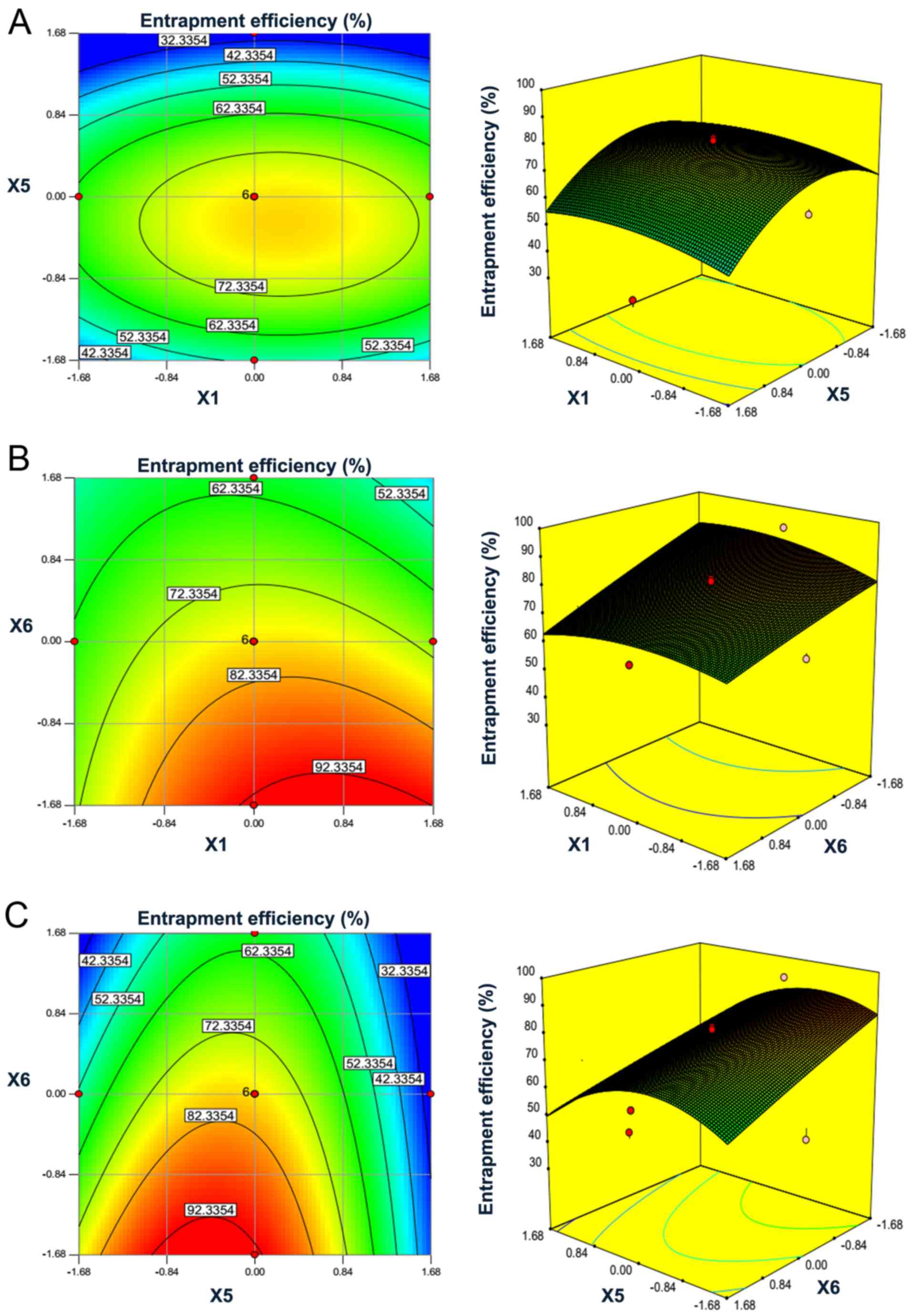
obtained. As shown in Fig. 3, a
visual interpretation of the interactions between the two
independent variables on the entrapment efficiency was observed,
while the third variable was held at zero level. The circular
contour plots of response surfaces suggest that the interaction is
negligible among the corresponding variables. An elliptical or
saddle nature of the contour plots indicates the significance of
the interactions between the corresponding variables. In the case
of saddle contour plots, the optimum values are obtained at the
point of intersection of lines, which are formed by joining the
locus (30).
