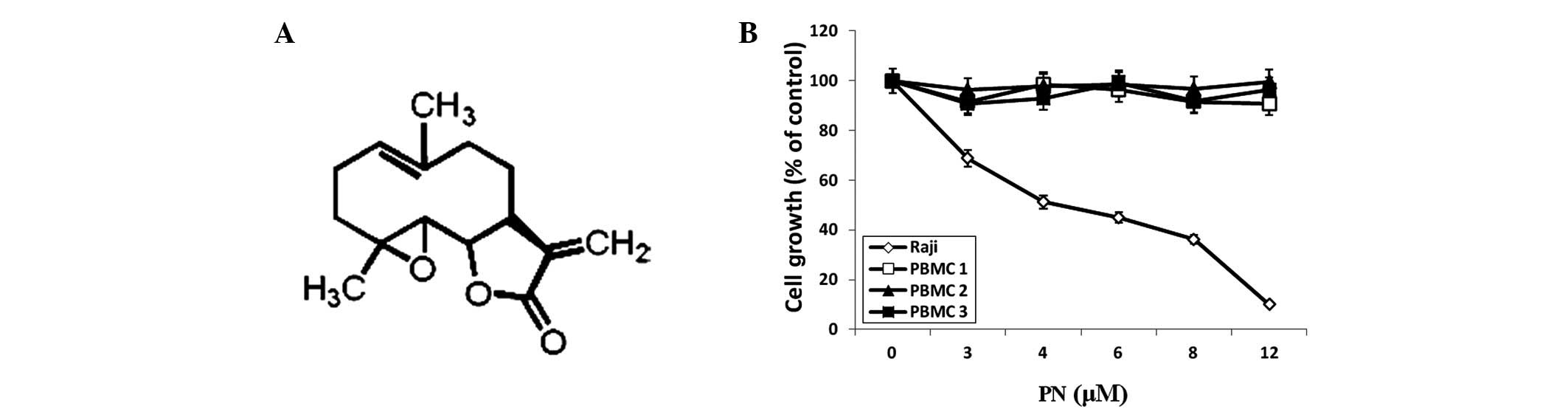
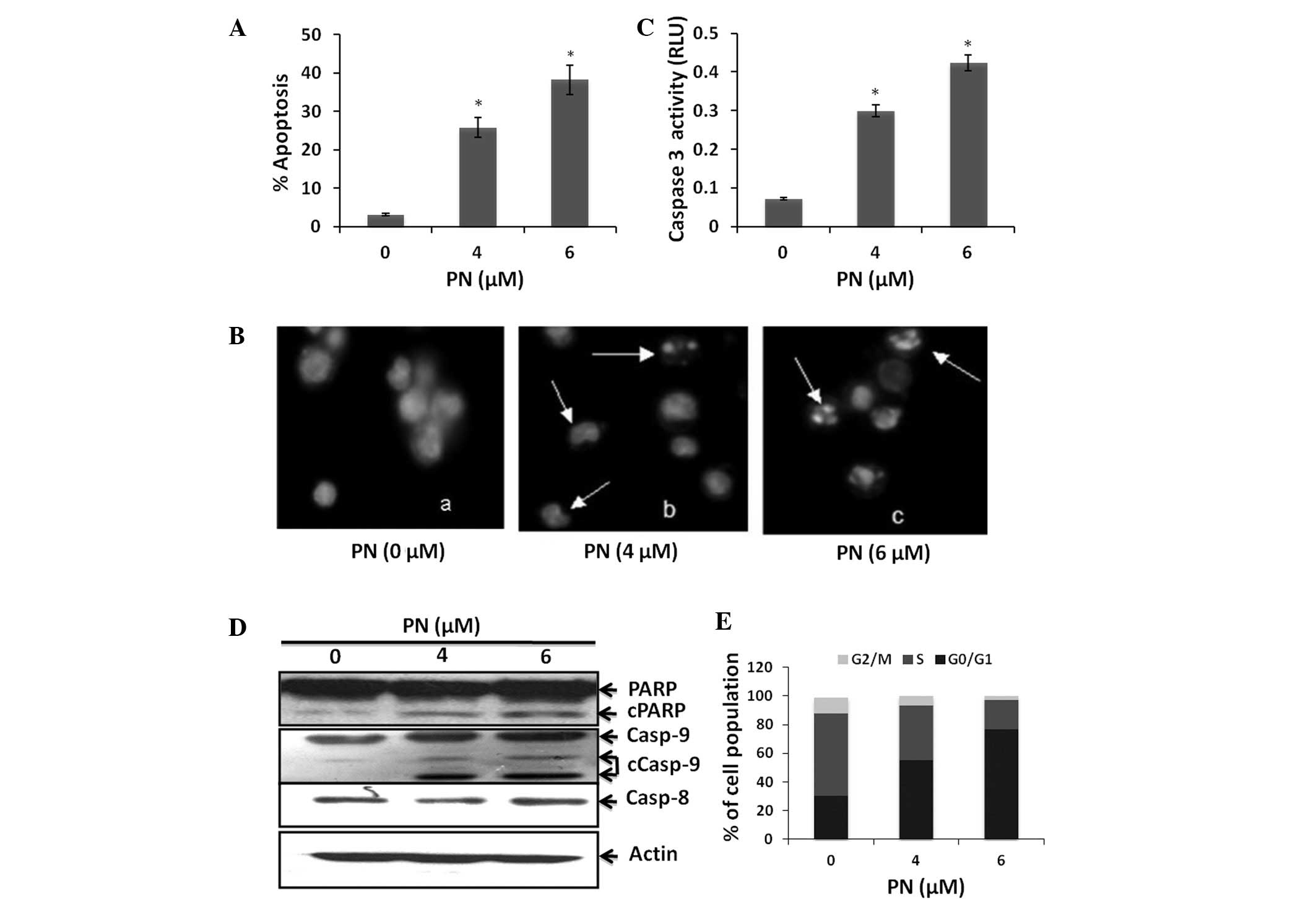
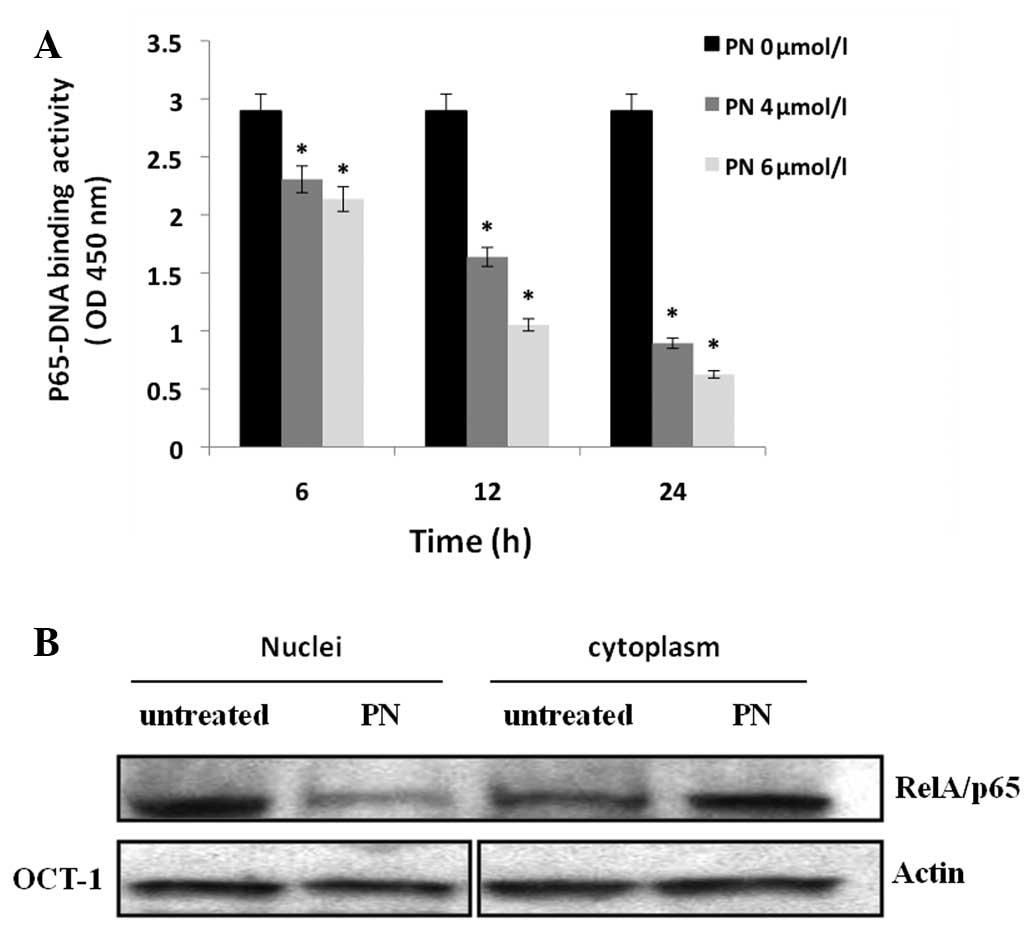
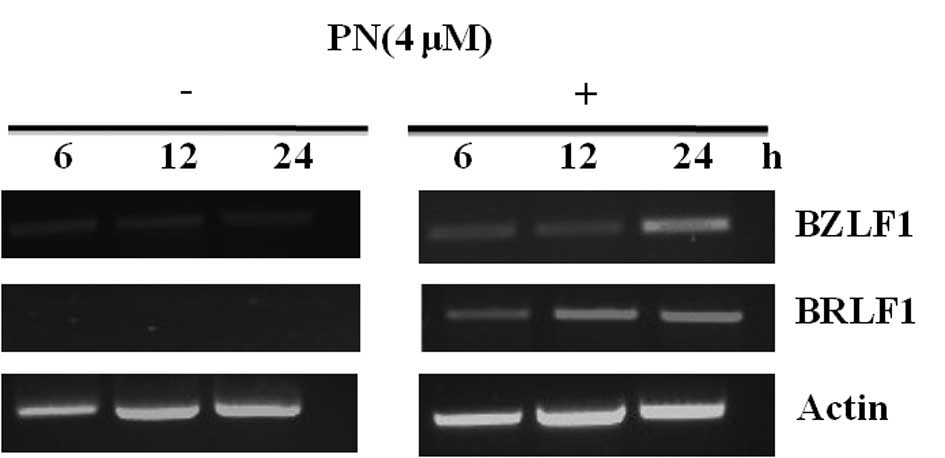
|
1
|
Yang L, Parkin DM, Whelan S, Zhang S, Chen
Y, Lu F and Li L: Statistics on cancer in China: cancer
registration in 2002. Eur J Cancer Prev. 14:329–335. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohen JI, Kimura H, Nakamura S, Ko YH and
Jaffe ES: Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease
in non-immunocompromised hosts: a status report and summary of an
international meeting, 8–9 September 2008. Ann Oncol. 20:1472–1482.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thorley-Lawson DA and Gross A: Persistence
of the Epstein-Barr virus and the origins of associated lymphomas.
N Engl J Med. 350:1328–1337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thorley-Lawson DA and Allday MJ: The
curious case of the tumour virus: 50 years of Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 6:913–924. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen JI, Bollard CM, Khanna R and
Pittaluga S: Current understanding of the role of Epstein-Barr
virus in lymphomagenesis and therapeutic approaches to
EBV-associated lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 49(Suppl 1): 27–34. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perrine SP, Hermine O, Small T, et al: A
phase 1/2 trial of arginine butyrate and ganciclovir in patients
with Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoid malignancies. Blood.
109:2571–2578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu DX, Tanhehco Y, Chen J, et al:
Bortezomib-induced enzyme-targeted radiation therapy in
herpesvirus-associated tumors. Nat Med. 14:1118–1122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Landais E, Saulquin X, Scotet E, et al:
Direct killing of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected B cells by CD4
T cells directed against the EBV lytic protein BHRF1. Blood.