Fig. 3A and B
demonstrate that entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides
was increased with the increase of ultrasound time from 5 to 10
min, while it was decreased when the ultrasound time was >10
min. The result was similar to a previous publication (31). The entrapment efficiency was
increased with the ratio of phospholipids to cholesterol until a
peak was detected at ~3:1 (w:w). In Fig. 3B, the saddle contour plots
demonstrated that interactions between phospholipids to cholesterol
ratio and phospholipids to ACEI peptides ratio also reached optimum
levels. Fig. 3C shows that the
entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides increased with the
decrease of the ratio of phospholipids to ACEI peptides from 25:1
to 15:1 (w:w) when the ratio of phospholipids to cholesterol was
set. There was a saddle in the contour plot (Fig. 3C), indicating the significance of
interactions between ultrasound time and the ratio of phospholipids
to ACEI peptides.
Validation of the experimental
design
The optimum conditions for the entrapment efficiency
of liposomal ACEI peptides were calculated based on the data
obtained using the ‘response optimizer’ option of Design-Expert
software. The optimal values of each variable in coded units were
as follows: X1=0.55, X5=−0.39 and
X6=−1. Their actual values were 4.1:1 (w:w) of
phospholipids to cholesterol ratio (X1), 8.05 min of
ultrasound time (X5) and 15:1 (w:w) of phospholipids to
ACEI peptides ratio (X6), respectively. The model
predicted that the entrapment efficiency of liposomal ACEI peptides
could reach 90.86% by using the above optimized condition of the
variables. The experiments were repeated three times to validate
the suitability of the model equations. The entrapment efficiency
(91.25±0.182%, n=3) was obtained from the real experiments,
indicating validation of the RSM model.
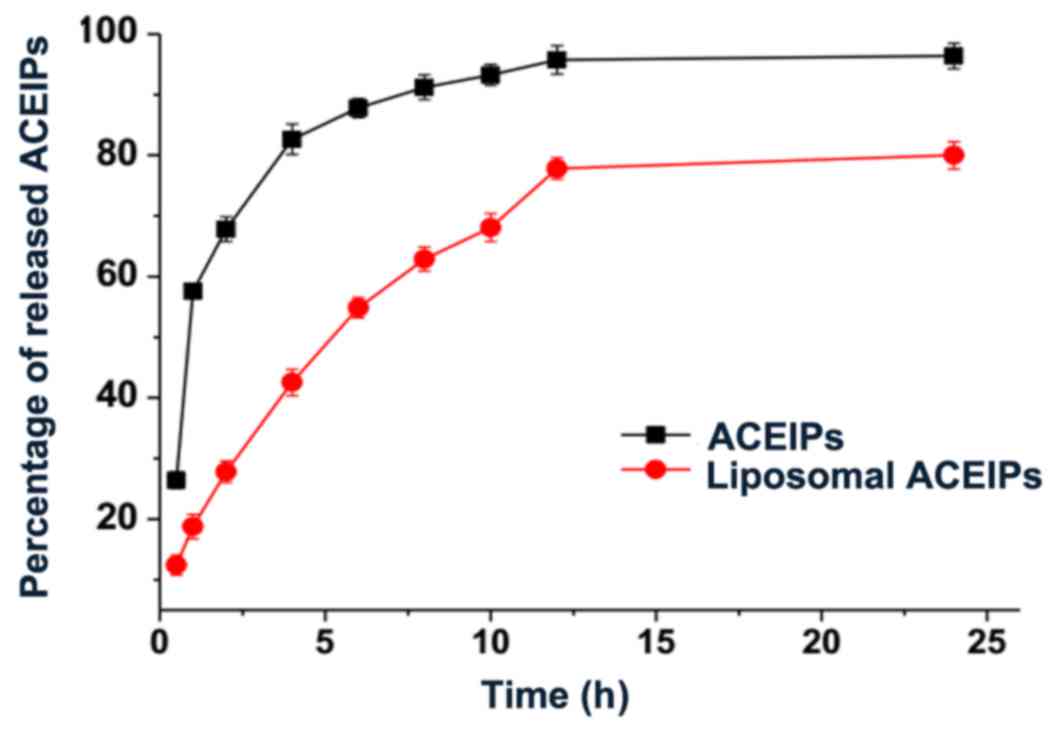
ACEI peptides release assay
The liposomal ACEI peptides were subjected to
release experiments in vitro in order to provide information
about the efficiency of release of ACEI peptides from liposome. As
reported in Fig. 4, the percentage
of ACEI peptides released in phosphate buffer was 95.74% after 12
h, whereas it was 77.83% after 12 h for liposomal ACEI peptides.
The release of liposome-entrapped ACEI peptides was significantly
delayed compared with ACEI peptides in phosphate buffer.
Furthermore, the fitted equation of the percentage of ACEI peptides
released vs. release time was calculated based on different release
models (zero-order dynamic, one-order dynamic, Korsmeyer-Peppas,
Higuchi, logistic) (32,33). The logistic model and one-order
dynamic model were well-fitted with the release percentage of ACEI
peptides (adjusted R2 of 0.9883 and 0.9841,
respectively).
In conclusion, liposomal ACEI peptides derived from
sunflower protein hydrolysates were prepared with the aims of
improving entrapment efficiency and sustaining release. The ratio
of phospholipids to cholesterol, ultrasound time and the ratio of
phospholipids to ACEIPs were notable factors affecting entrapment
efficiency. Under optimal experimental conditions, the entrapment
efficiency of liposomal ACEIPs was 91.25±0.182%. The percentage of
released of liposomal ACEIPs was reduced by 17.91% compared with
ACEIPs in phosphate buffer after 12 h. However, there are some
limitations of the present study. The release of liposome-entrapped
ACEIPs in simulated gastric fluid and simulated intestinal fluid
was not investigated, and the stability of liposomes was also not
analyzed under long durations of preservation; further
investigation is required.
Acknowledgements
The present study was partially supported by a grant
of College Students' Innovative Training Program of China (grant
no. 201410759048).
References
|
1
|
Ogihara T, Mikami H, Katahira K and Otsuka
A: Comparative study of the effects of three angiotensin converting
enzyme inhibitors on the cough reflex. Am J Hypertens. 4:46S–51S.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ong L and Shah NP: Influence of probiotic
Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. helveticus on proteolysis, organic
acid profiles and ACE-inhibitory activity of cheddar cheeses
ripened at 4, 8 and 12 degrees C. J food sci. 73:M111–M120. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ong L and Shah NP: Release and
identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides
as influenced by ripening temperatures and probiotic adjuncts in
cheddar cheeses. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 41:1555–1566. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hwang JS: Impact of processing on
stability of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory
peptides obtained from tuna cooking juice. Food Res Int.
43:902–906. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Liu S, Ye R, Cai G, Ji B and Wu Y:
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory tripeptides from
rice protein hydrolysate: Purification and characterization. J
Functional Foods. 5:1684–1692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gu Y and Wu J: LC-MS/MS coupled with QSAR
modeling in characterising of angiotensin I-converting enzyme
inhibitory peptides from soybean proteins. Food Chem.
141:2682–2690. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
White BL, Sanders TH and Davis JP:
Potential ACE-inhibitory activity and nanoLC-MS/MS sequencing of
peptides derived from aflatoxin contaminated peanut meal. LWT-Food
Sci Technol. 56:537–542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ngo DH, Ryu B and Kim SK: Active peptides
from skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin diminish angiotensin-I
converting enzyme activity and intracellular free radical-mediated
oxidation. Food Chem. 143:246–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Udenigwe CC, Lin YS, Hou WC and Aluko RE:
Kinetics of the inhibition of renin and angiotensin I-converting
enzyme by flaxseed protein hydrolysate fractions. J Functional
Foods. 1:199–207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vaštag Ž, Popović L, Popović S, Krimer V
and Peričin D: Production of enzymatic hydrolysates with
antioxidant and angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity
from pumpkin oil cake protein isolate. Food Chem. 124:1316–1321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Megias C, del Mar Yust M, Pedroche J,
Lquari H, Girón-Calle J, Alaiz M, Millán F and Vioque J:
Purification of an ACE inhibitory peptide after hydrolysis of
sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) protein isolates. J agric food
chem. 52:1928–1932. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Megias C, Pedroche J, Yust Mdel M, Alaiz
M, Girón-Calle J, Millan F and Vioque J: Affinity purification of
angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides using immobilized
ACE. J Agric Food Chem. 54:7120–7124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du B, Li Y, Li XAY, Chen C and Zhang Z:
Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of
2-methoxyestradiol-loaded liposomes. Int J Pharm. 384:140–147.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Milla P, Dosio F and Cattel L: PEGylation
of proteins and liposomes: A powerful and flexible strategy to
improve the drug delivery. Current Drug Metab. 13:105–119. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Vemuri S and Rhodes CT: Preparation and
characterization of liposomes as therapeutic delivery systems: A
review. Pharm Acta Helv. 70:95–111. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andrade CA, Correia MT, Coelho LC,
Nascimento SC and Santos-Magalhaes NS: Antitumor activity of
Cratylia mollis lectin encapsulated into liposomes. Int J Pharm.