103:1408–1416. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feng WH, Israel B, Raab-Traub N, Busson P
and Kenney SC: Chemotherapy induces lytic EBV replication and
confers ganciclovir susceptibility to EBV-positive epithelial cell
tumors. Cancer Res. 62:1920–1926. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hailfinger S, Nogai H, Pelzer C, et al:
Malt1-dependent RelB cleavage promotes canonical NF-kappaB
activation in lymphocytes and lymphoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:14596–14601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song YJ and Kang MS: Roles of TRAF2 and
TRAF3 in Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-induced
alternative NF-kappaB activation. Virus Genes. 41:174–180. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cahir-McFarland ED, Davidson DM, Schauer
SL, Duong J and Kieff E: NF-kappa B inhibition causes spontaneous
apoptosis in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:6055–6060. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chaudhary PM, Jasmin A, Eby MT and Hood L:
Modulation of the NF-kappa B pathway by virally encoded death
effector domains-containing proteins. Oncogene. 18:5738–5746. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Izumi KM and Kieff ED: The Epstein-Barr
virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor
necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate
B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-kappaB. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:12592–12597. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Keller SA, Schattner EJ and Cesarman E:
Inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV-infected primary
effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 96:2537–2542. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smolinski AT and Pestka JJ: Comparative
effects of the herbal constituent parthenolide (Feverfew) on
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory gene expression in murine
spleen and liver. J Inflamm (Lond). 2:62005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pareek A, Suthar M, Rathore GS and Bansal
V: Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium L.): A systematic review.
Pharmacogn Rev. 5:103–110. 2011.
|
|
19
|
deGraffenried LA, Chandrasekar B,
Friedrichs WE, et al: NF-kappa B inhibition markedly enhances
sensitivity of resistant breast cancer tumor cells to tamoxifen.
Ann Oncol. 15:885–890. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakshatri H, Rice SE and Bhat-Nakshatri P:
Antitumor agent parthenolide reverses resistance of breast cancer
cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
through sustained activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Oncogene.
23:7330–7344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dai Y, Guzman ML, Chen S, et al: The NF
(Nuclear factor)-kappaB inhibitor parthenolide interacts with
histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce MKK7/JNK1-dependent
apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol.
151:70–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Israel BF and Kenney SC: Virally targeted
therapies for EBV-associated malignancies. Oncogene. 22:5122–5130.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Flemington EK: Herpesvirus lytic
replication and the cell cycle: arresting new developments. J
Virol. 75:4475–4481. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Zhao Y, Zeng L, Tang M, El-Deeb A,
Li JJ and Cao Y: BZLF1 controlled by family repeat domain induces
lytic cytotoxicity in Epstein-Barr virus-positive tumor cells.
Anticancer Res. 24:67–74. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen YL, Law PY and Loh HH: Inhibition of
PI3K/Akt signaling: an emerging paradigm for targeted cancer
therapy. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 5:575–589. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng WH and Kenney SC: Valproic acid
enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy in EBV-positive tumors by
increasing lytic viral gene expression. Cancer Res. 66:8762–8769.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Urier G, Buisson M, Chambard P and
Sergeant A: The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates
transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1
binding sites. EMBO J. 8:1447–1453. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zalani S, Holley-Guthrie E and Kenney S:
Epstein-Barr viral latency is disrupted by the immediate-early
BRLF1 protein through a cell-specific mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:9194–9199. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mogensen TH and Paludan SR: Molecular
pathways in virus-induced cytokine production. Microbiol Mol Biol
Rev. 65:131–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hiscott J, Kwon H and Genin P: Hostile
takeovers: viral appropriation of the NF-kappaB pathway. J Clin
Invest. 107:143–151. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Santoro MG, Rossi A and Amici C: NF-kappaB
and virus infection: who controls whom. EMBO J. 22:2552–2560. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brown HJ, Song MJ, Deng H, Wu TT, Cheng G
and Sun R: NF-kappaB inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J
Virol. 77:8532–8540. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kwok BH, Koh B, Ndubuisi MI, Elofsson M
and Crews CM: The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide
from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits
IkappaB kinase. Chem Biol. 8:759–766. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hayashi S, Koshiba K, Hatashita M, et al:
Thermosensitization and induction of apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest
human prostate cancer androgen-independent cell lines. Int J Mol
Med. 28:1033–1042. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gunn EJ, Williams JT, Huynh DT, et al: The
natural products parthenolide and andrographolide exhibit
anti-cancer stem cell activity in multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma.
52:1085–1097. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ghashghaeinia M, Toulany M, Saki M, et al:
The NFkB pathway inhibitors Bay 11-7082 and parthenolide induce
programmed cell death in anucleated Erythrocytes. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 27:45–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|