278:435–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pereira-Lachataignerais J, Pons R, Panizza
P, Courbin L, Rouch J and Lopez O: Study and formation of vesicle
systems with low polydispersity index by ultrasound method. Chem
Phys Lipids. 140:88–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Silva R, Little C, Ferreira H and
Cavaco-Paulo A: Incorporation of peptides in phospholipid
aggregates using ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem. 15:1026–1032. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shaw GJ, Meunier JM, Huang SL, Lindsell
CJ, McPherson DD and Holland CK: Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis
with tPA-loaded echogenic liposomes. Thromb Res. 124:306–310. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Villanueva A, Vioque J, Sánchez-Vioque R,
Clemente A, Pedroche J, Bautista J and Millán F: Peptide
characteristics of sunflower protein hydrolysates. J Amer Oil Chem
Soc. 76:1455–1460. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dadzie R, Ma H, Abano E, Qu W and Mao S:
Optimization of process conditions for production of angiotensin
I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from vital wheat
gluten using response surface methodology. Food Sci Biotechnol.
22:1531–1537. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yu Z, Liu B, Zhao W, Yin Y, Liu J and Chen
F: Primary and secondary structure of novel ACE-inhibitory peptides
from egg white protein. Food Chem. 133:315–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferreira H, Lúcio M, Lima JL, Matos C and
Reis S: Interaction of clonixin with EPC liposomes used as membrane
models. J Pharm Sci. 94:1277–1287. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cortesi R, Argnani R, Esposito E, Dalpiaz
A, Scatturin A, Bortolotti F, Lufino M, Guerrini R, Cavicchioni G,
Incorvaia C, et al: Cationic liposomes as potential carriers for
ocular administration of peptides with anti-herpetic activity. Int
J Pharm. 317:90–100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong JM, Chung YC and Hwang JH: Enhanced
adjuvantic property of polymerized liposome as compared to a
phospholipid liposome. J Biotechnol. 94:255–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang YZ, Gao JQ, Liang WQ and Nakagawa S:
Preparation and characterization of liposomes encapsulating
chitosan nanoparticles. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:387–390. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moeller EH, Holst B, Nielsen LH, Pedersen
PS and Østergaard J: Stability, liposome interaction and in vivo
pharmacology of ghrelin in liposomal suspensions. Int J Pharm.
390:13–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McDonald DB, Grantham WJ, Tabor WL and
Murphy MJ: Global and local optimization using radial basis
function response surface models. Applied Math Model. 31:2095–2110.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dong X, Pan R, Zou S, He M and Wang C:
Oxidative degradation of the sulfated polysaccharide isolated from
sea cucumber Holothuria nobilis. Process Biochem. 50:294–301. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Murthy MSRC, Swaminathan T, Rakshit SK and
Kosugi Y: Statistical optimization of lipase catalyzed hydrolysis
of methyloleate by response surface methodology. Bio Eng. 22:35–39.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chang L and Zhao Y: Studies on preparation
and properties of Vc nano liposomes. J Appli Sci Eng Innov.
1:237–240. 2014.
|
|
32
|
Nounou MM, El-Khordagui LK, Khalafallah NA
and Khalil SA: In vitro release of hydrophilic and hydrophobic
drugs from liposomal dispersions and gels. Acta Pharm. 56:311–324.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boyd BJ, Whittaker DV, Khoo SM and Davey
G: Lyotropic liquid crystalline phases formed from glycerate
surfactants as sustained release drug delivery systems. Int J
Pharm. 309:218–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|